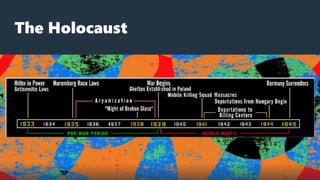
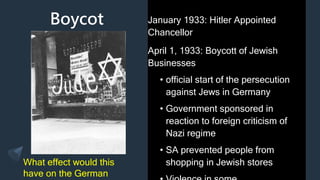
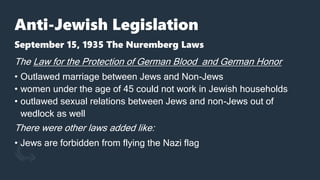
The Holocaust began in 1933 with the establishment of Dachau concentration camp and the Nazi boycott of Jewish businesses. Over the next several years, the Nazi regime passed numerous anti-Jewish laws that stripped Jews of their rights and freedoms. Events like the book burnings of 1933 and Kristallnacht pogrom in 1938 increased the persecution of Jews. The Wannsee Conference in 1942 formalized the "Final Solution" which systematized the genocide of European Jews through ghettos, concentration camps, forced labor camps, transit camps, and killing centers.