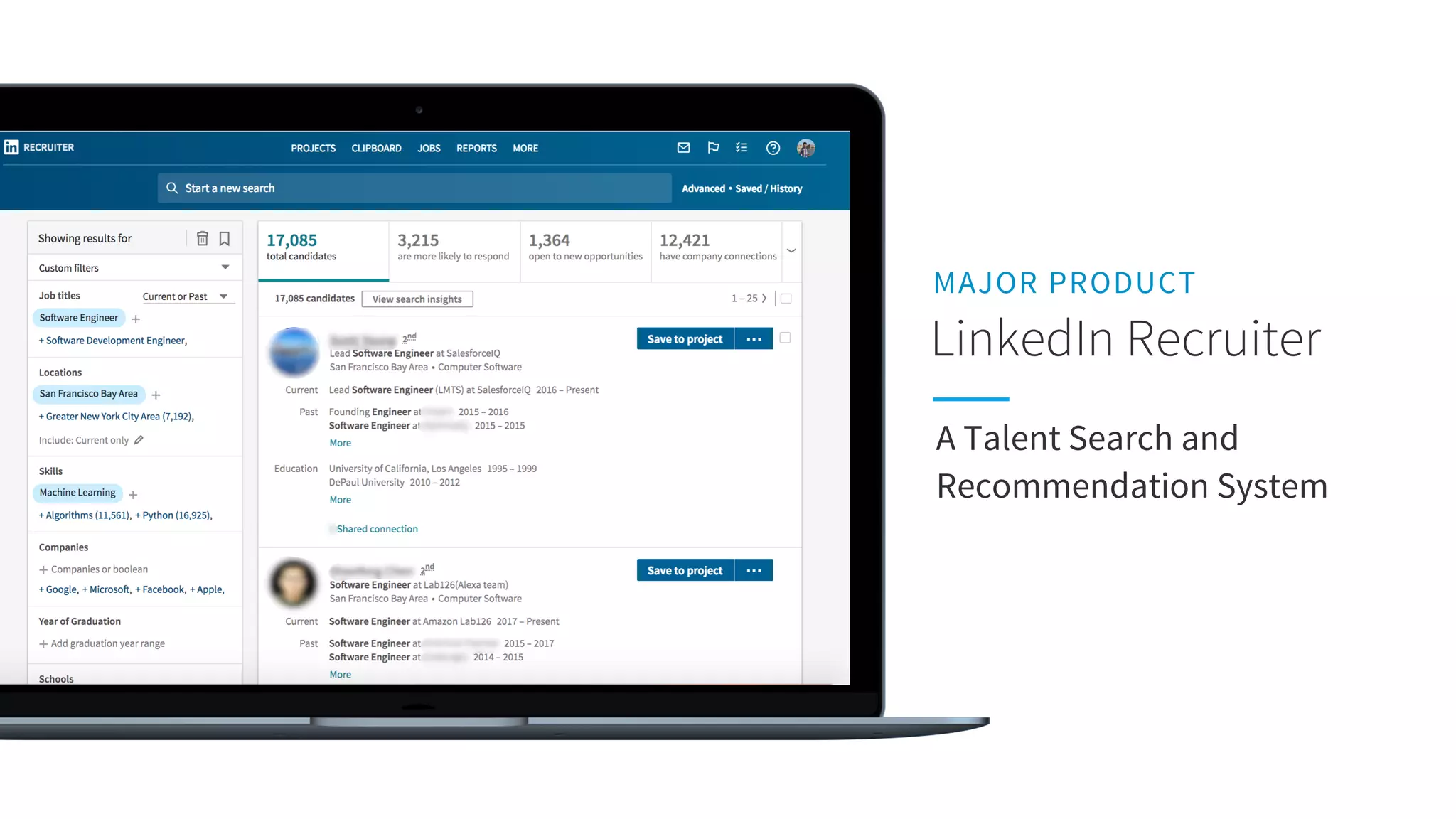
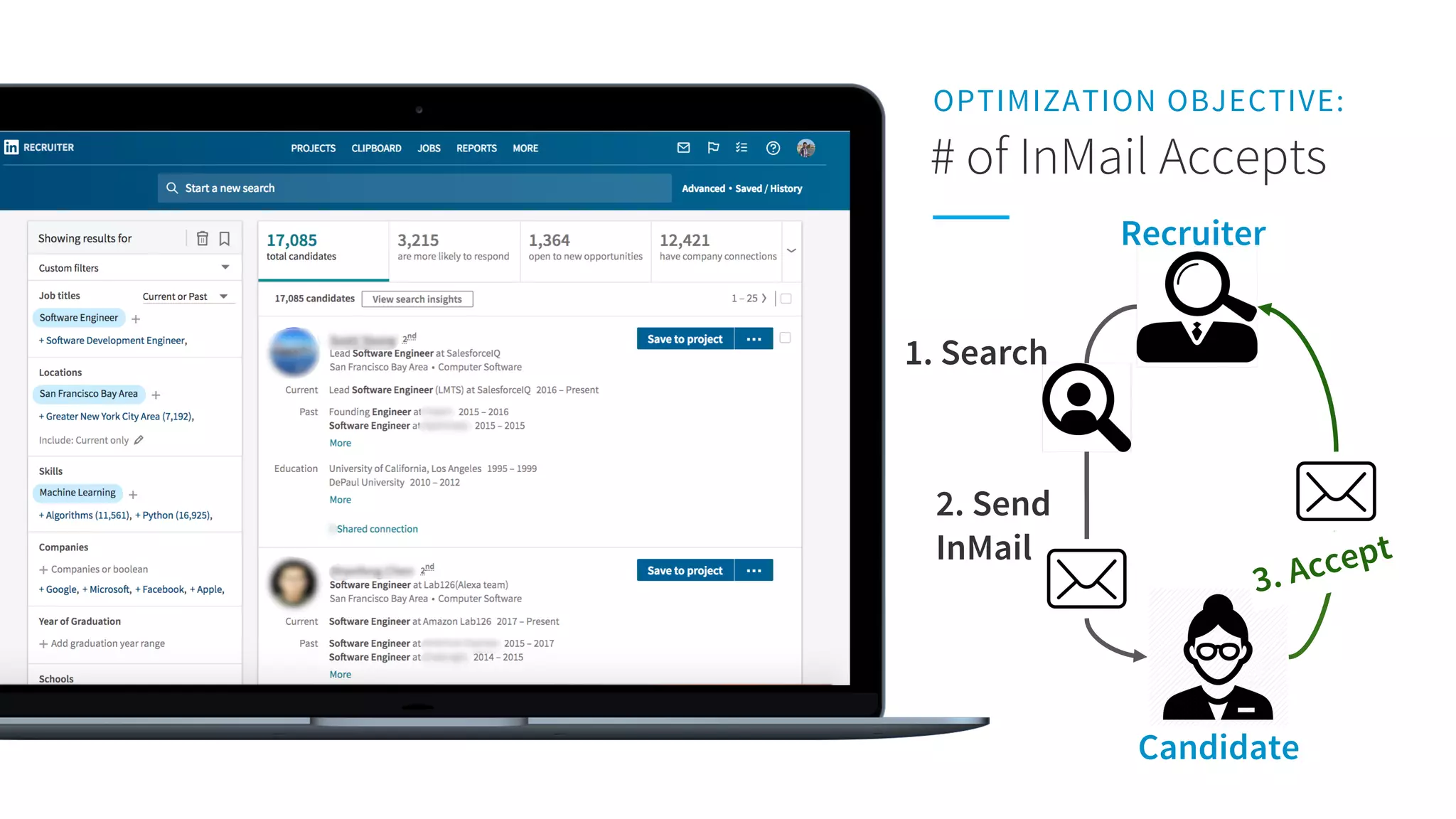
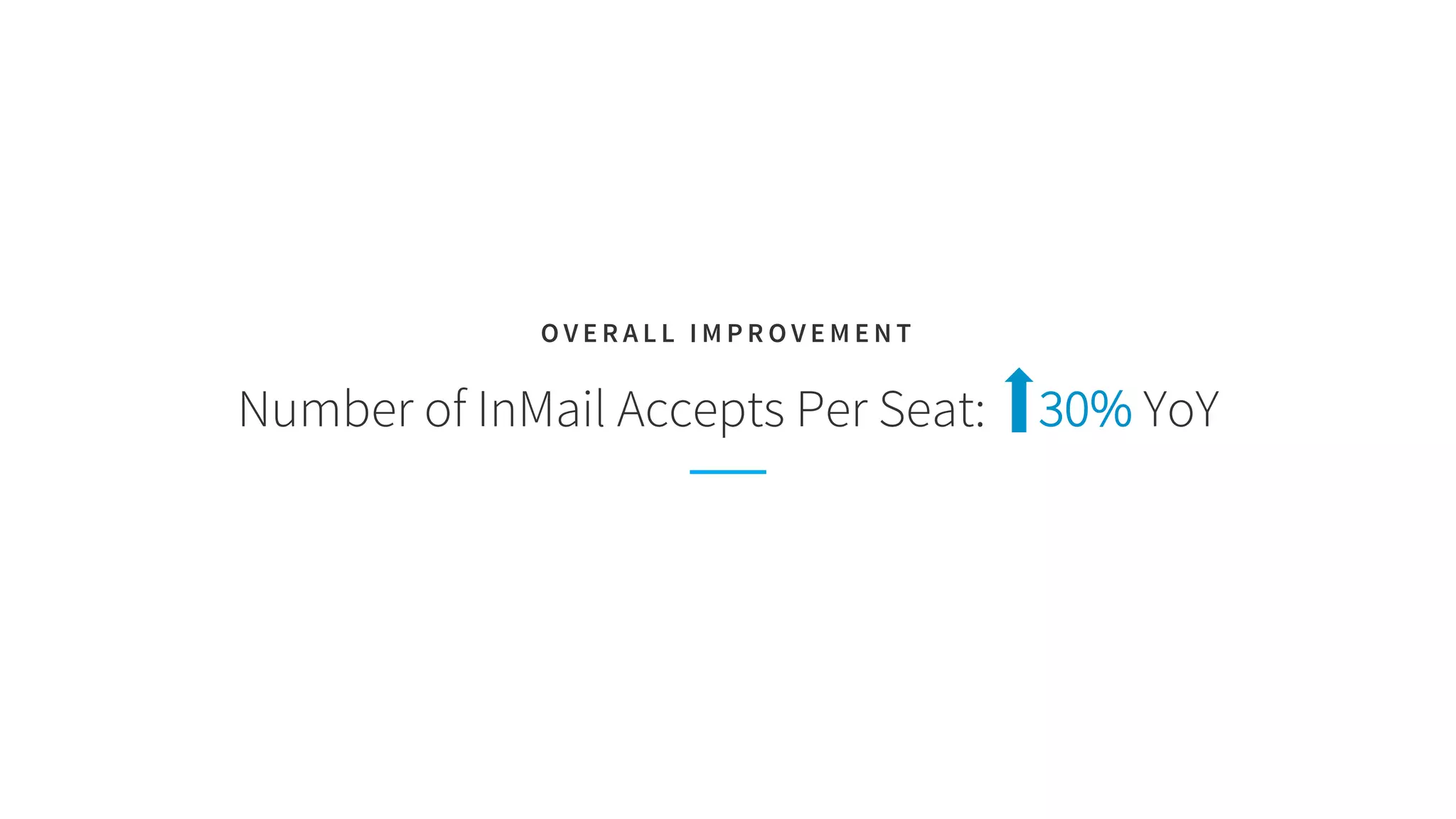
