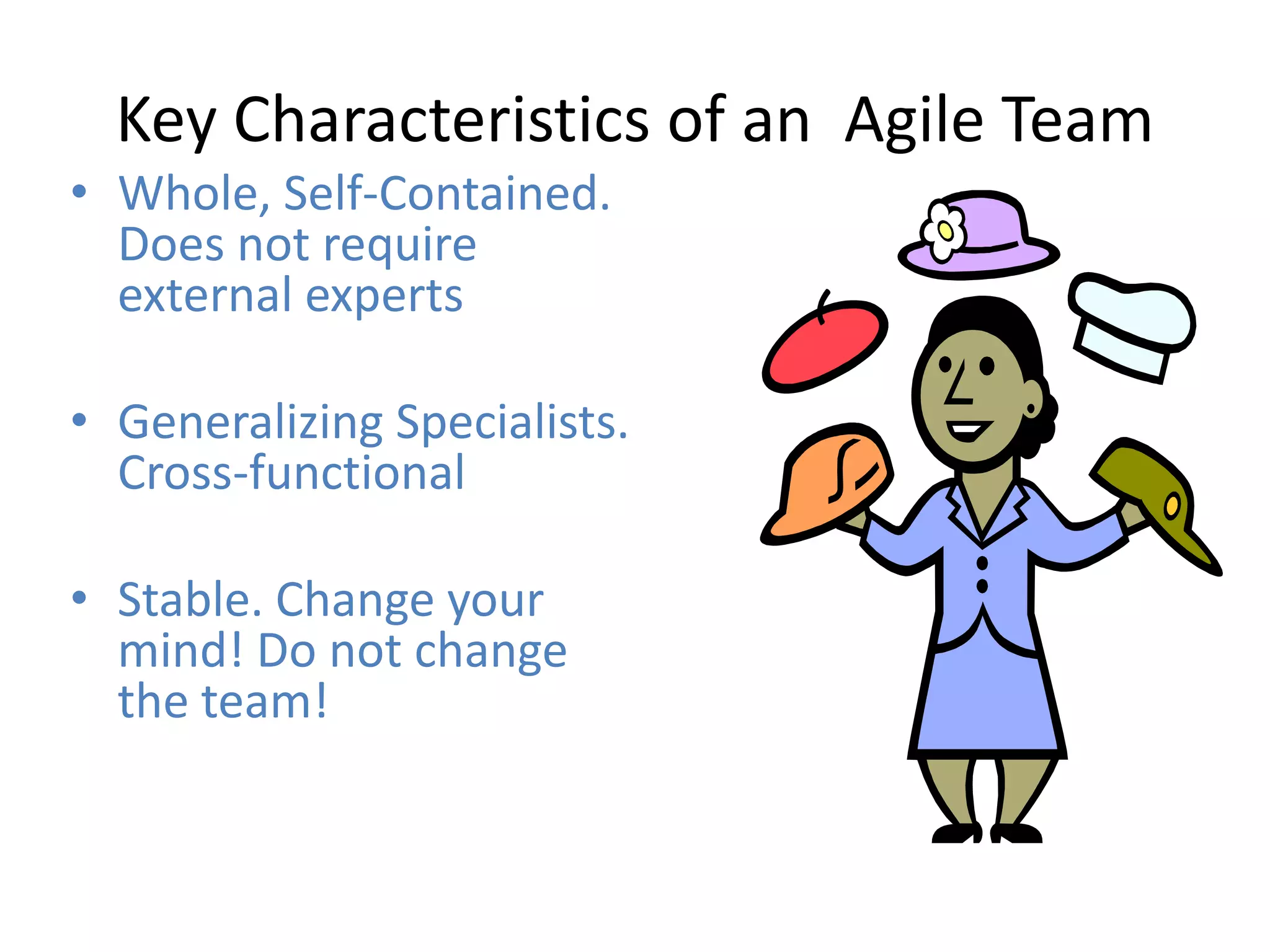
