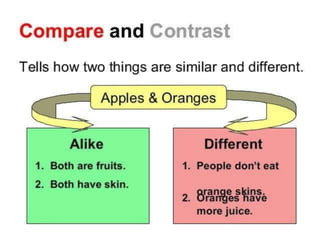
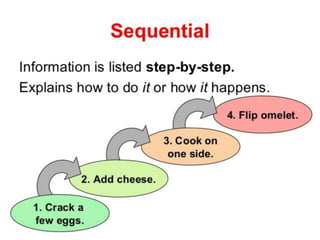
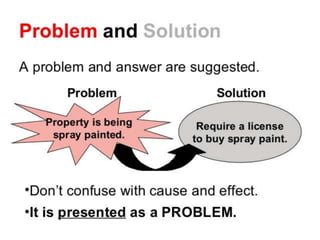
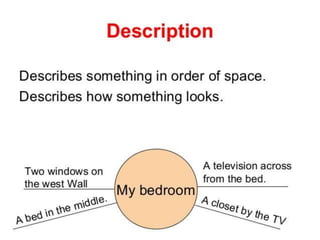
The document outlines various common text structures used in writing, including compare-contrast, cause-effect, sequence, problem-solution, descriptive, question-answer, and cyclical structures. Each structure is described with its definition, characteristics, and examples of transition words that can be used to enhance clarity. The information serves as a guide for understanding how to effectively organize ideas in written form.