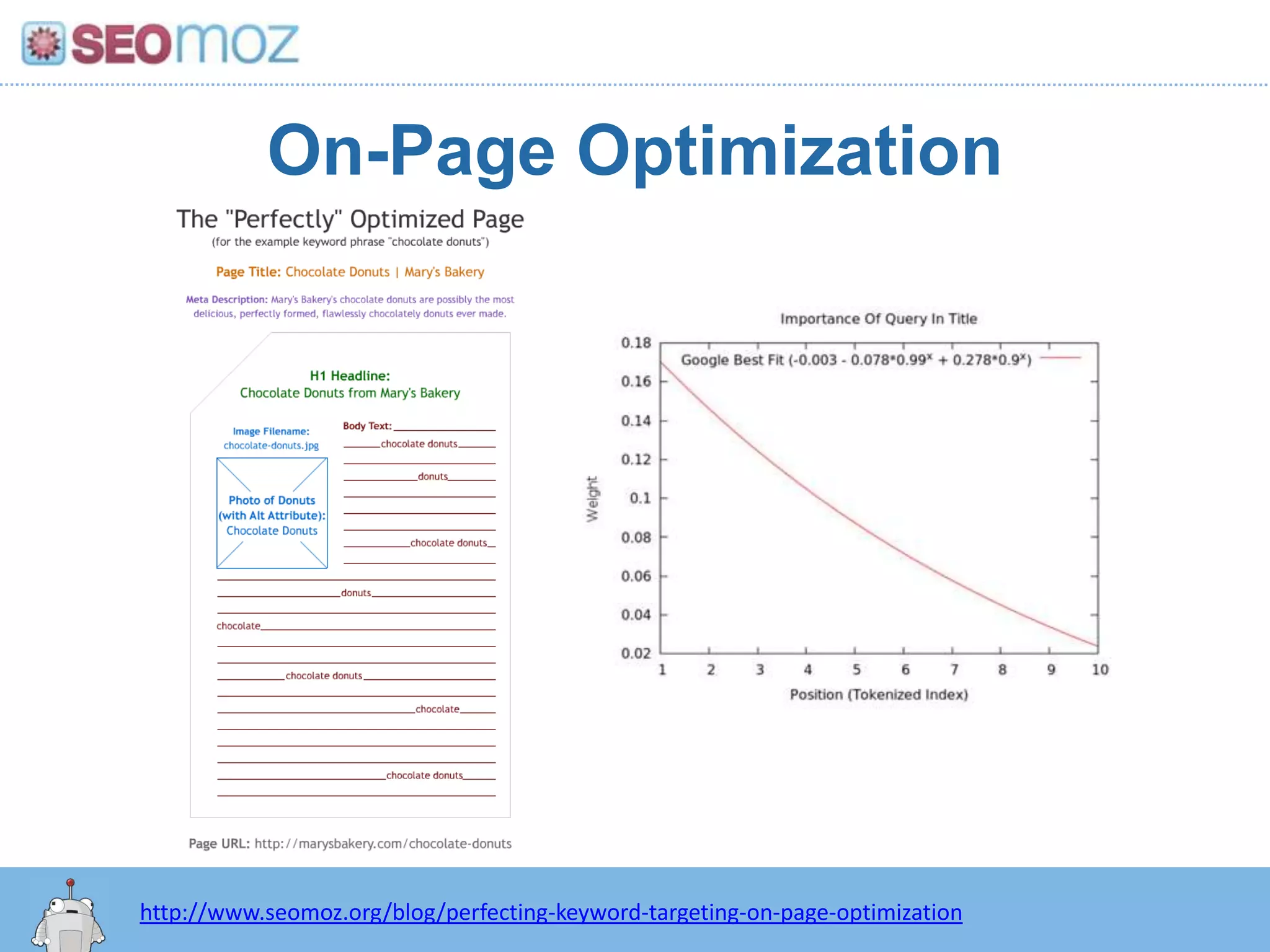
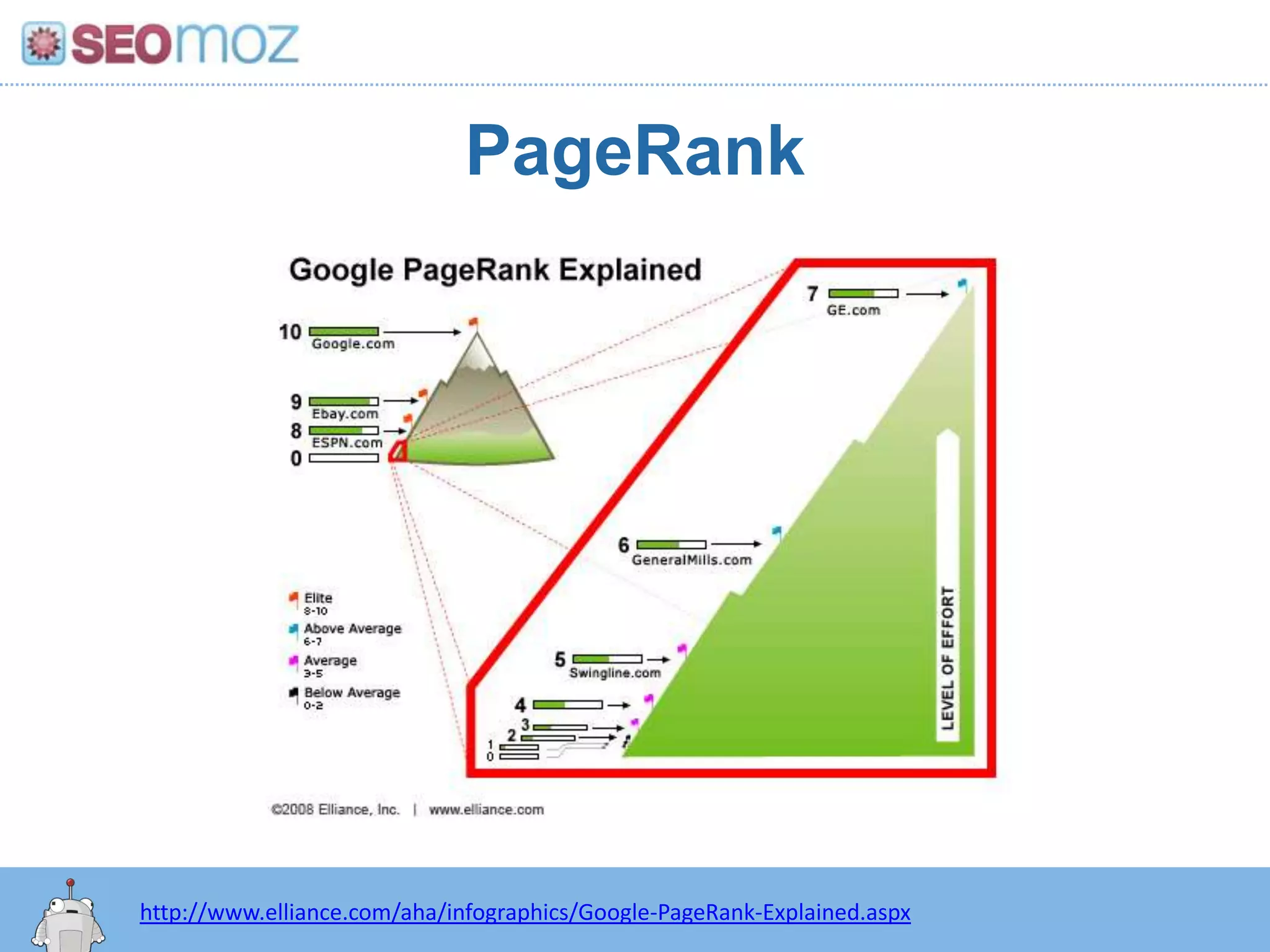
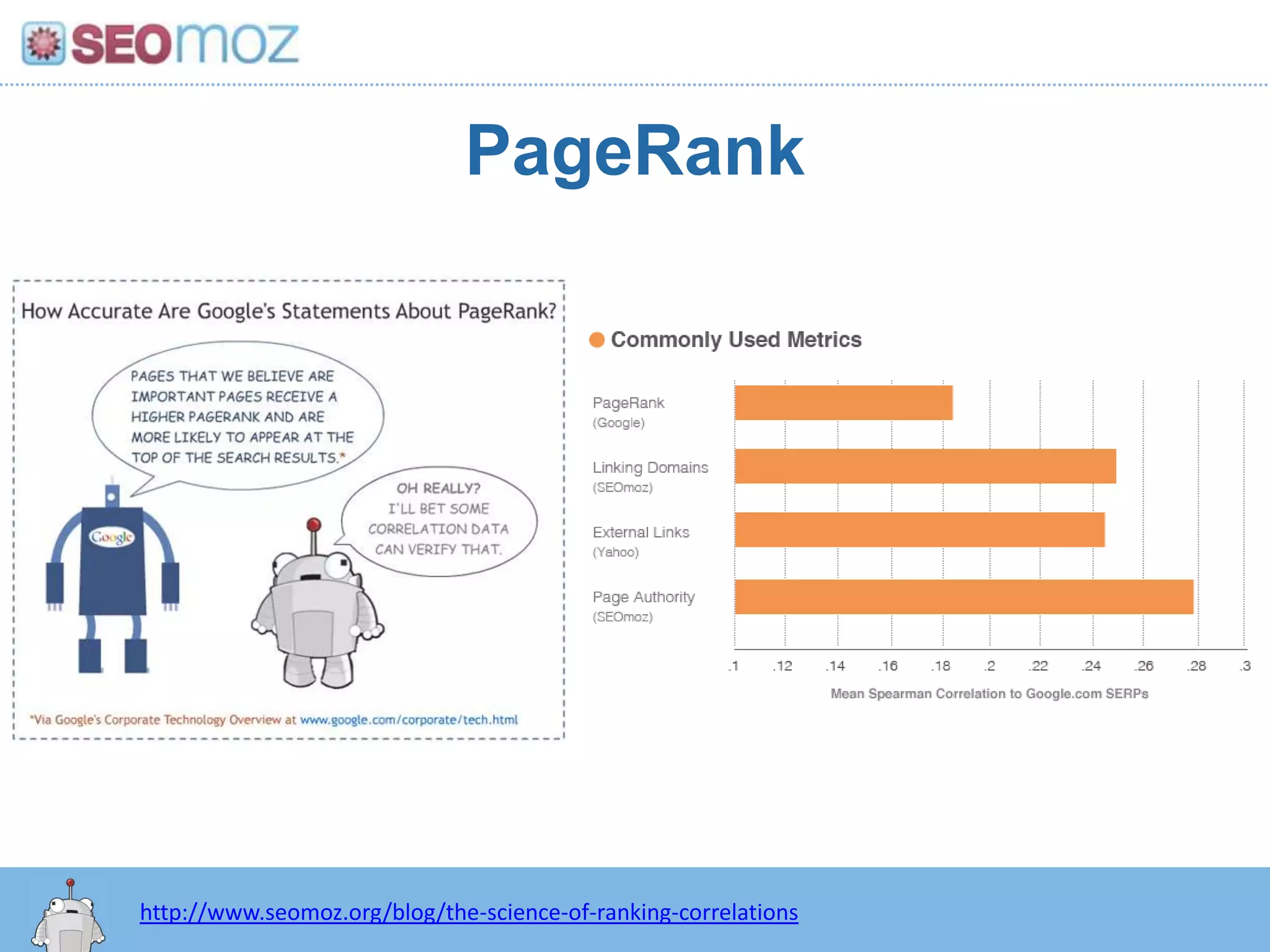
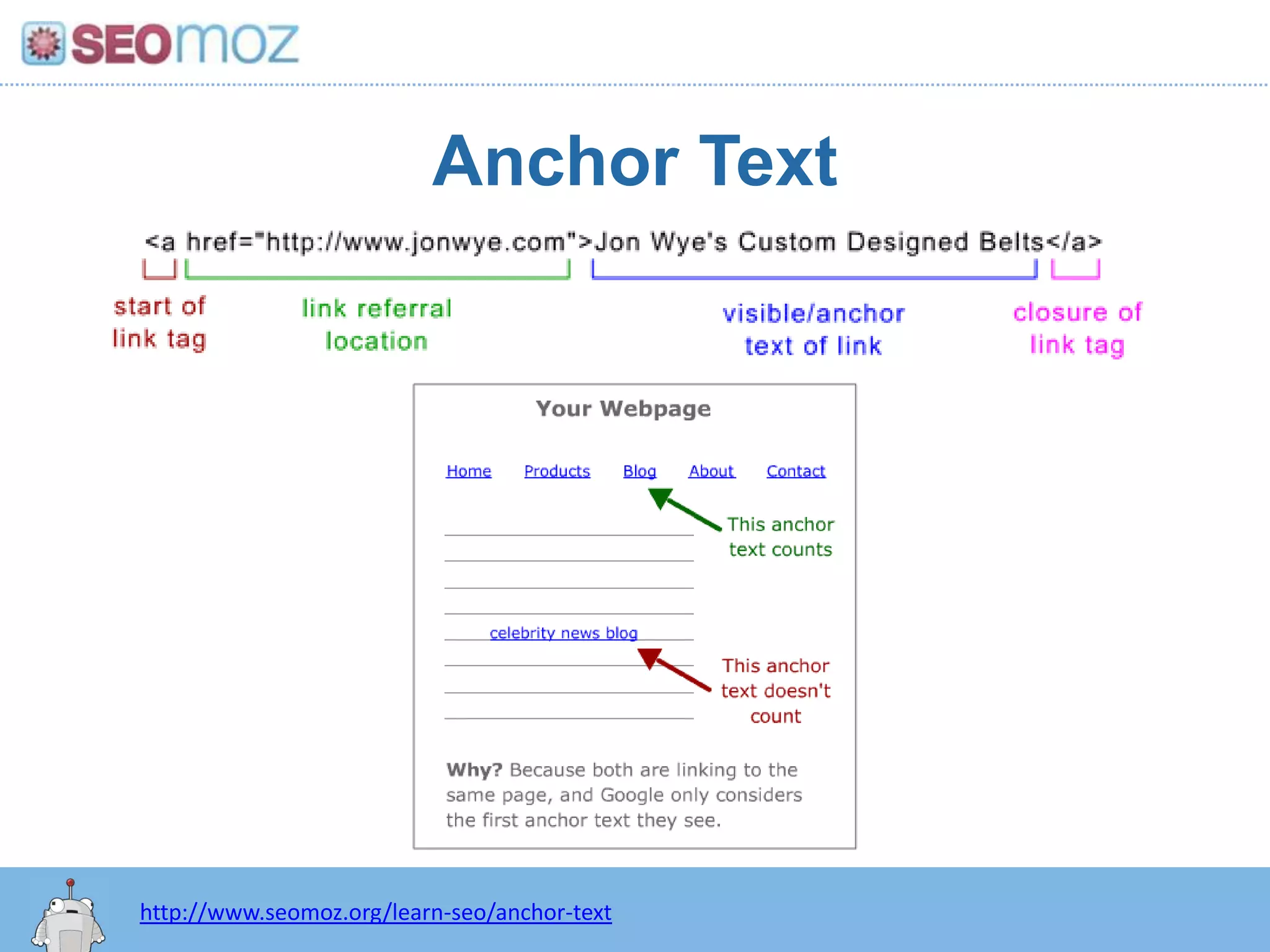
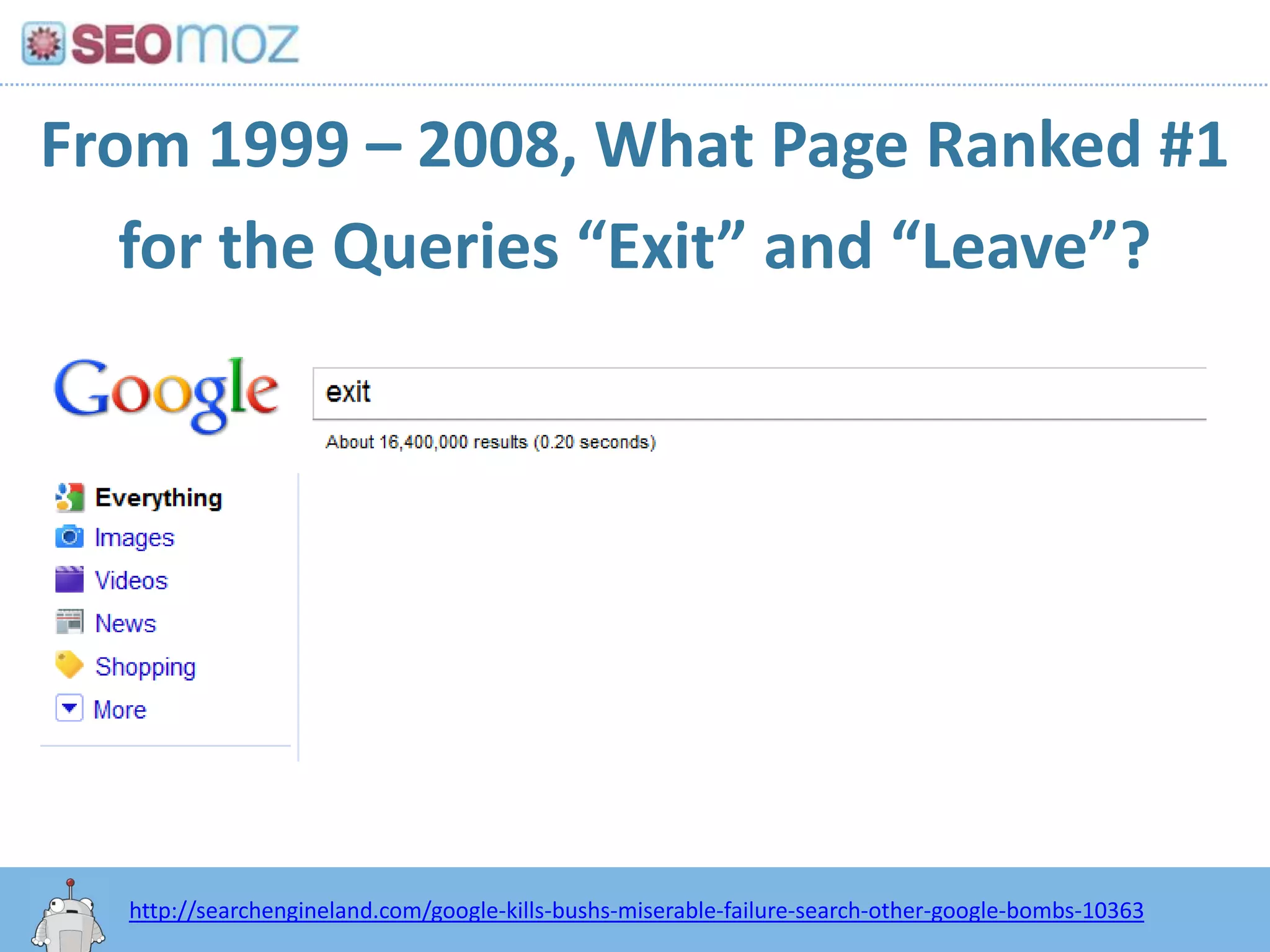
