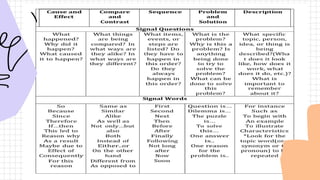
The document provides a comprehensive overview of academic writing, focusing on text structures such as description, problem-solution, sequence, cause-effect, and compare-contrast. It details the importance of these structures for organizing information and enhancing comprehension for readers. Additionally, it includes activities and evaluation questions to help understand and identify different text structures.














![3. These texts are basically descriptive, but
deal with two or more topics to highlight
similarities and differences between them.
This structure is useful in all subjects. Key
words include “more,” “less,” “as [adjective]
as,” “than” and “however.”
activity 2- identify the text structure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson2textstructure-241209005935-dd850fa6/85/LESSON-2_TEXT-STRUCTURE-pptx-16-320.jpg)














