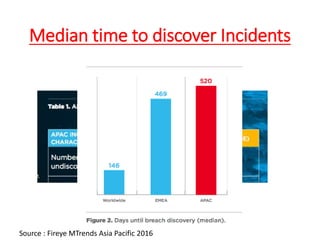
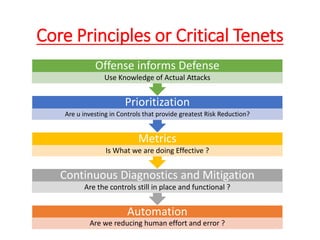
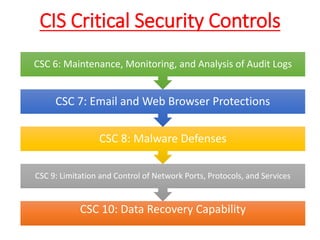
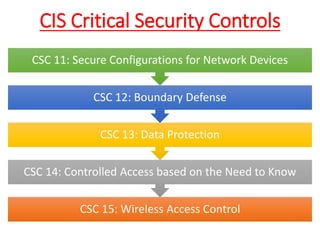
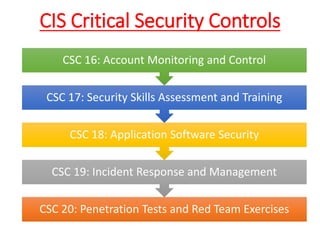
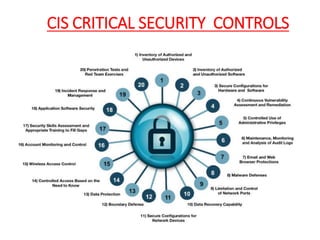
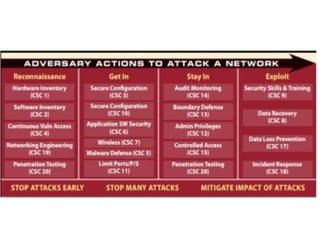
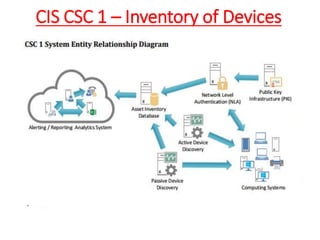
The document discusses the concept of 'fog of war' and the importance of the CIS Critical Security Controls (CIS CSC) for effective cyber defense. It outlines the top 5 foundational controls, their significance in improving security posture, and emphasizes the need for continuous assessment and automation in security measures. The author, Vikas Singh Yadav, shares his qualifications and experience in information security, presenting a roadmap for implementation and assessment of these controls.