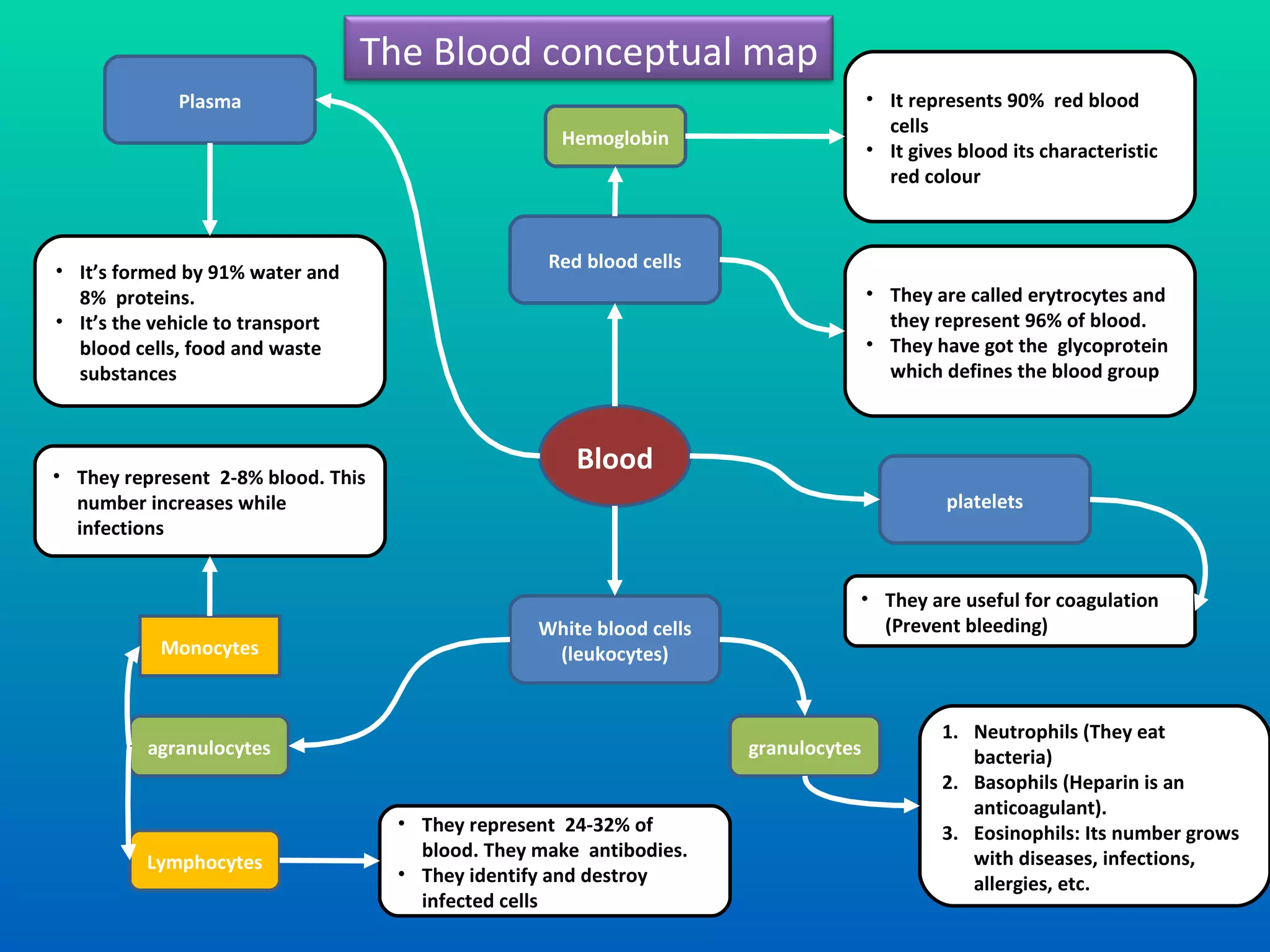
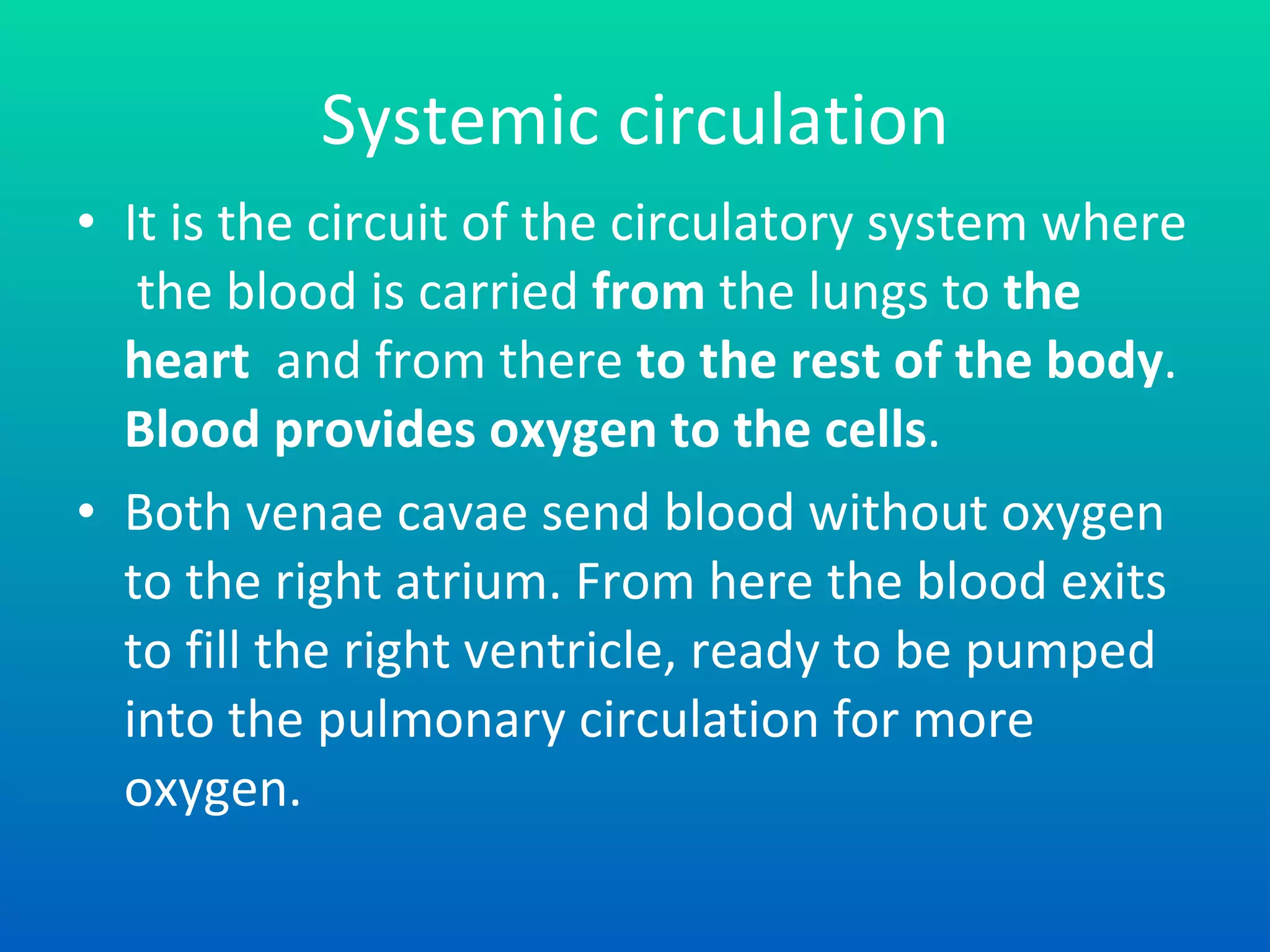
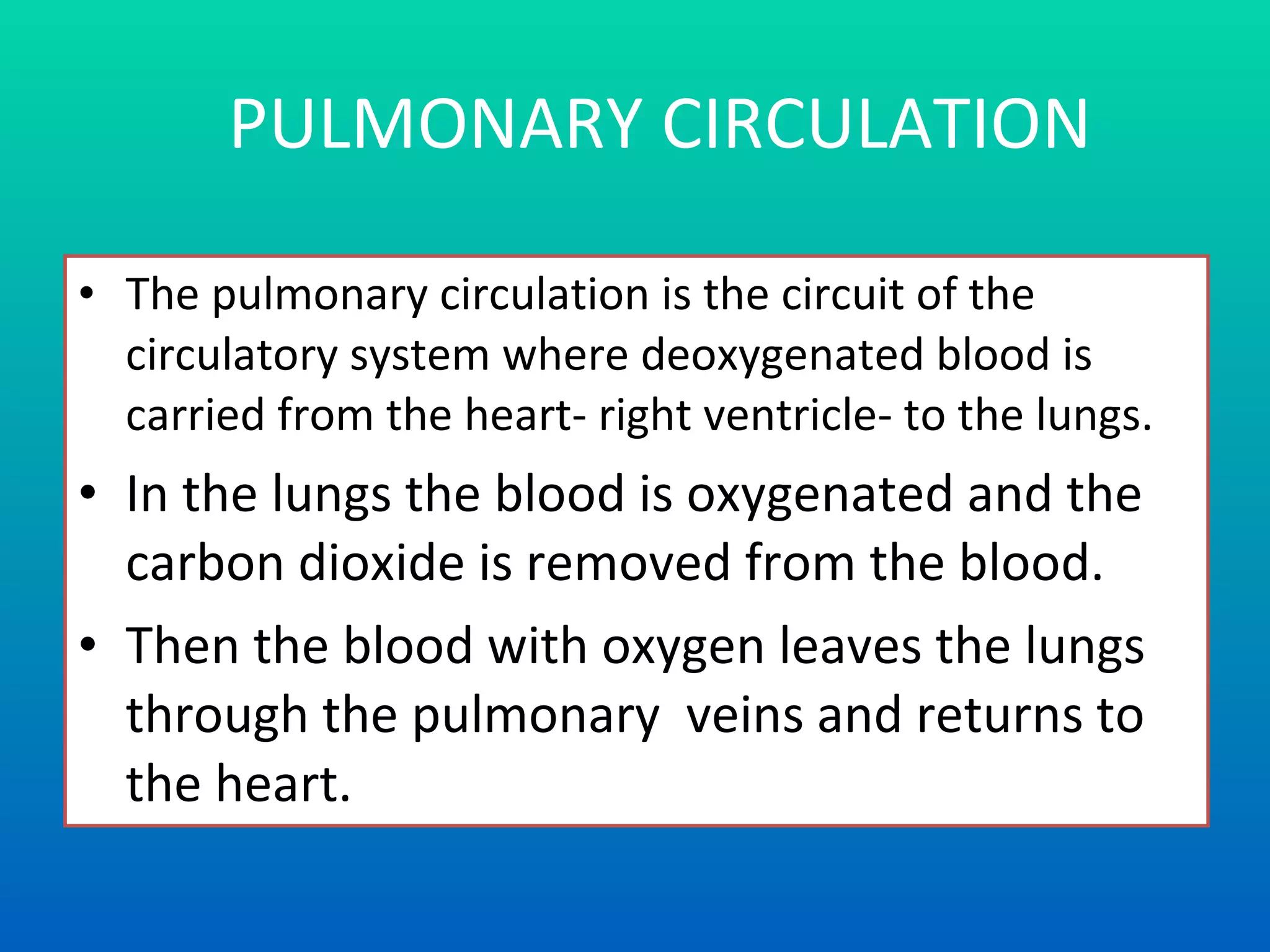
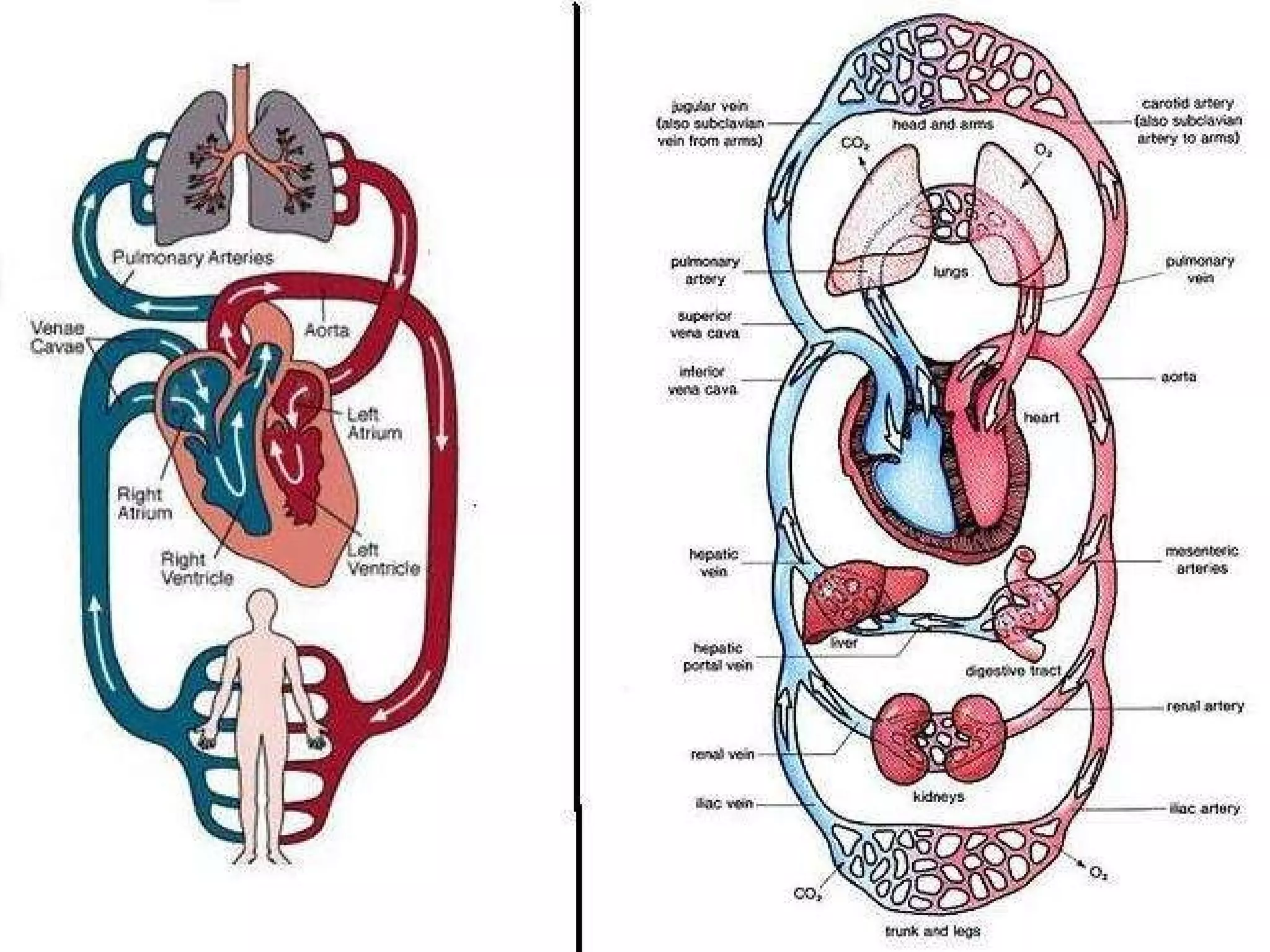
The document summarizes the key components and functions of the human circulatory system. It describes how blood is circulated from the heart through two circuits - pulmonary circulation to the lungs and systemic circulation to the rest of the body. The heart pumps blood continuously, and blood carries oxygen, nutrients, waste, and immune cells. Maintaining a healthy circulatory system requires exercise, a balanced diet, rest, and avoiding smoking, excess alcohol and drugs.