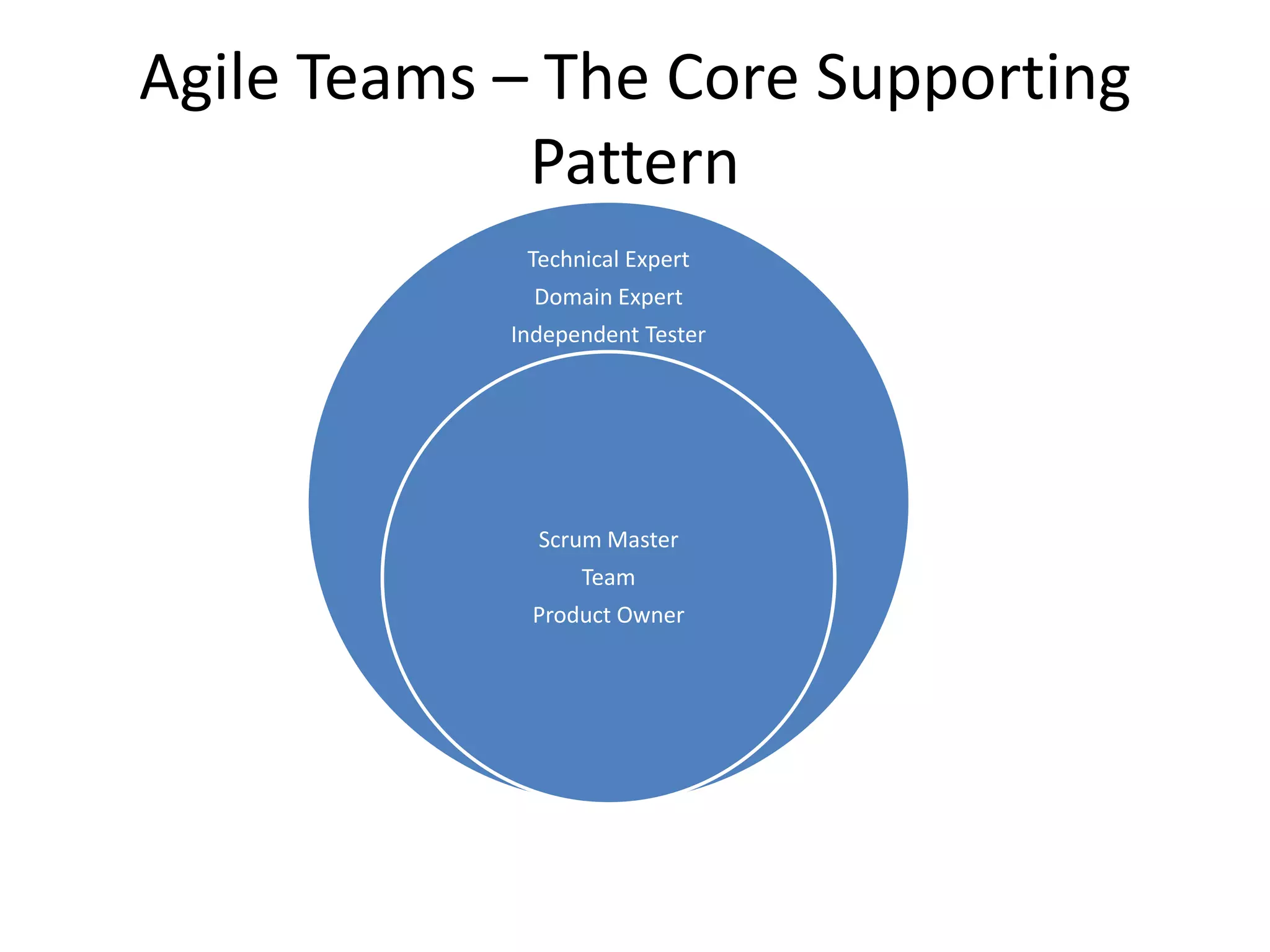
