This document provides an overview of processing big data with Azure Data Lake Analytics. It discusses:
1. Sean Forgatch who is a business intelligence consultant specializing in Azure big data solutions.
2. Talavant, Sean's company, which provides holistic big data strategies and implementations.
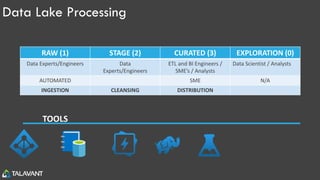
3. An introduction to big data concepts like volume, velocity and variety and how Azure tools like Data Warehouse, Data Lake, and Data Lake Analytics address these.
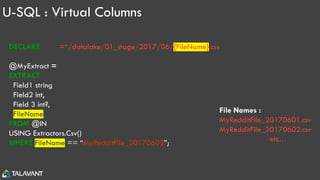
The document then goes into further detail on Data Lake concepts, Azure Data Lake Store, Azure Data Lake Analytics, and the U-SQL language for querying and analyzing data in the data lake.