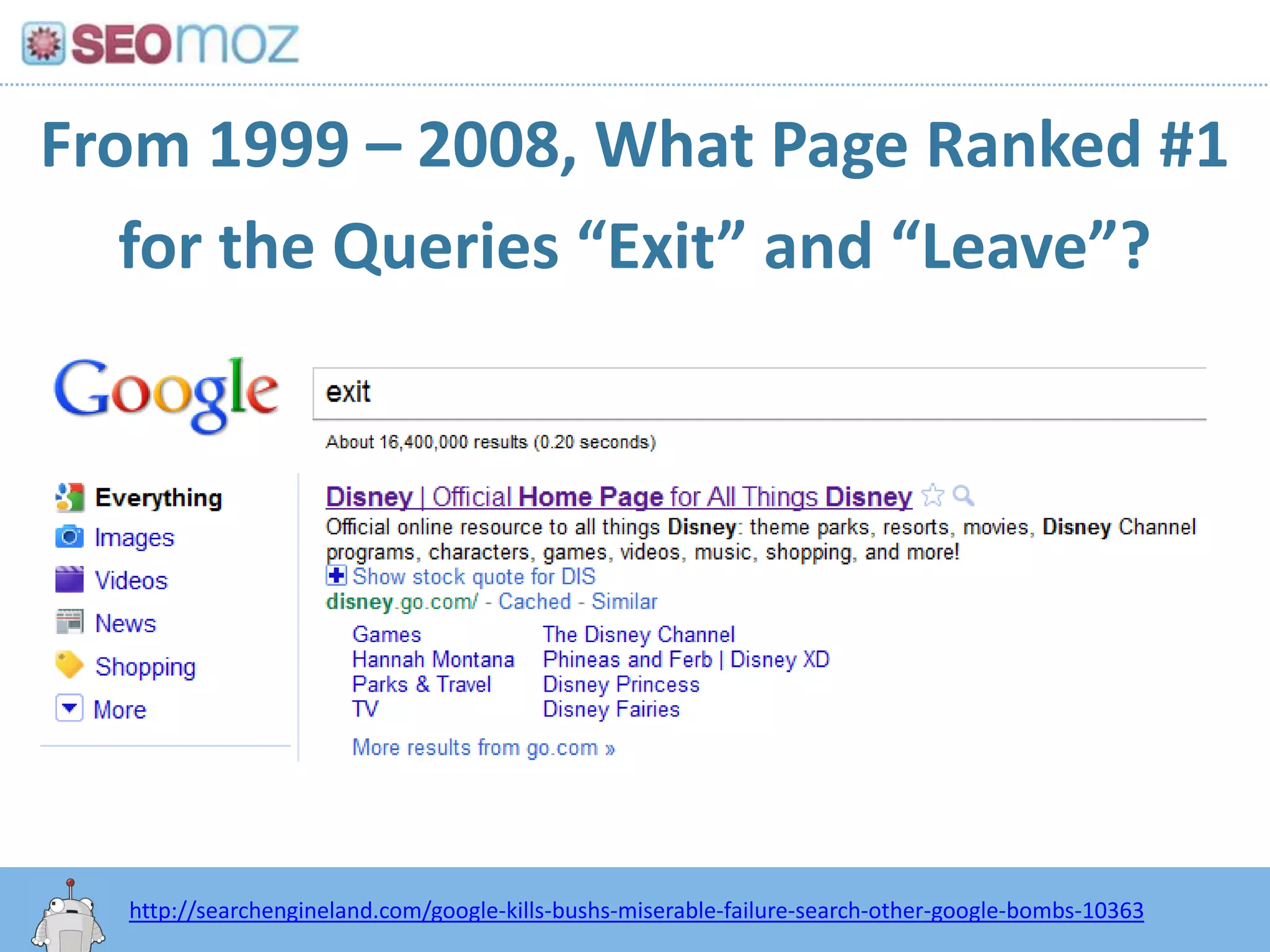
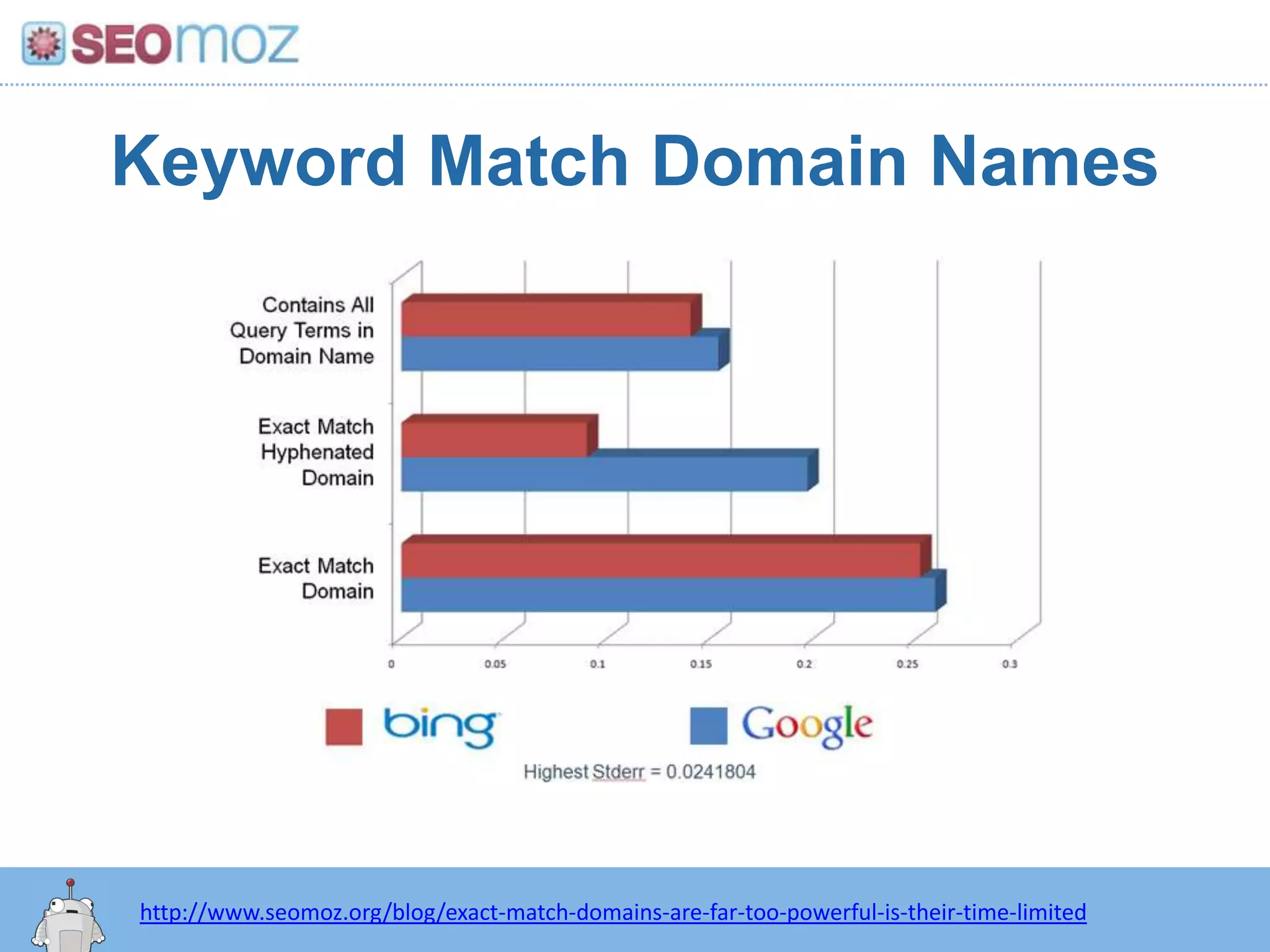
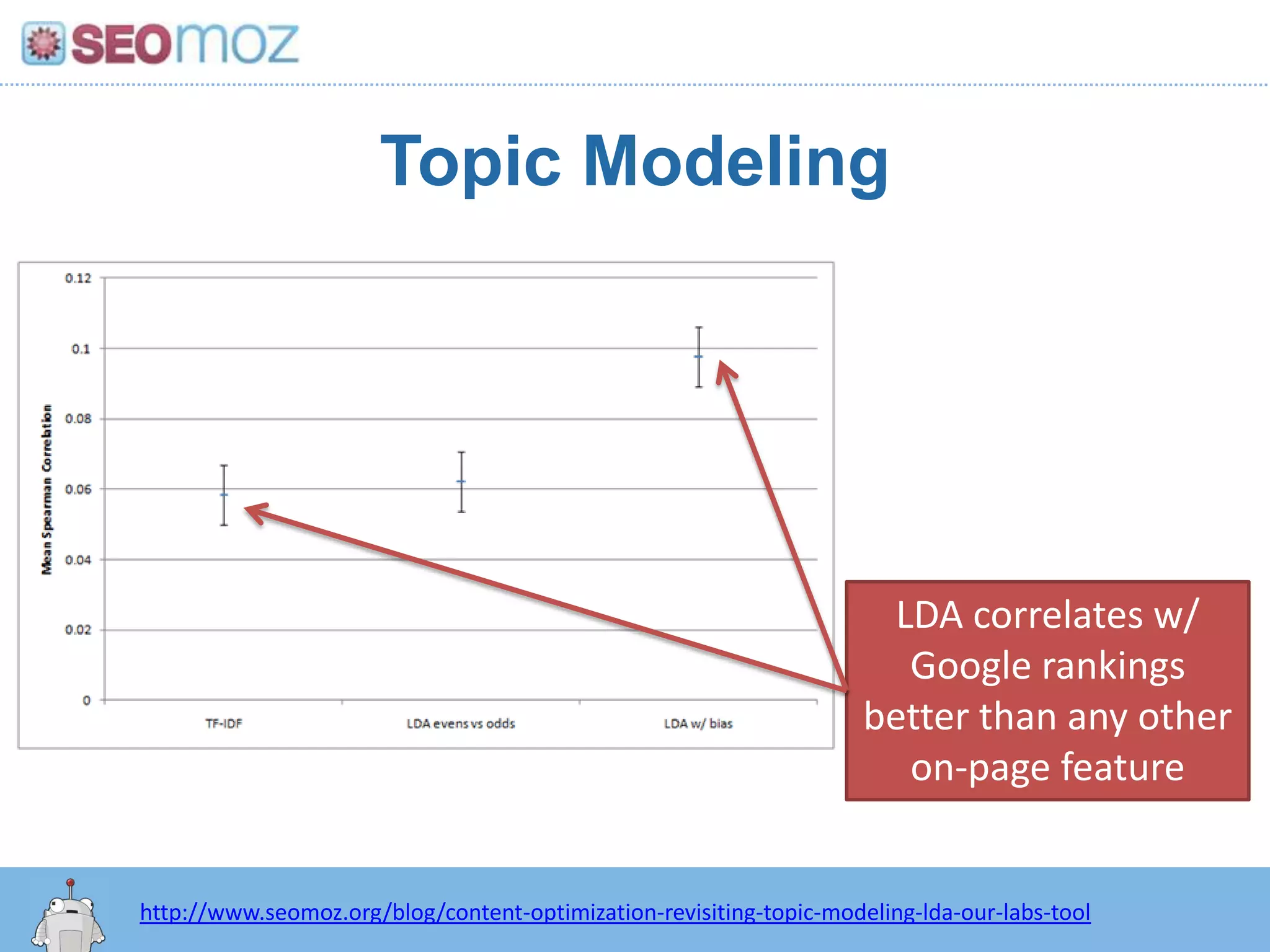
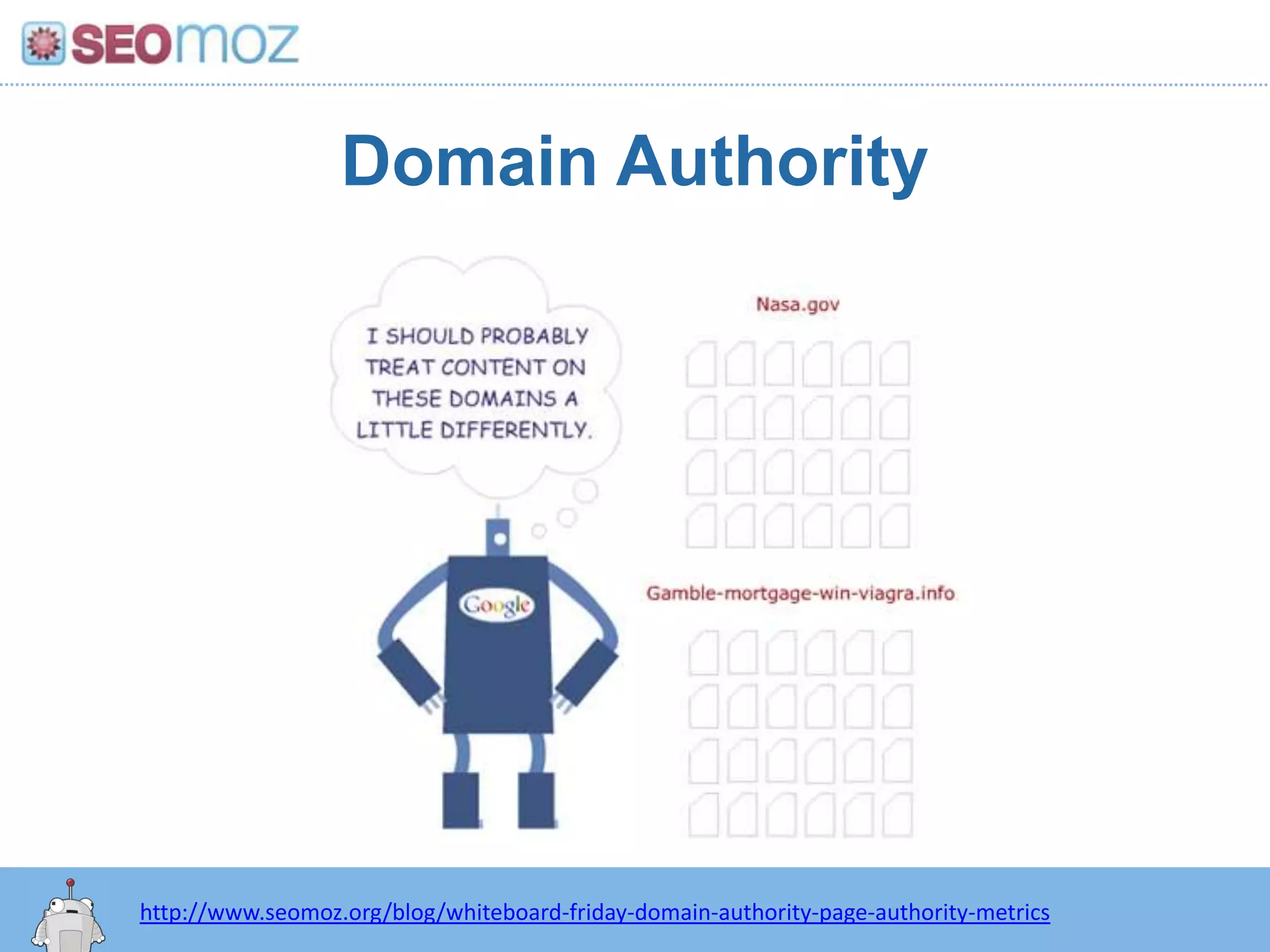
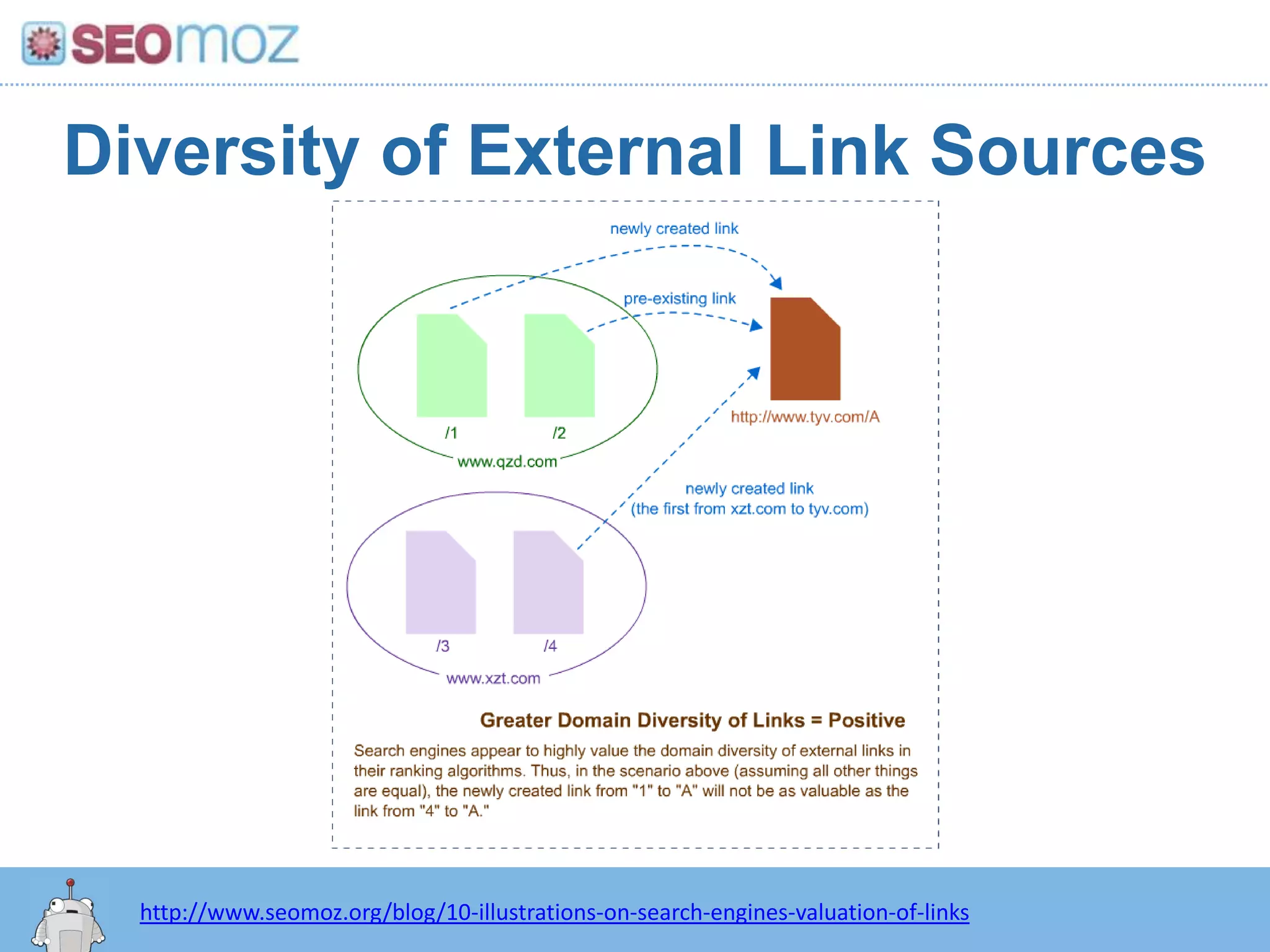
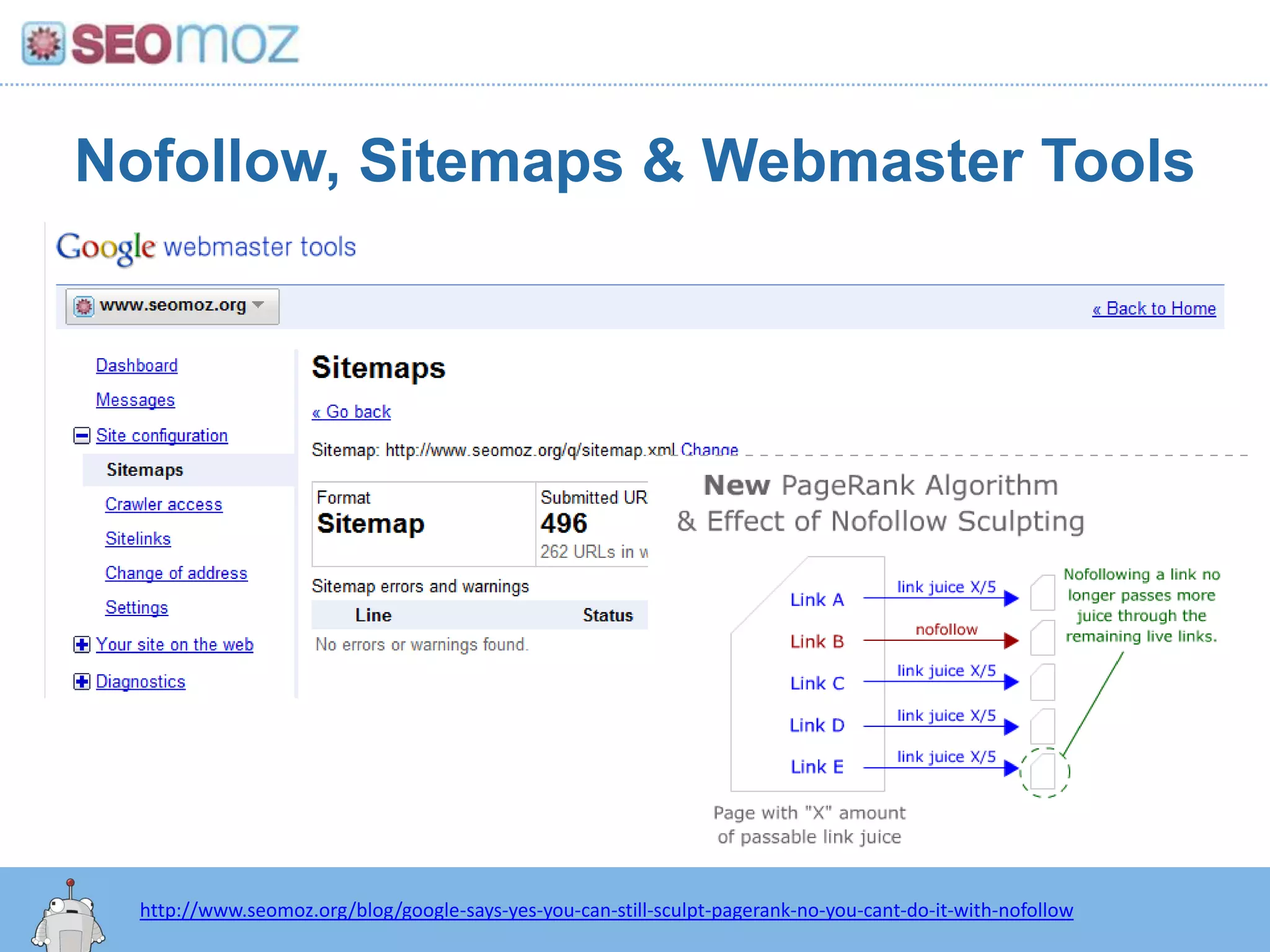
