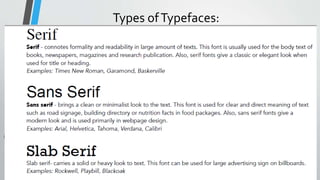
This document discusses text media and information literacy. It defines text as a simple format for presenting information that can be handwritten, printed, or displayed digitally. Text comes in both formal sources like published books and newspapers, as well as informal sources like blogs and social media. When consuming text media, it is important to consider who created it, the language and perspectives used, and what information may be omitted. When creating text media, the target audience, purpose, content, style, and format should be considered. Font, typeface, emphasis, alignment and other design principles can be used to organize and draw attention to text.