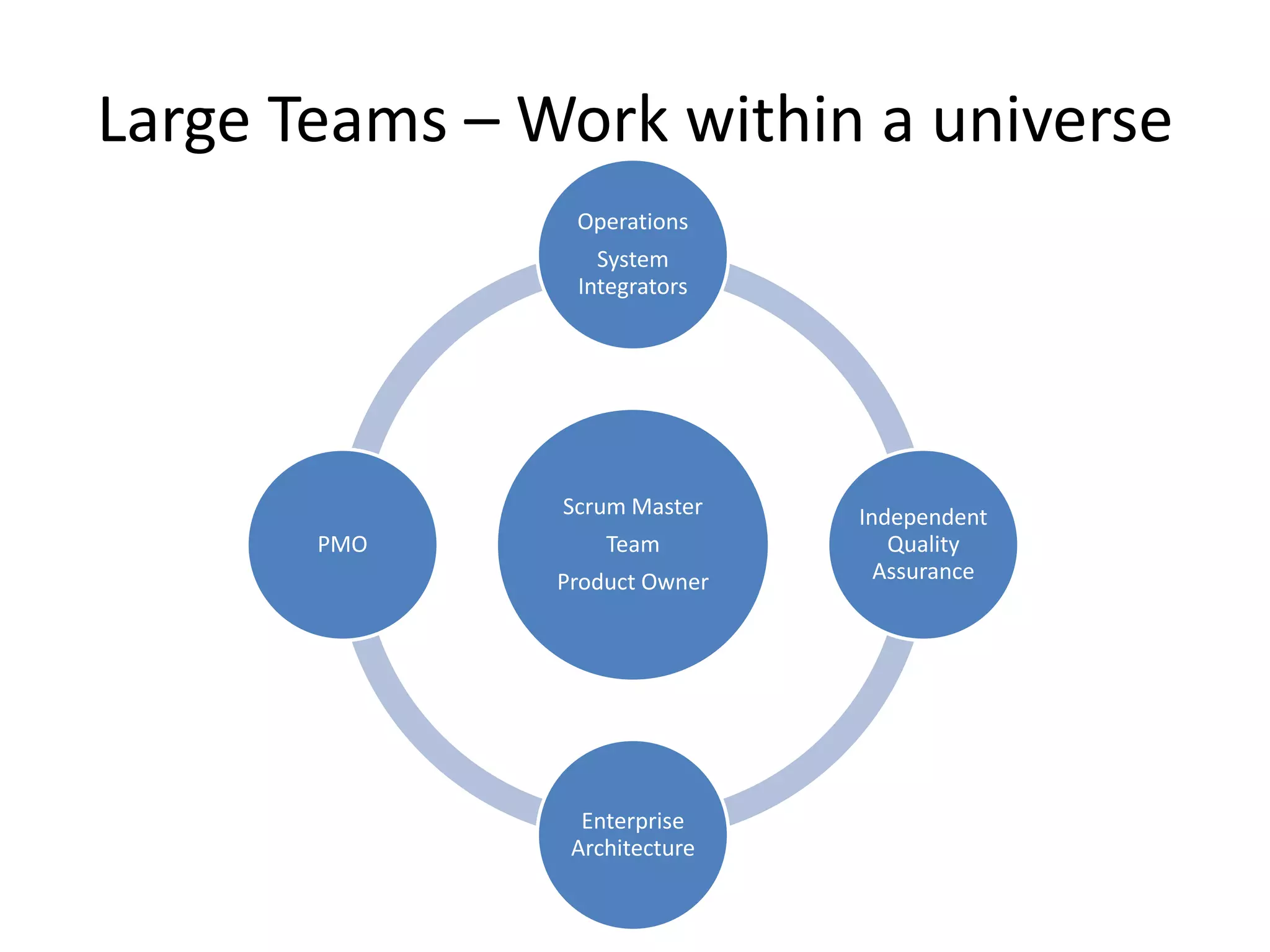