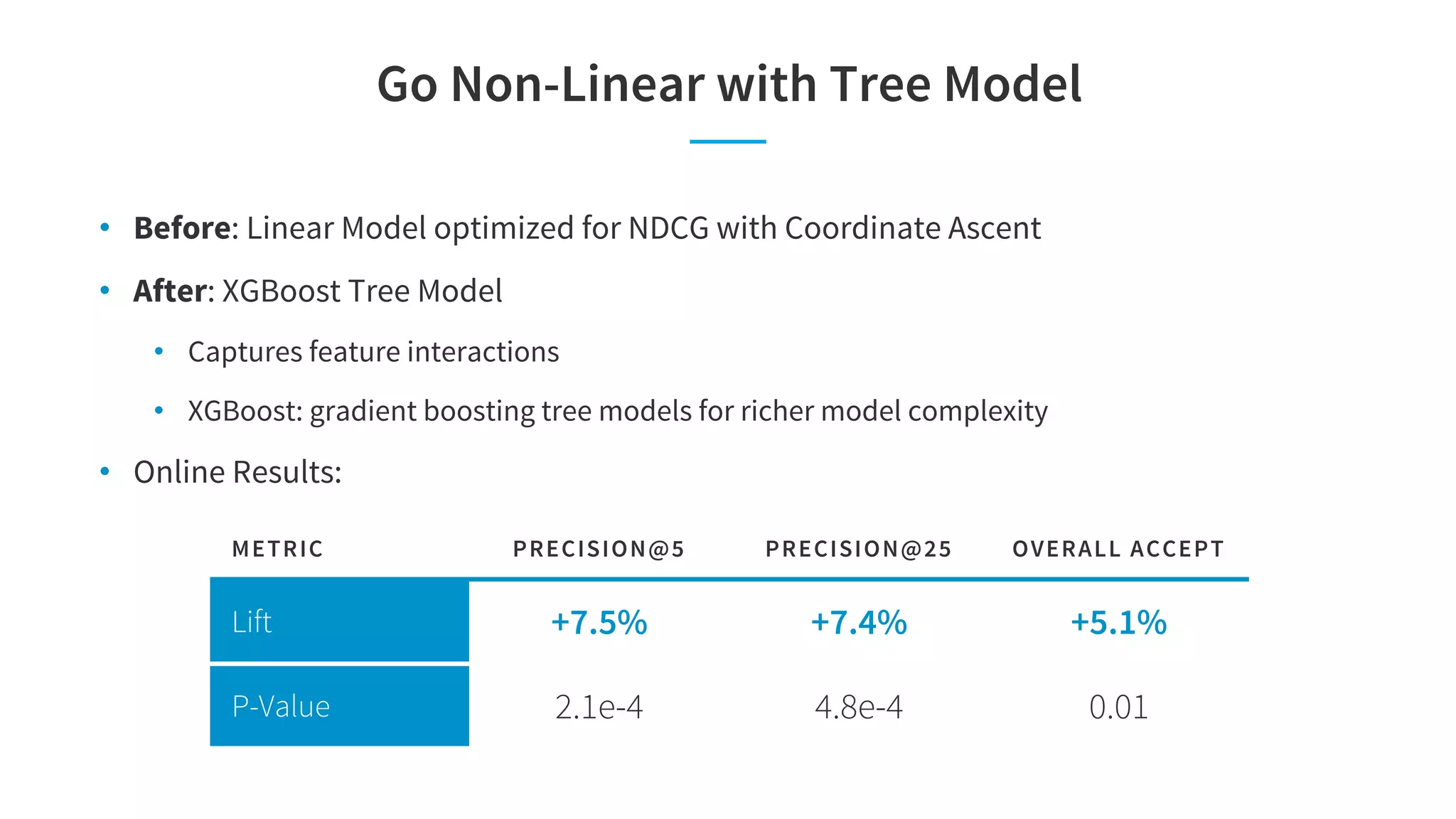
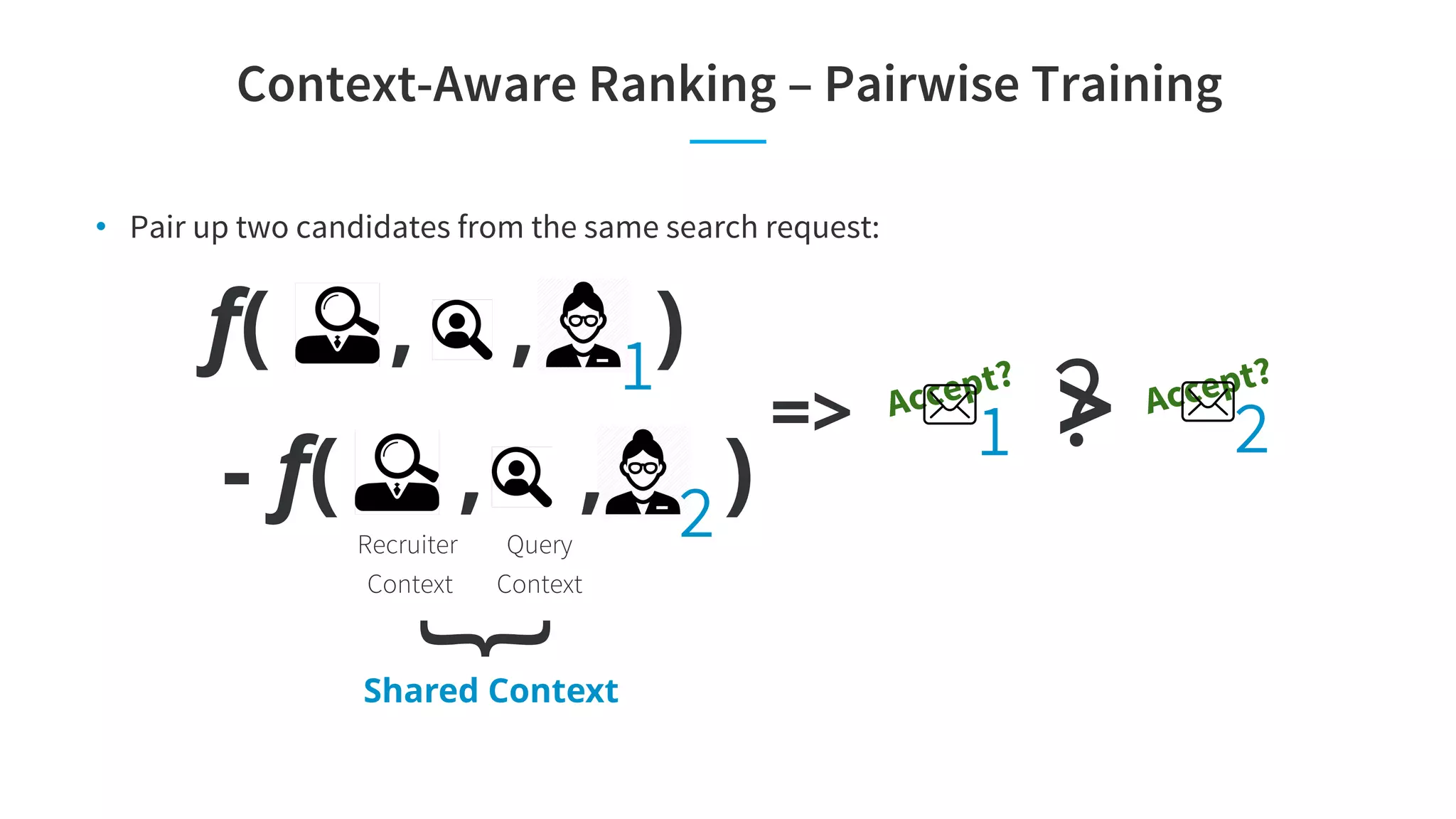
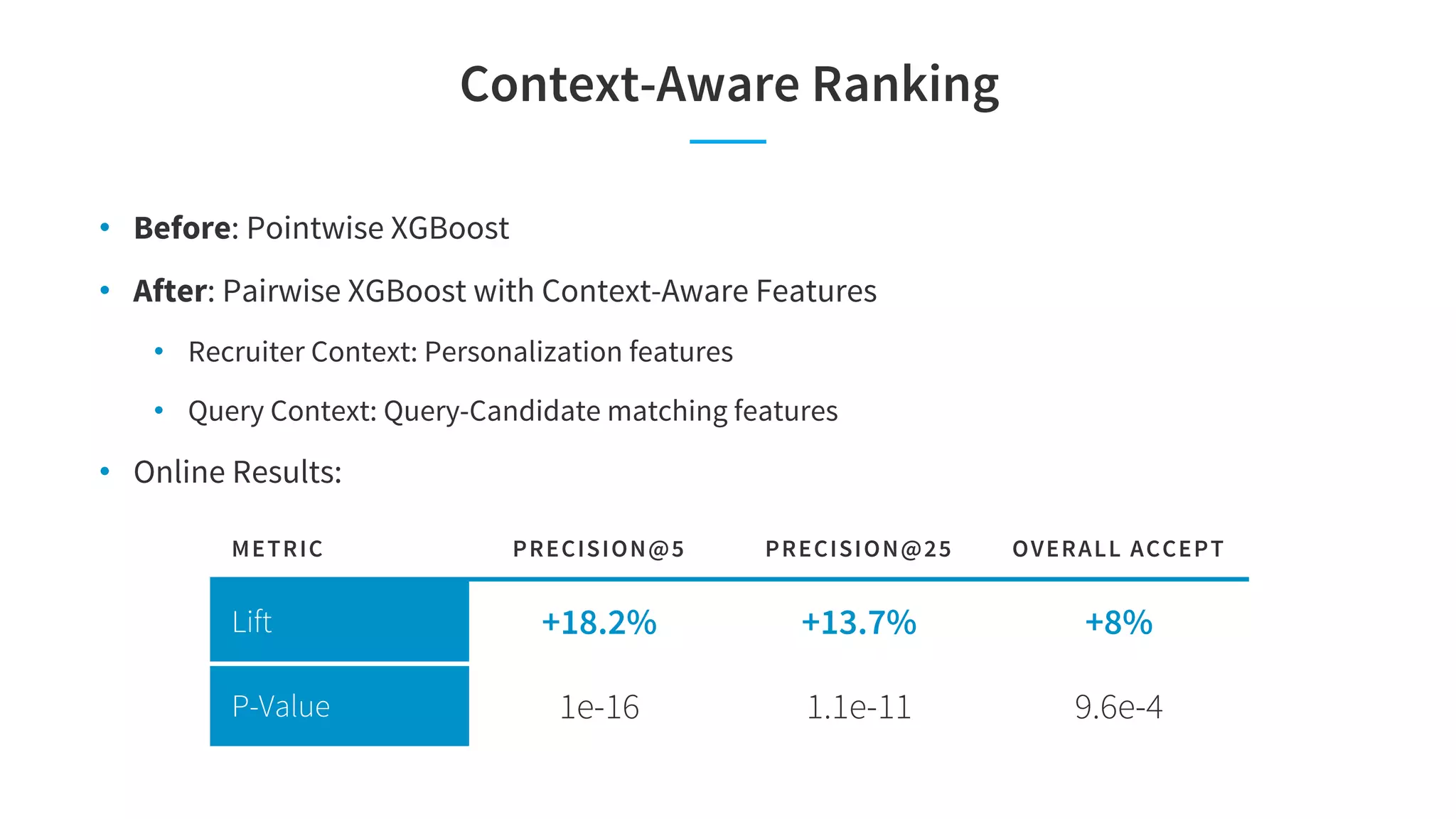
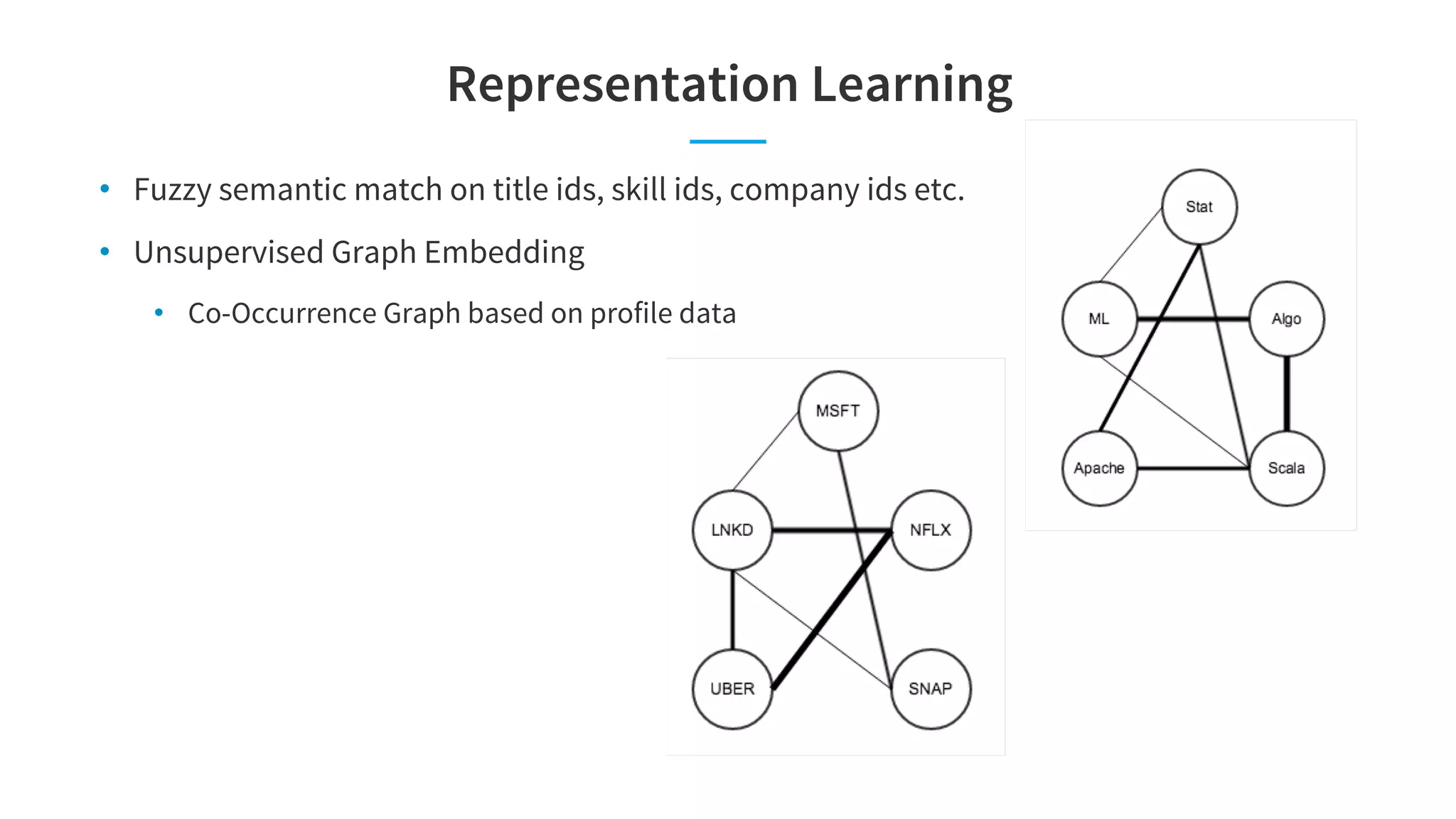
