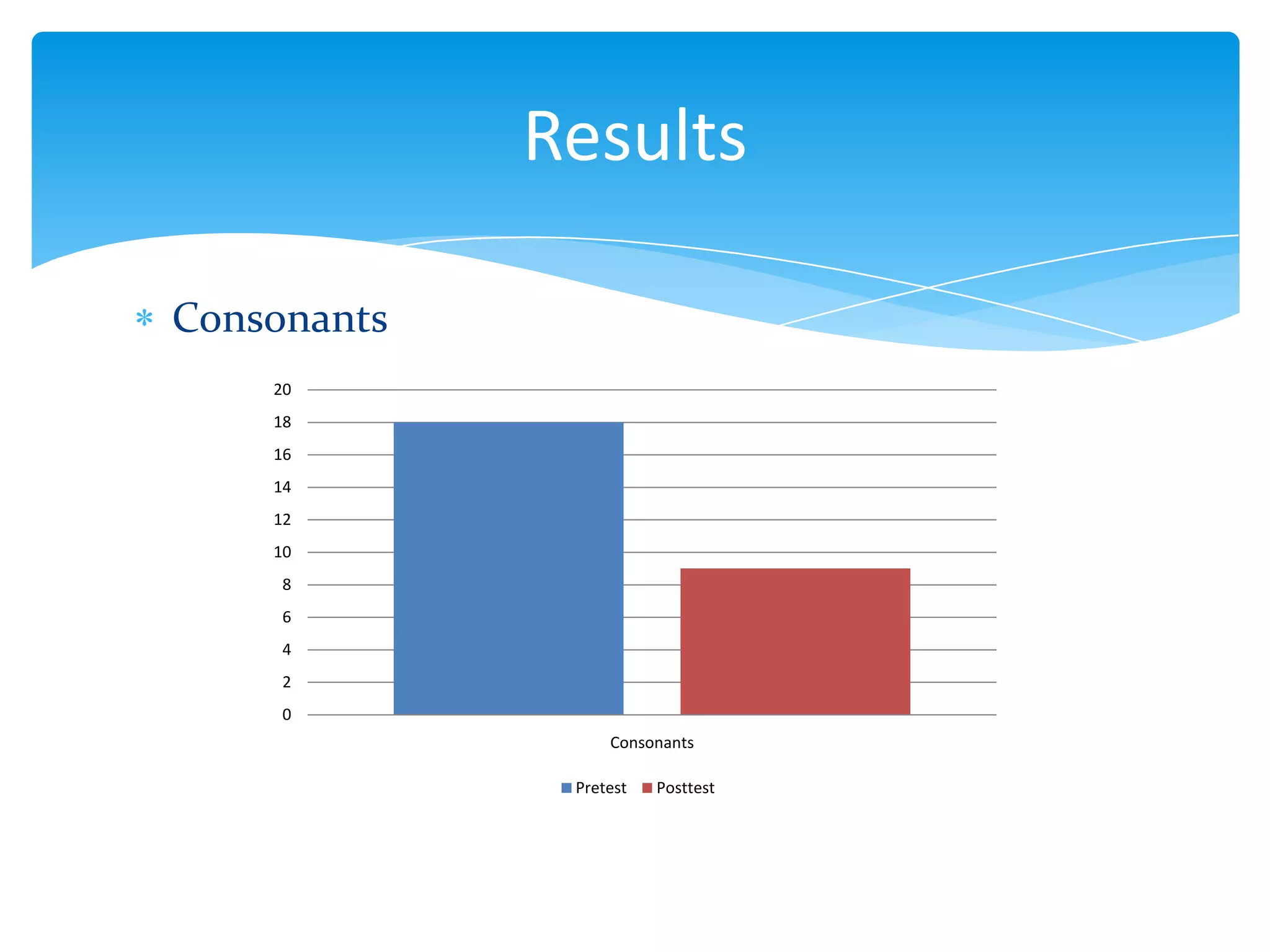
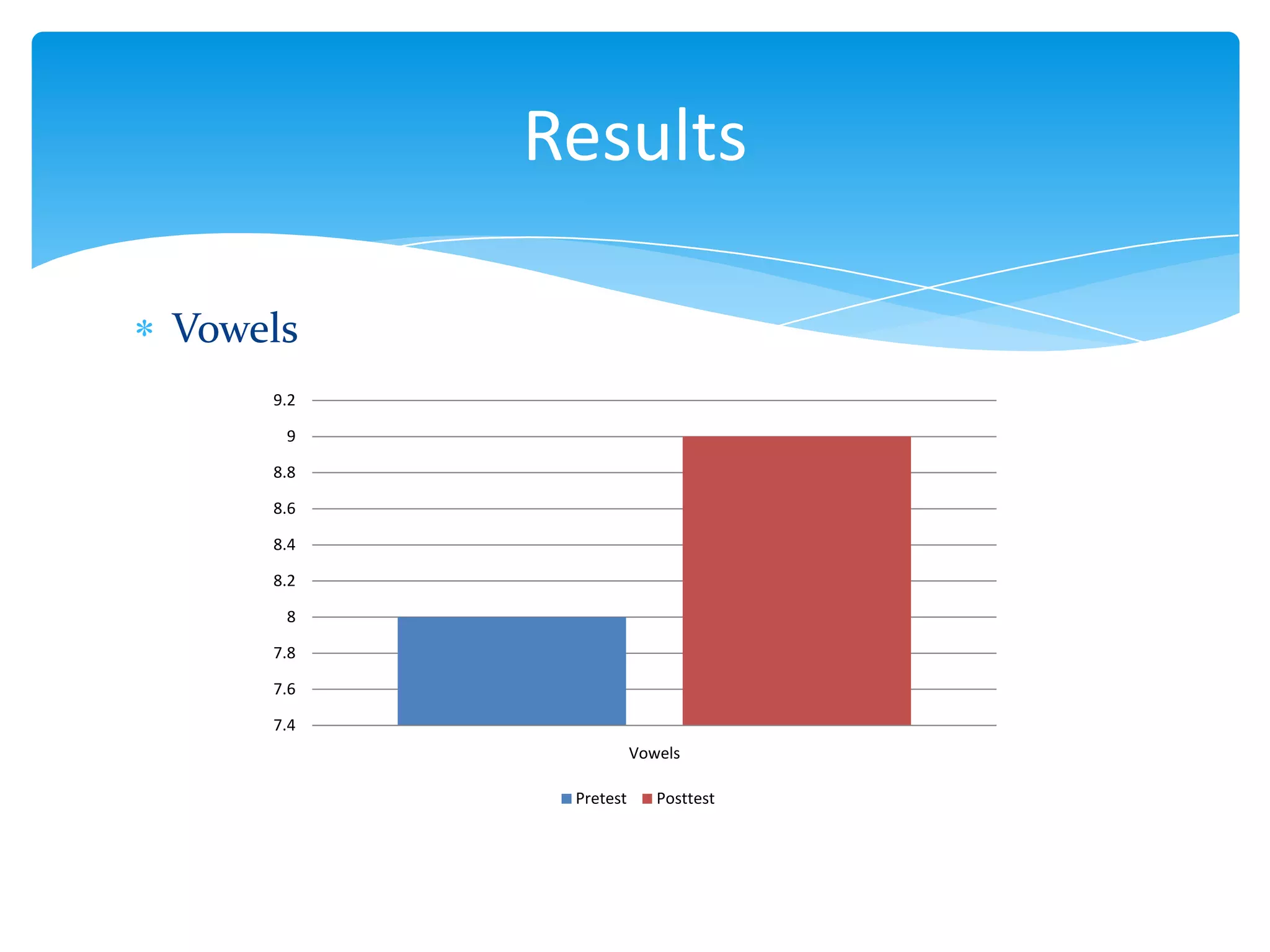
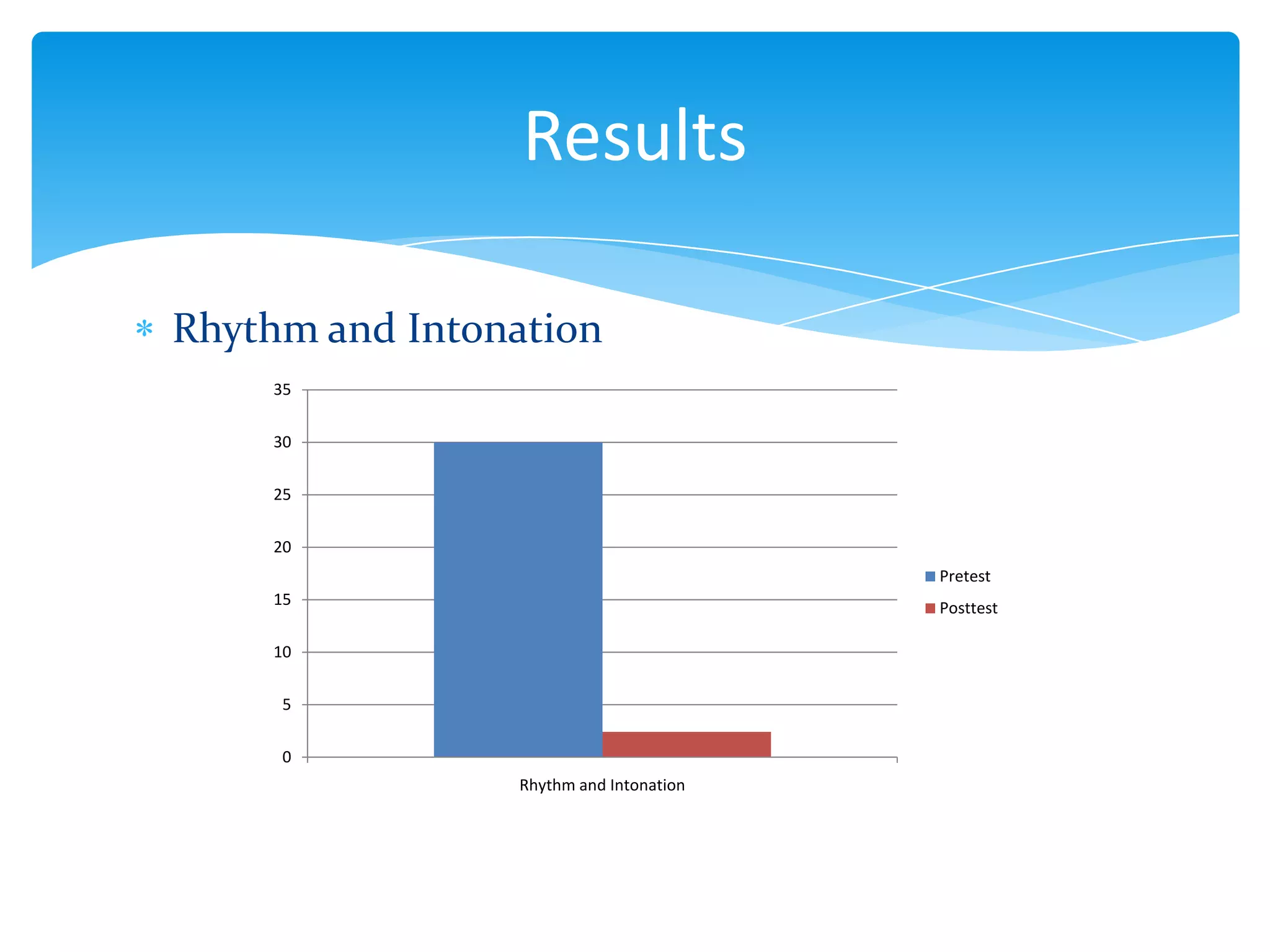
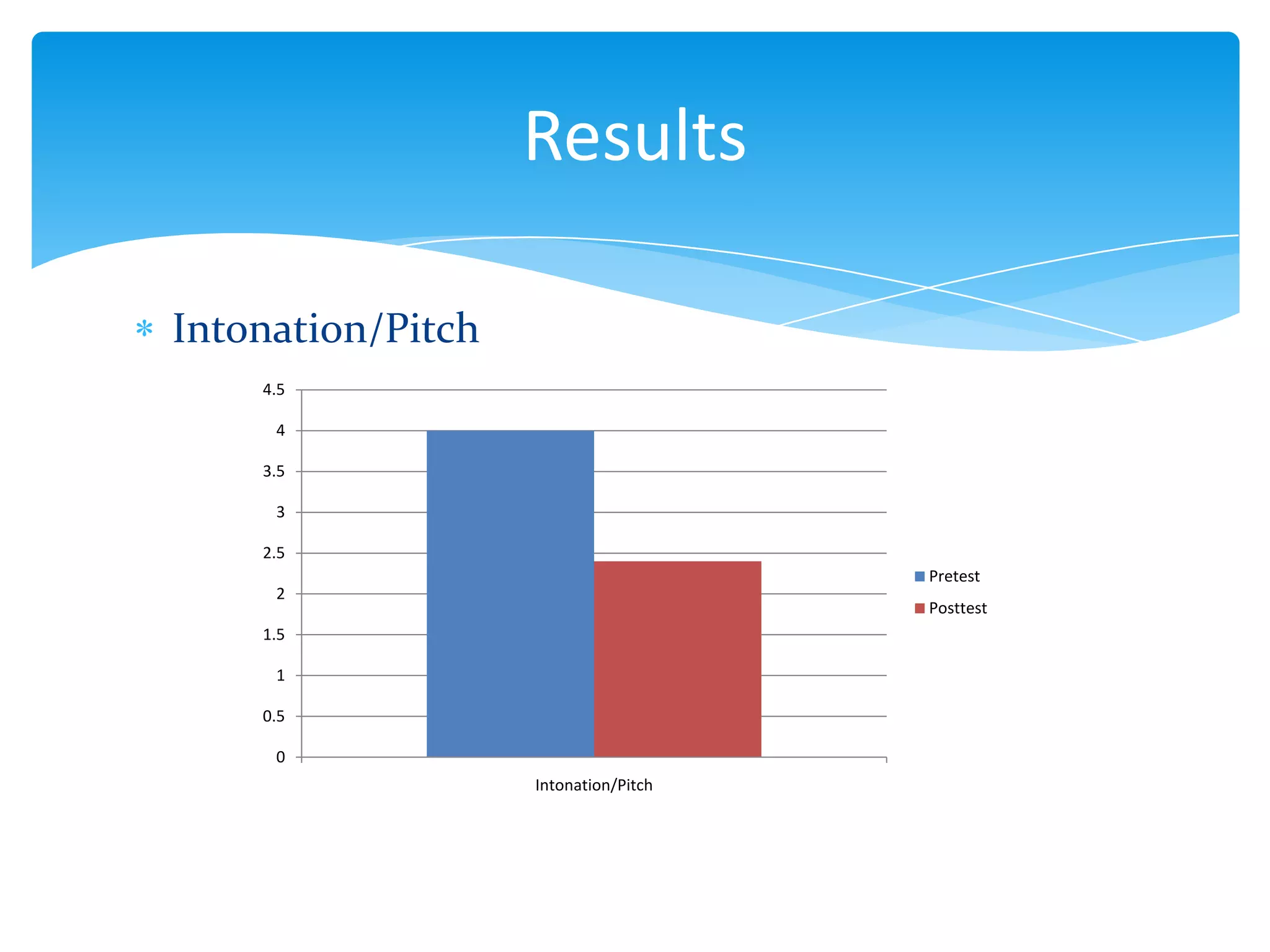
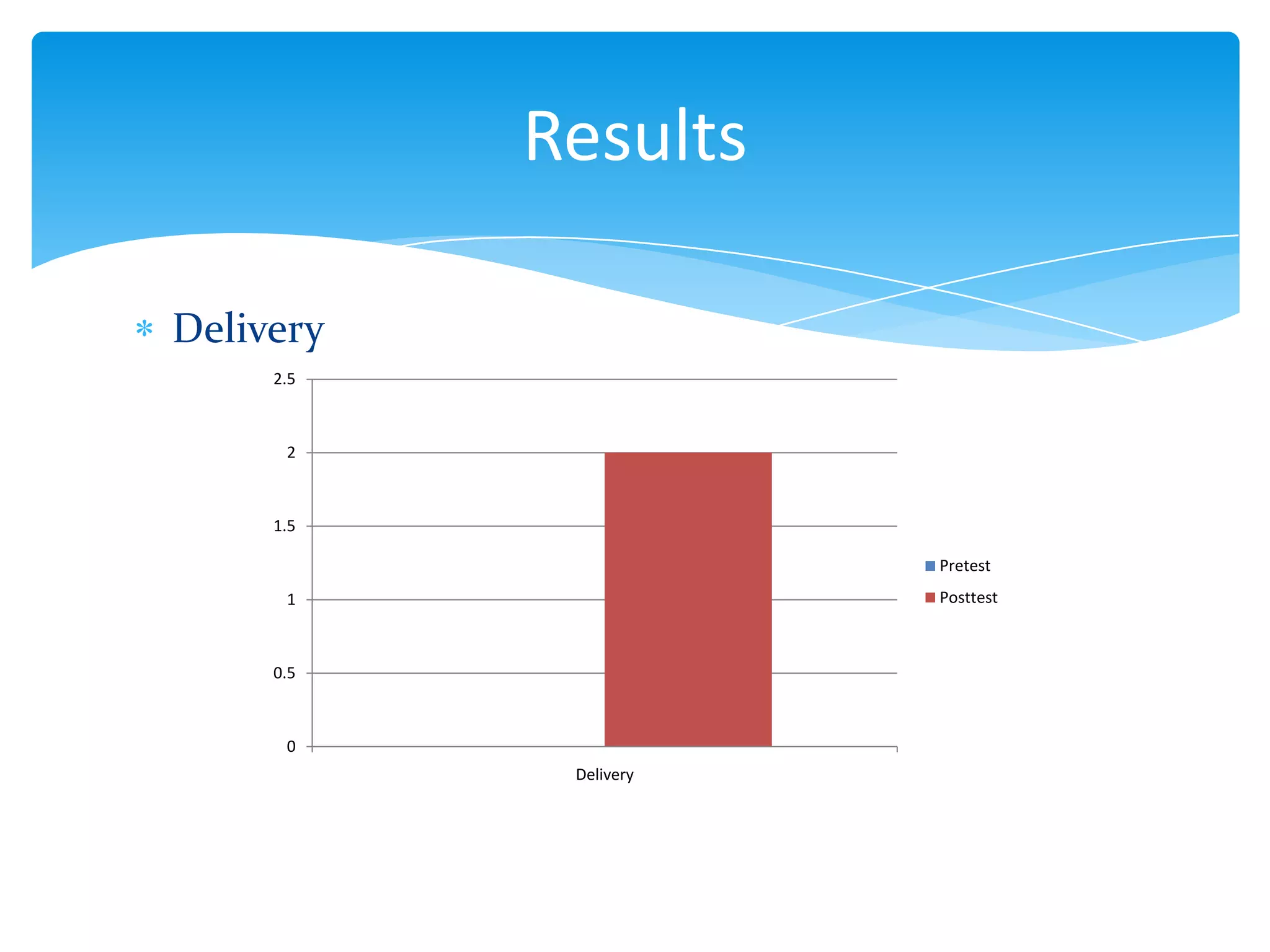
This document summarizes a thesis that studied the effects of explicit pronunciation instruction on elementary to intermediate EFL students' intelligibility when reading aloud. It conducted an 8-session pedagogical intervention teaching pronunciation features like vowels, consonants, word stress, rhythm, and intonation. Pre- and post-tests of students reading passages were analyzed and showed improvements in intelligibility across various elements of speech. The study concluded that explicit instruction helps increase EFL students' intelligibility when reading aloud and provides necessary knowledge for language teachers. Some limitations were the short intervention time and lack of measuring spontaneous speech improvement.