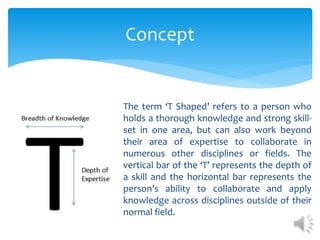
T-shaped people have a deep skill in one area but can also collaborate across disciplines. The concept originated in 1991 but grew popular due to Tim Brown of IDEO describing people with a core skill but also empathy to take on other skills. Benefits include improved communication, flexibility, lower risk, and fewer bottlenecks. Drawbacks can include not all having equal skills, identity crises over abilities, misunderstanding collaboration as delegation, and not having the right tools. One can become T-shaped by working with others, taking introductory training, gaining hands-on experience, obtaining mentoring, working on learning teams, reading extensively, challenging oneself, and communicating goals.