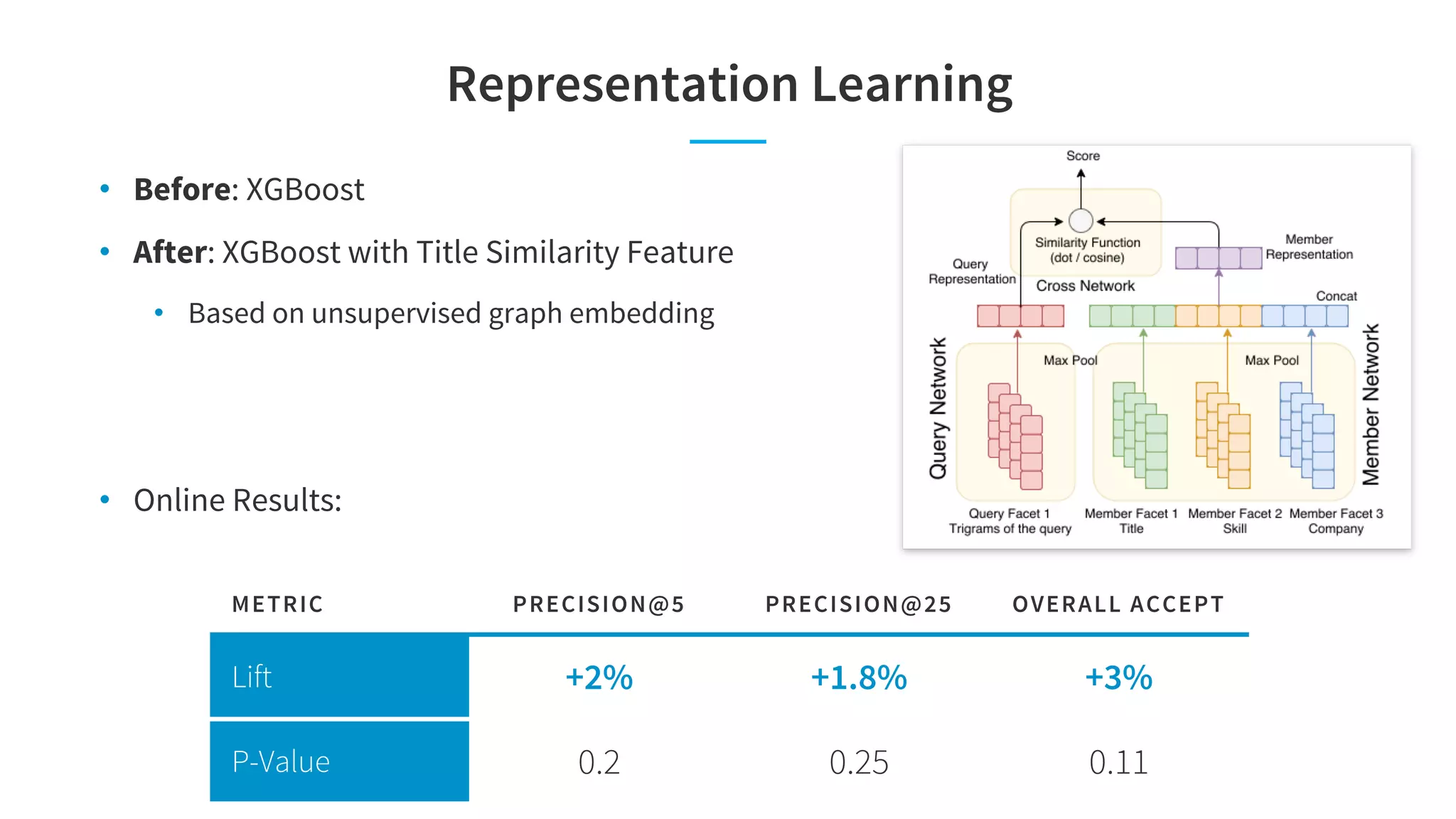
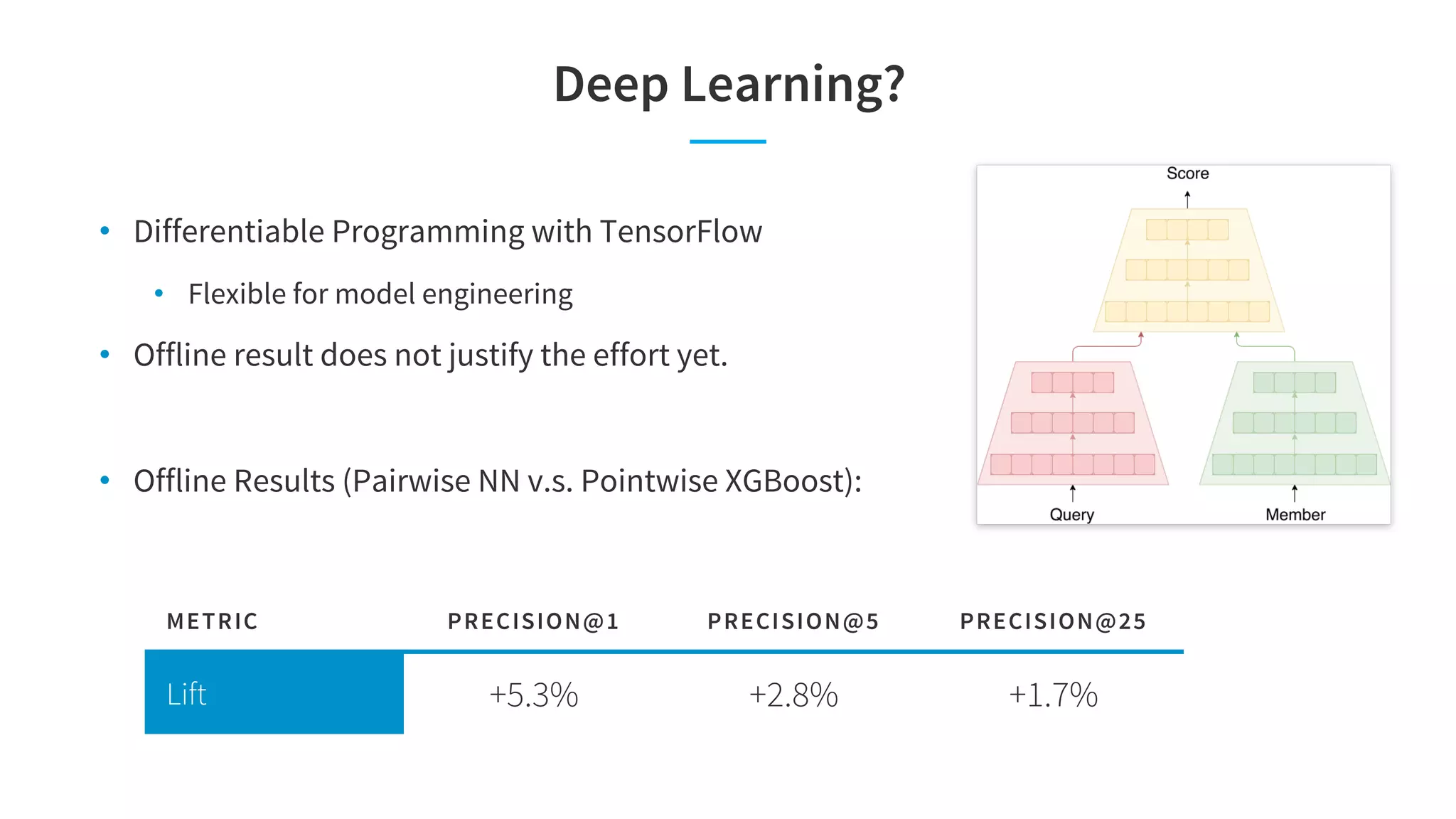
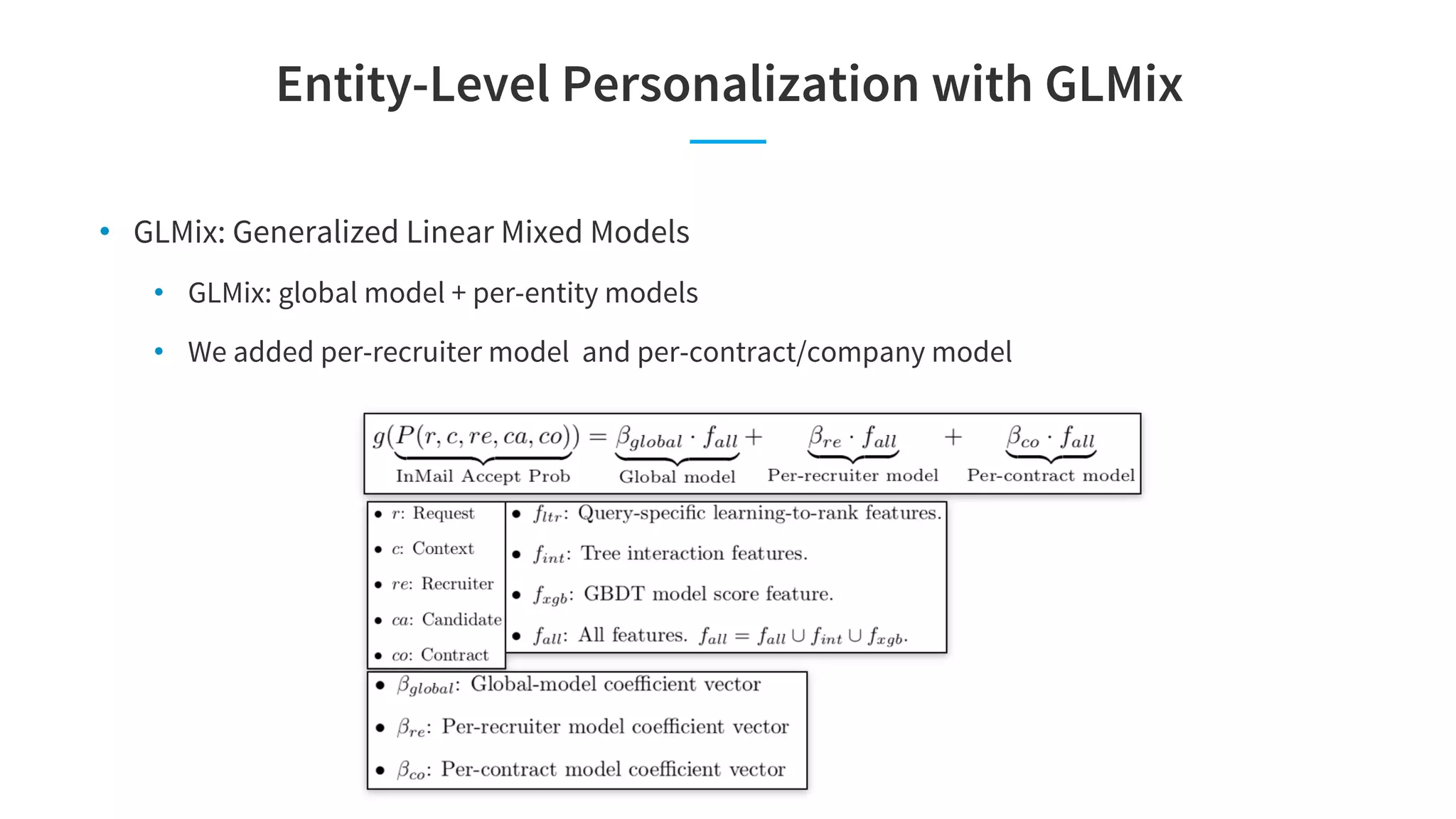
