This document summarizes a teacher refresher course held in London from August 1st-12th, 2011. It discusses four sessions of the course:
1. The introductory session where teachers introduced themselves and completed a chart about their teaching experiences. They also tried to solve a riddle about the number of steps a walking couple would take.
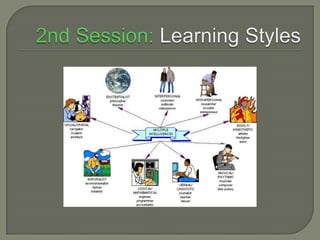
2. A session on learning styles and Howard Gardner's theory of multiple intelligences, which identifies eight types of intelligence.
3. A session reviewing different language teaching approaches, where teachers discussed the characteristics of approaches like communicative language teaching and suggestopedia.
4. A session revisiting dictation that presented different types of dictations,