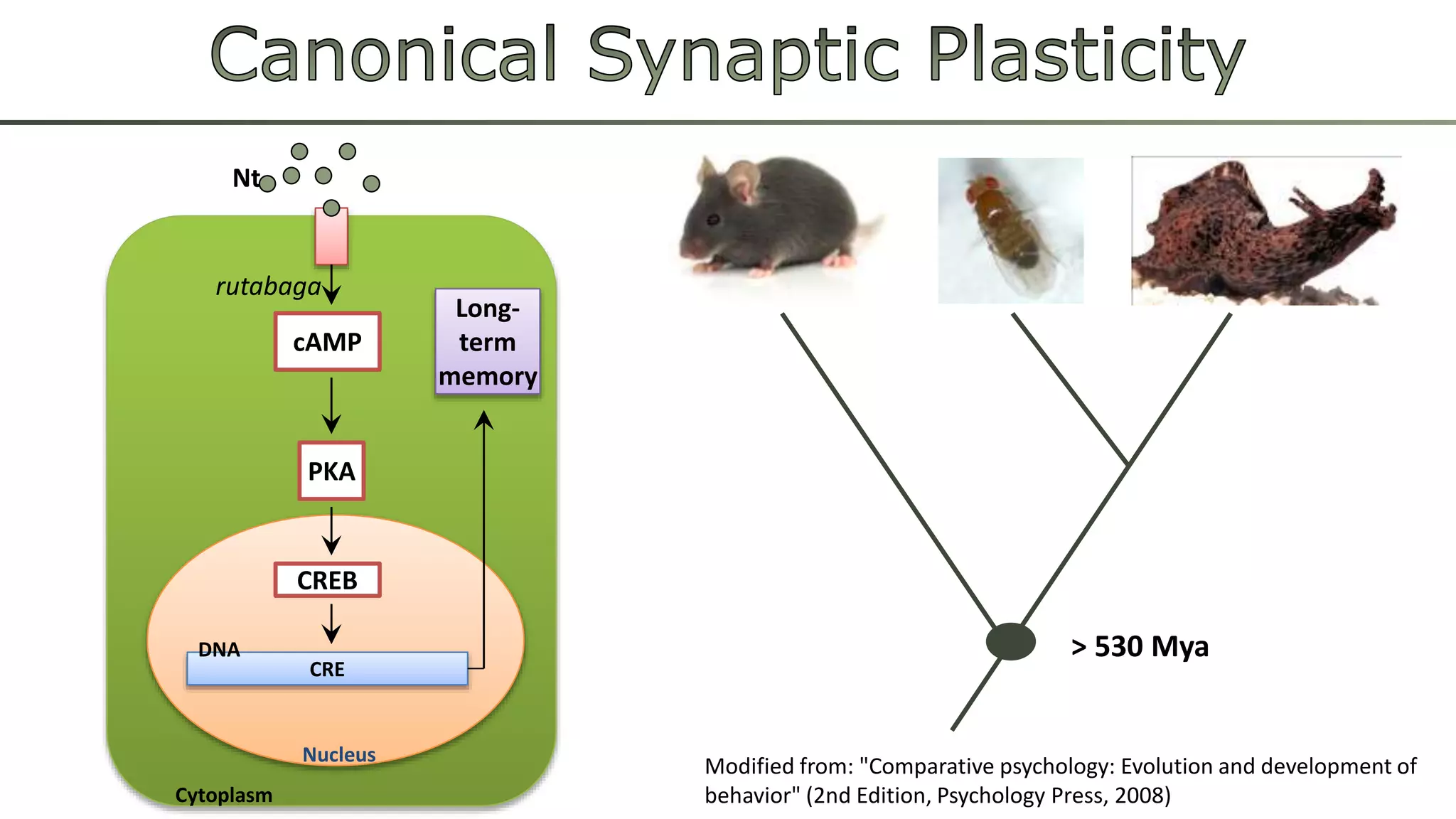
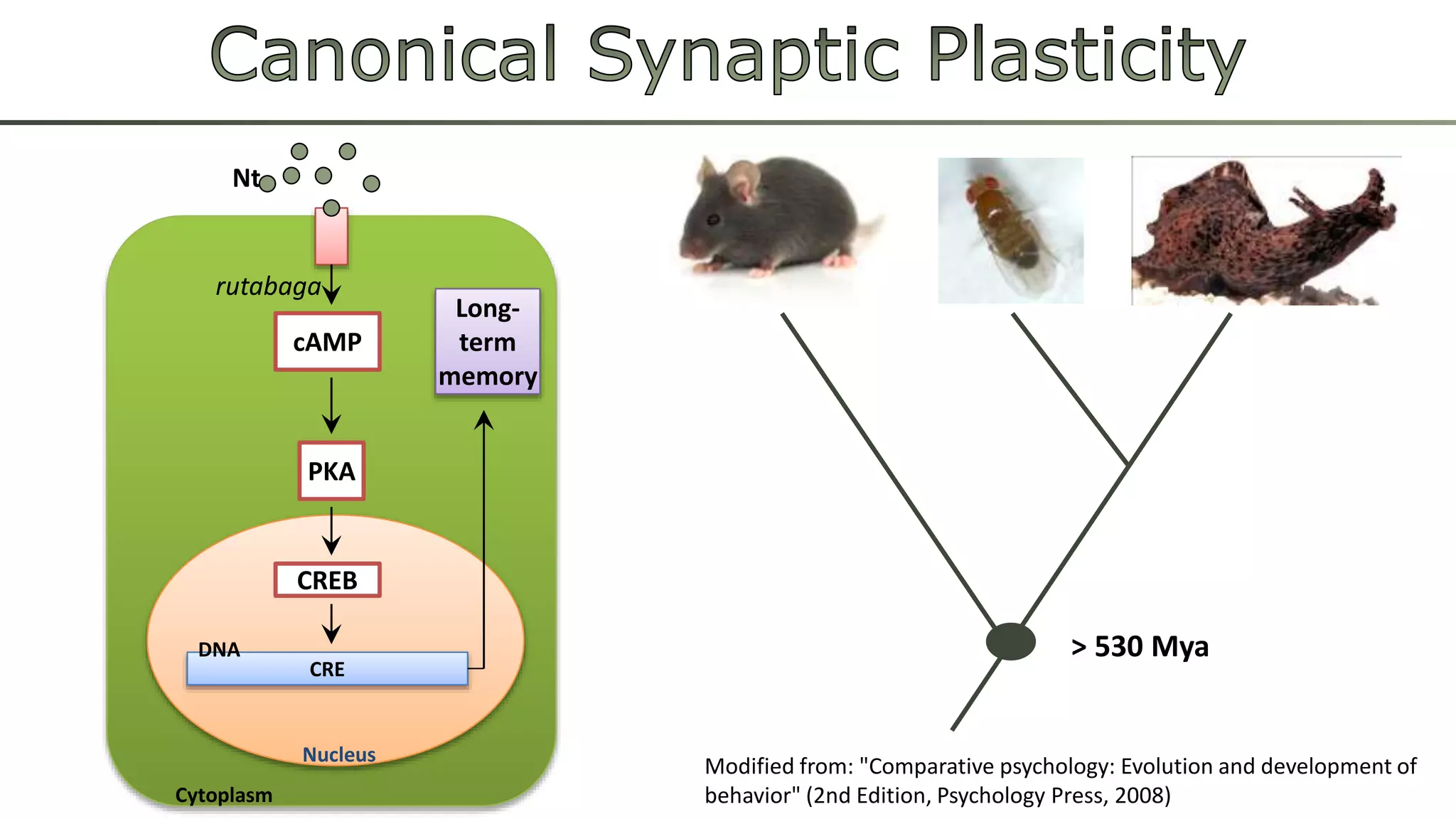
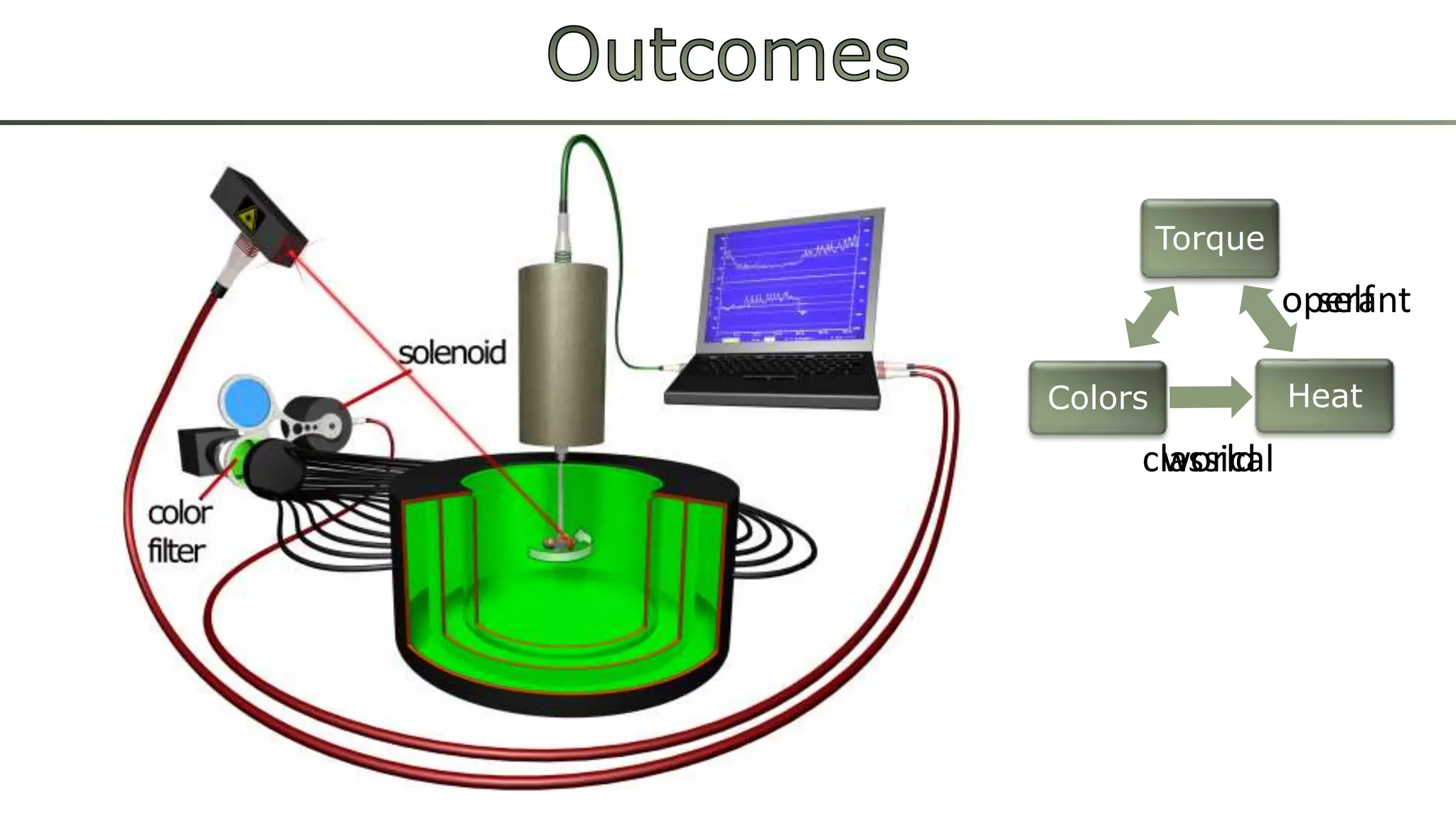
