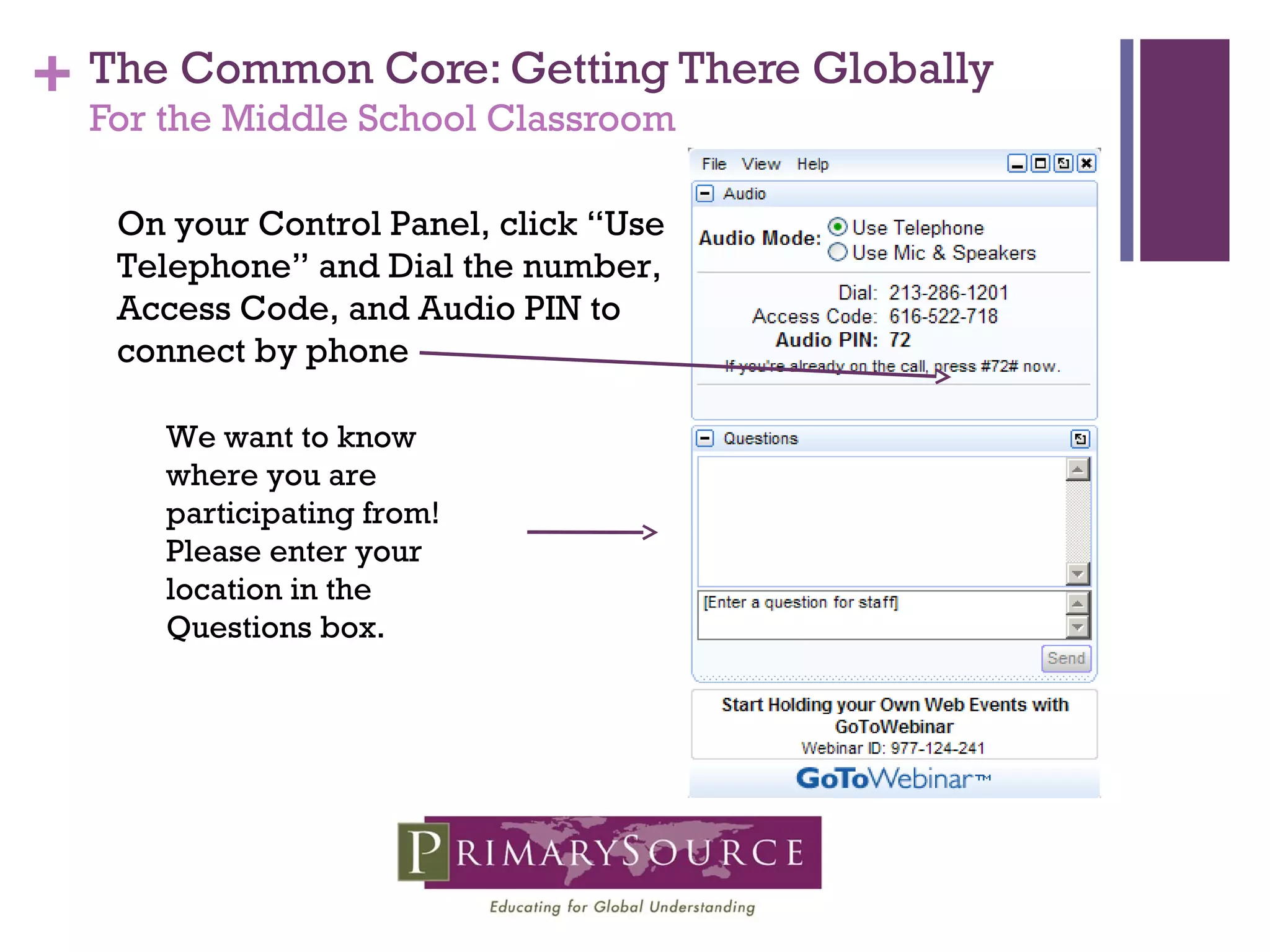
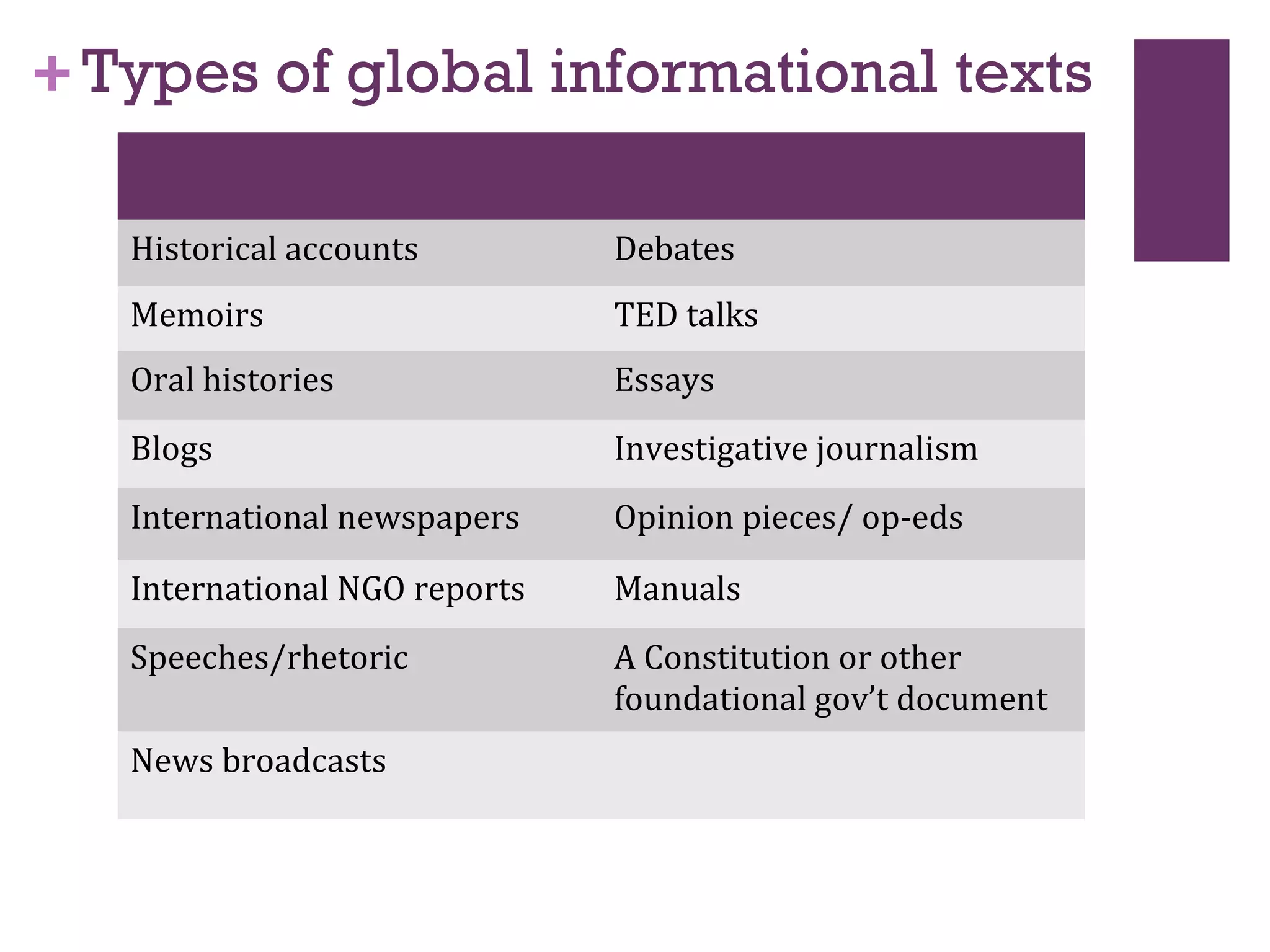
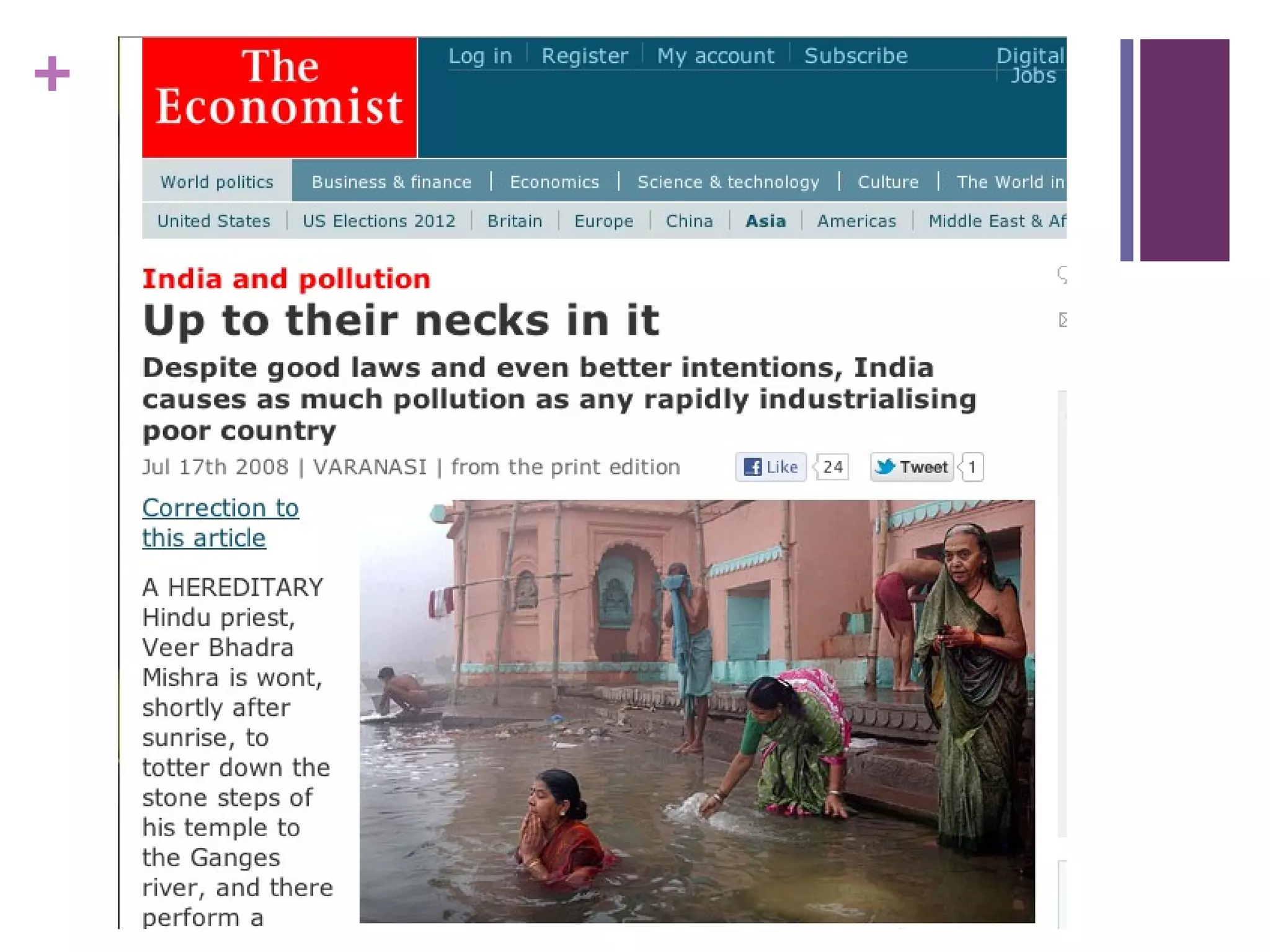
The document discusses strategies for integrating global content into middle school classrooms to meet Common Core standards. It provides an overview of the Common Core, highlighting skills like critical thinking, analysis of complex texts, and literacy across genres. Examples are given of using memoirs, speeches, images and other informational texts to analyze central ideas, point of view, and integrate visuals with text. Resources for finding international nonfiction are also shared.