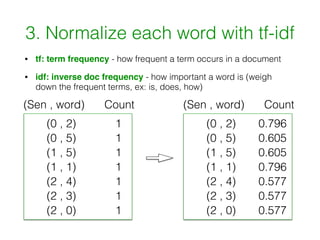
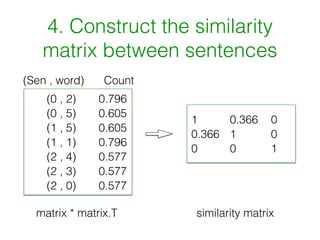
Textrank is a graph-based method for summarization that works by (1) separating text into sentences, (2) building a sparse matrix of word counts in each sentence, (3) normalizing words with tf-idf scores, (4) constructing a similarity matrix between sentences based on shared words, and (5) using PageRank to score sentences based on their similarity to other sentences.


![1. Separate the Text into Sentences
• Apply PunktSentenceTokenizer from the Python
NLTK Library
“Hi world! Hello
world! This is
Andrew.”
[“Hi world!”, “Hello
world!”, “This is
Andrew.”]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/textrankalgorithm-141001134151-phpapp02/85/Textrank-algorithm-3-320.jpg)
![2. Build a sparse matrix of words and
the count it appears in each sentence
[“Hi world!”, “Hello
world!”, “This is
Andrew.”]
(Sen , word) Count
(0 , 2)
(0 , 5)
(1 , 5)
(1 , 1)
(2 , 4)
(2 , 3)
(2 , 0)
1
1
1
1
1
1
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/textrankalgorithm-141001134151-phpapp02/85/Textrank-algorithm-4-320.jpg)