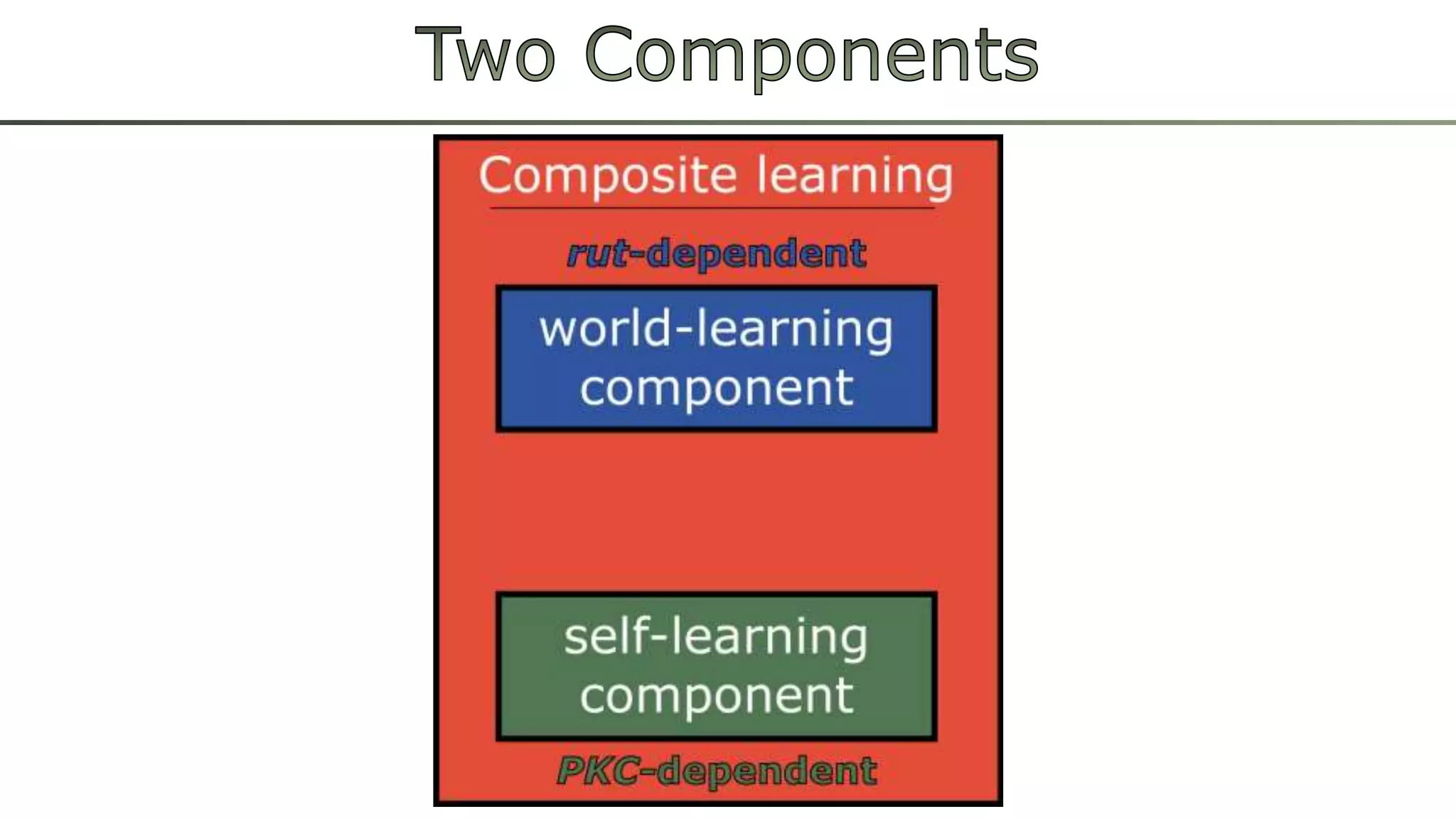
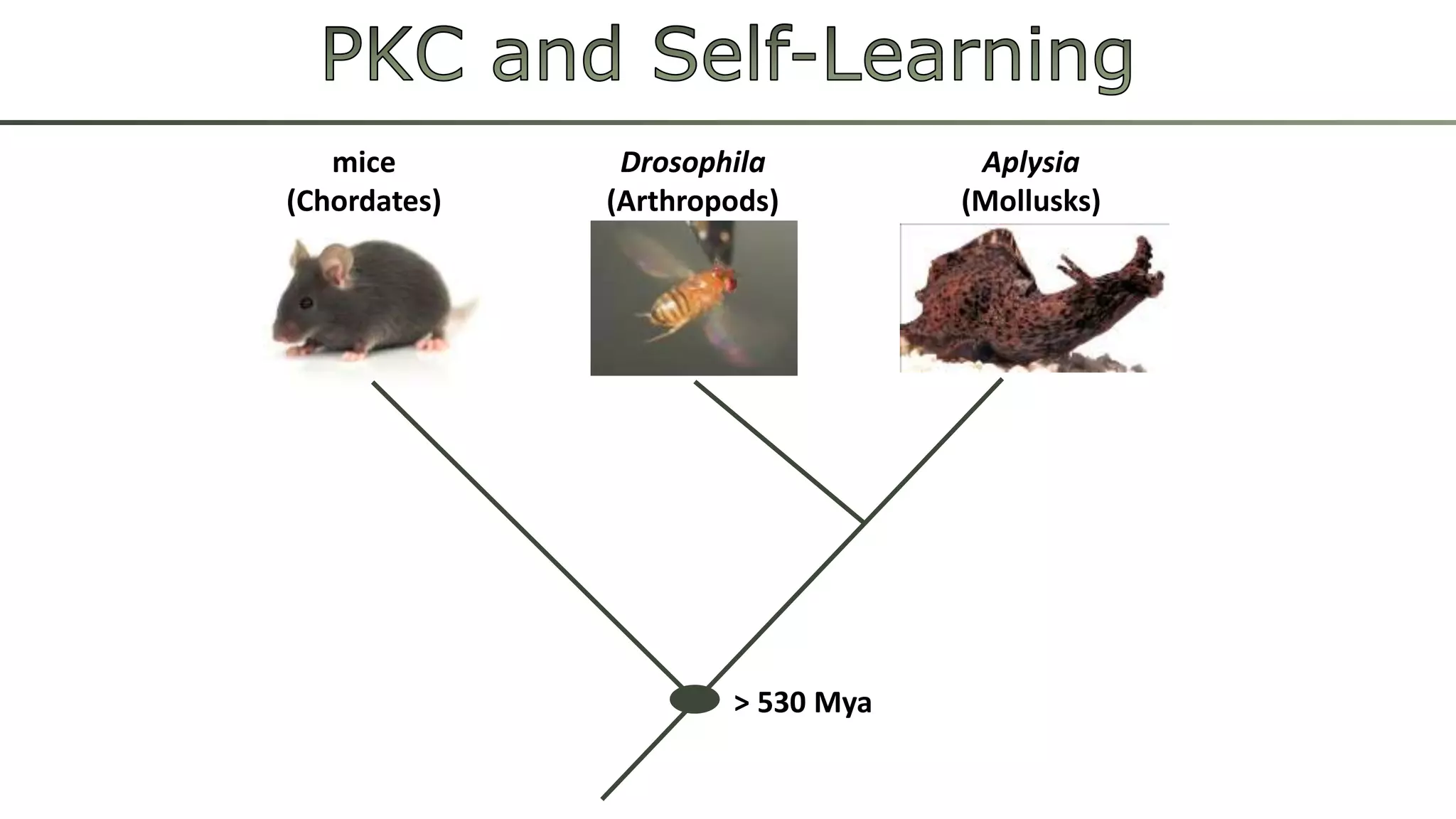
