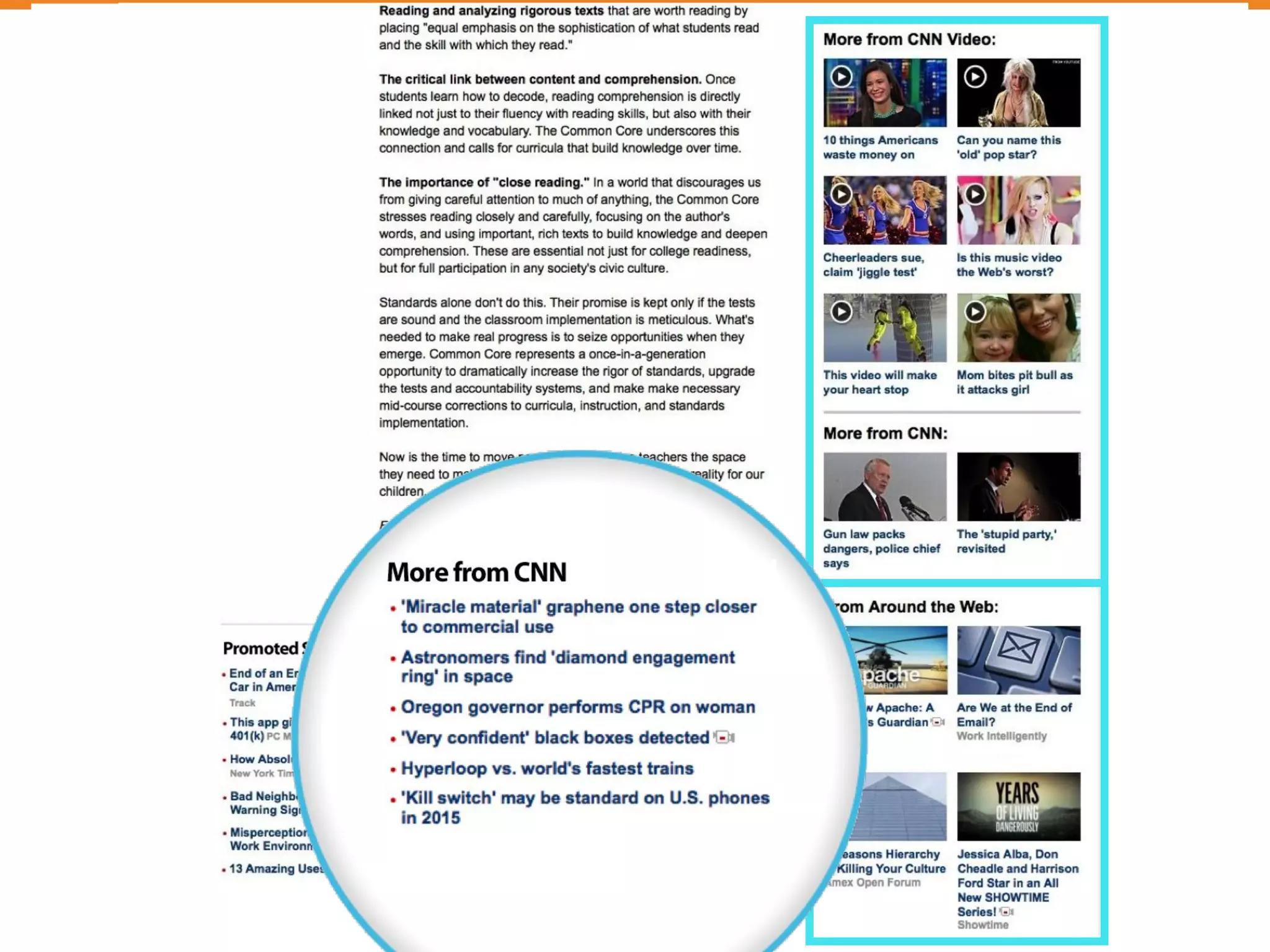
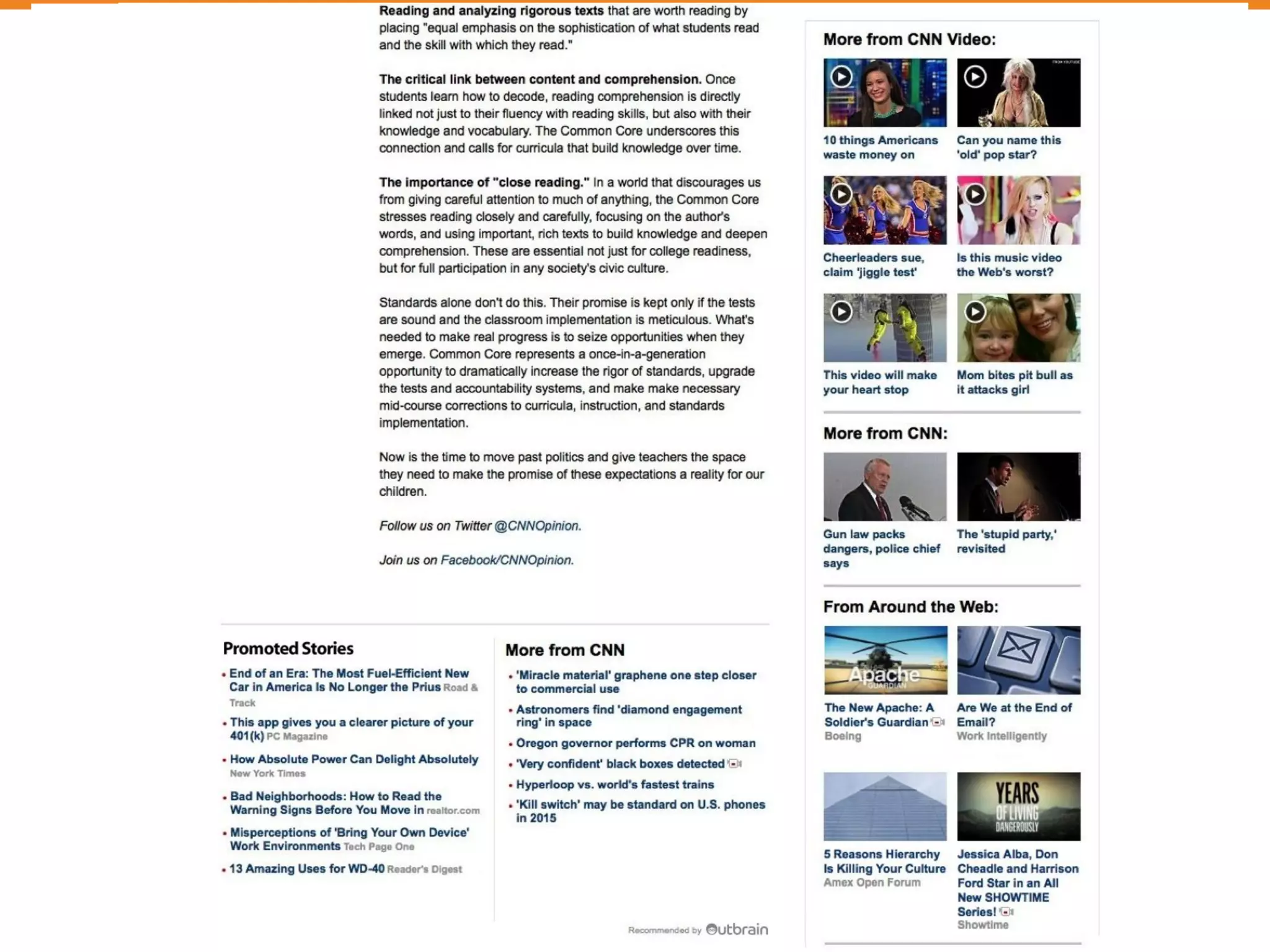
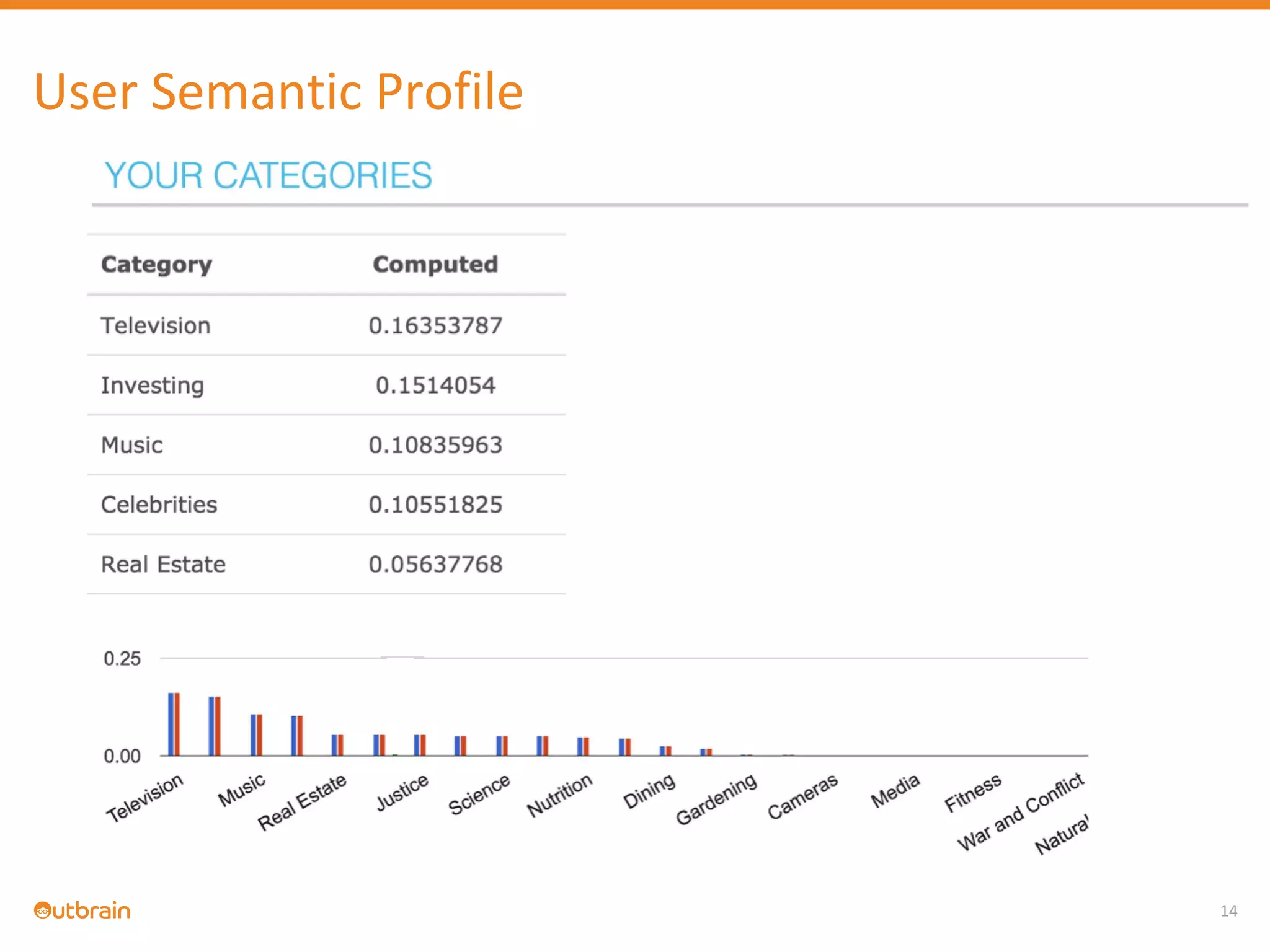
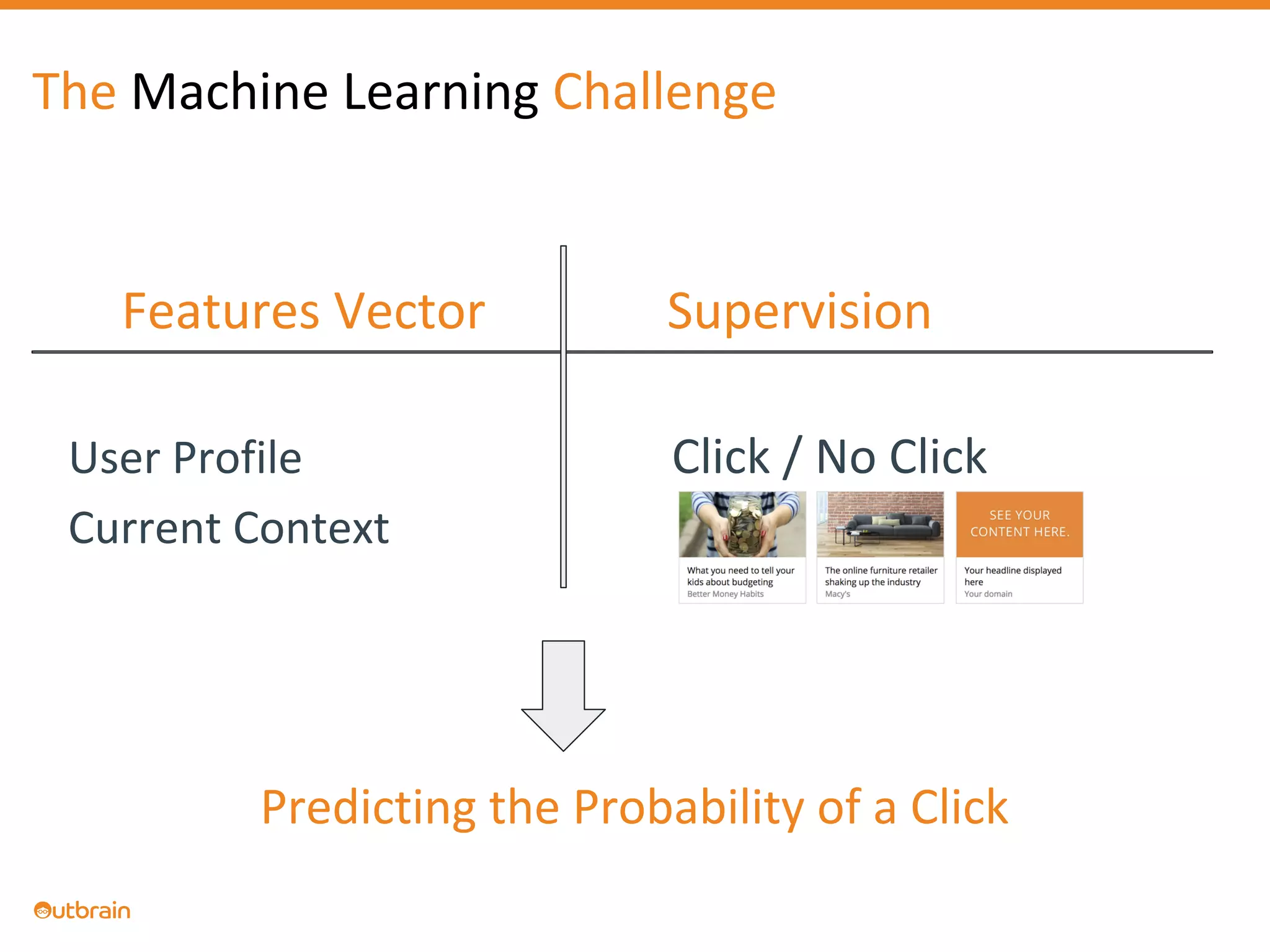