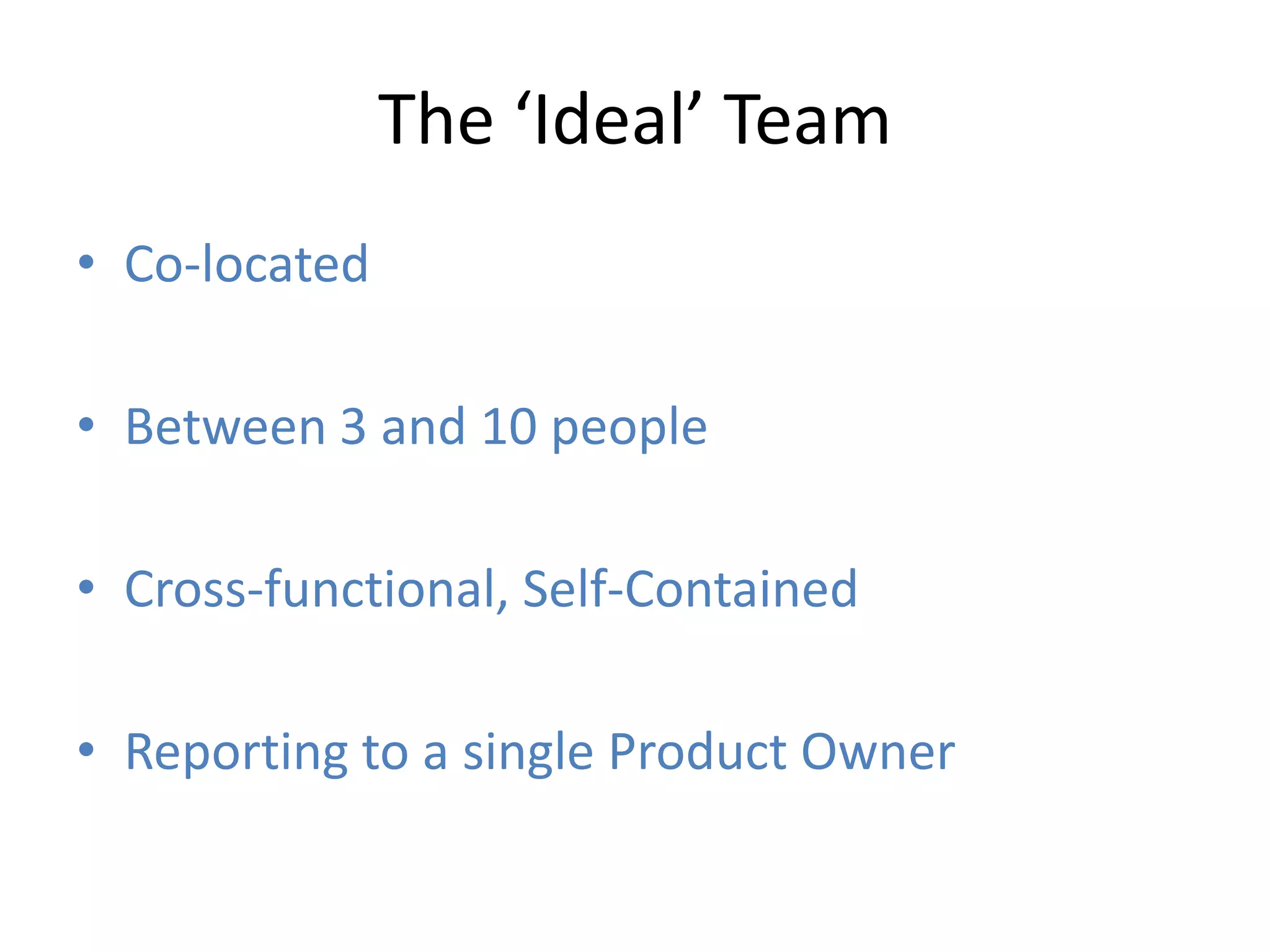
