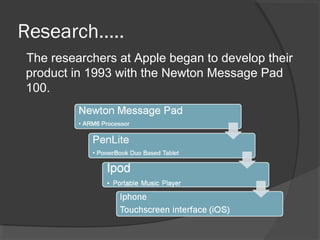
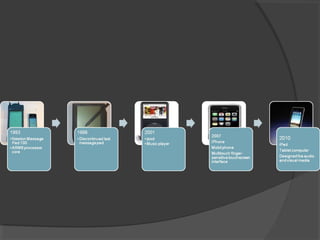
The document discusses the potential uses of the iPad in classrooms. It notes that the iPad could save schools money by allowing students to access textbooks digitally rather than purchasing physical copies. The iPad would also give students more opportunities to use technology by providing access to the internet, apps, videos and other digital learning tools. For successful adoption of the iPad, teachers would need to see the educational benefits and be given time to learn how to integrate the technology into their lessons. Early adopting teachers could help drive interest from other teachers and students.