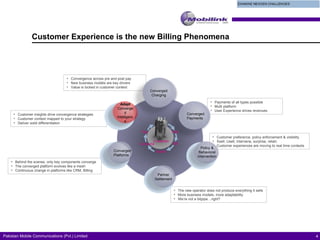
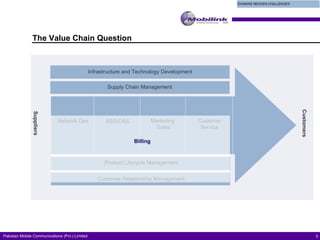
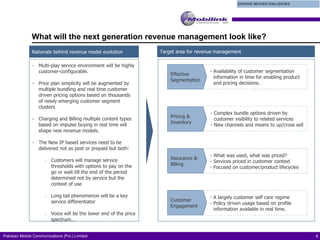
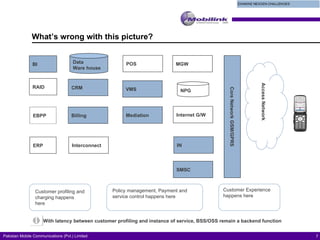
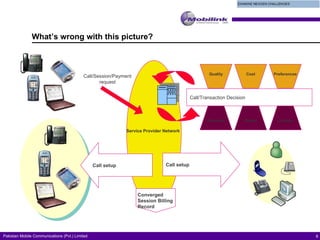
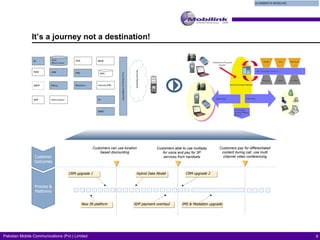
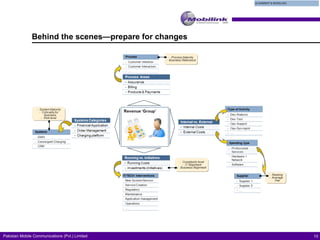
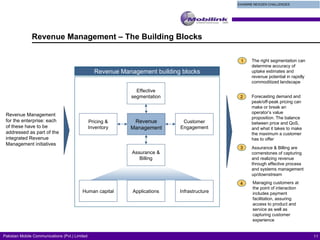
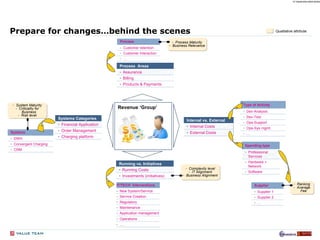
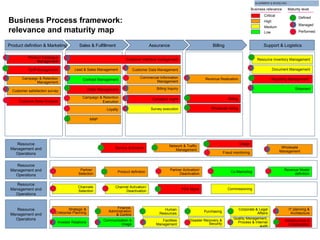
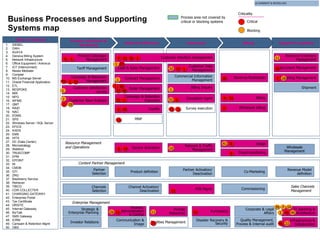
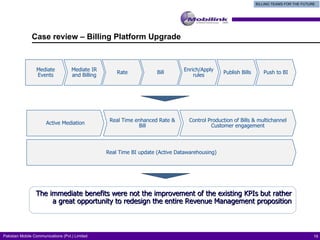
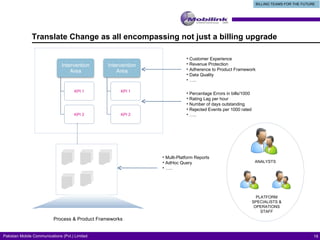
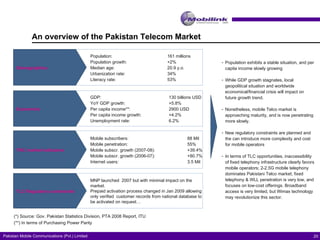
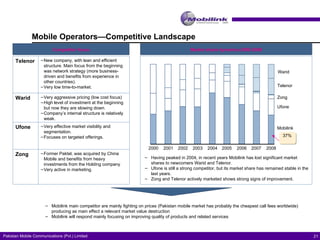
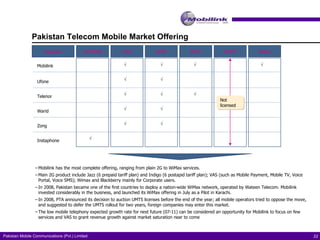
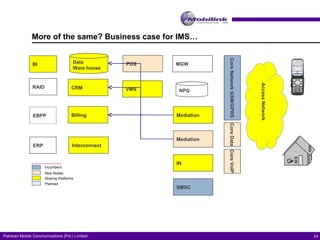
The document discusses the evolving landscape of billing and revenue management in the telecommunication sector, emphasizing the integration of effective customer engagement, pricing strategies, and billing systems to optimize revenue streams. It highlights challenges such as customer segmentation, demand forecasting, and technological advancements that impact billing processes, including real-time customer interactions. Additionally, it reviews market conditions and competitive dynamics within the Pakistan telecom market, underscoring the importance of adaptability and innovative business models to drive future growth.








![Thank you—any questions? Ehtisham Rao Director Business Intelligence & Billing, Mobilink +00923008499114 [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/billingsevolvingrole2011march-111029035435-phpapp02/85/Telecom-Billing-s-evolving-role-in-post-pc-era-29-320.jpg)