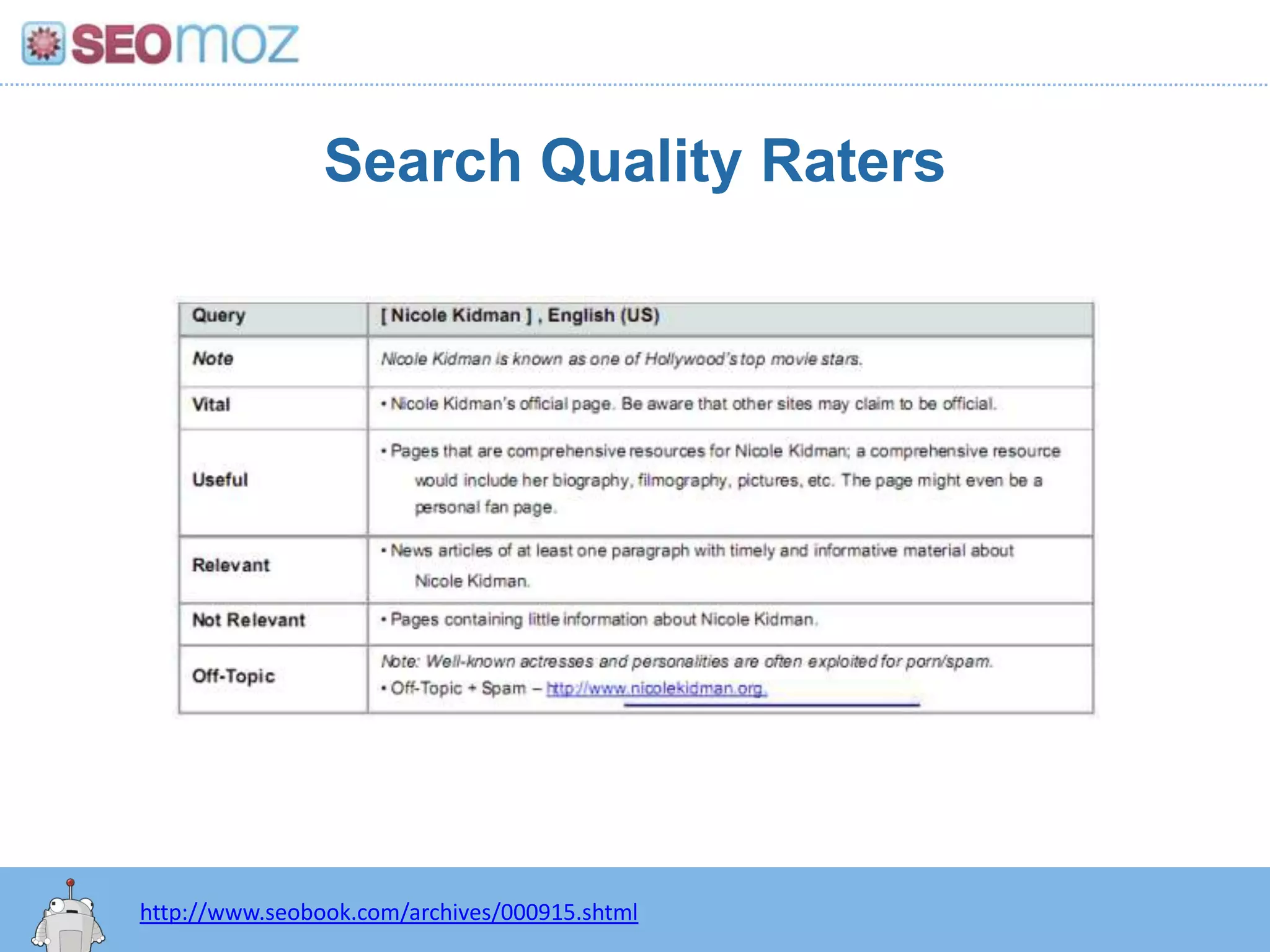
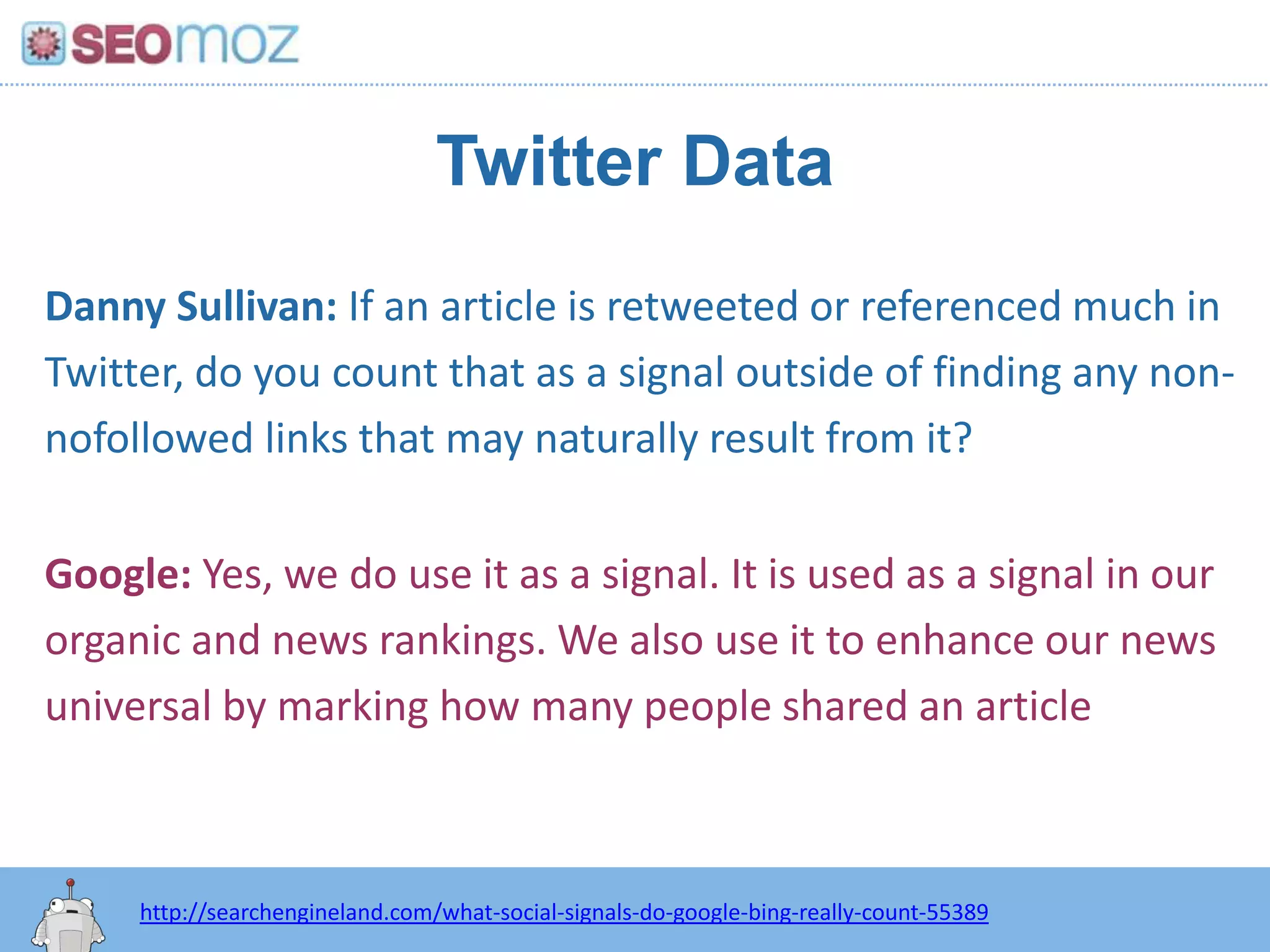
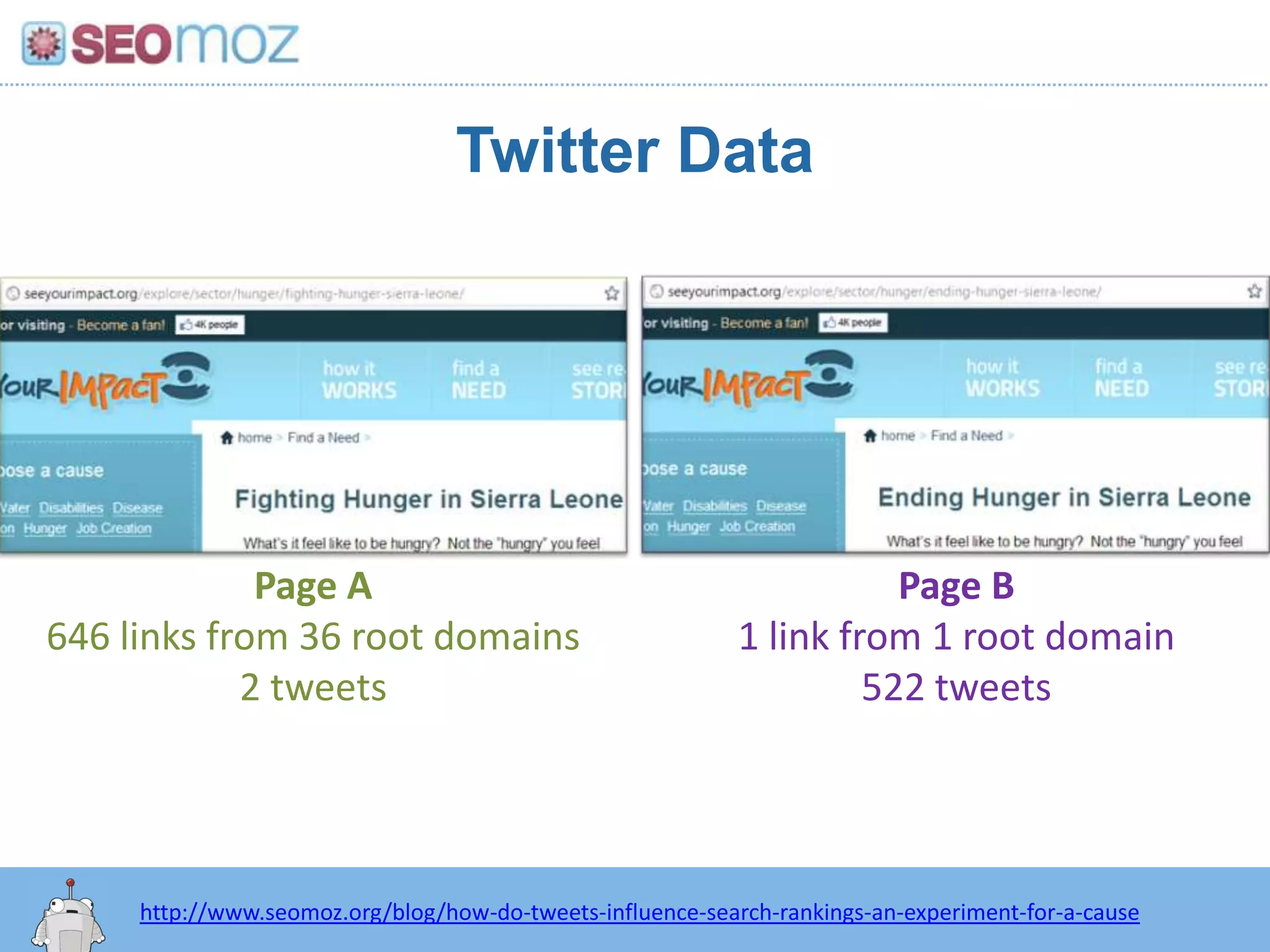
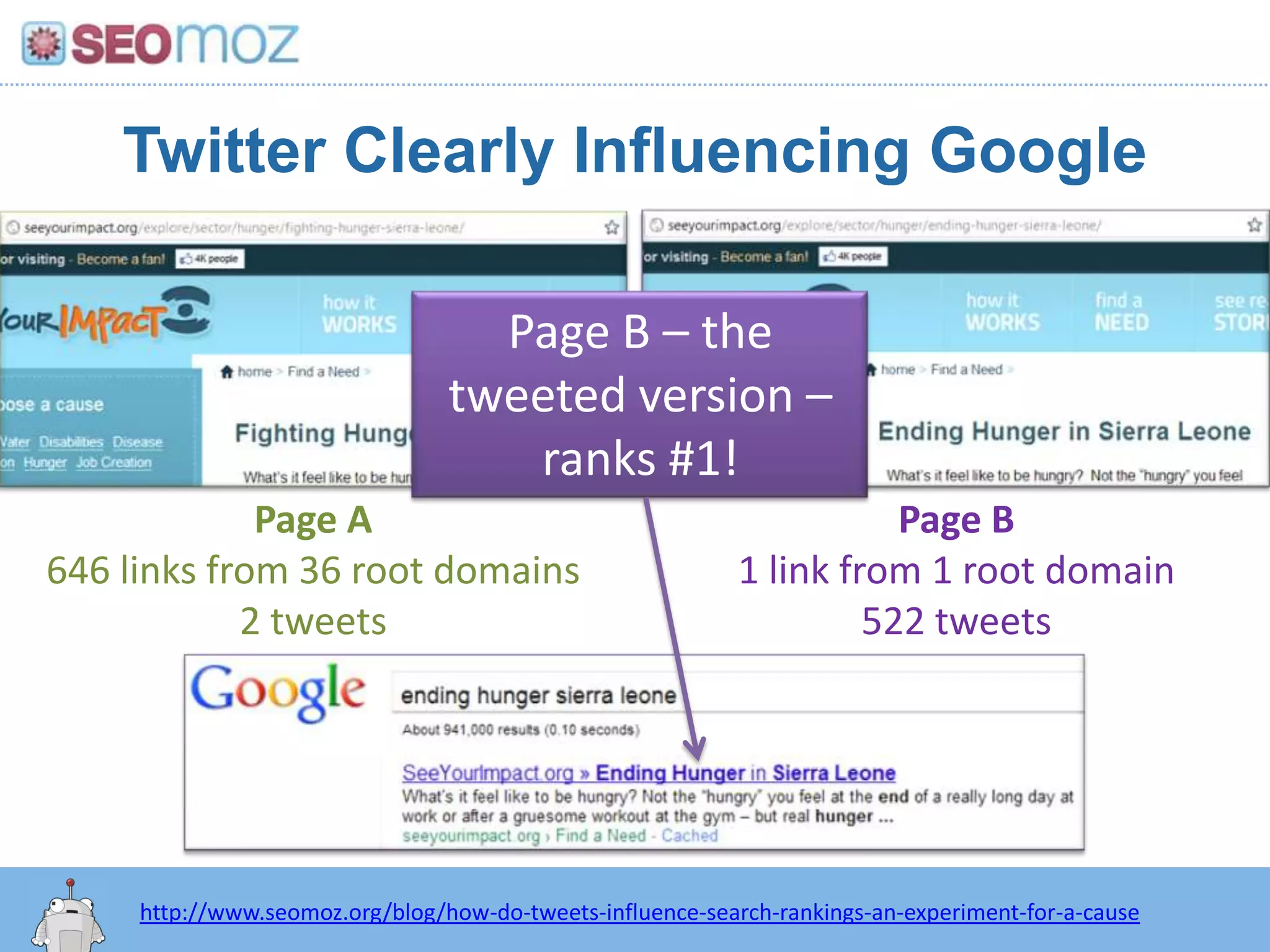
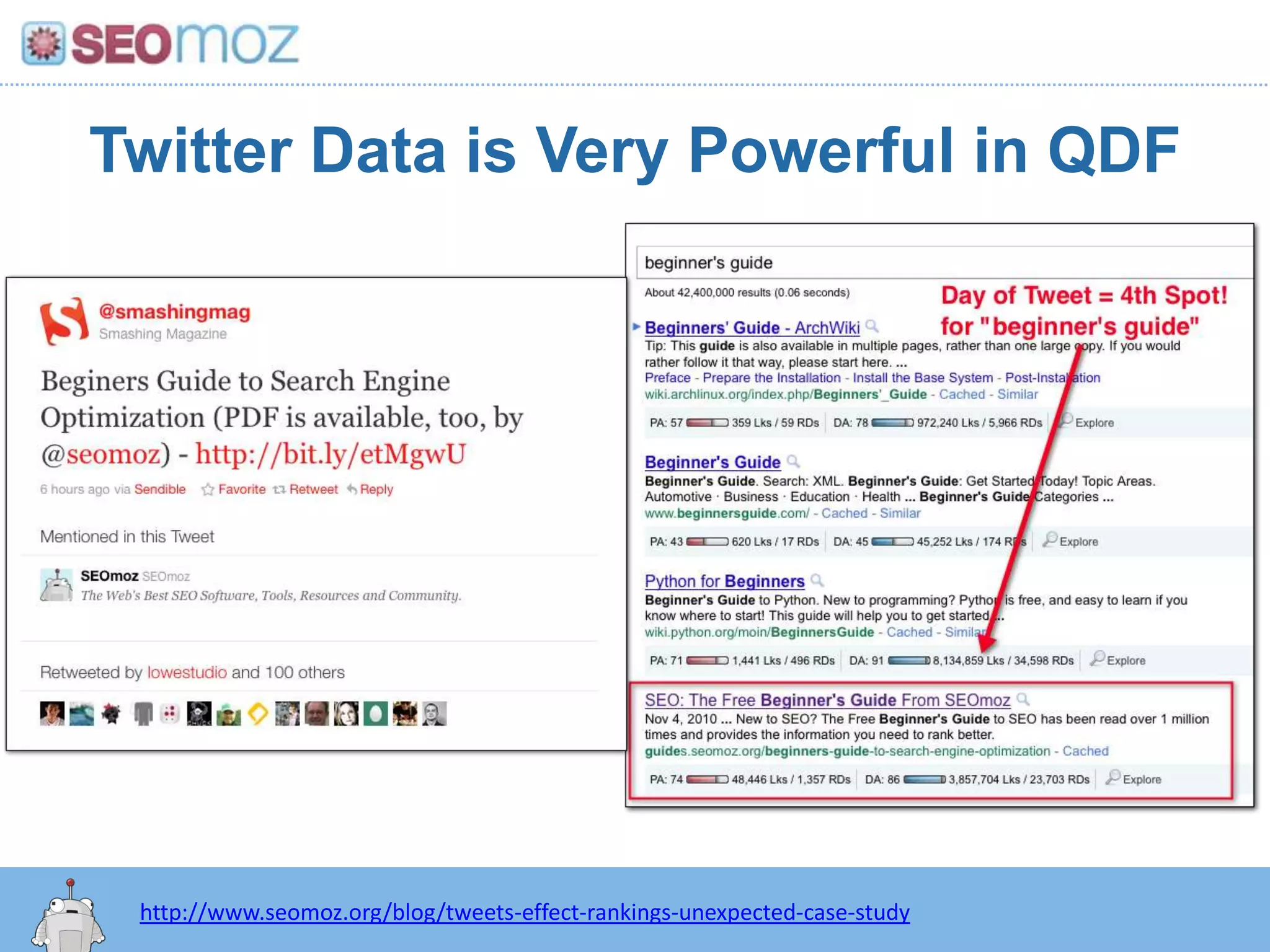