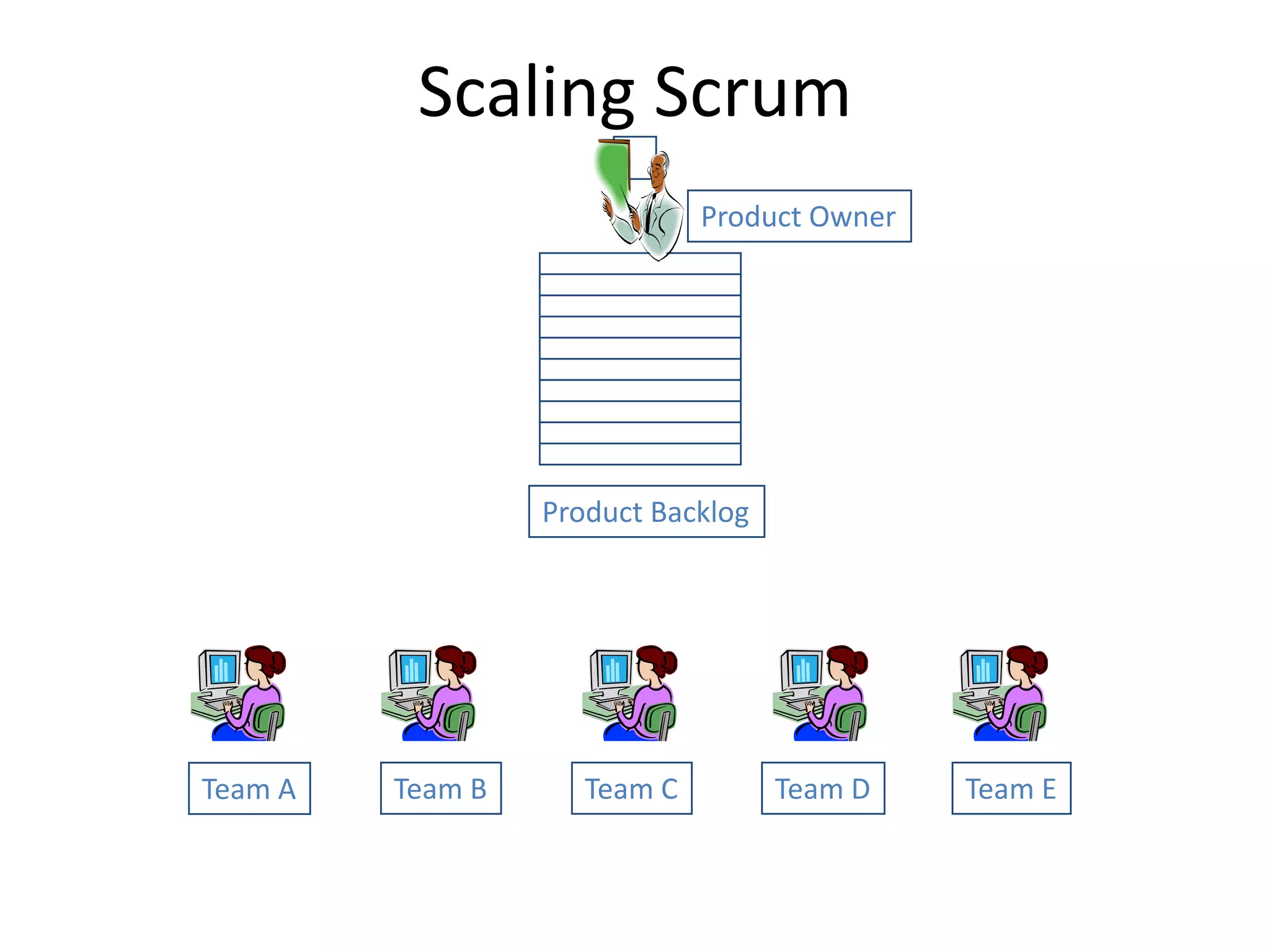