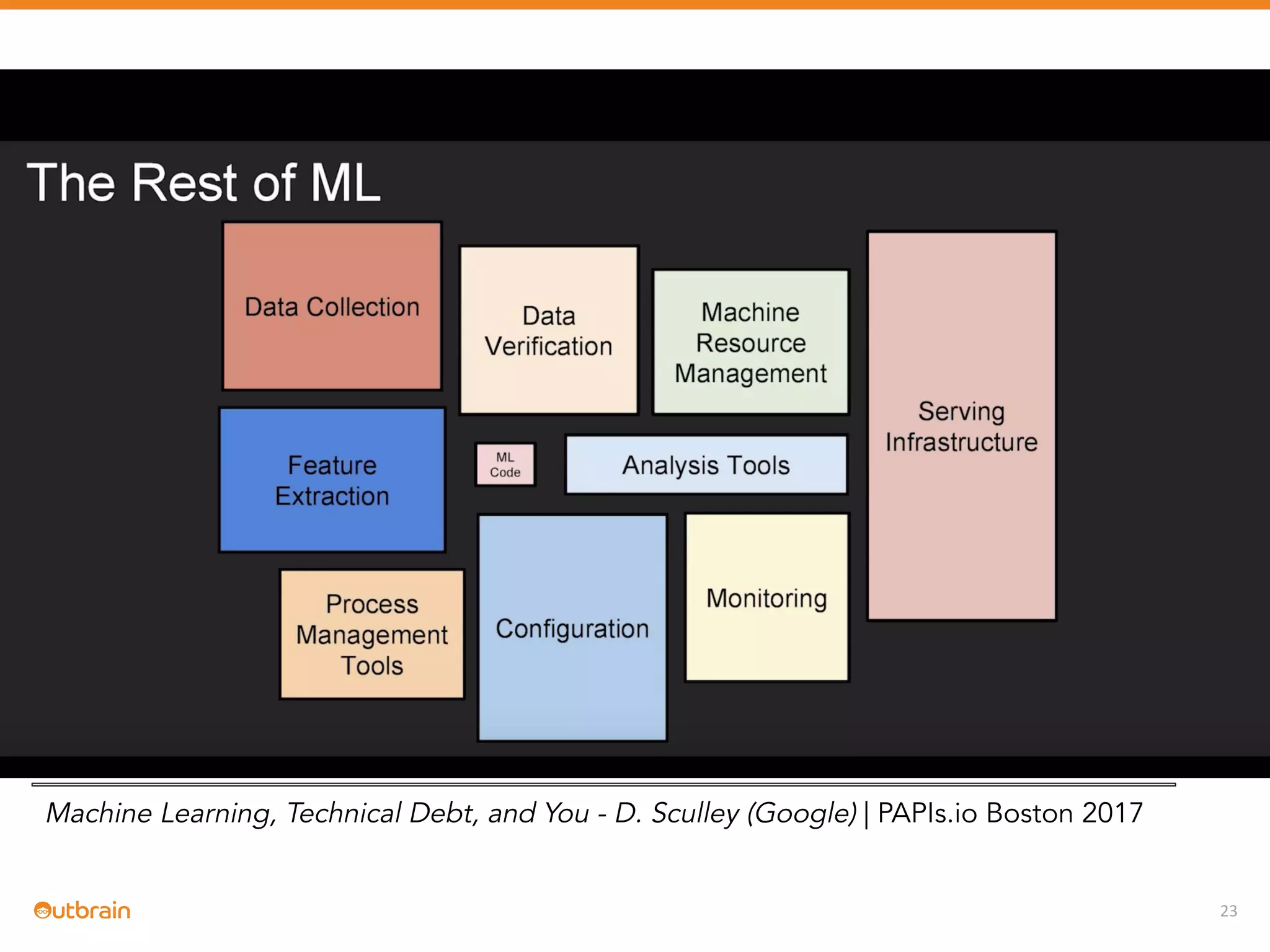
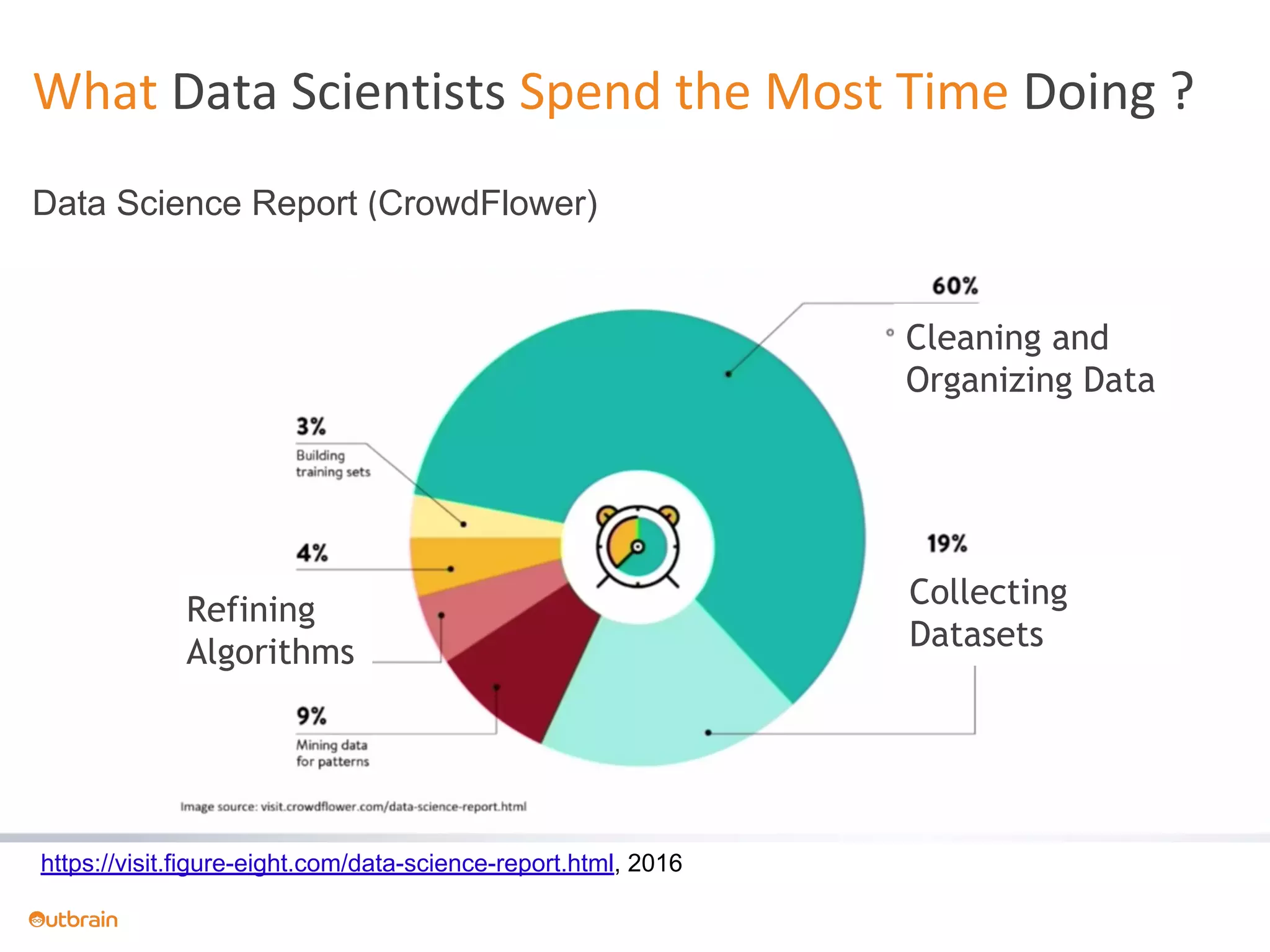
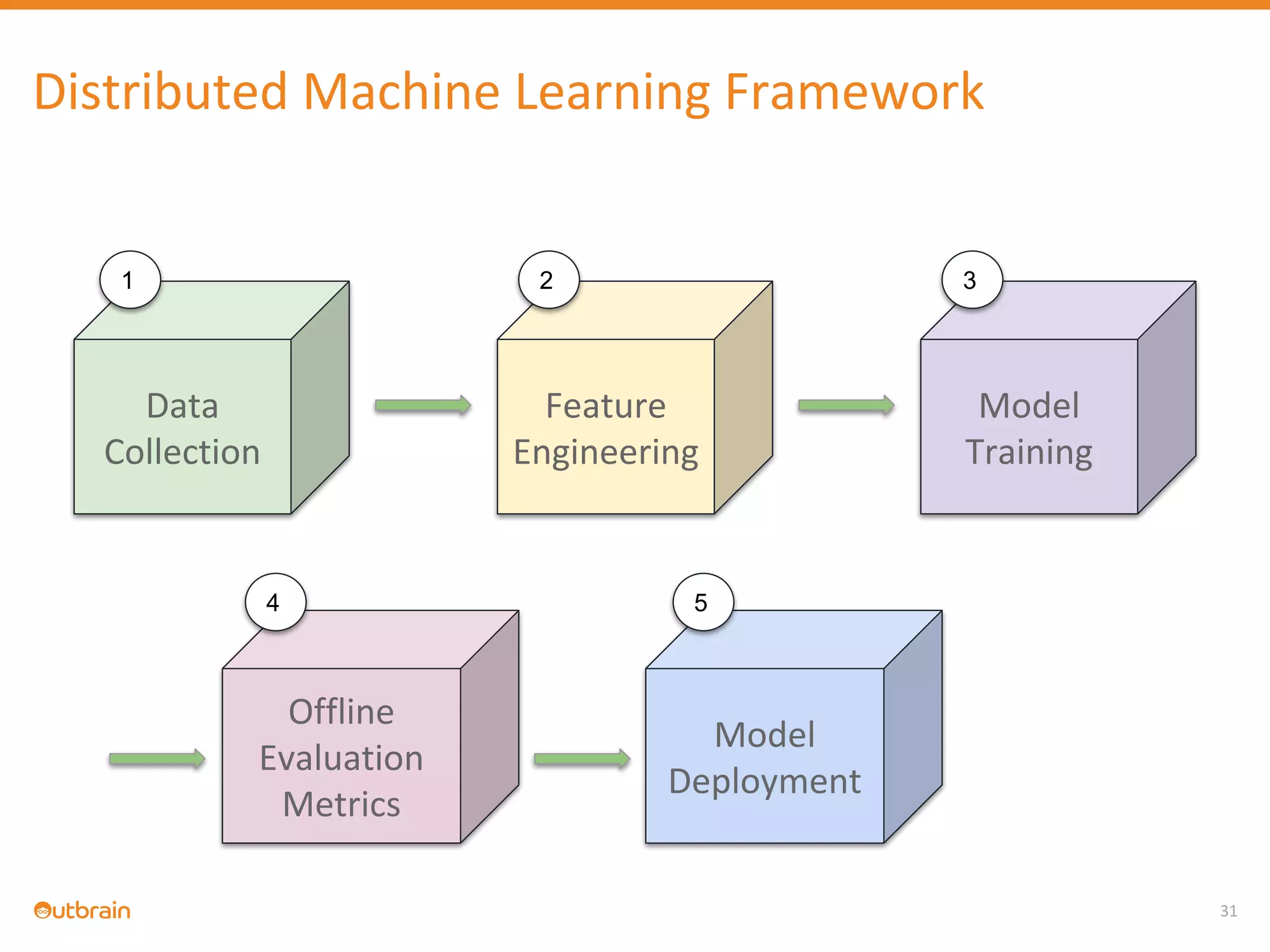
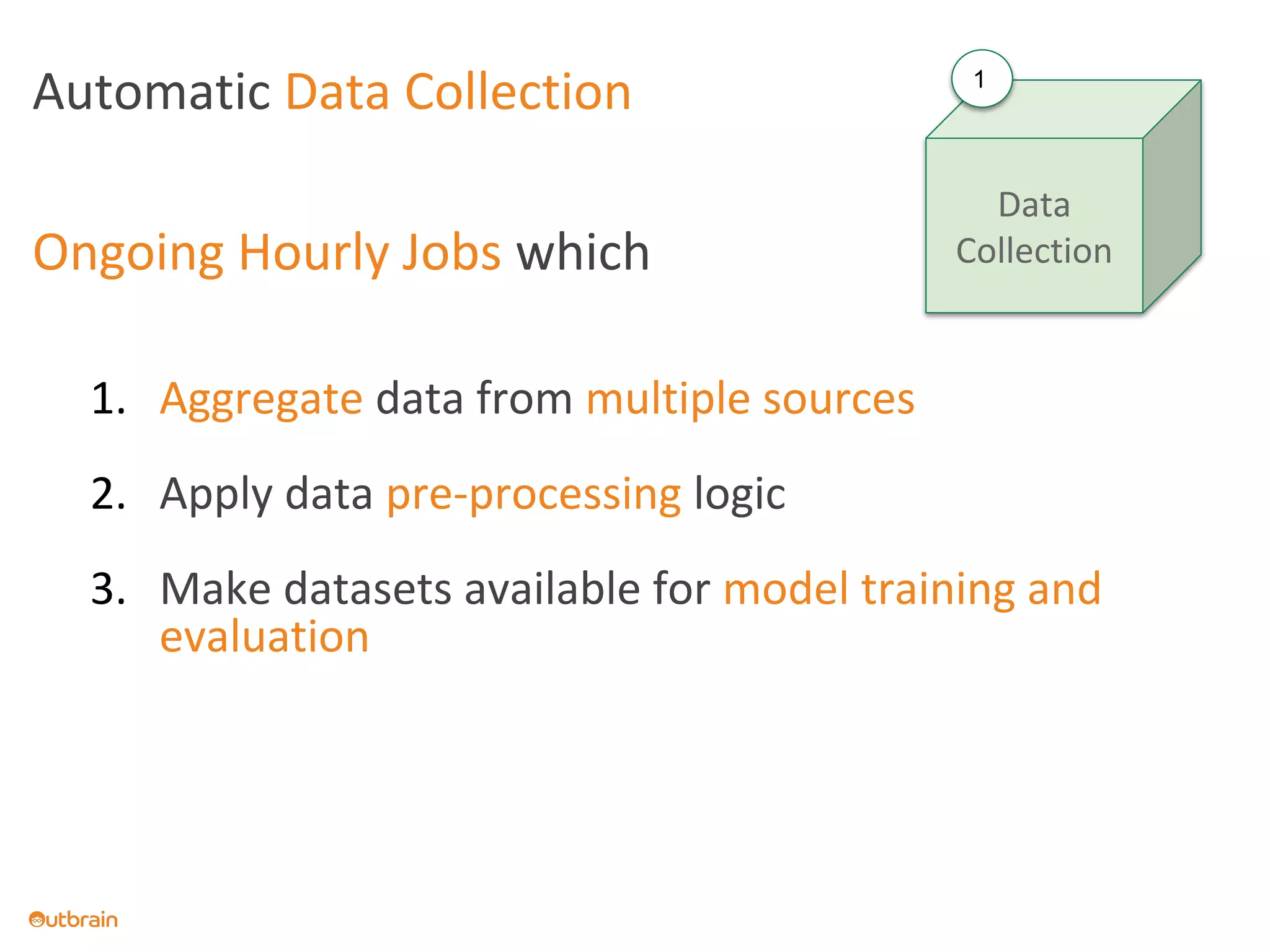
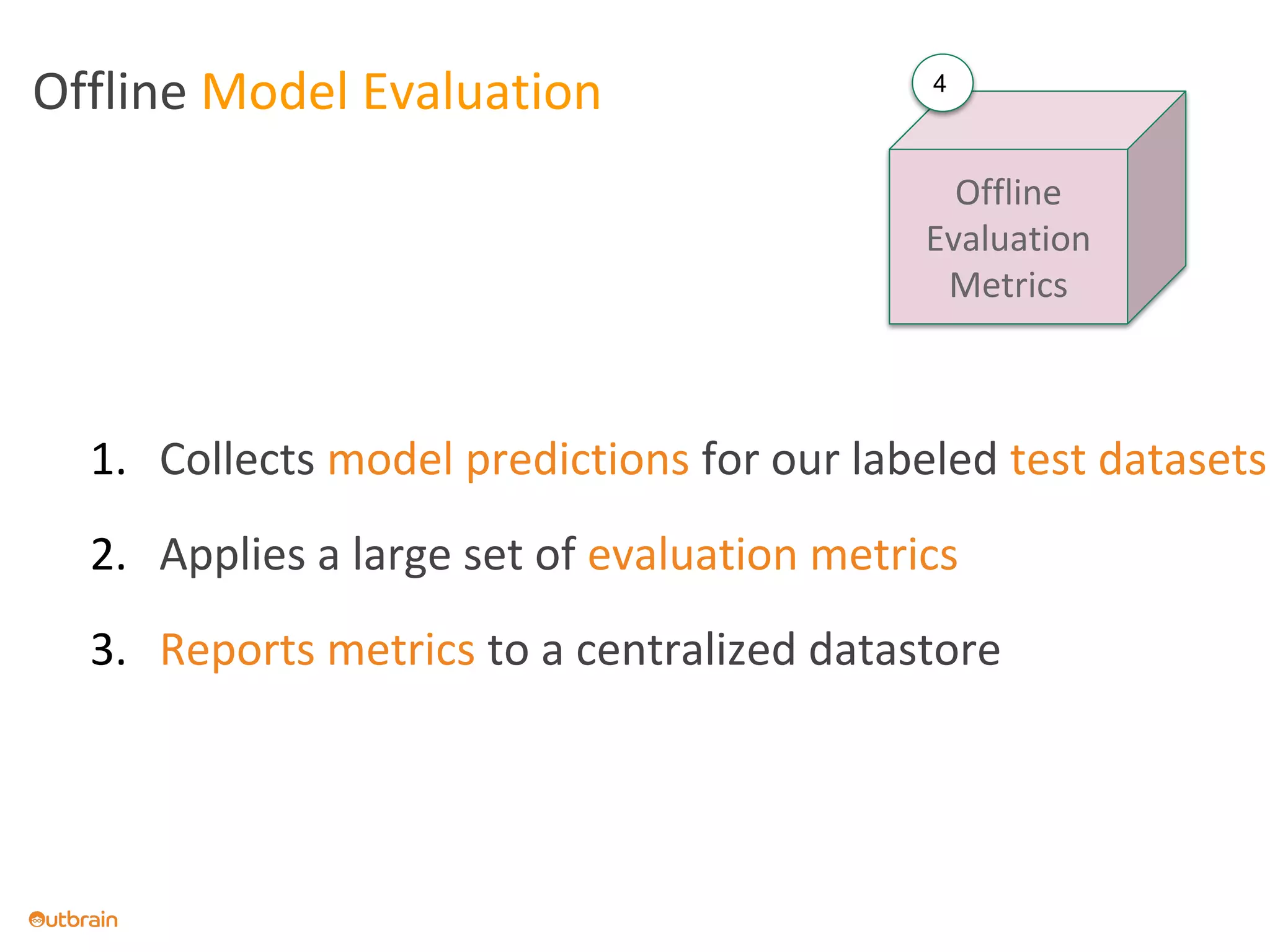