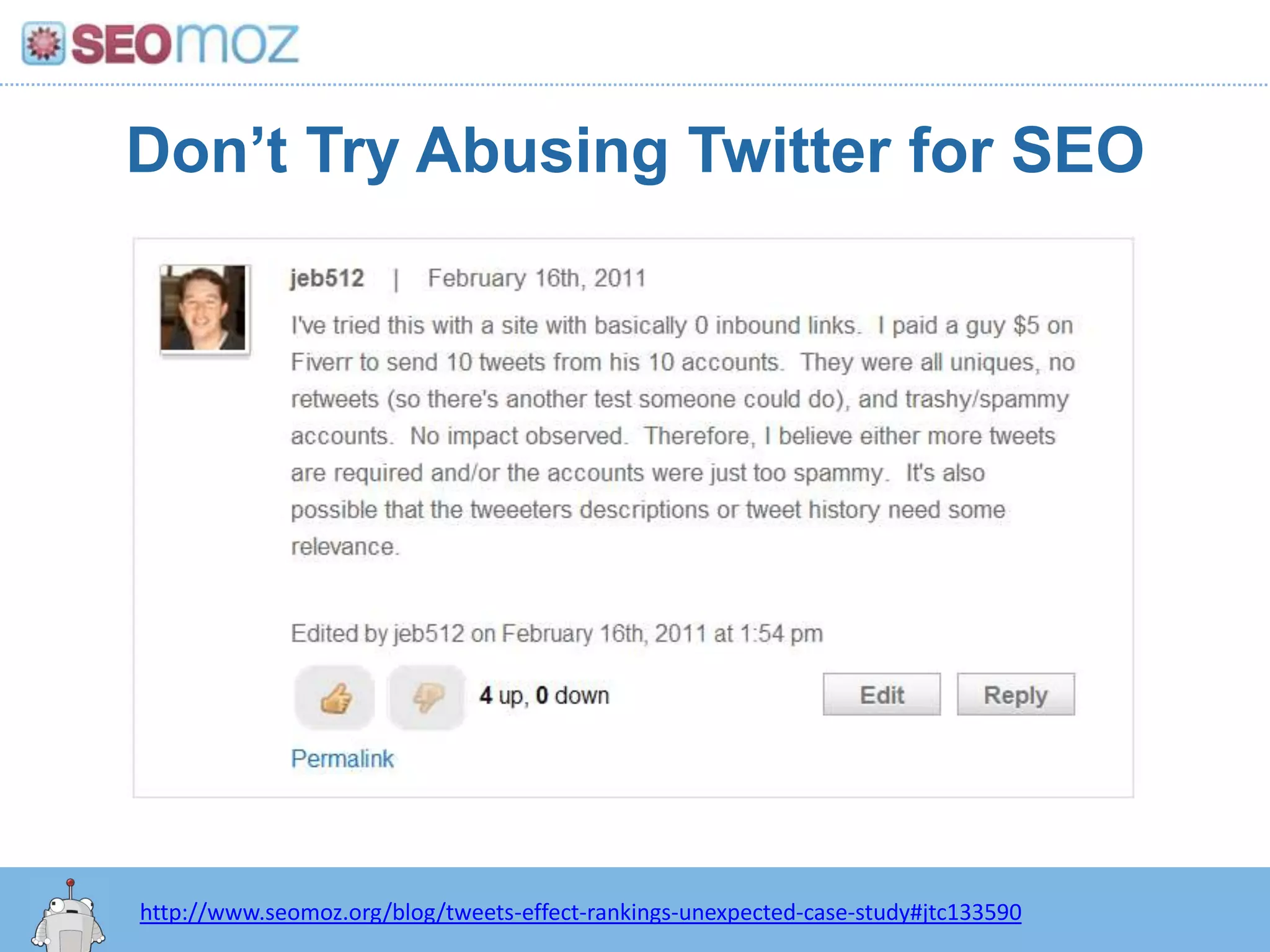
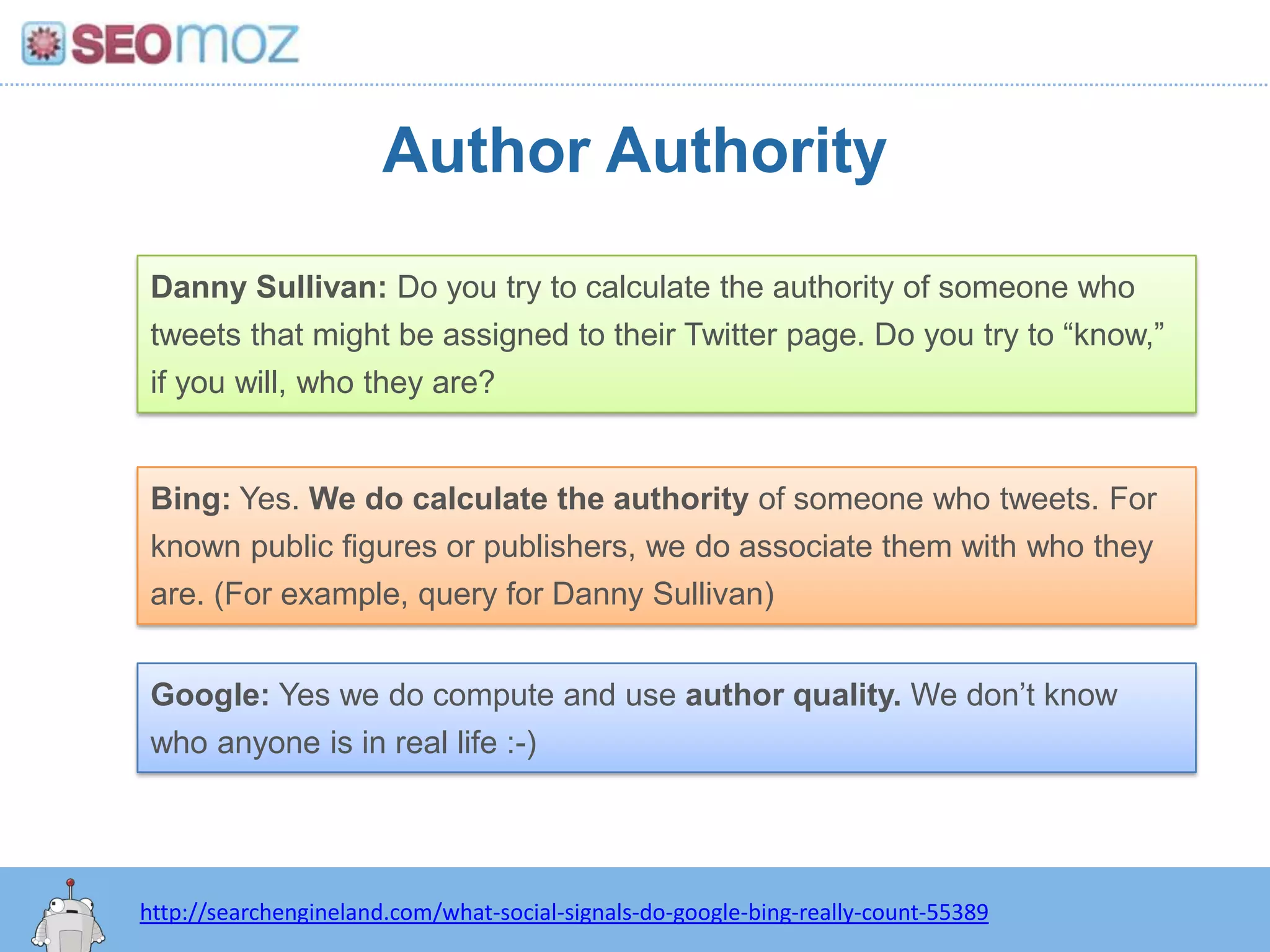
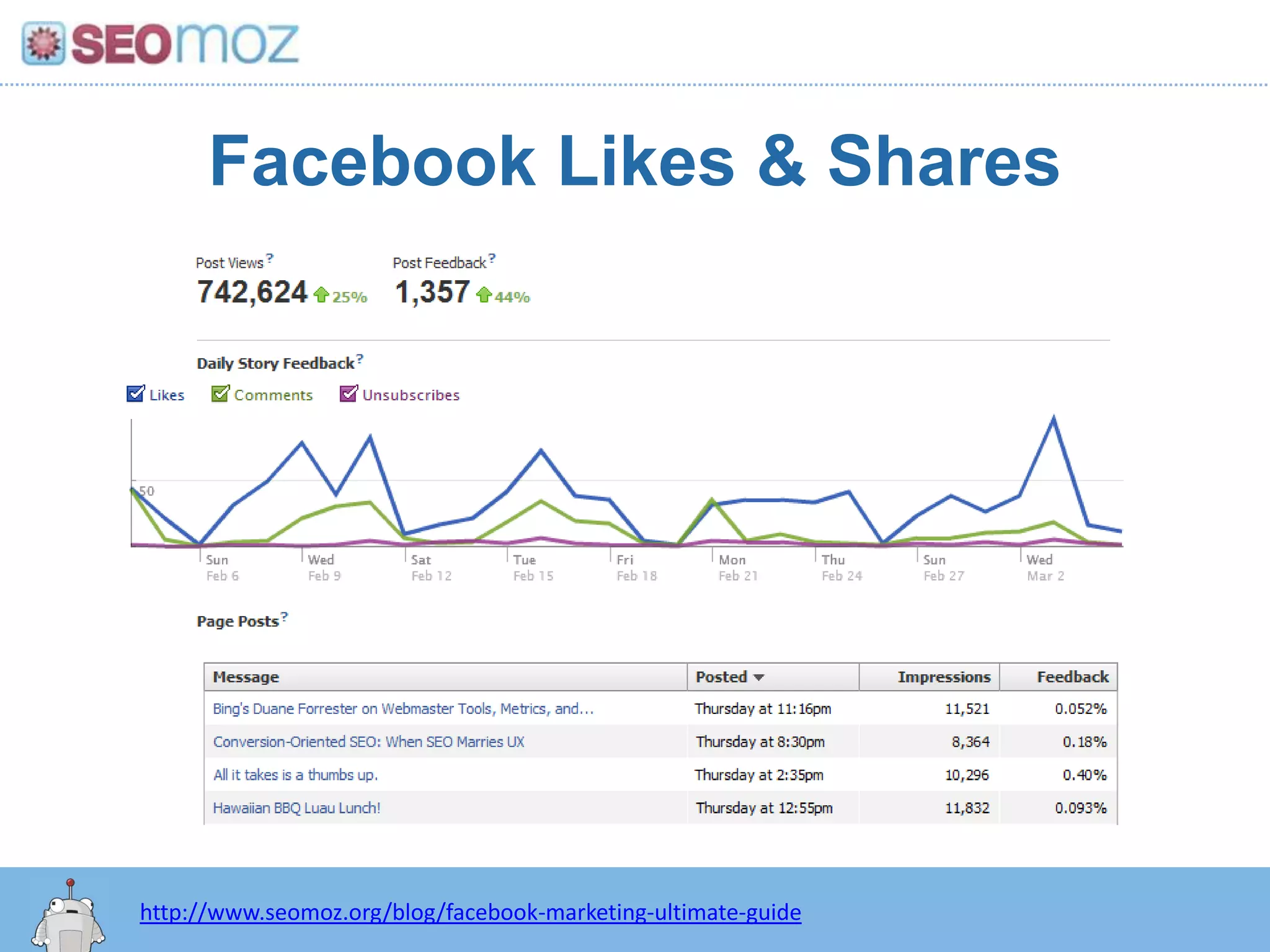
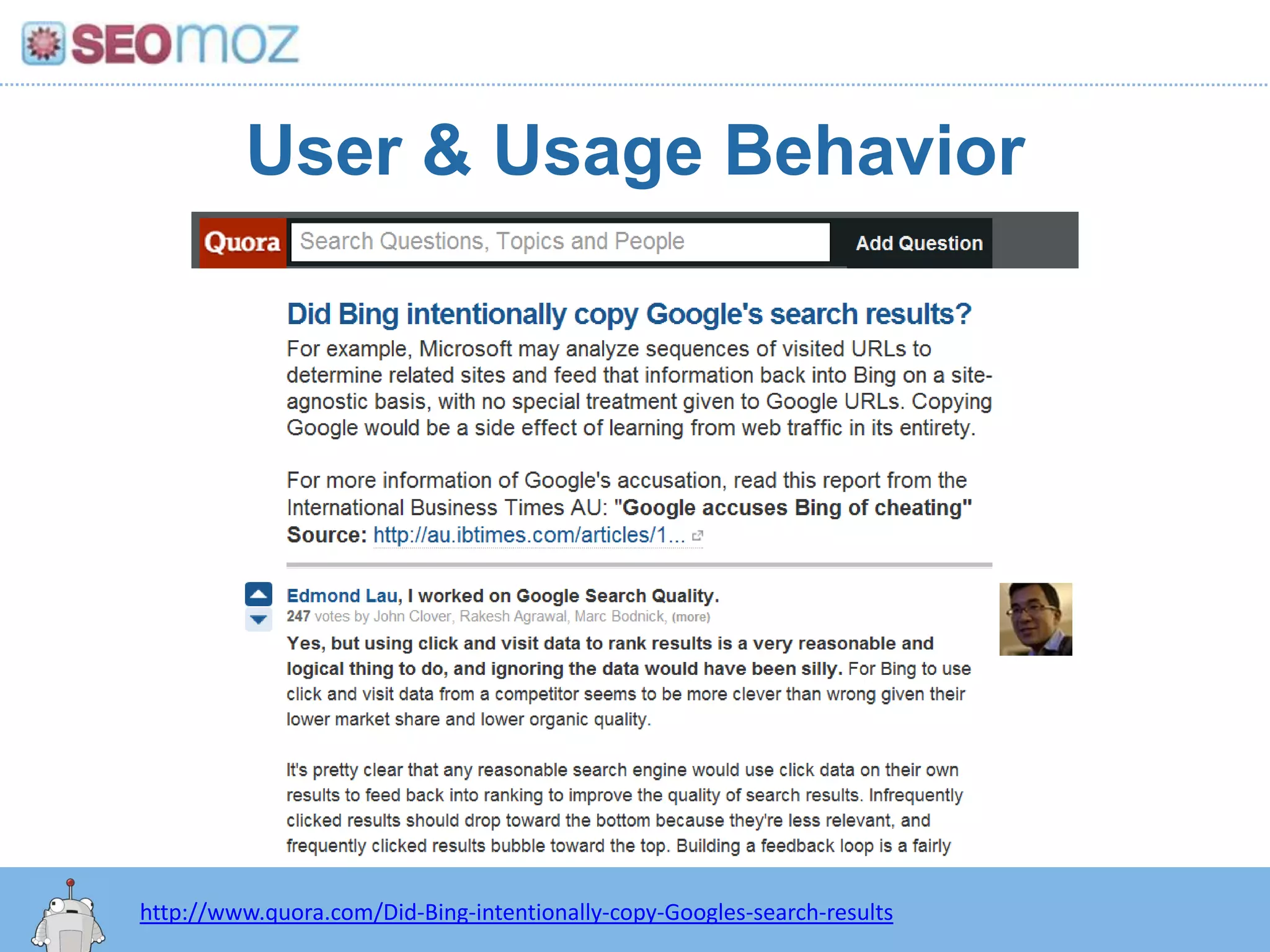
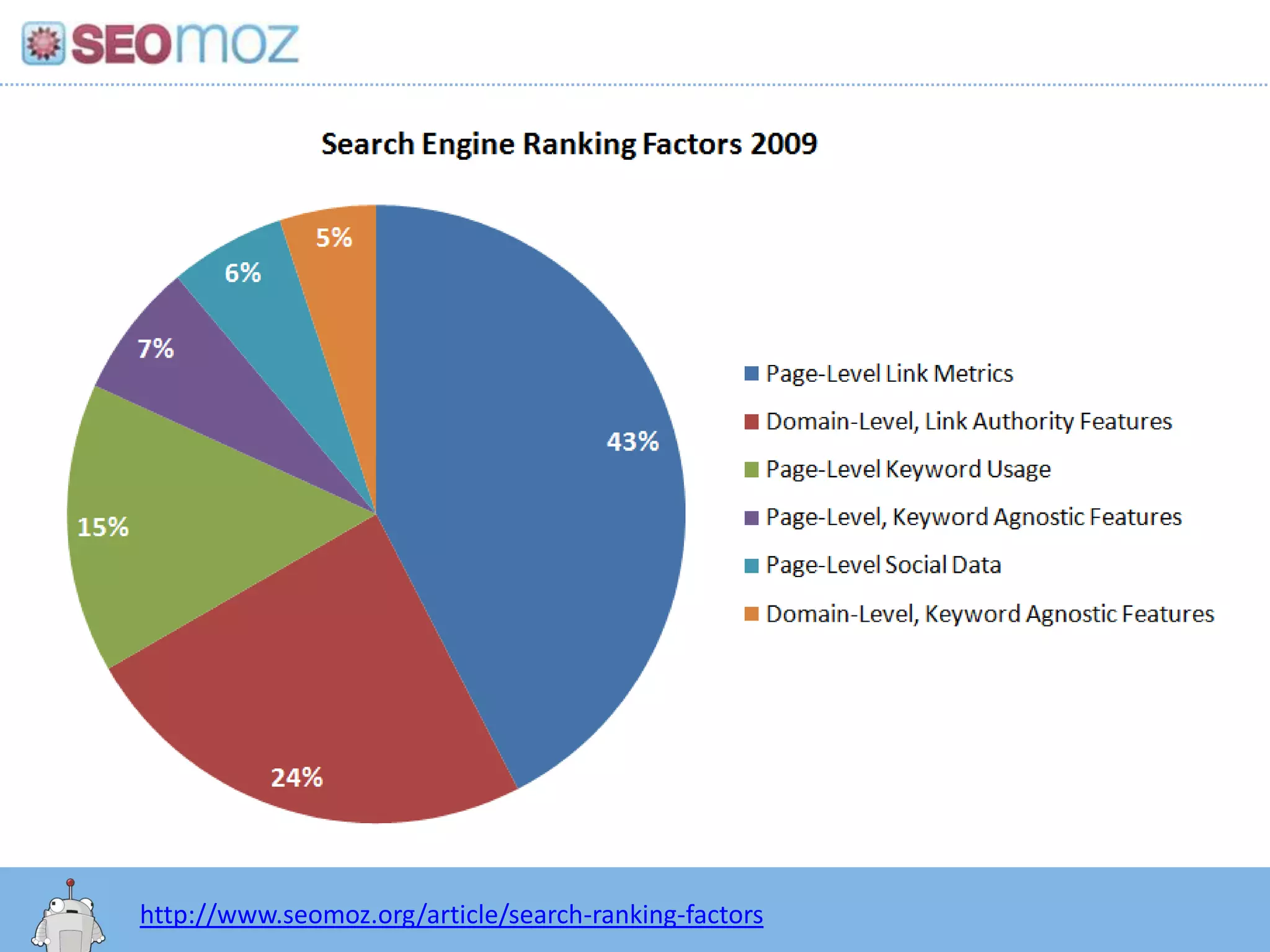