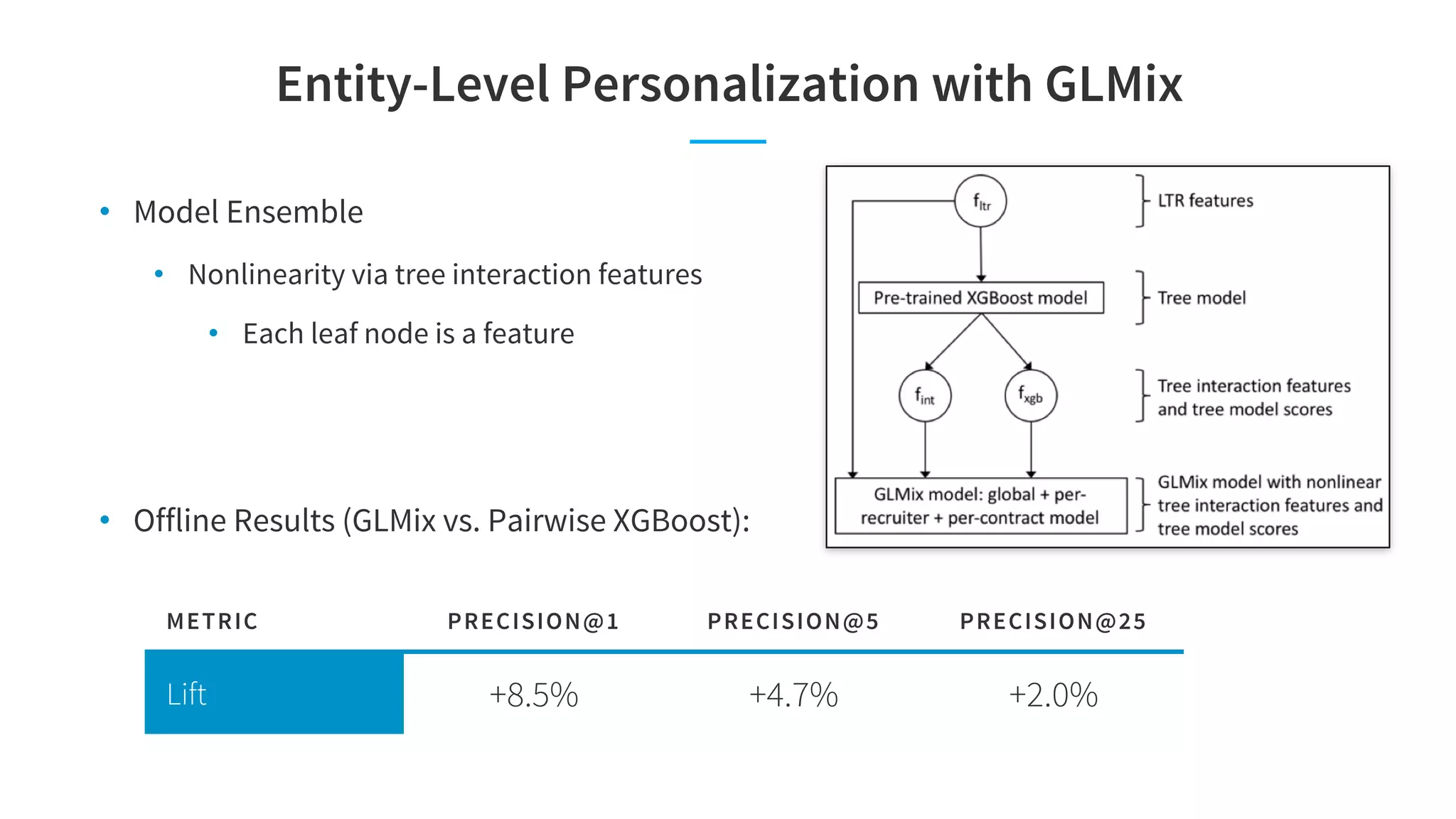
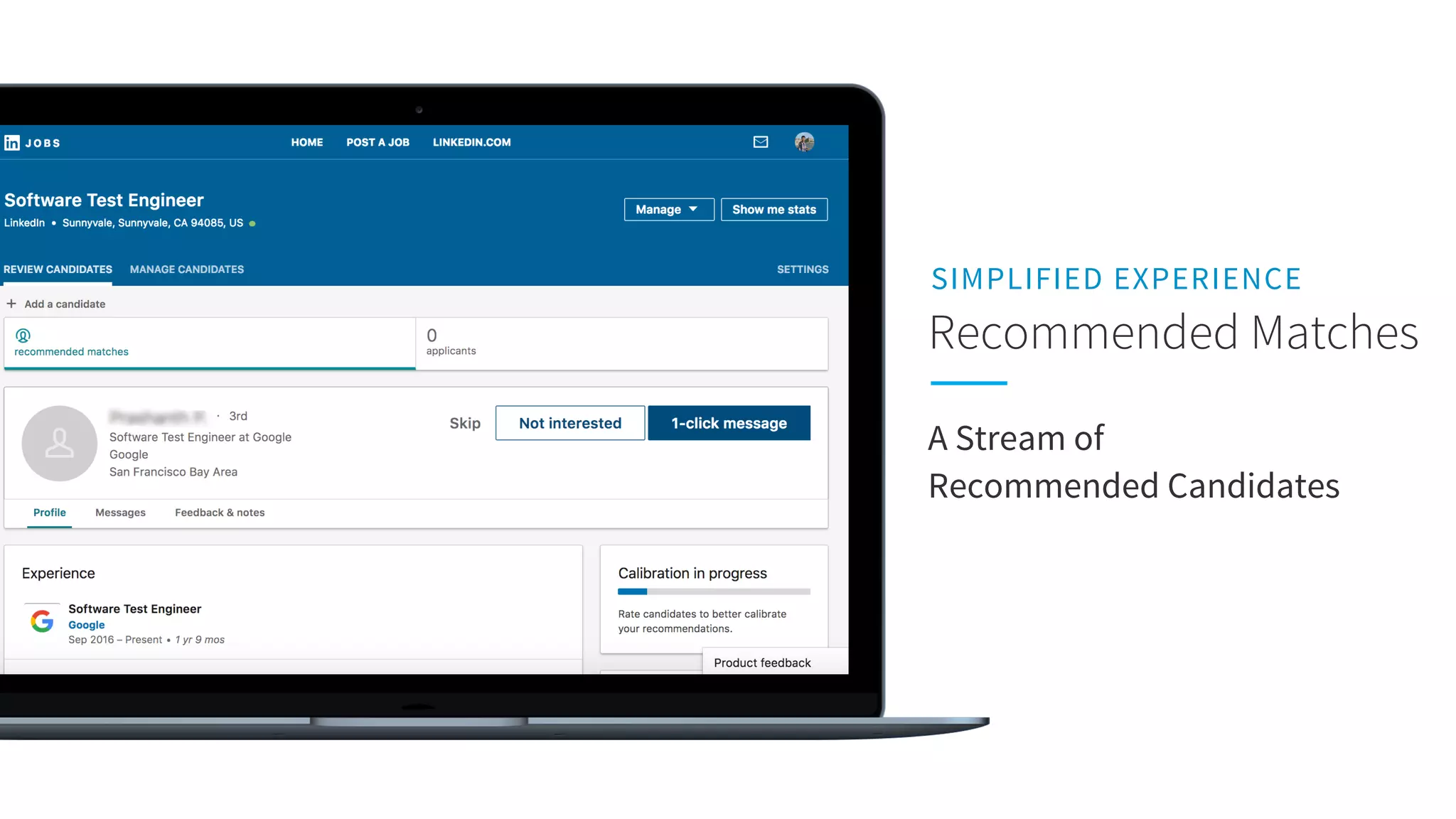
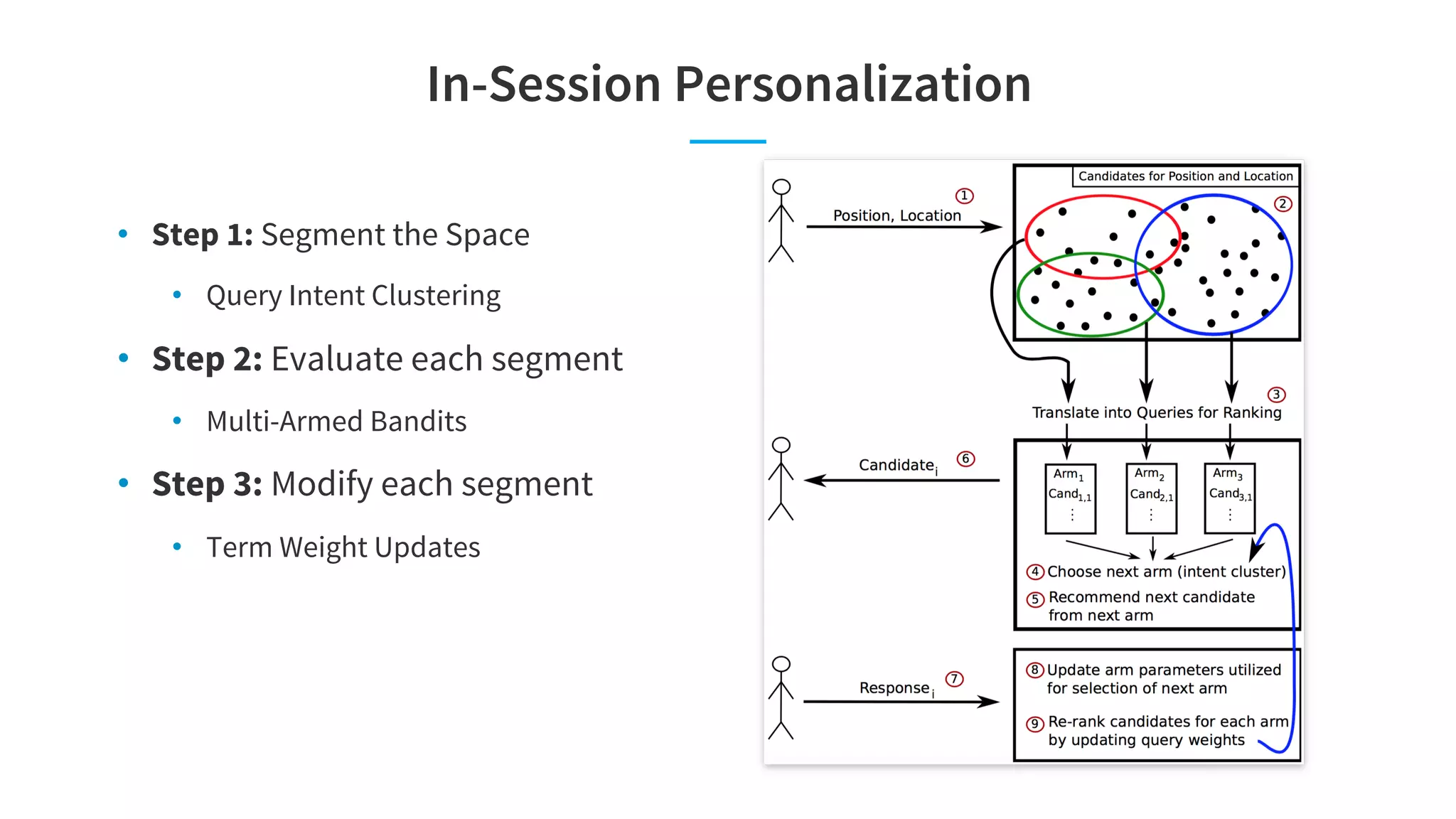
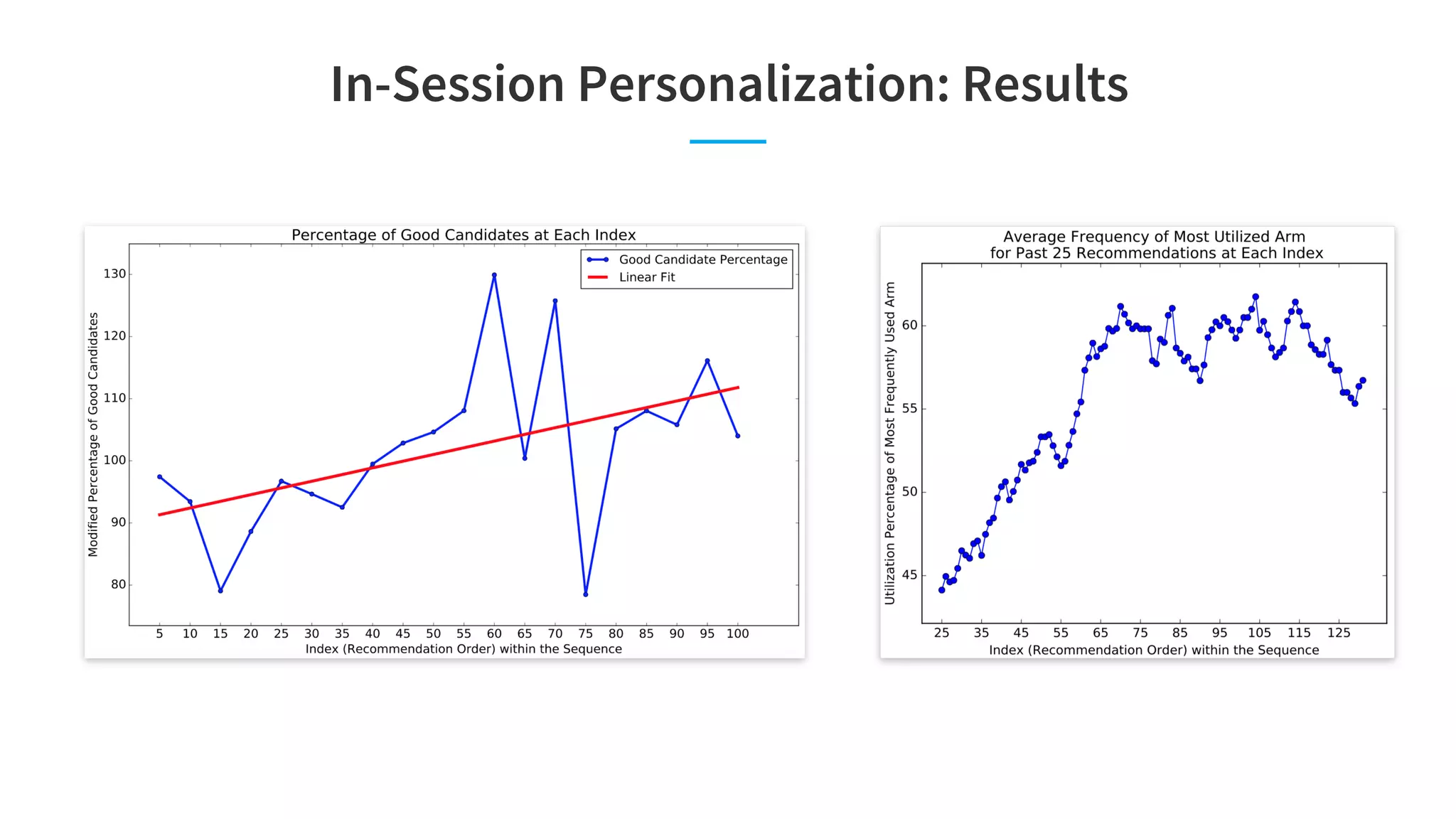