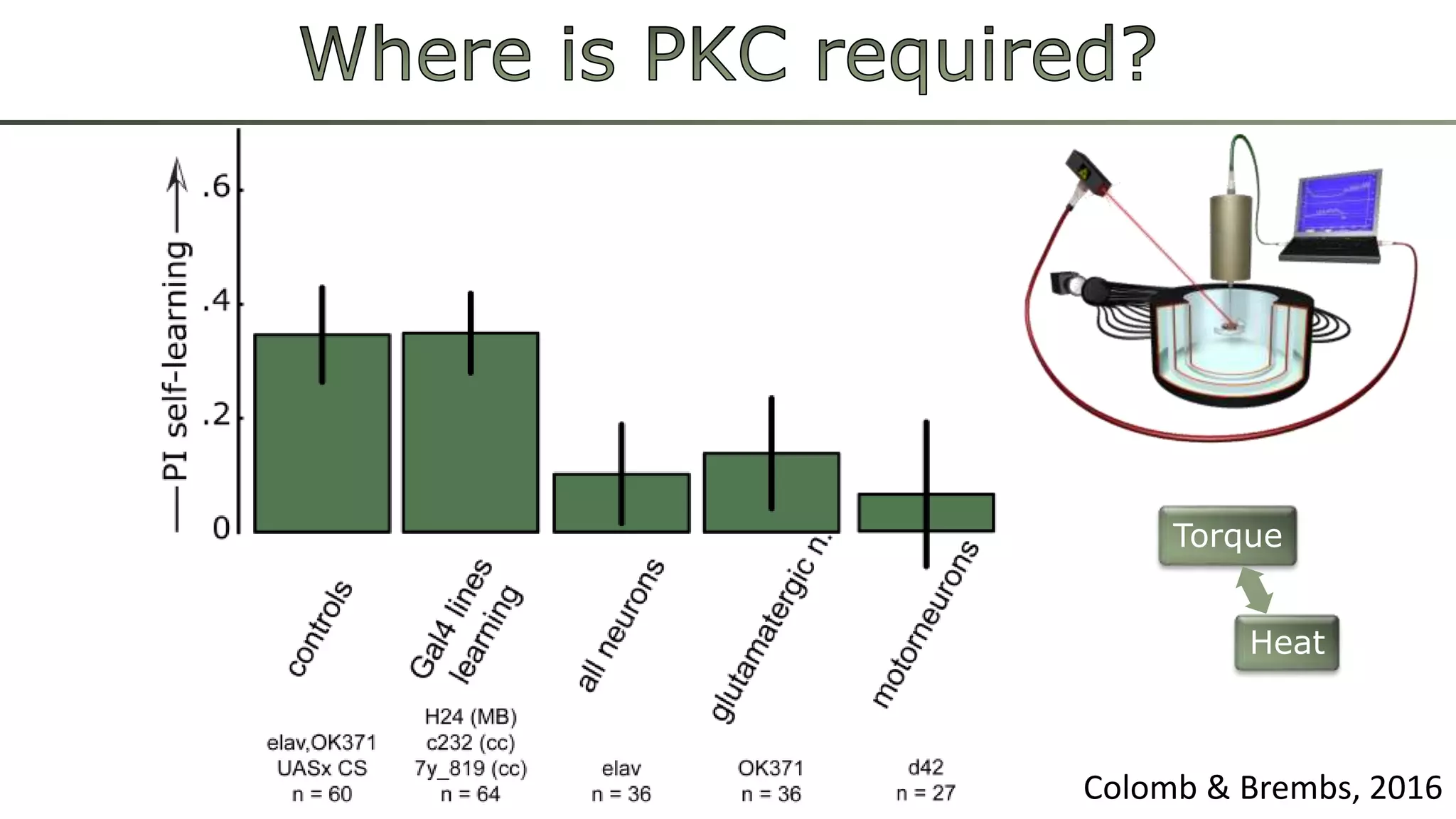
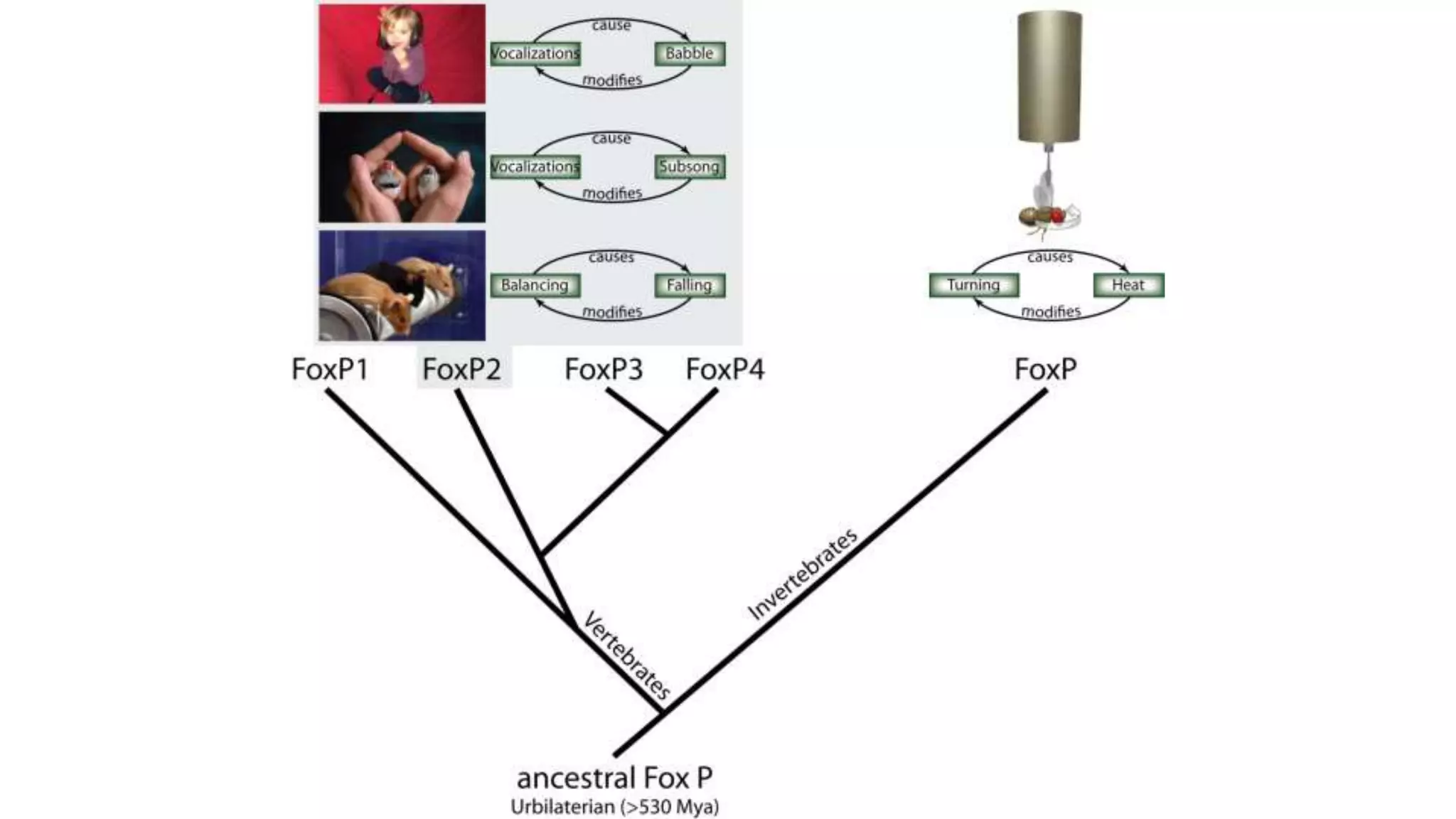
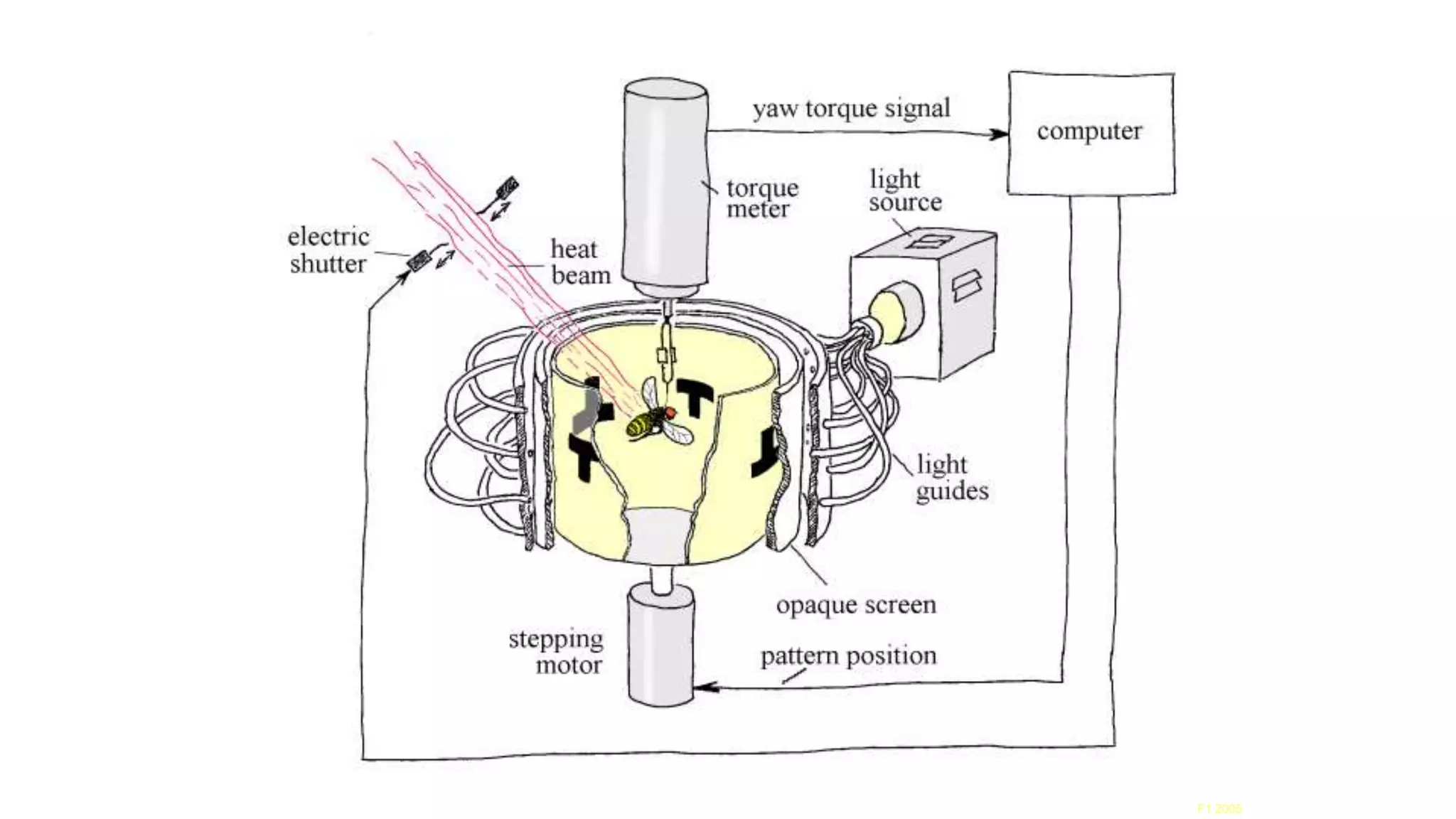