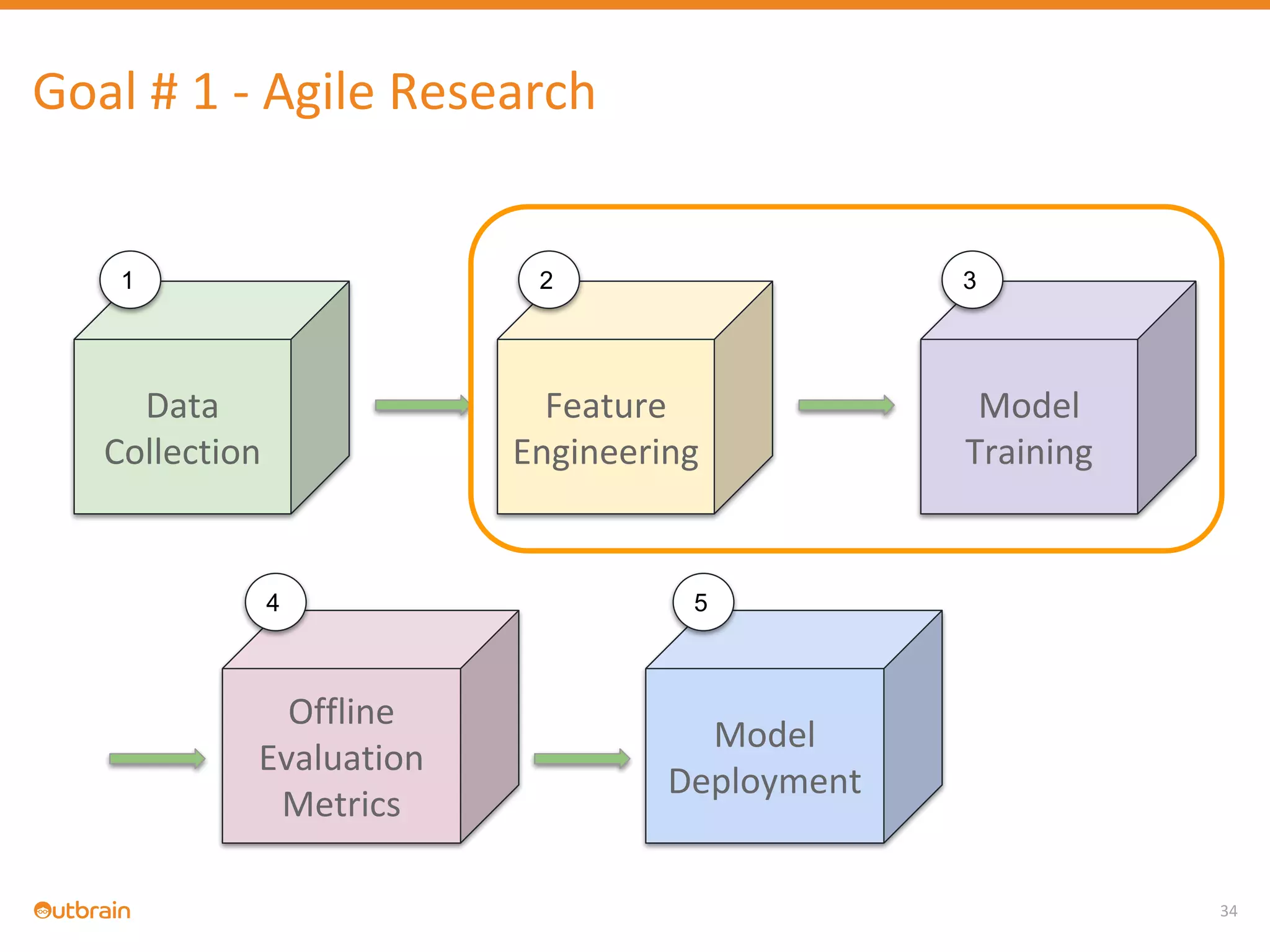
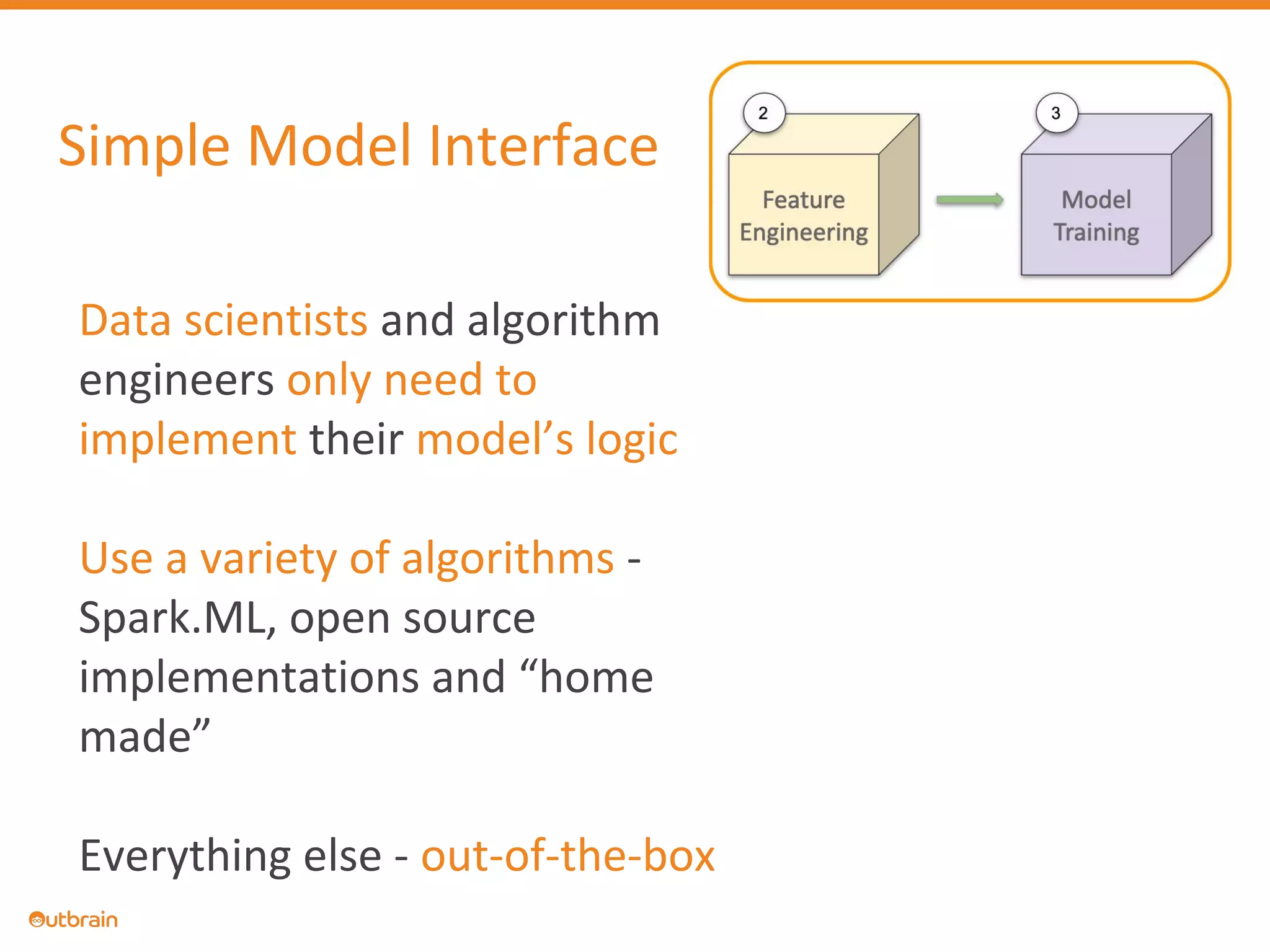
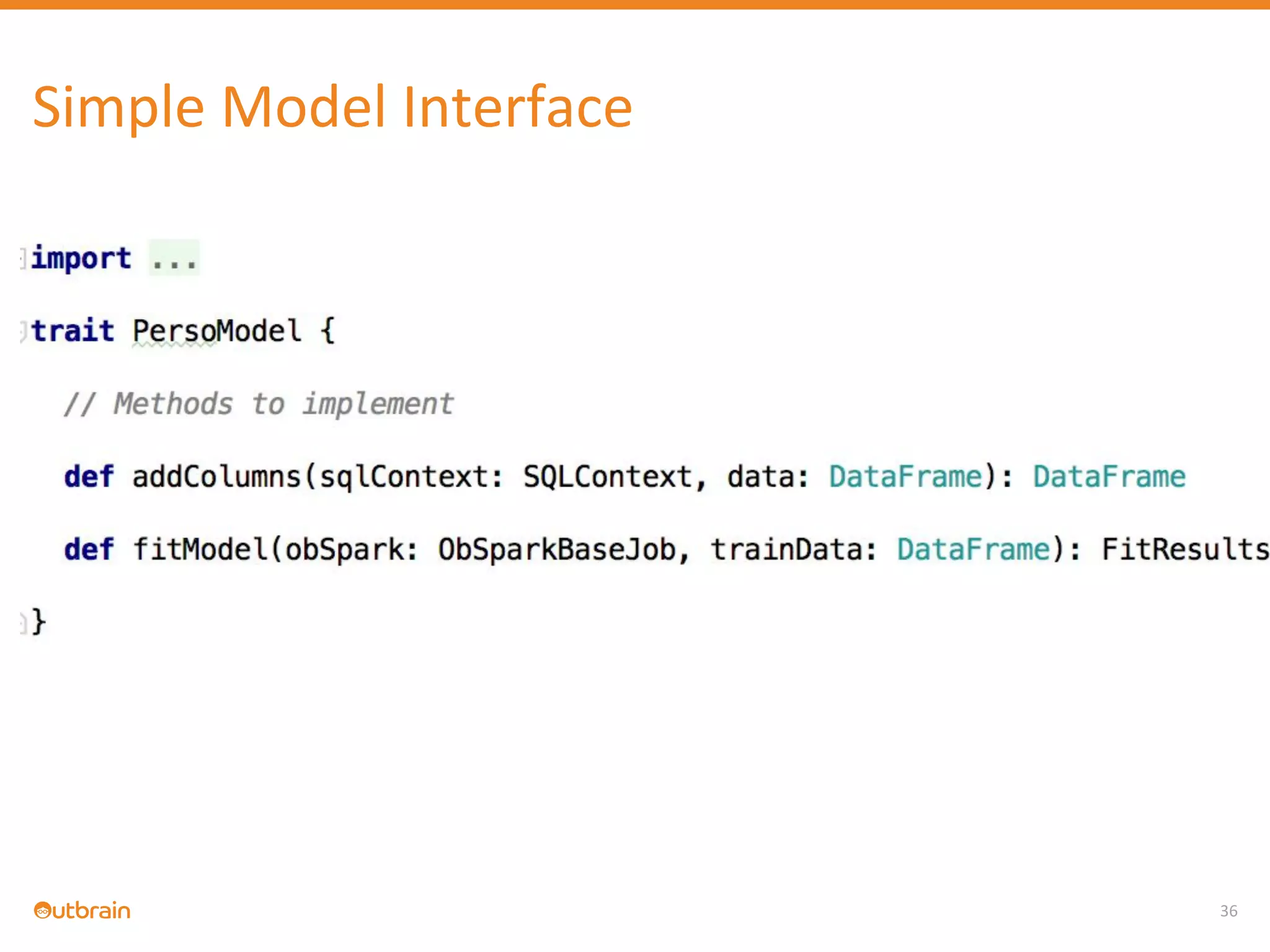
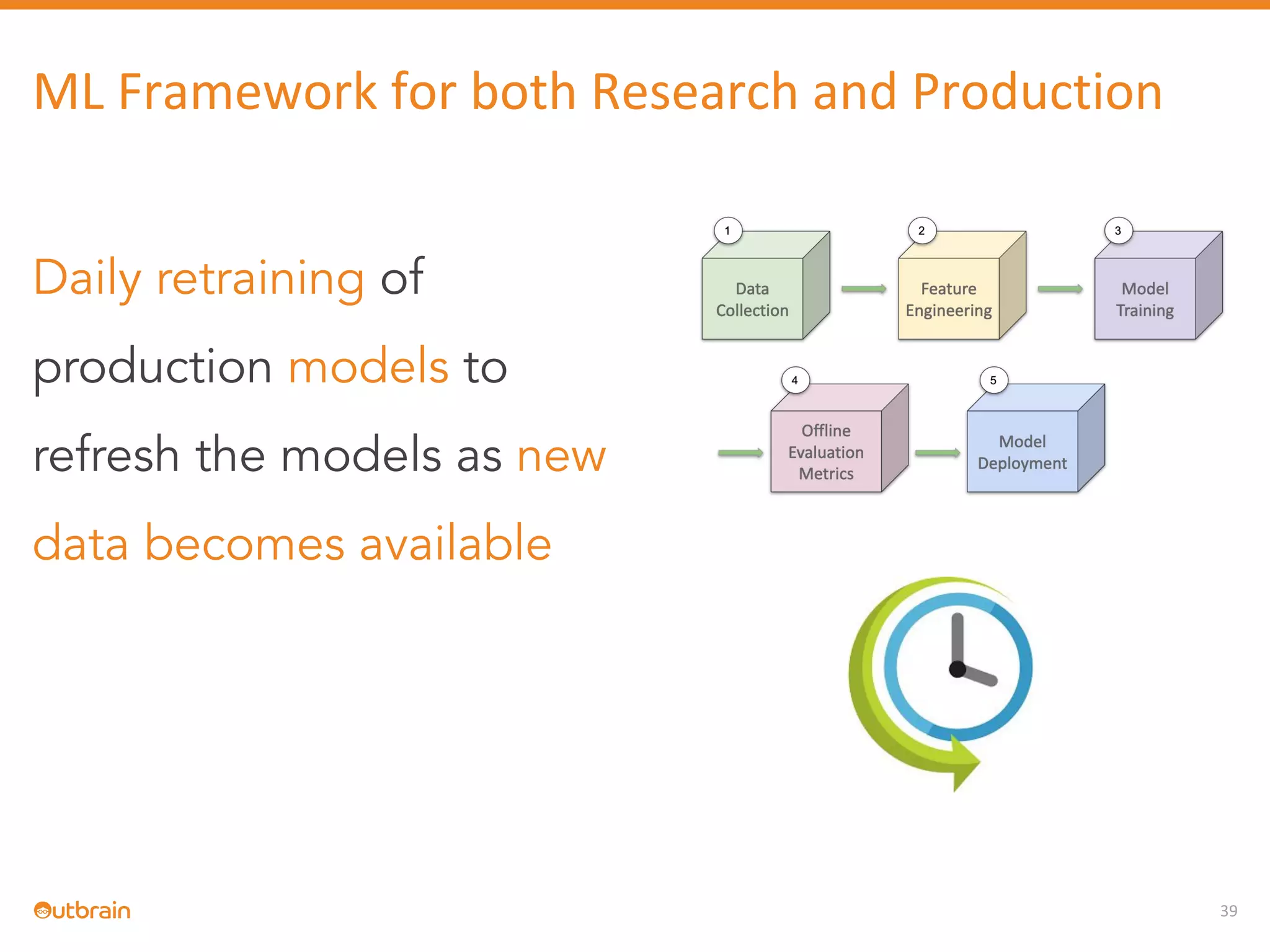