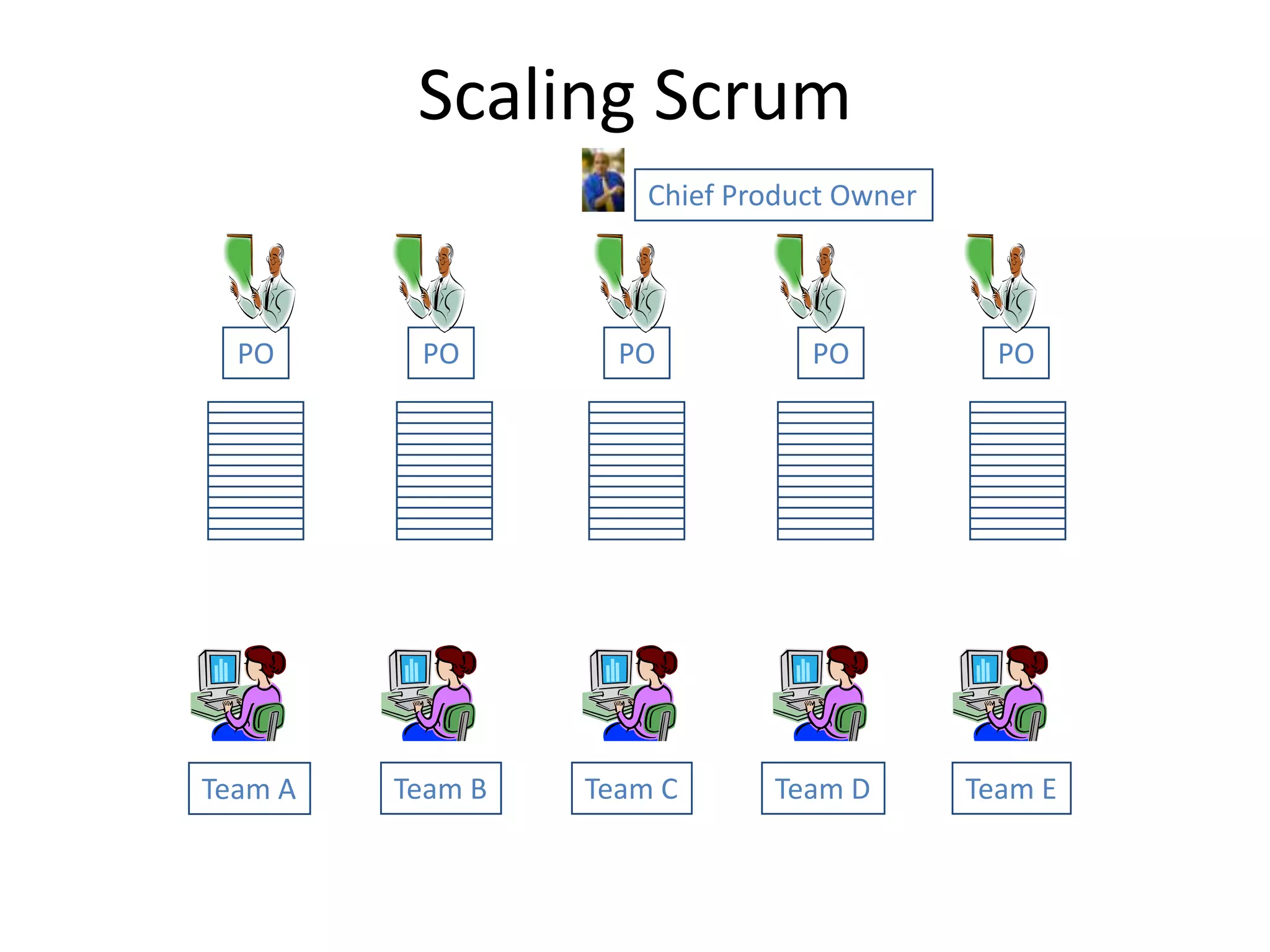