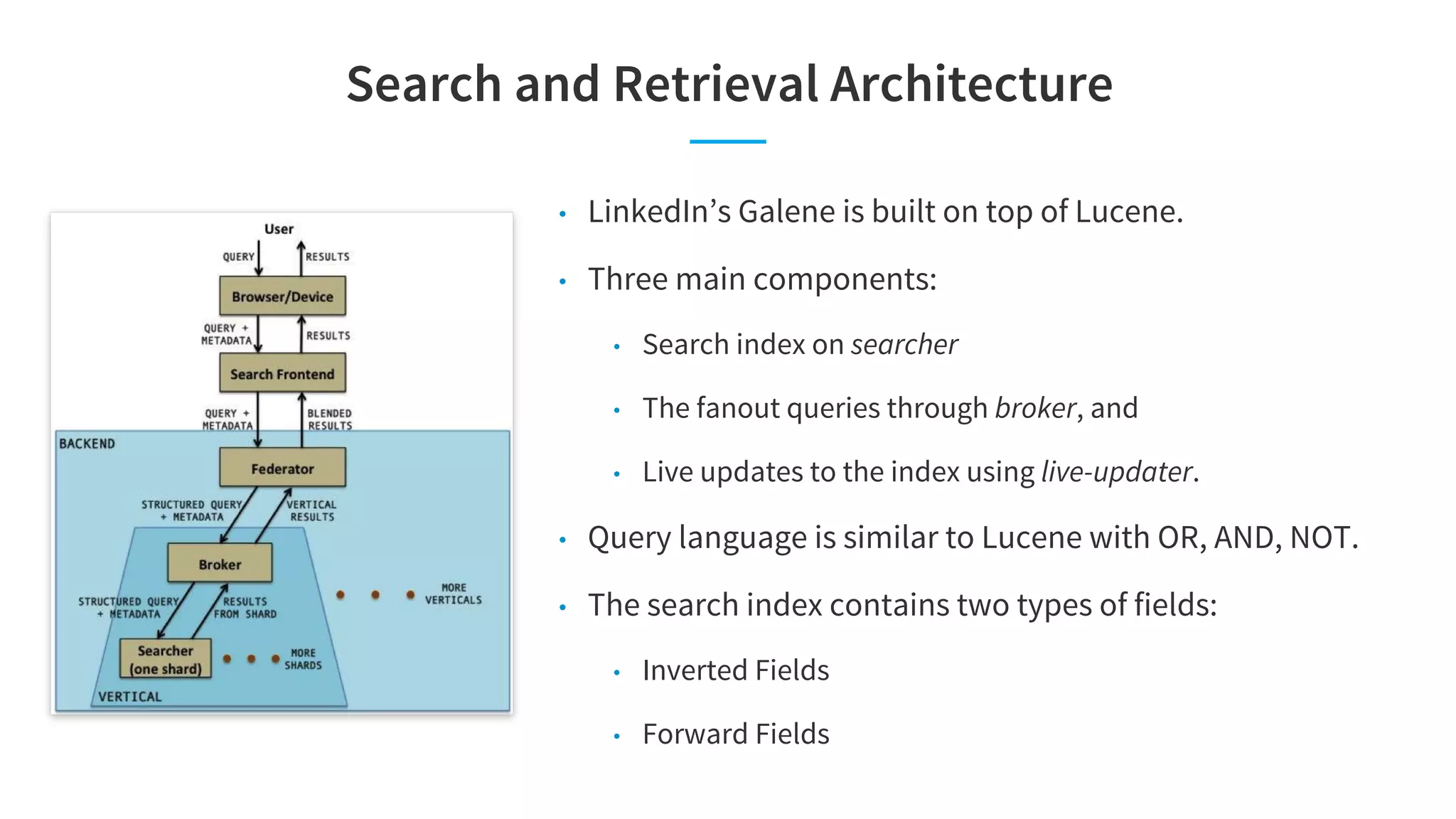
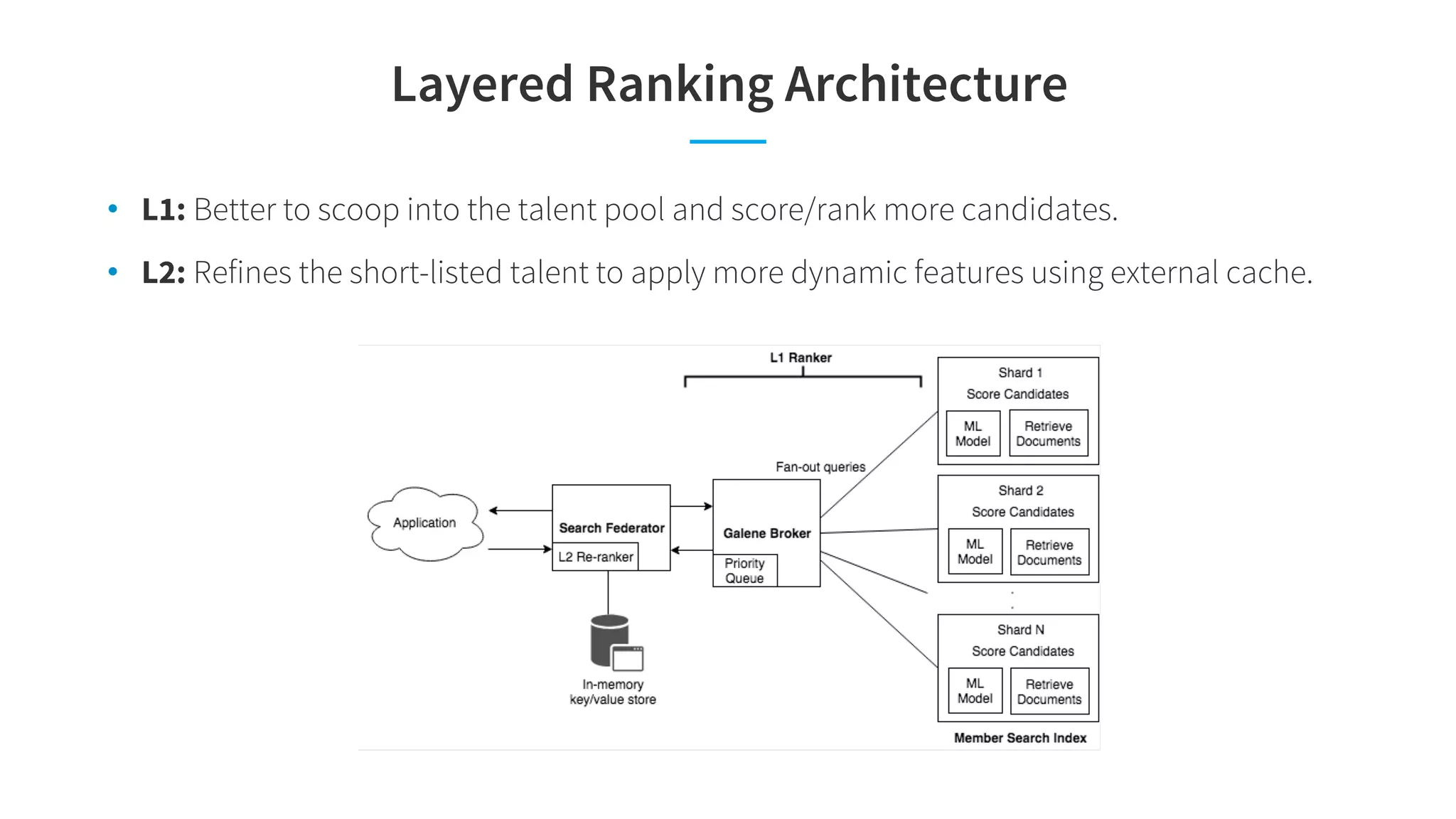
The document discusses LinkedIn's talent search and recommendation systems, highlighting challenges and lessons learned. Key topics include the development of ranking models, personalization strategies, and the architecture of the search system, leading to improvements in candidate recommendations. Techniques such as context-aware training and generalized linear mixed models (GLMIX) were employed to enhance the precision and effectiveness of searches.