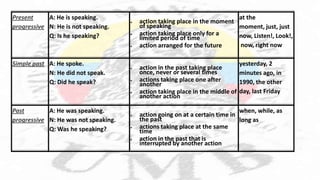
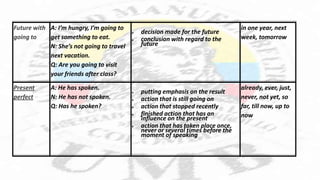
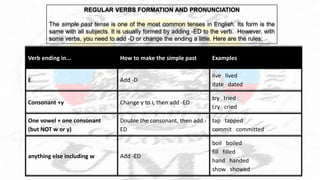
The document discusses English tenses. It begins by stating that only two tenses - present and past - are marked in the verb alone in English. The other approximately thirty tenses are marked by auxiliary words. Understanding the basic tenses allows one to effectively convey time in language production. It then provides a table outlining several common tenses - including present, present progressive, simple past, past progressive, future with "going to", and present perfect - along with their affirmative/negative/question forms, uses, and common signal words. The document concludes by reviewing the rules for forming the simple past tense of regular verbs in English.