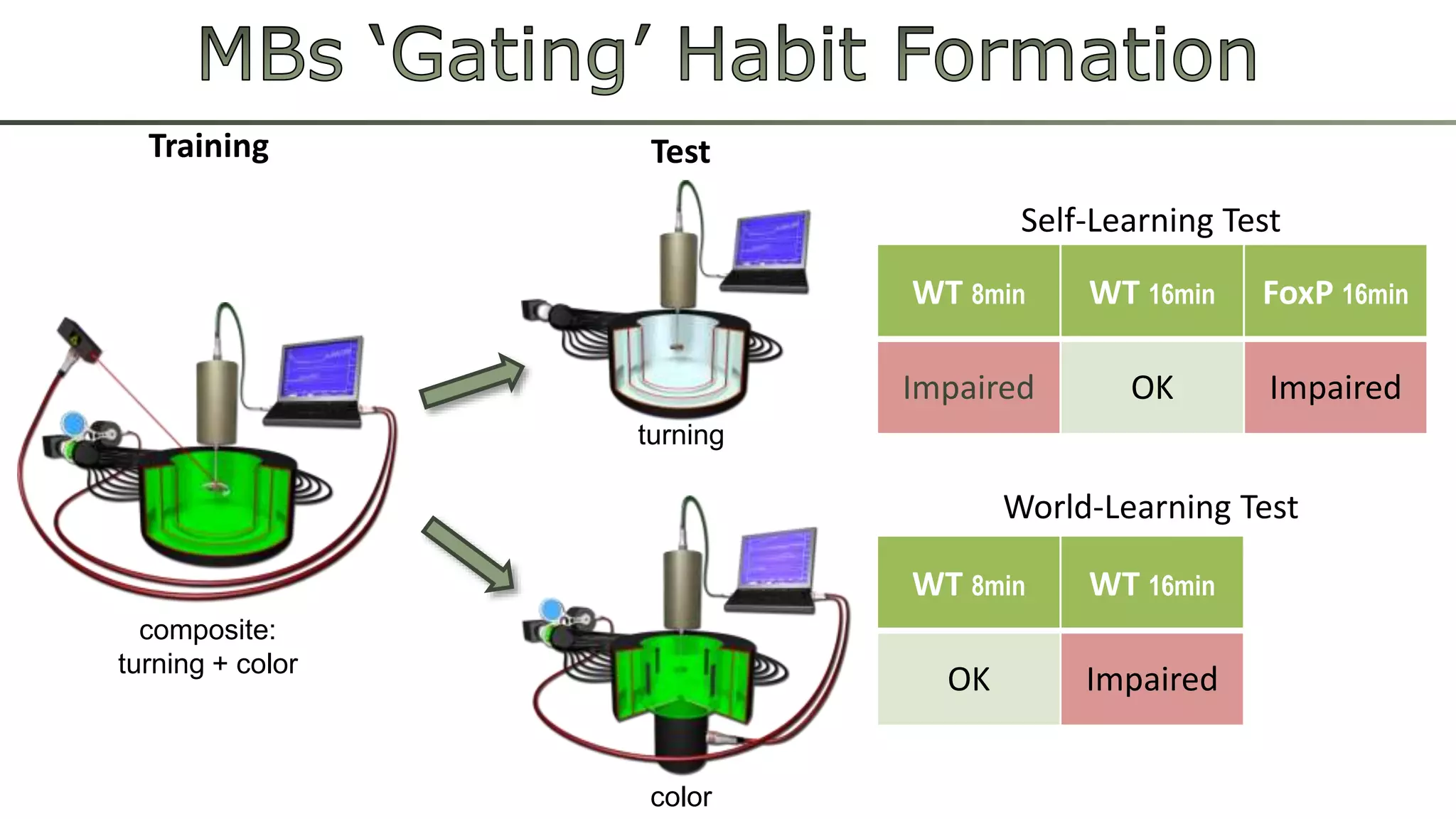
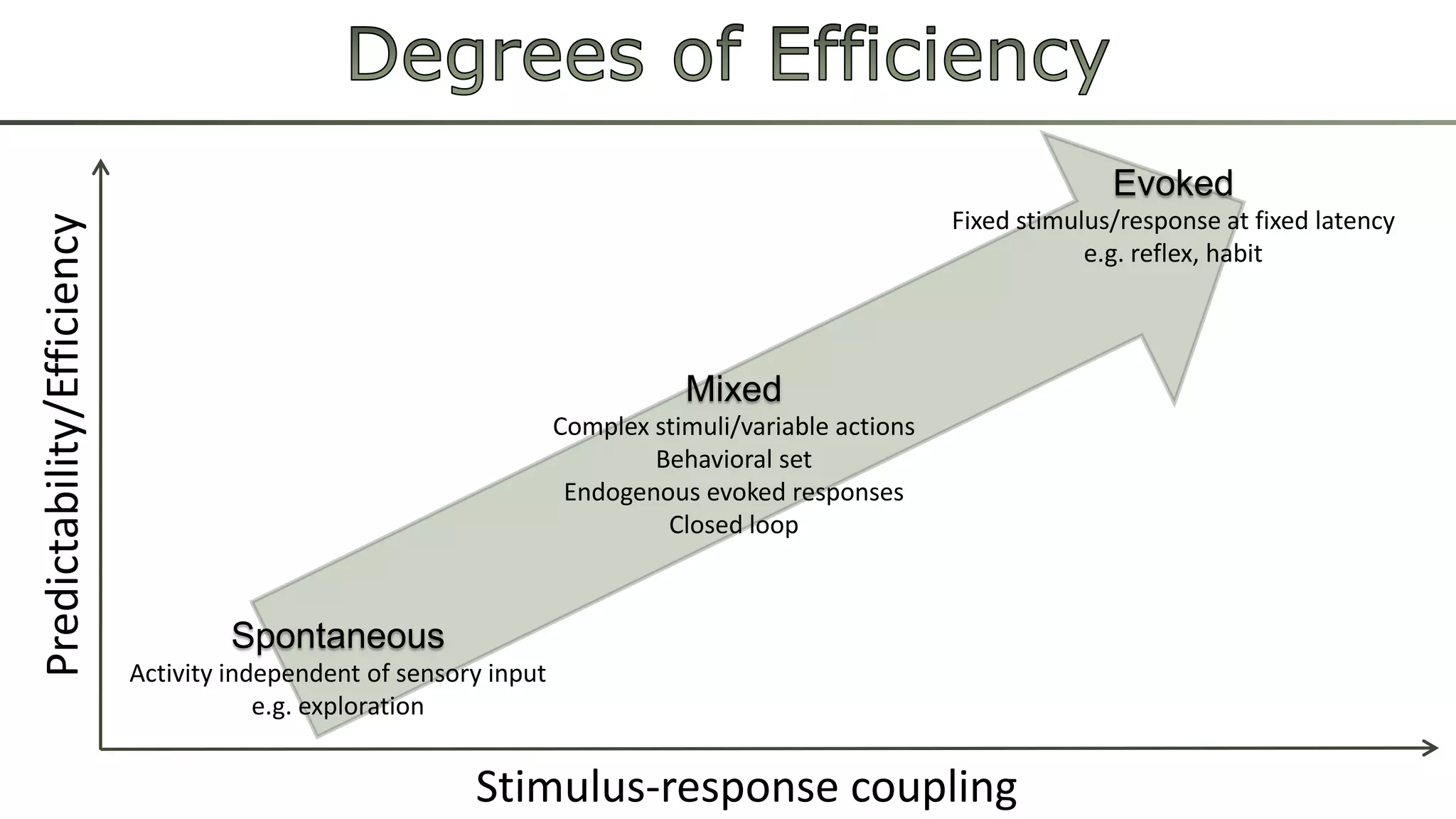
The document discusses various learning systems and behavioral variability in animals, referencing studies on Aplysia, Drosophila, and mice. It explores concepts of operant and classical conditioning, long-term memory mechanisms, and the role of specific proteins in synaptic plasticity. The content is derived from comparative psychology literature and emphasizes evolutionary perspectives on learning and behavior.