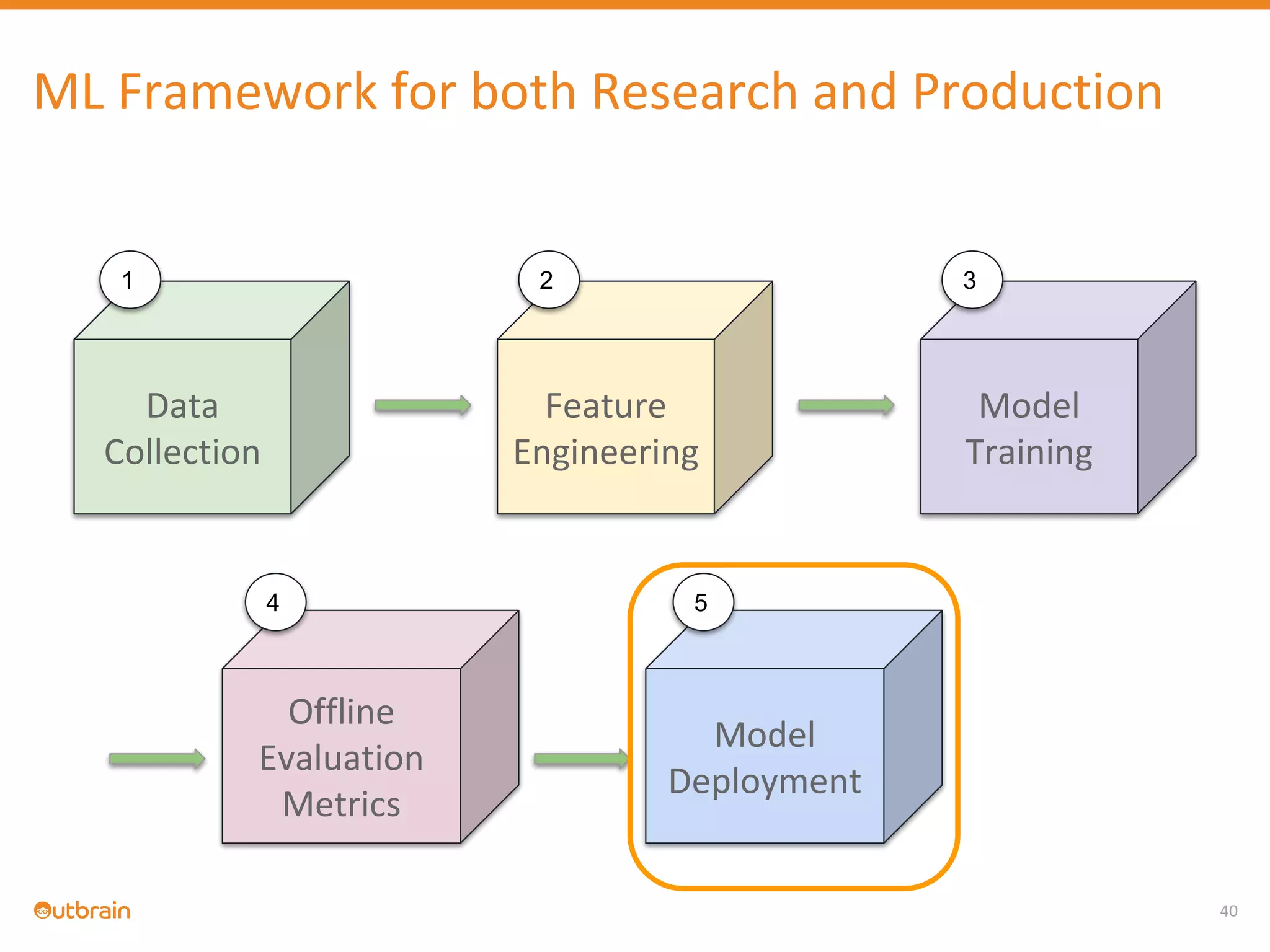
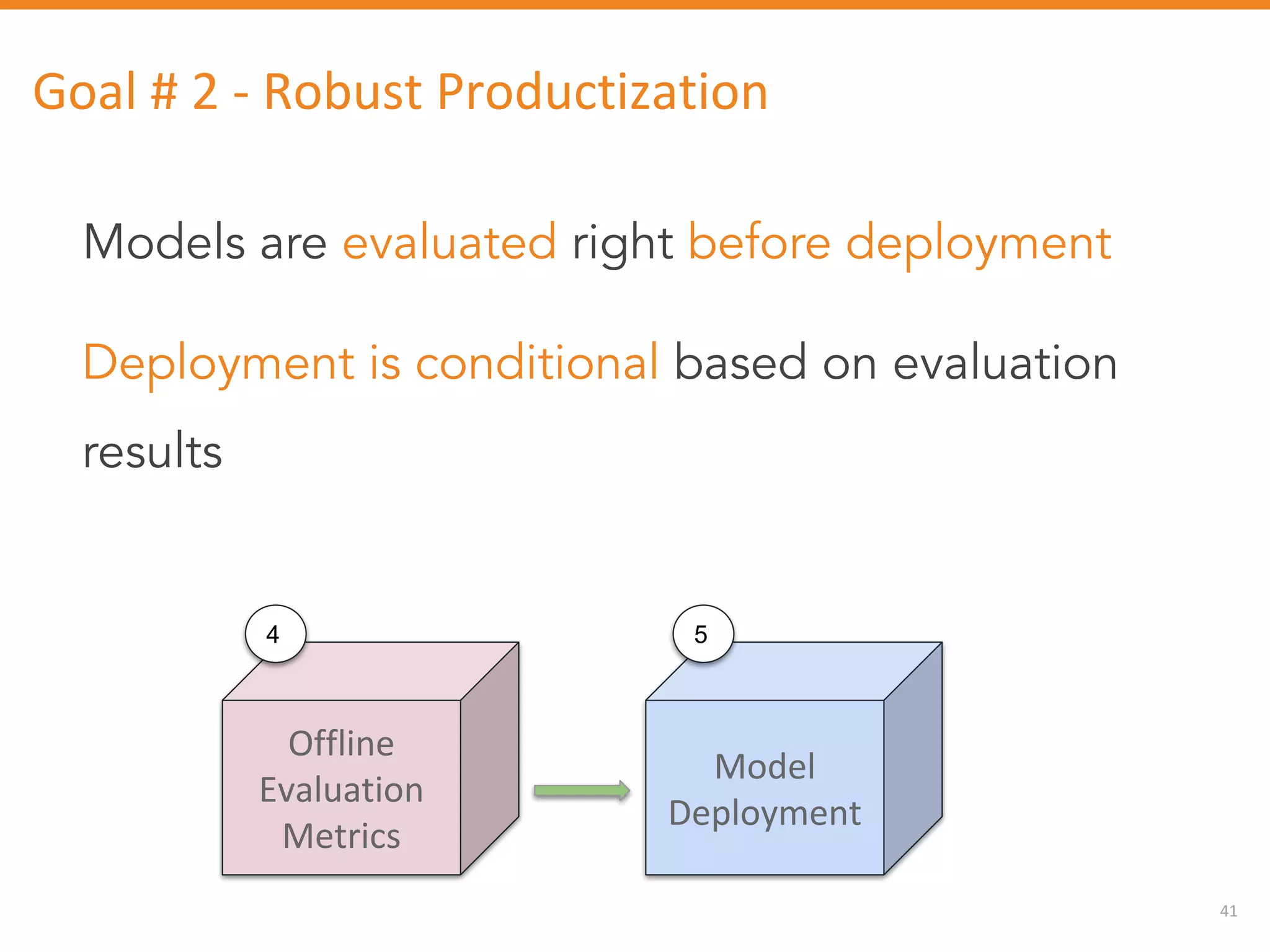
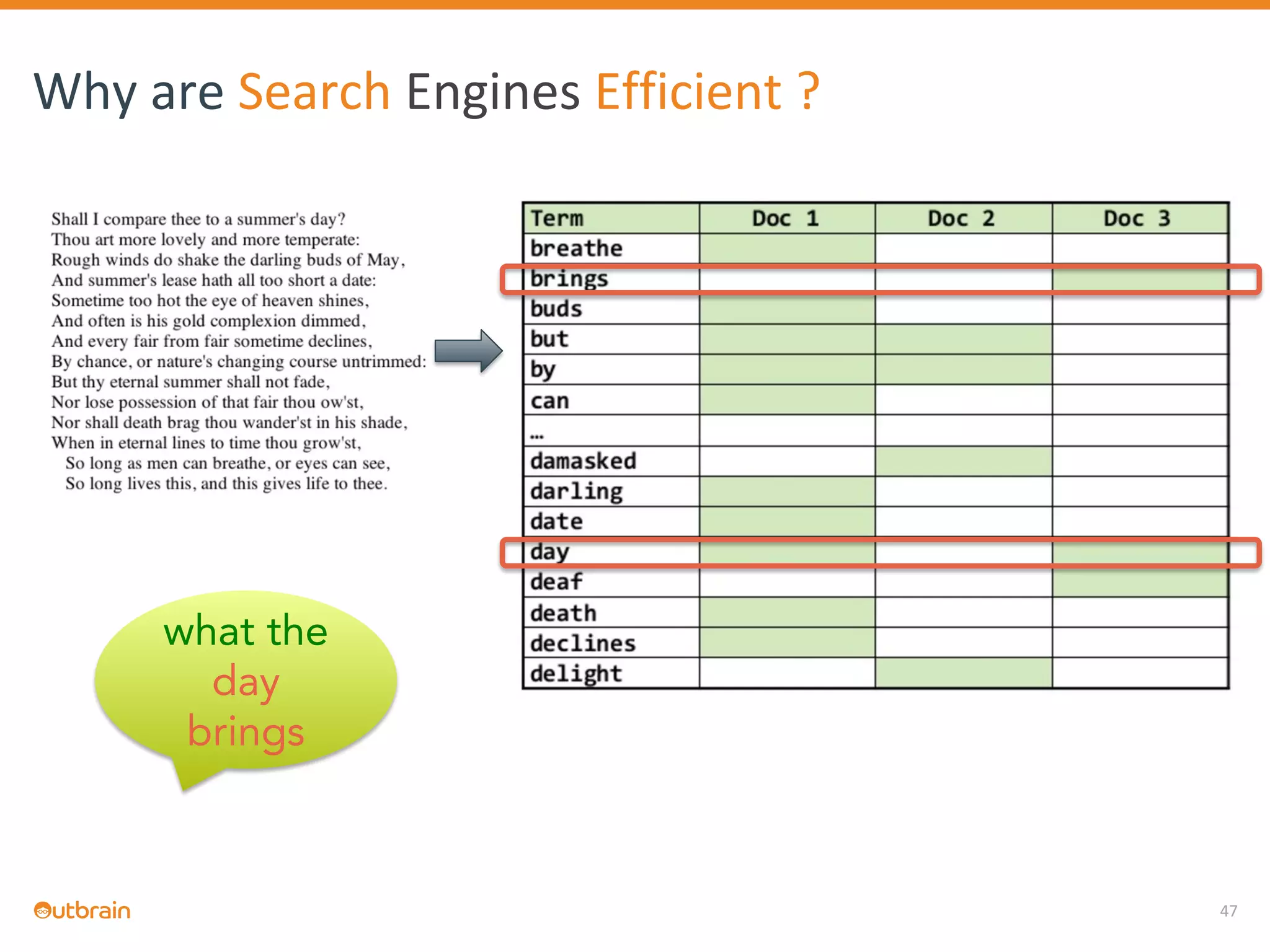
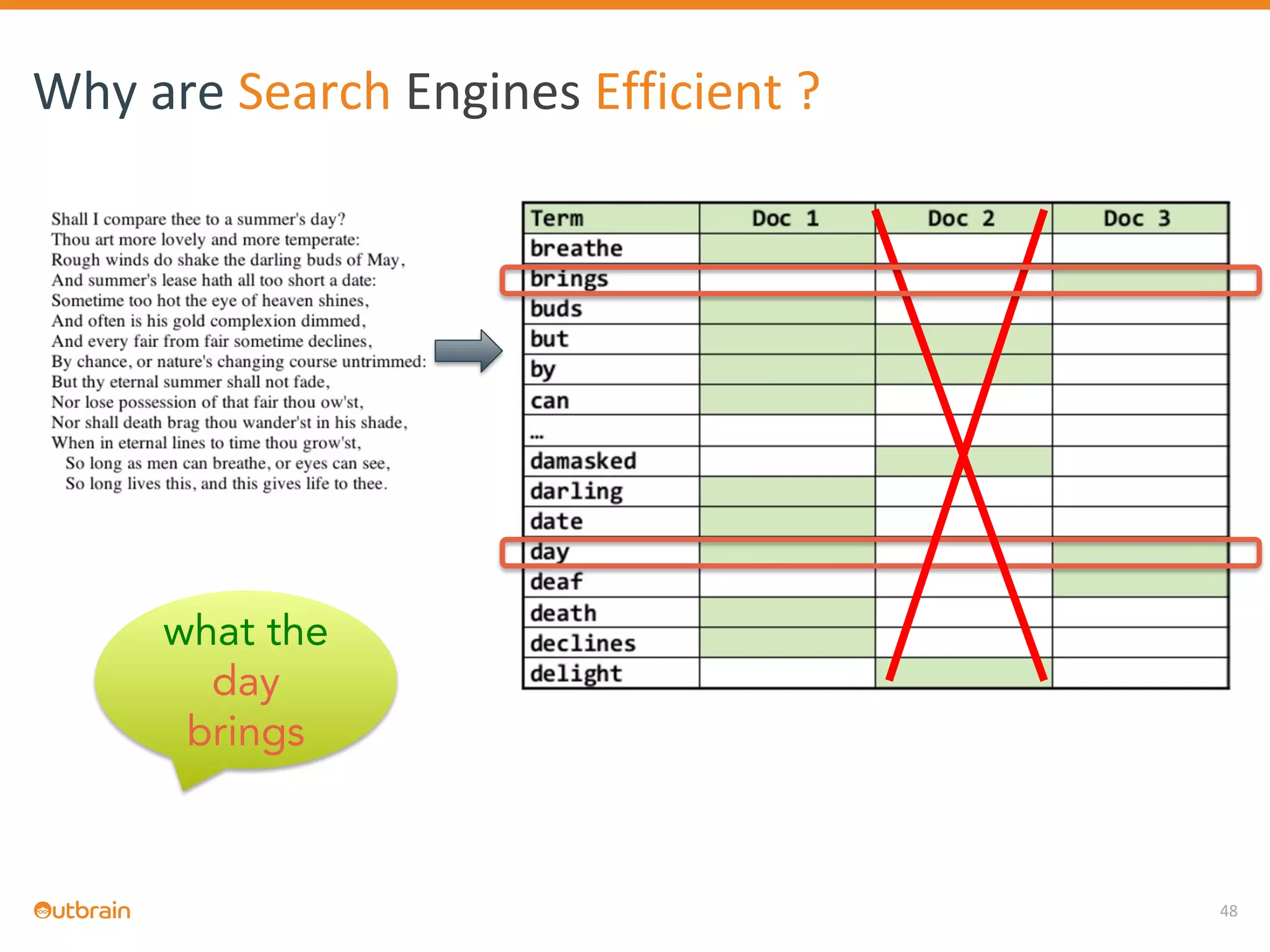
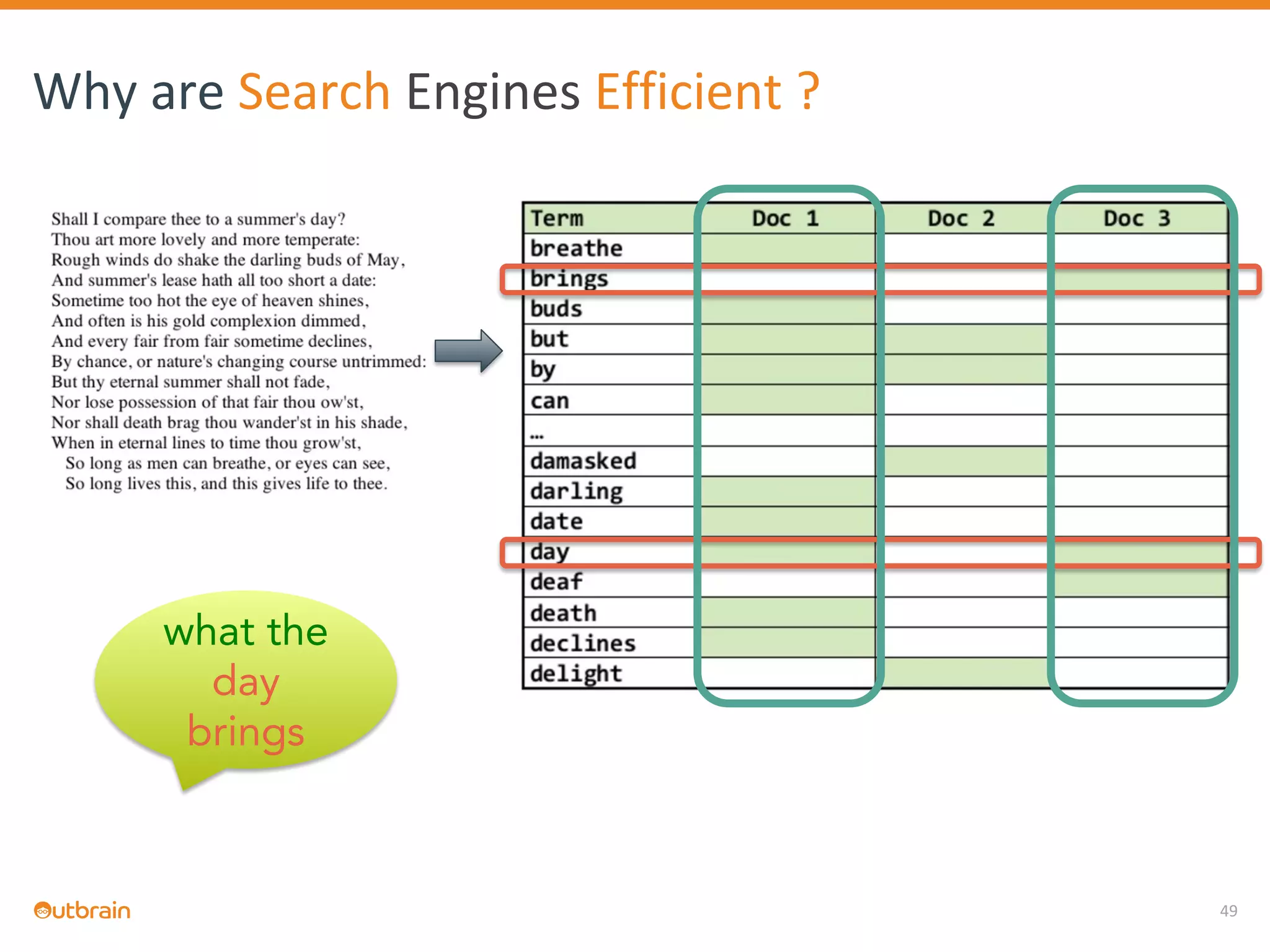
