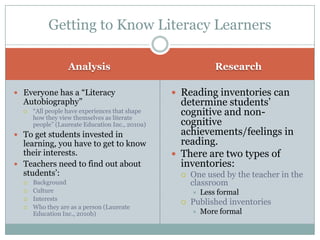
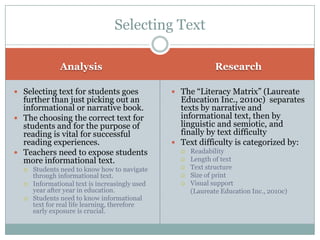
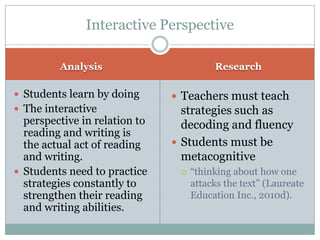
This document discusses strategies for getting to know literacy learners and selecting appropriate texts. It emphasizes the importance of learning about students' backgrounds, interests, and literacy experiences. Teachers should use reading inventories and activities like "Me Stews" to understand their students as individuals. When selecting texts, factors like readability, length, structure, print size, and visual support should be considered to match texts to students' abilities. The document also outlines perspectives like interactive, critical, and responsive that teachers can adopt to strengthen students' reading, writing, analysis, and connection-making skills through strategies such as decoding practice, author studies, and response journals.







![References
Clyde, J. A. (2003). Stepping inside the story world: The subtext strategy—a tool for connecting
and comprehending. The Reading Teacher, 57(2), 150–160.
Laureate Education, Inc. (Producer). (2010a). Literacy autobiographies [Video webcast]. Retrieved from :
https://class.waldenu.edu/webapps/portal/frameset.jsp?tab_tab_group_id=_2_1&url=%2Fwebapps%2Fbla
ckboard%2Fexecute%2Flauncher%3Ftype%3DCourse%26id%3D_2823070_1%26url%3D
Laureate Education, Inc. (Producer). (2010b). Getting to know your students [Video webcast]. Retrieved from :
https://class.waldenu.edu/webapps/portal/frameset.jsp?tab_tab_group_id=_2_1&url=%2Fwebapps%2Fbla
ckboard%2Fexecute%2Flauncher%3Ftype%3DCourse%26id%3D_2823070_1%26url%3D
Laureate Education, Inc. (Producer). (2010c). Analyzing and selecting text[Video webcast]. Retrieved from :
https://class.waldenu.edu/webapps/portal/frameset.jsp?tab_tab_group_id=_2_1&url=%2Fwebapps%2Fbla
ckboard%2Fexecute%2Flauncher%3Ftype%3DCourse%26id%3D_2823070_1%26url%3D
Laureate Education, Inc. (Producer). (2010d). Response perspective [Video webcast]. Retrieved from
https://class.waldenu.edu/webapps/portal/frameset.jsp?tab_tab_group_id=_2_1&url=%2F
webapps%2Fblackboard%2Fexecute%2Flauncher%3Ftype%3DCourse%26id%3D_2823
070_1%26url%3D
Laureate Education, Inc. (Producer). (2010e). Reading and writing connection[Video webcast]. Retrieved from
https://class.waldenu.edu/webapps/portal/frameset.jsp?tab_tab_group_id=_2_1&url=%2F
webapps%2Fblackboard%2Fexecute%2Flauncher%3Ftype%3DCourse%26id%3D_2823
070_1%26url%3D
Molden, K. (2007). Critical literacy, the right answer for the reading classroom: Strategies to move beyond
comprehension for reading improvement. Reading Improvement, 44(1), 50–56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haering2-130807090915-phpapp01/85/Literate-Environment-Analysis-11-320.jpg)