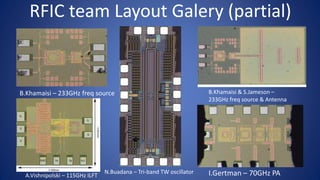
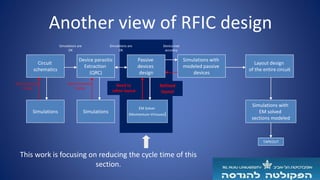
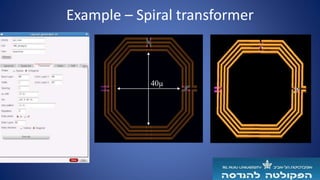
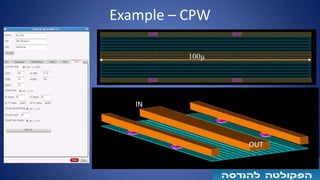
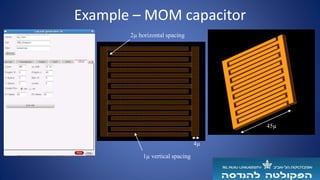
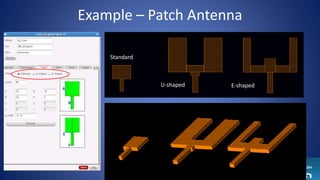
The document describes a semi-automated layout generation tool for inductors and antennas in the 70-300GHz range developed at Tel Aviv University. The tool uses Skill scripts in Virtuoso to generate common RF passive components like spiral inductors, transformers, CPW lines, and patch antennas in a few seconds. It aims to reduce the time spent on manual layout design and allow engineers to more efficiently try different layout variants for optimization. The initial version was used successfully in an RF research project and the developers are working to expand the tool's capabilities and integrate it into the standard RFIC design flow.