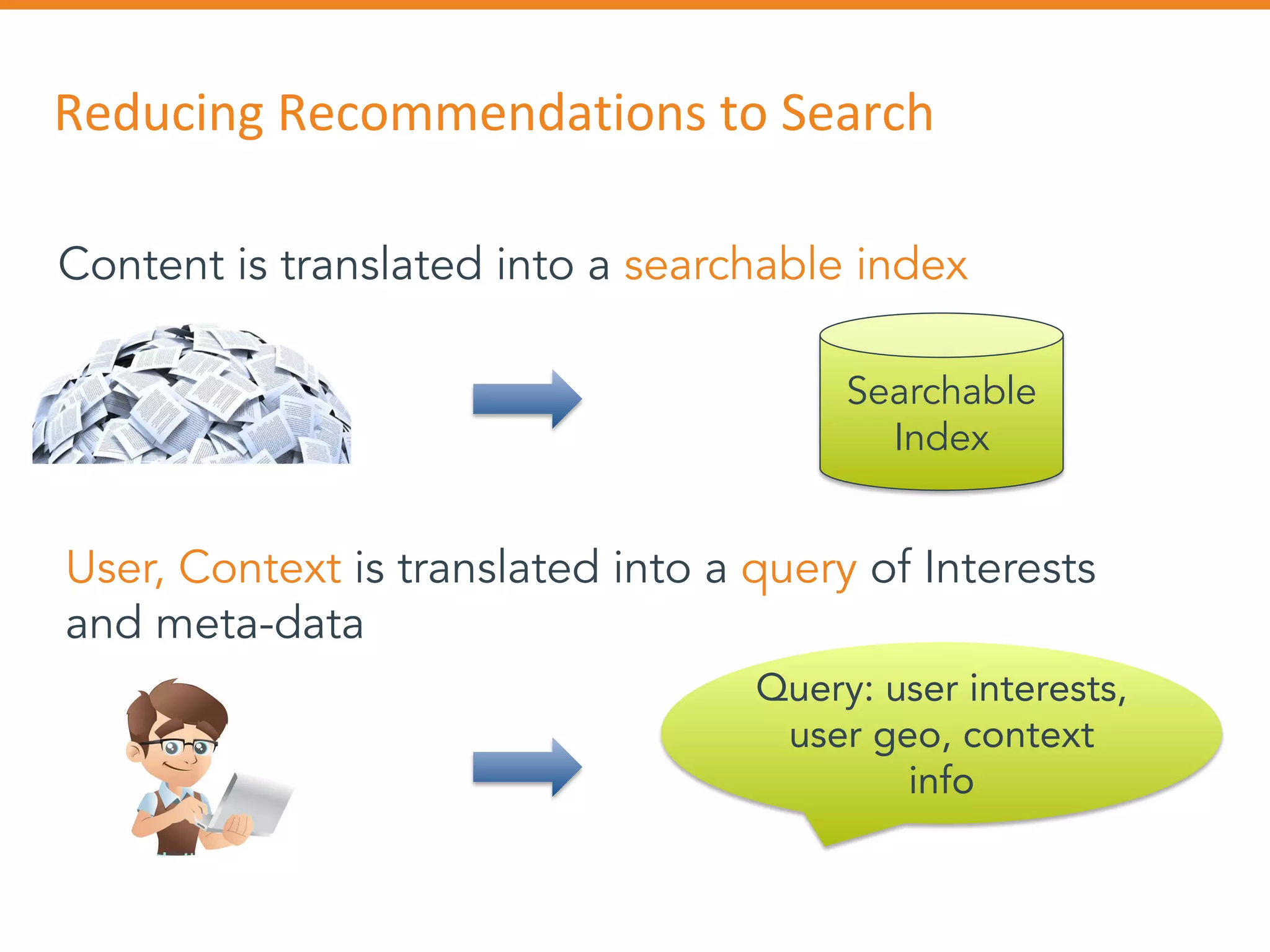
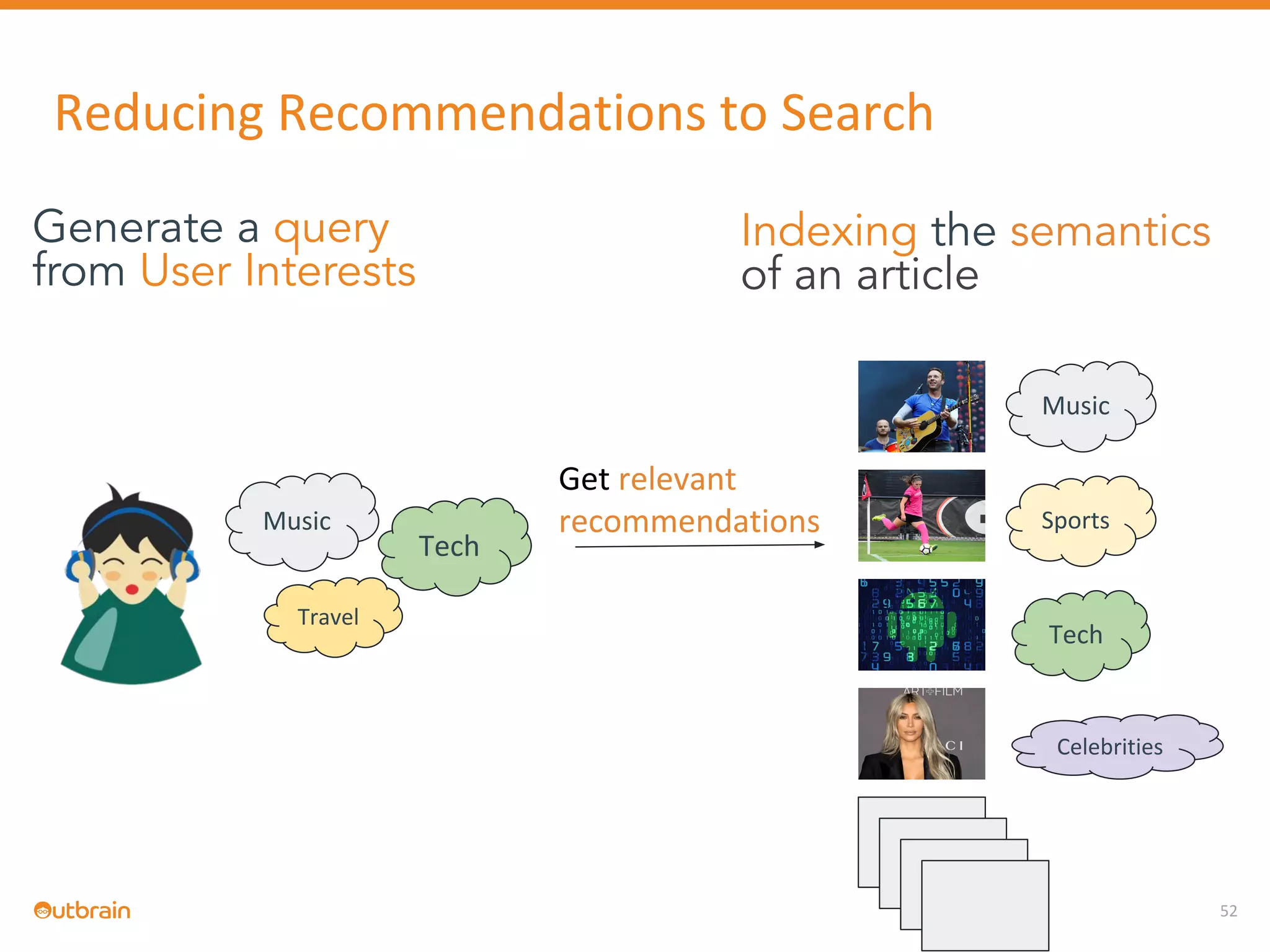
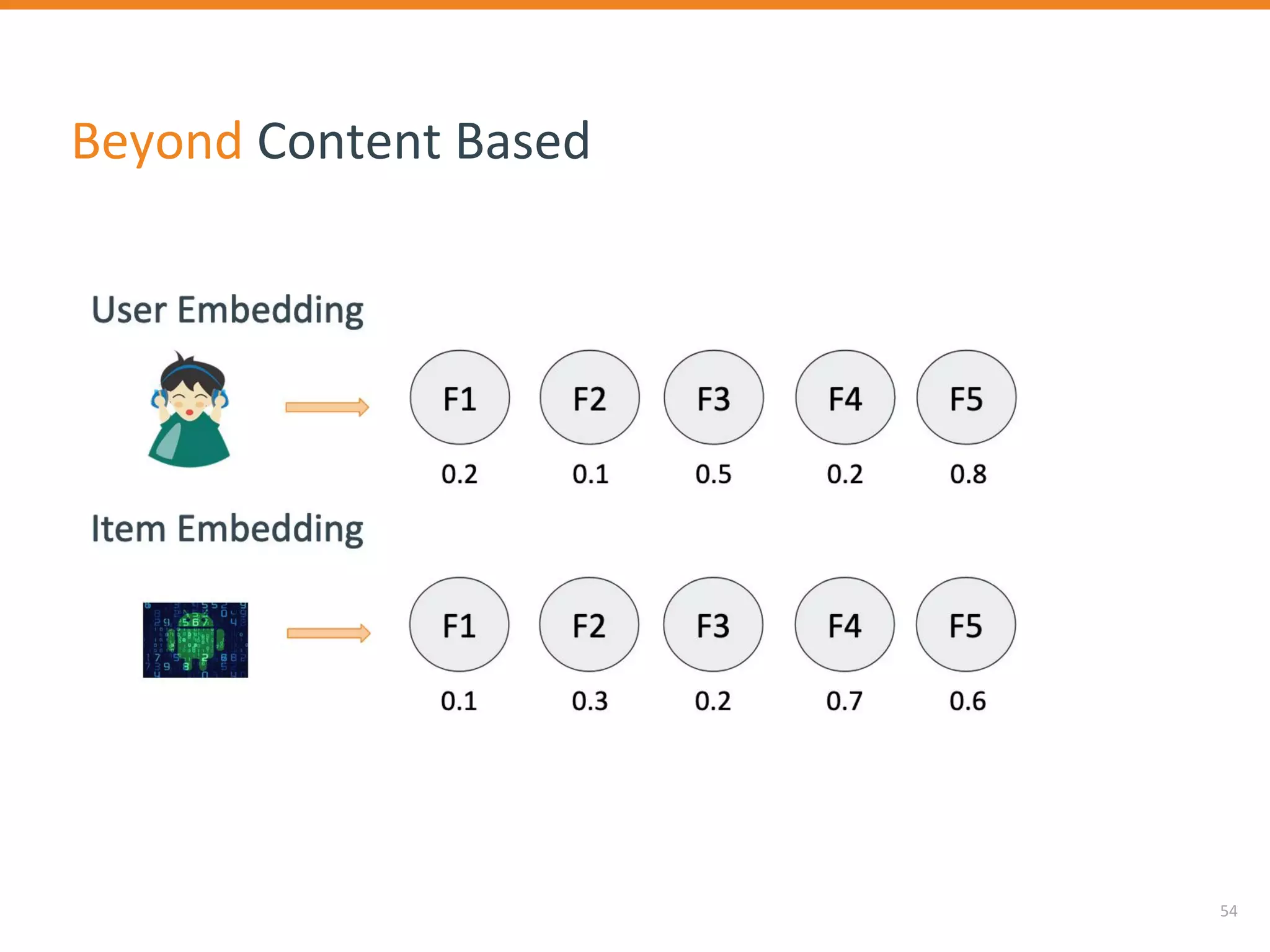
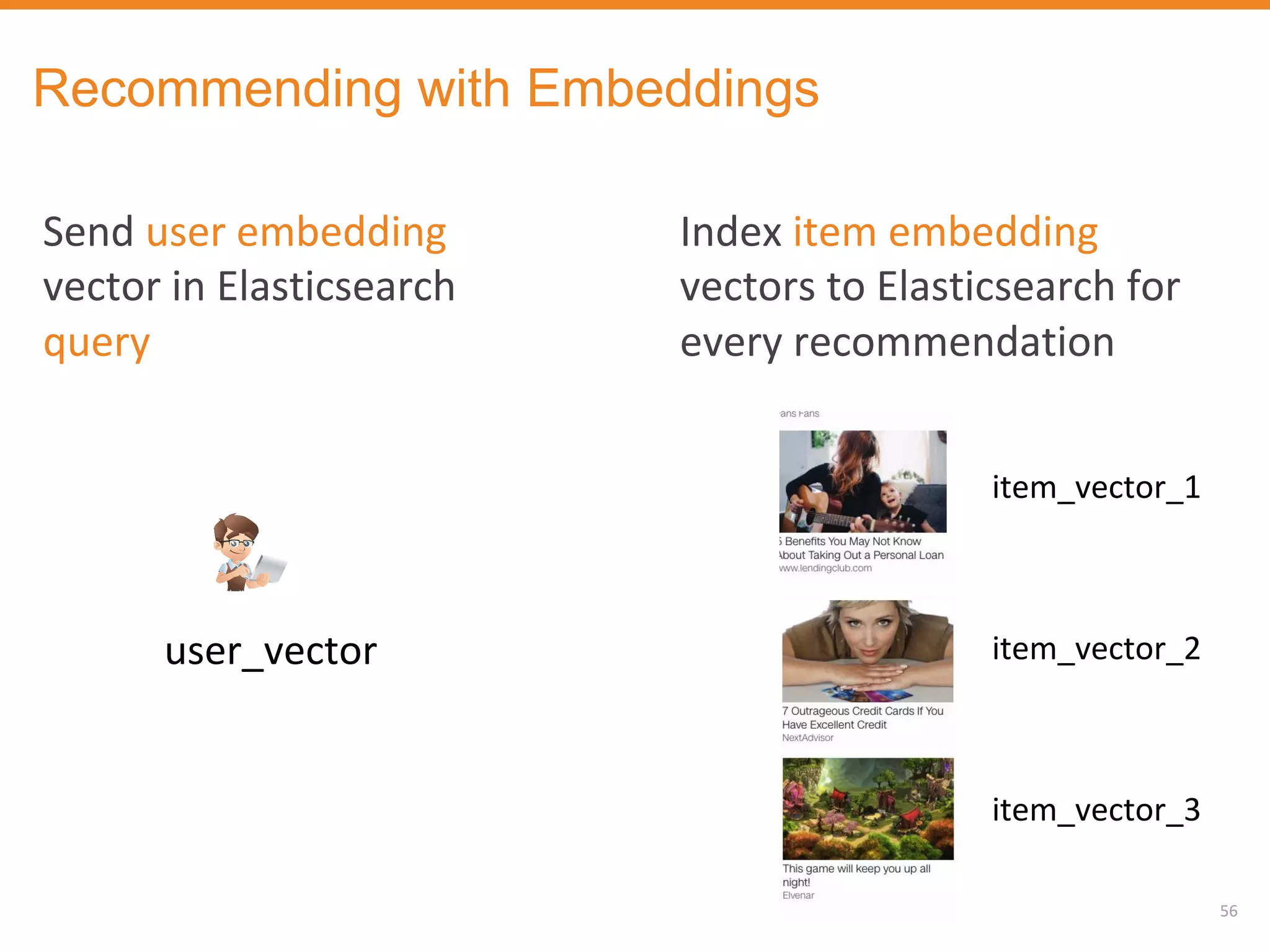
