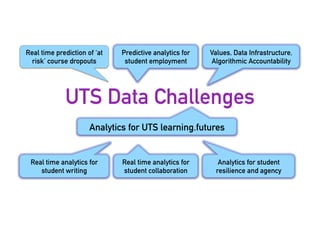
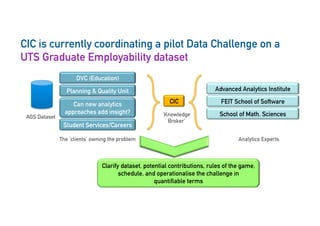
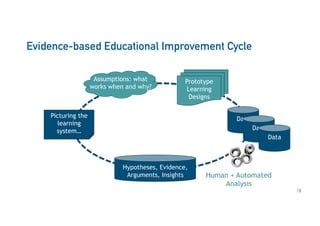
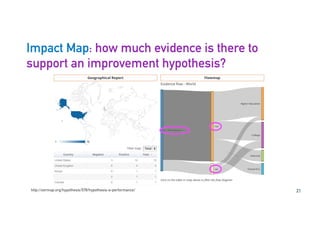
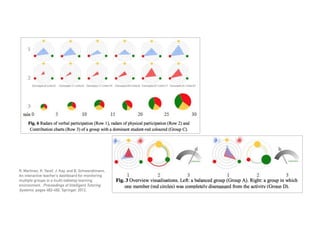
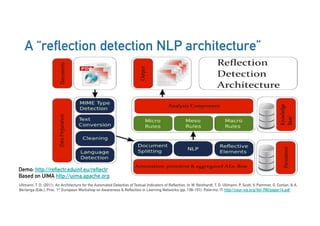
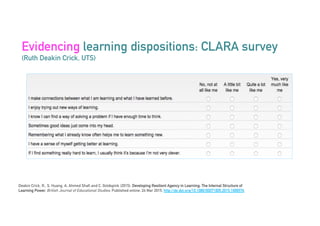
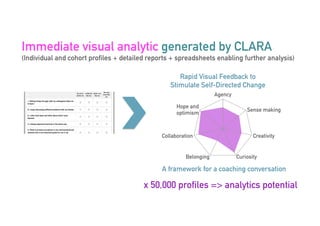
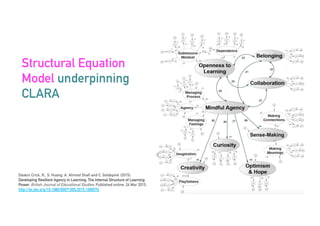
The Connected Intelligence Centre at UTS works as a creative incubator to catalyze thinking about the use of data and analytics across various faculties and units at UTS. It coordinates various data challenges and projects involving analyzing real UTS datasets to provide insights. These include predicting student dropout or employment outcomes. It also explores designing analytics for student collaboration and learning dispositions. Ensuring algorithmic accountability and human-centered values are key priorities for its work.