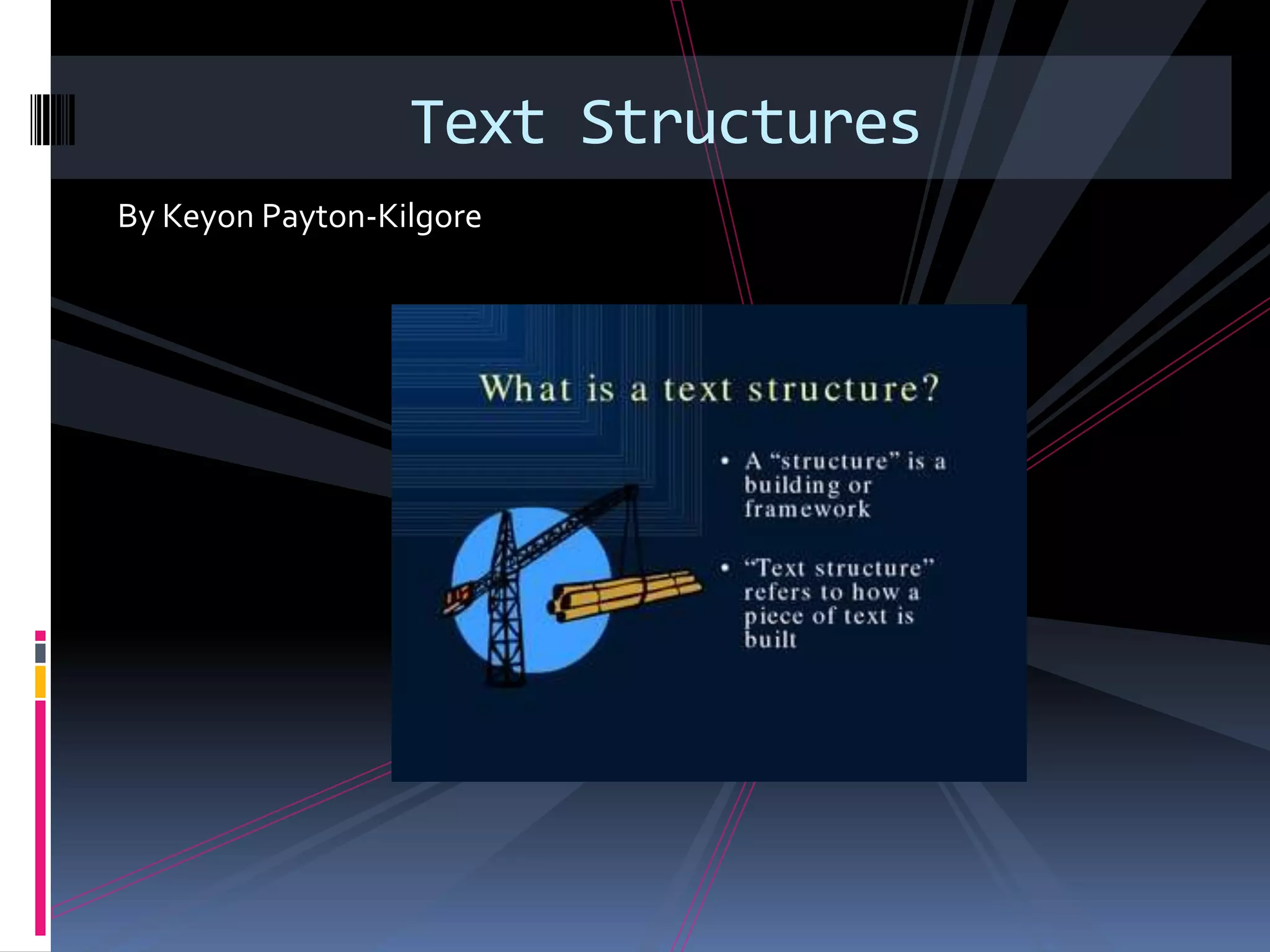
The document summarizes several common text structures: chronology, compare-contrast, question-answer, problem-solution, cause-and-effect, and description. For each structure, key clues and signal words are provided to help identify the structure, along with example questions readers can ask to analyze how the structure is used.