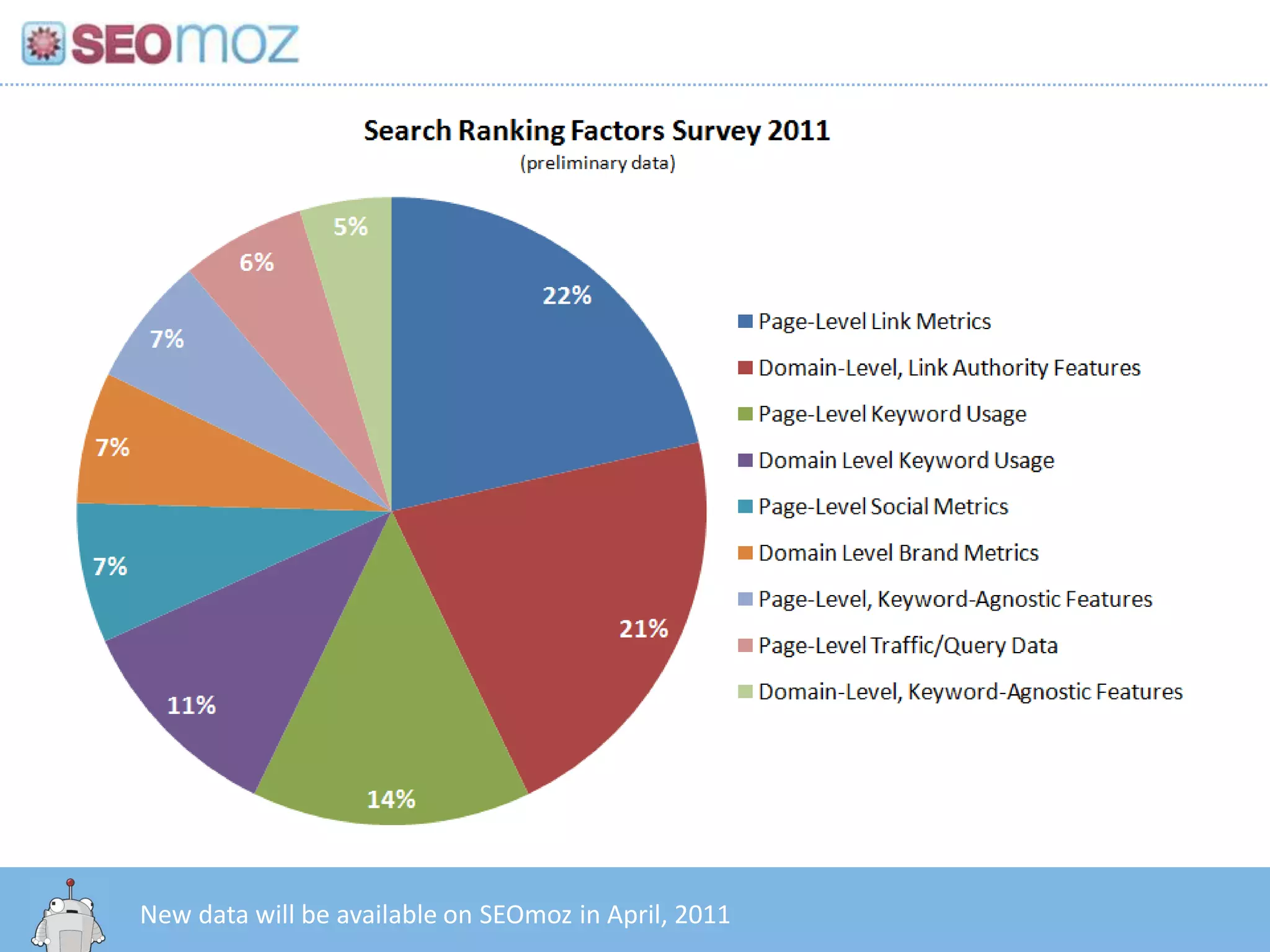
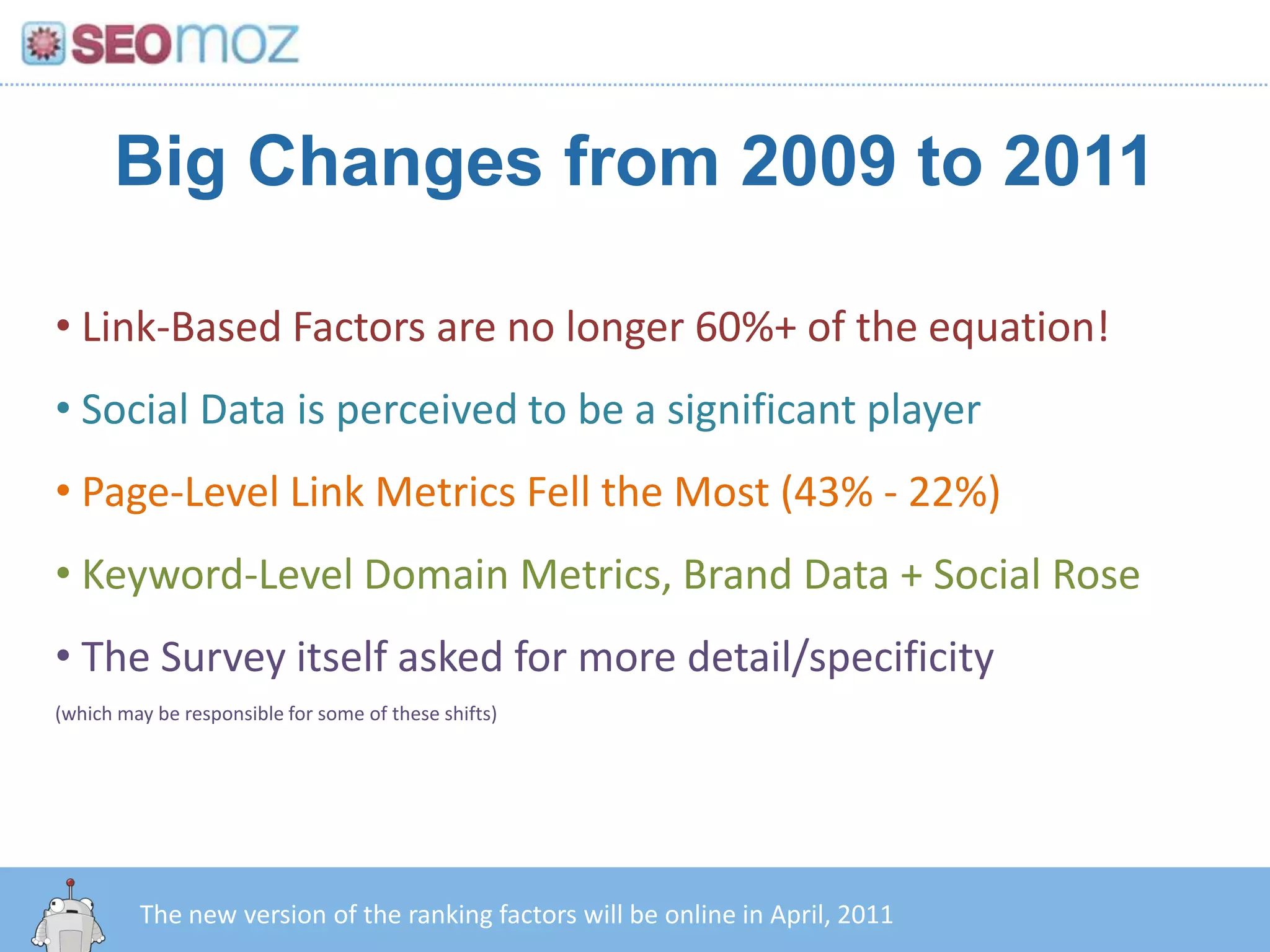
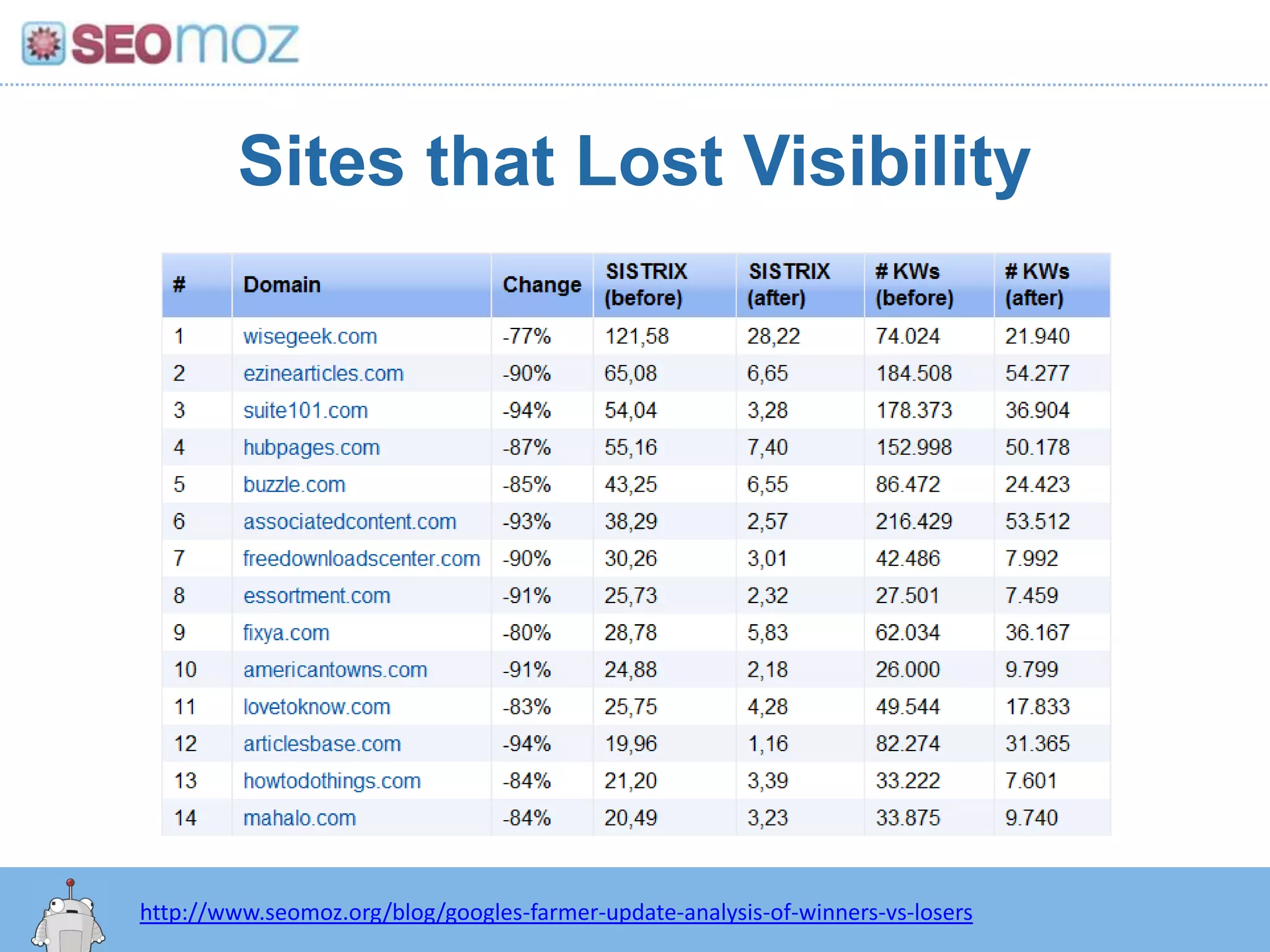
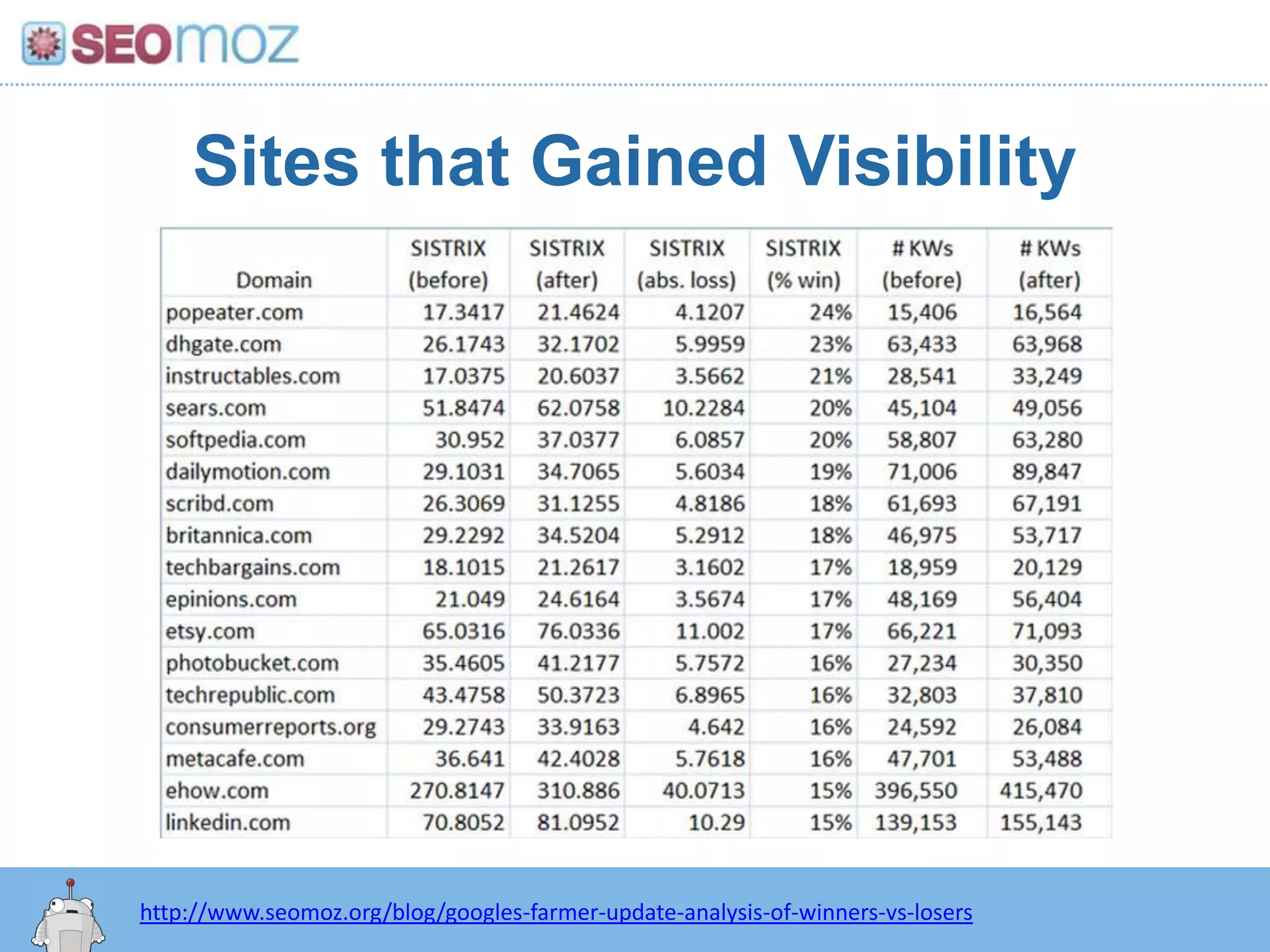
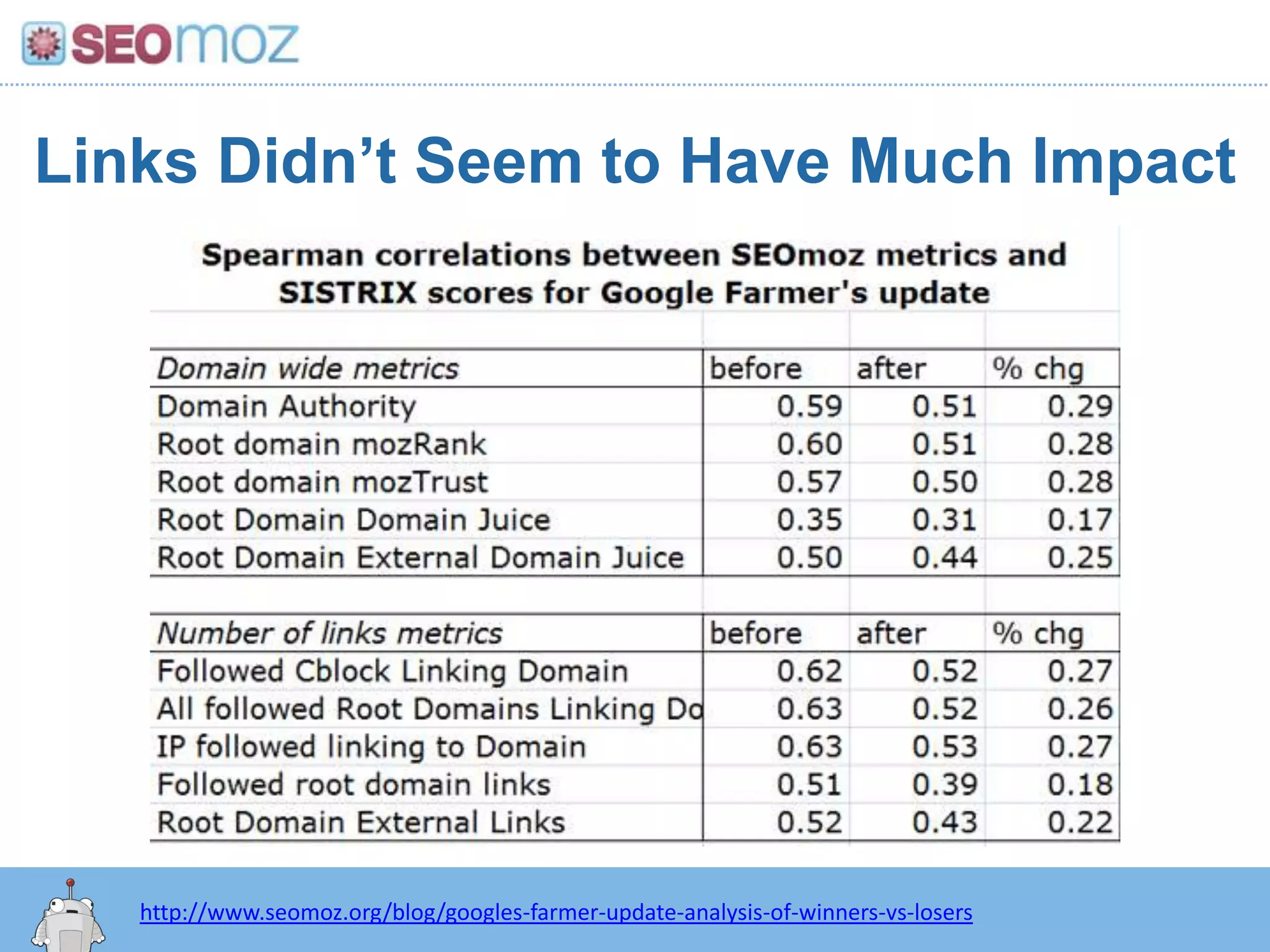
