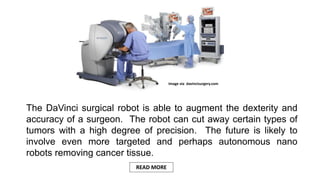
The document discusses how technology can assist in the fight against cancer, highlighting innovations such as digital therapies, wearables, and big data analyses that improve patient recruitment and treatment outcomes. Key advancements include 3D printing for creating replacement body parts, the use of AI in personalized treatment recommendations, and liquid biopsies for non-invasive tumor detection. The presentation emphasizes the potential of emerging technologies to revolutionize cancer research and treatment methodologies.