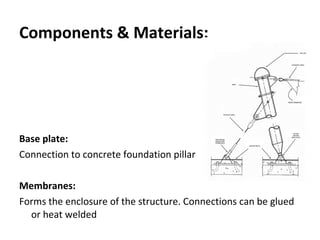
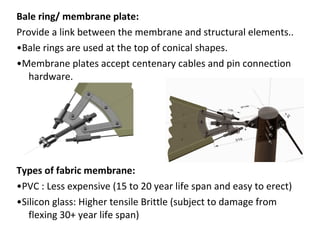
The document discusses tent structures, providing definitions and describing key components. It notes that tent structures have existed for nomadic peoples but are now used for camping and military purposes. The document outlines several common tent structure types including saddle roof, mast supported, and arc supported structures. It also describes common components like membranes, bale rings, and base plates. Both advantages like flexibility, reusability and environmental friendliness as well as disadvantages like lack of rigidity and thermal limitations are highlighted.