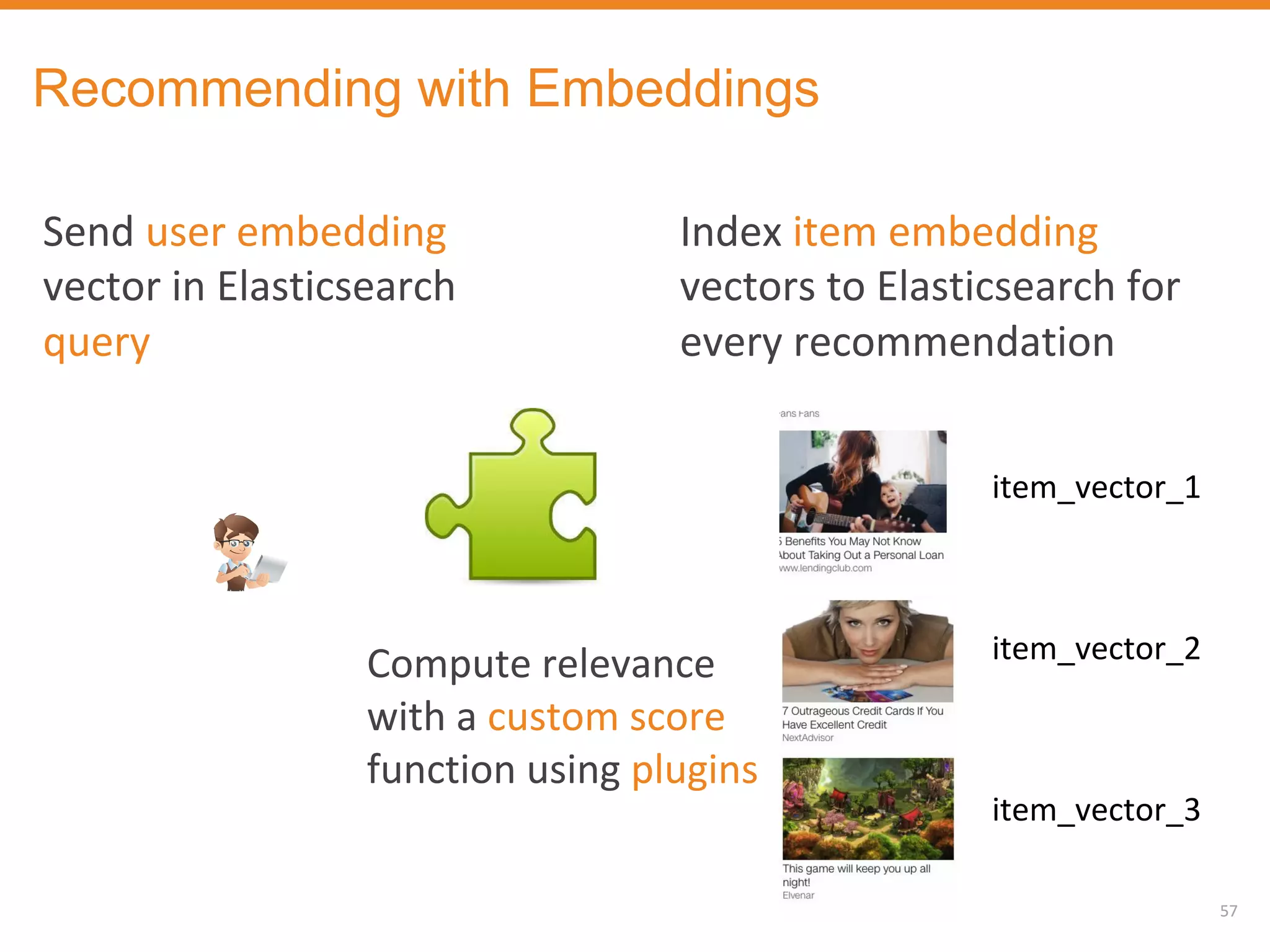
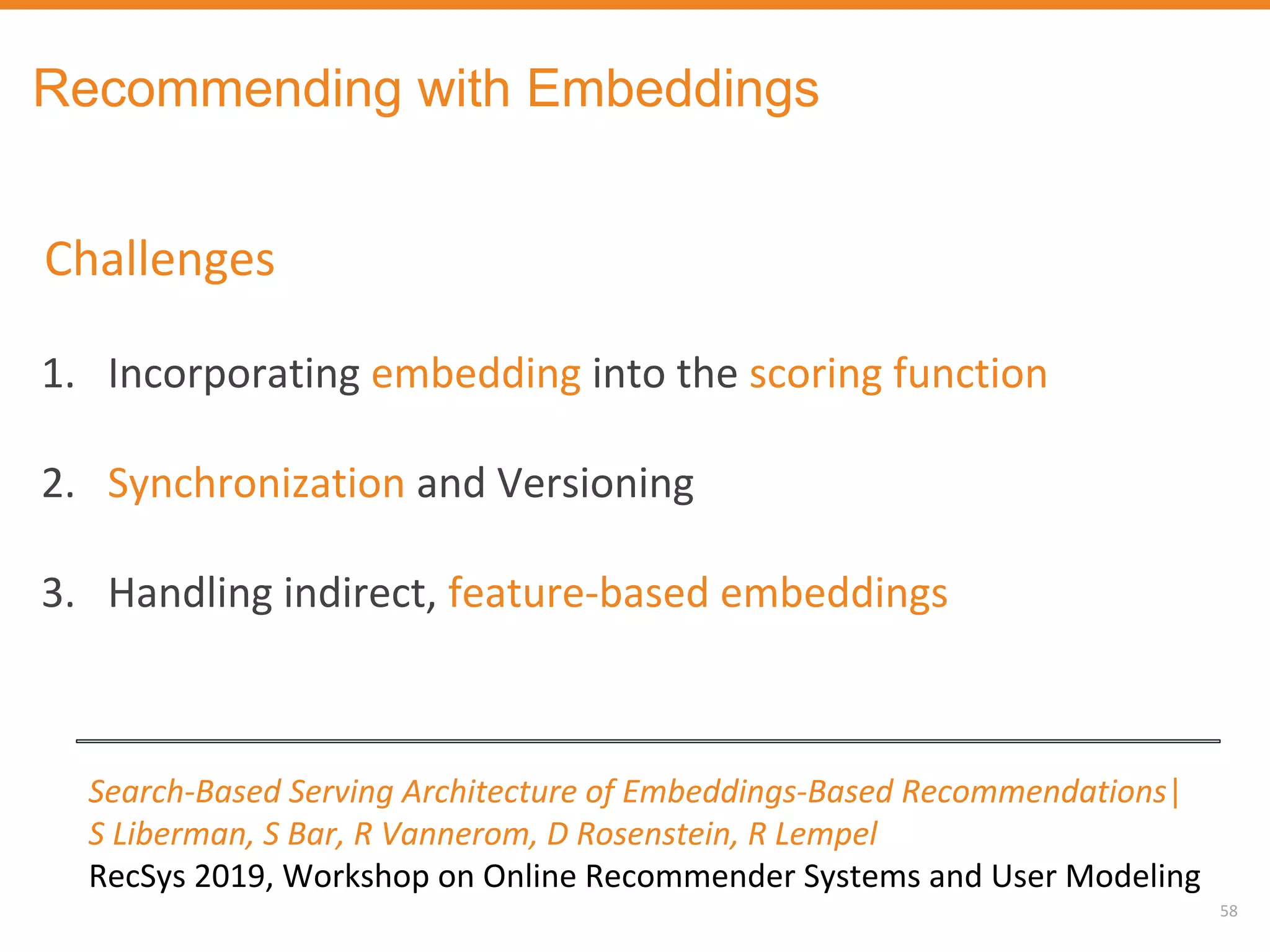
The document discusses Outbrain's methods for content-based personalization and recommendation systems using large-scale models and machine learning frameworks. It highlights the need for agile research and robust productization, focusing on data collection, feature engineering, and model deployment to enhance recommendations. Key takeaways emphasize investing in machine learning pipelines and automating model deployments for effective personalization.