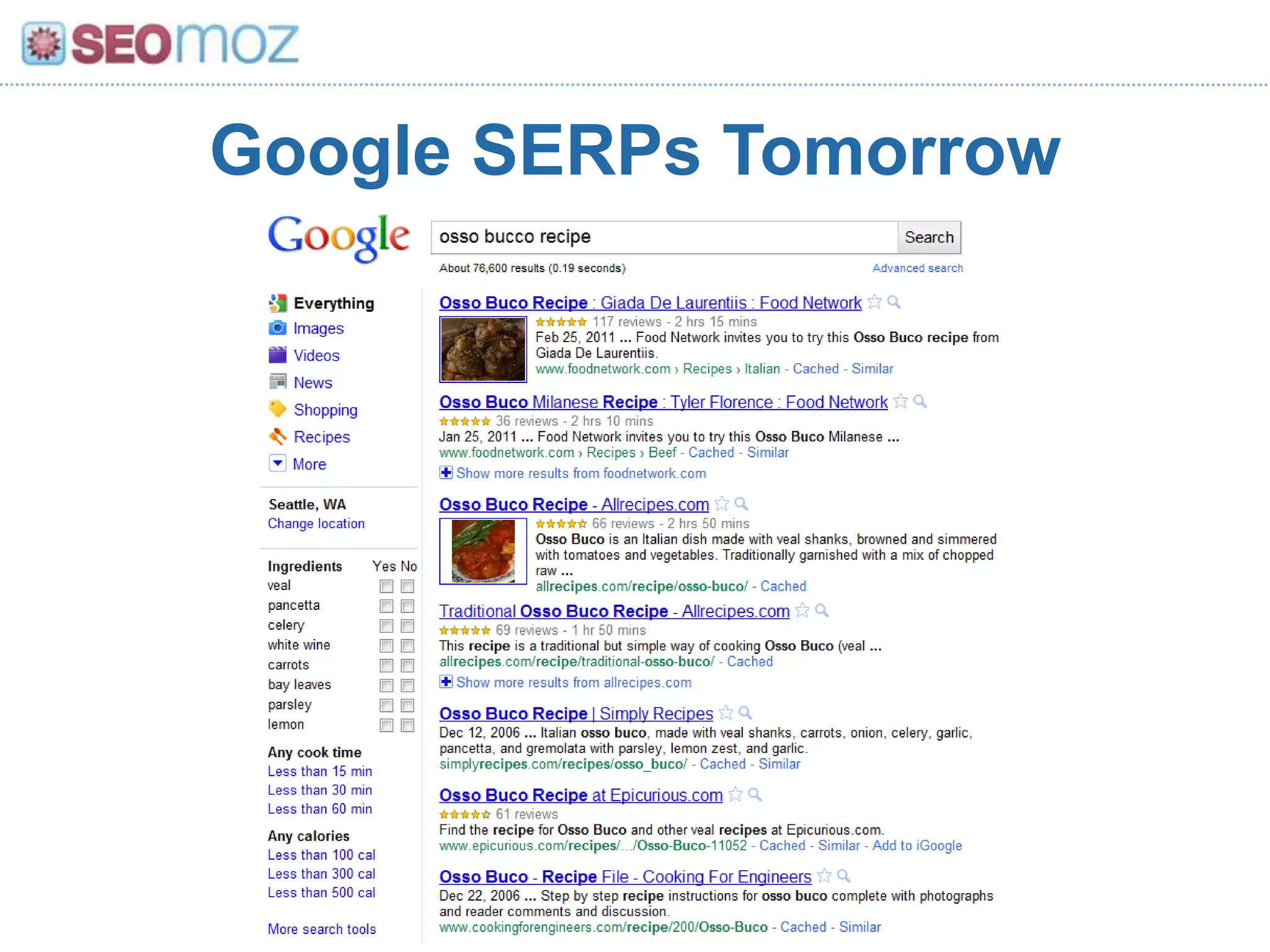
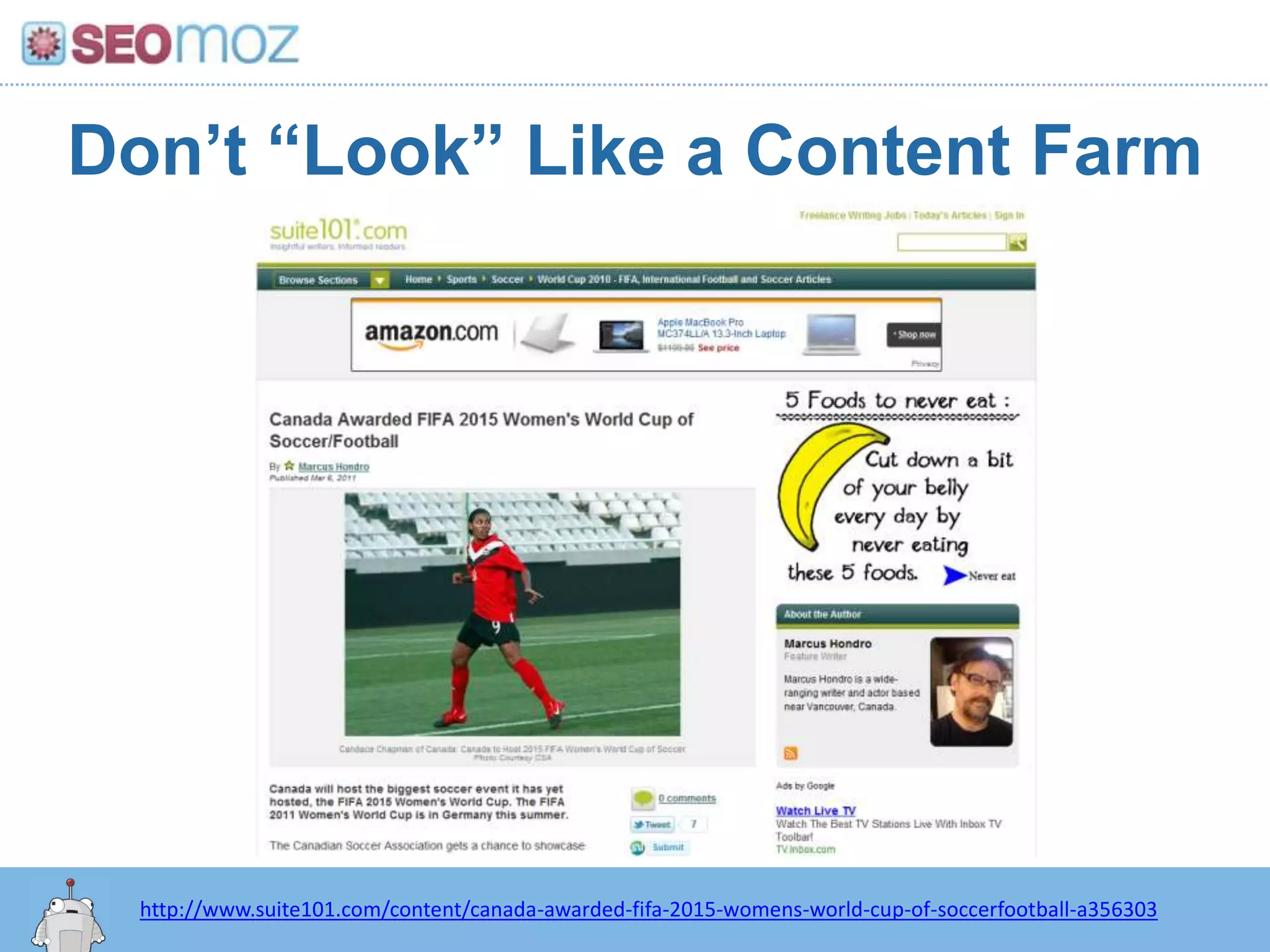
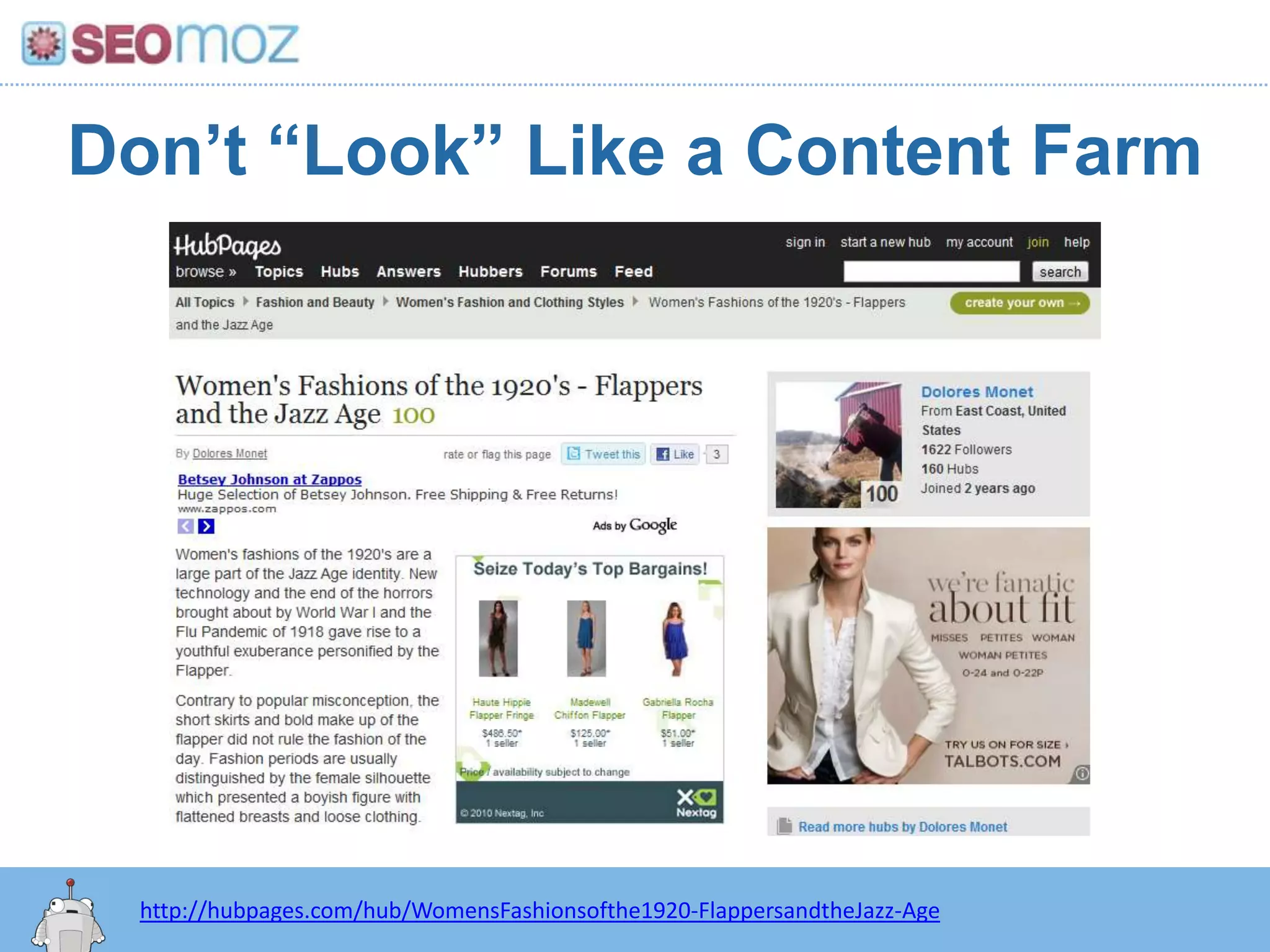
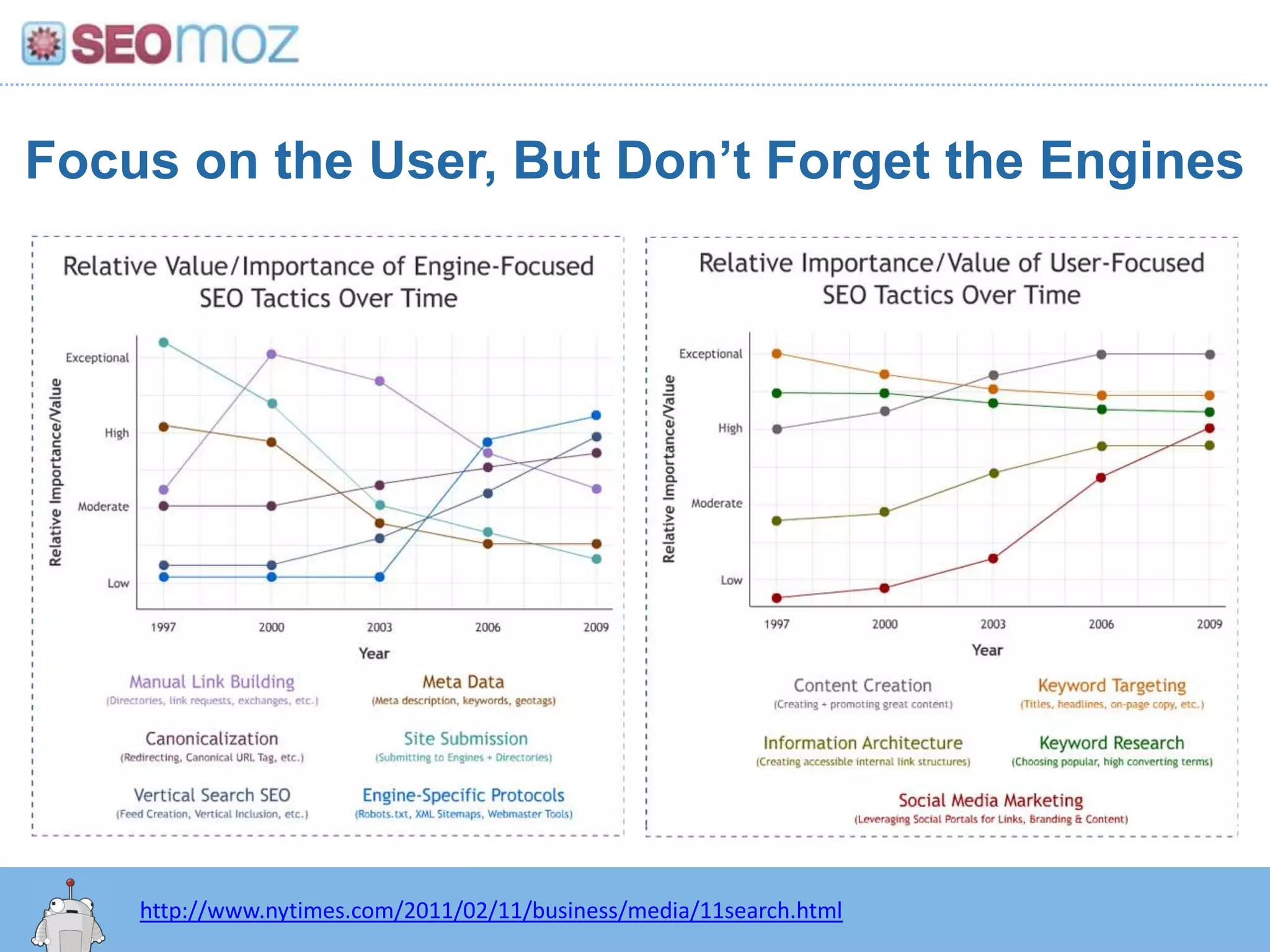
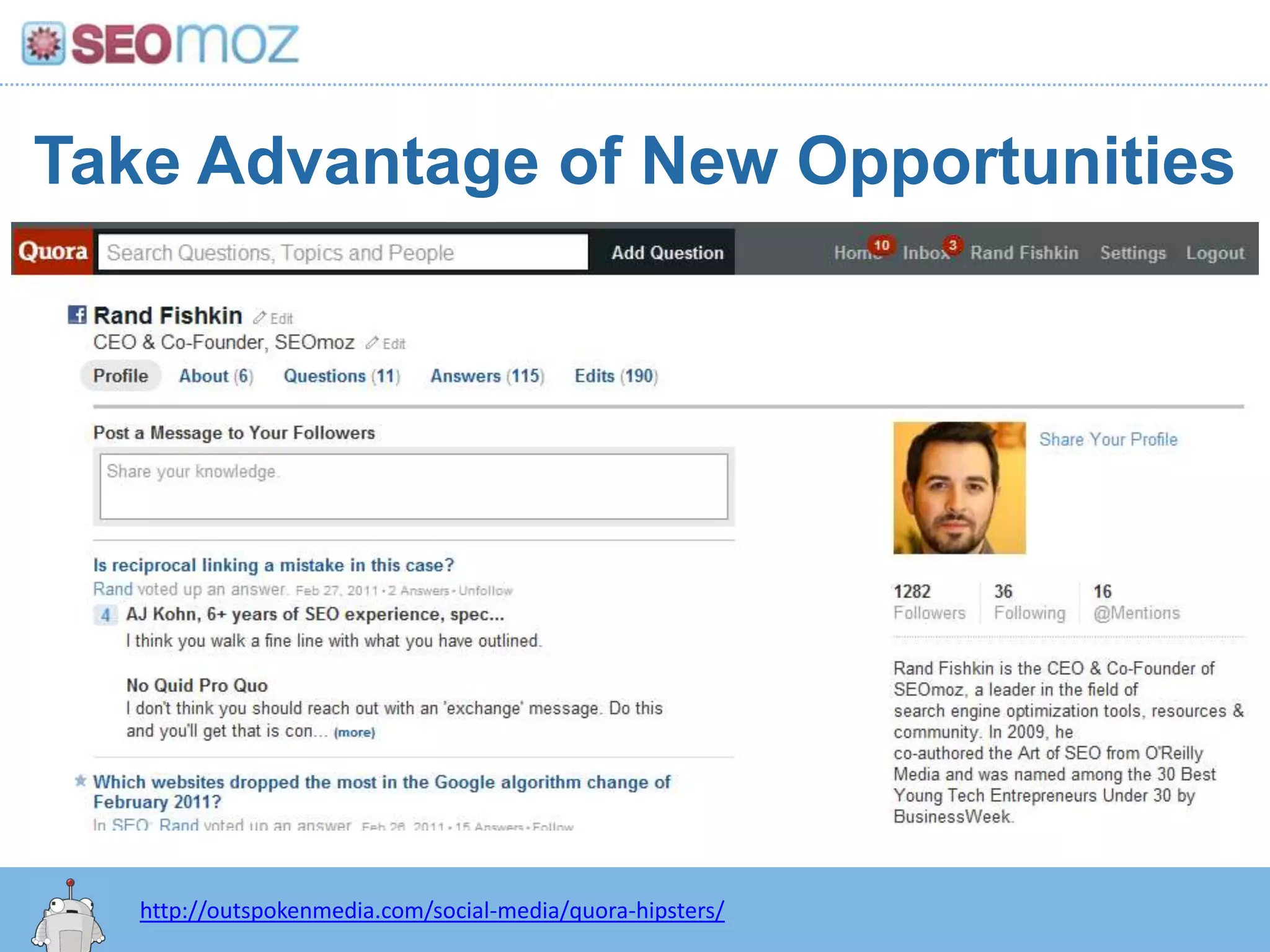
The document discusses the evolution of Google rankings from 1999 to 2011, detailing changes in algorithm factors such as on-page optimization, page rank, and the influence of social media signals. It emphasizes the shift from traditional link-based metrics to the importance of brand signals and user interaction data in determining rankings. Additionally, it outlines strategies for marketers to adapt to these changes and maintain effective SEO practices.