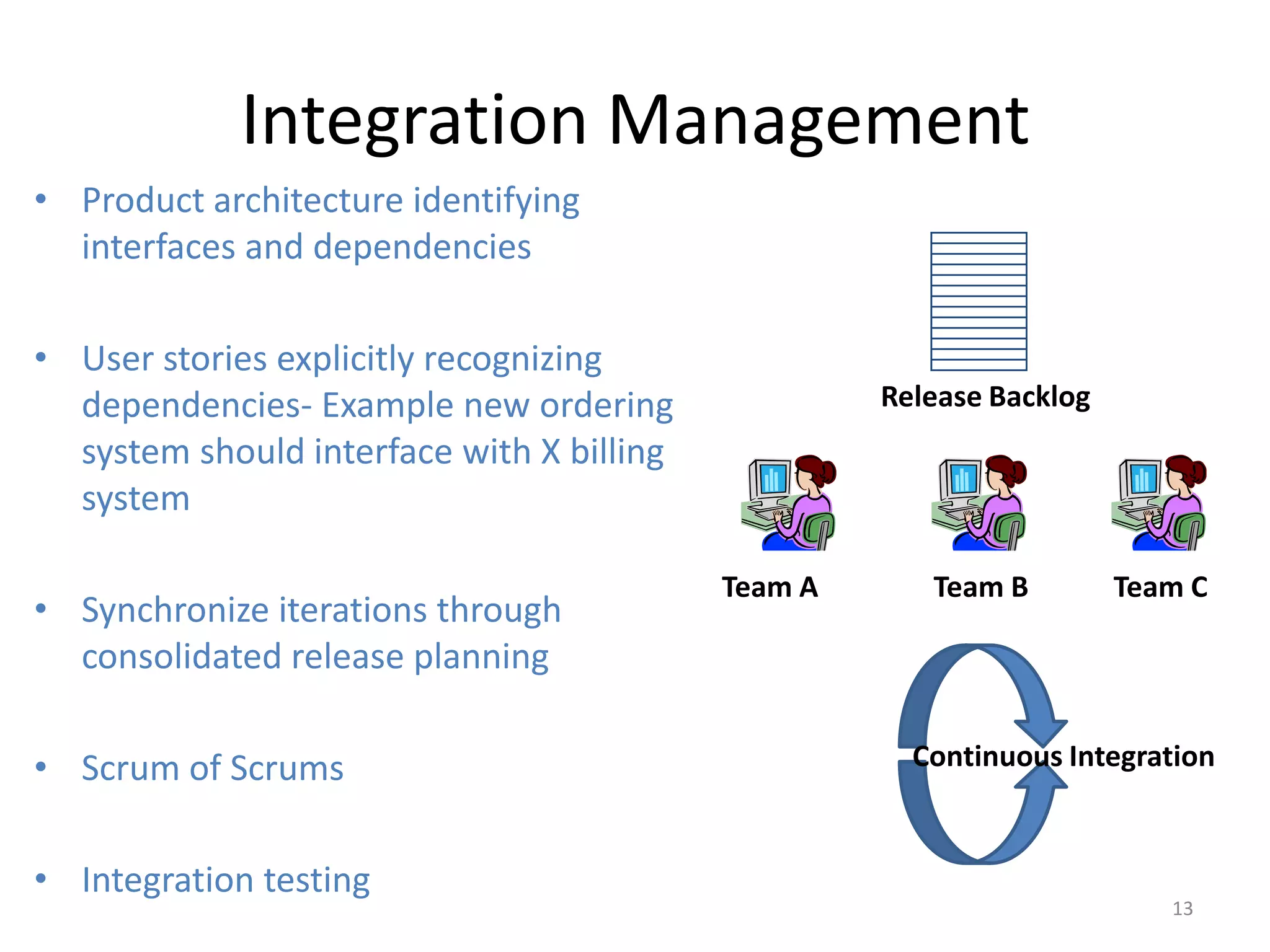
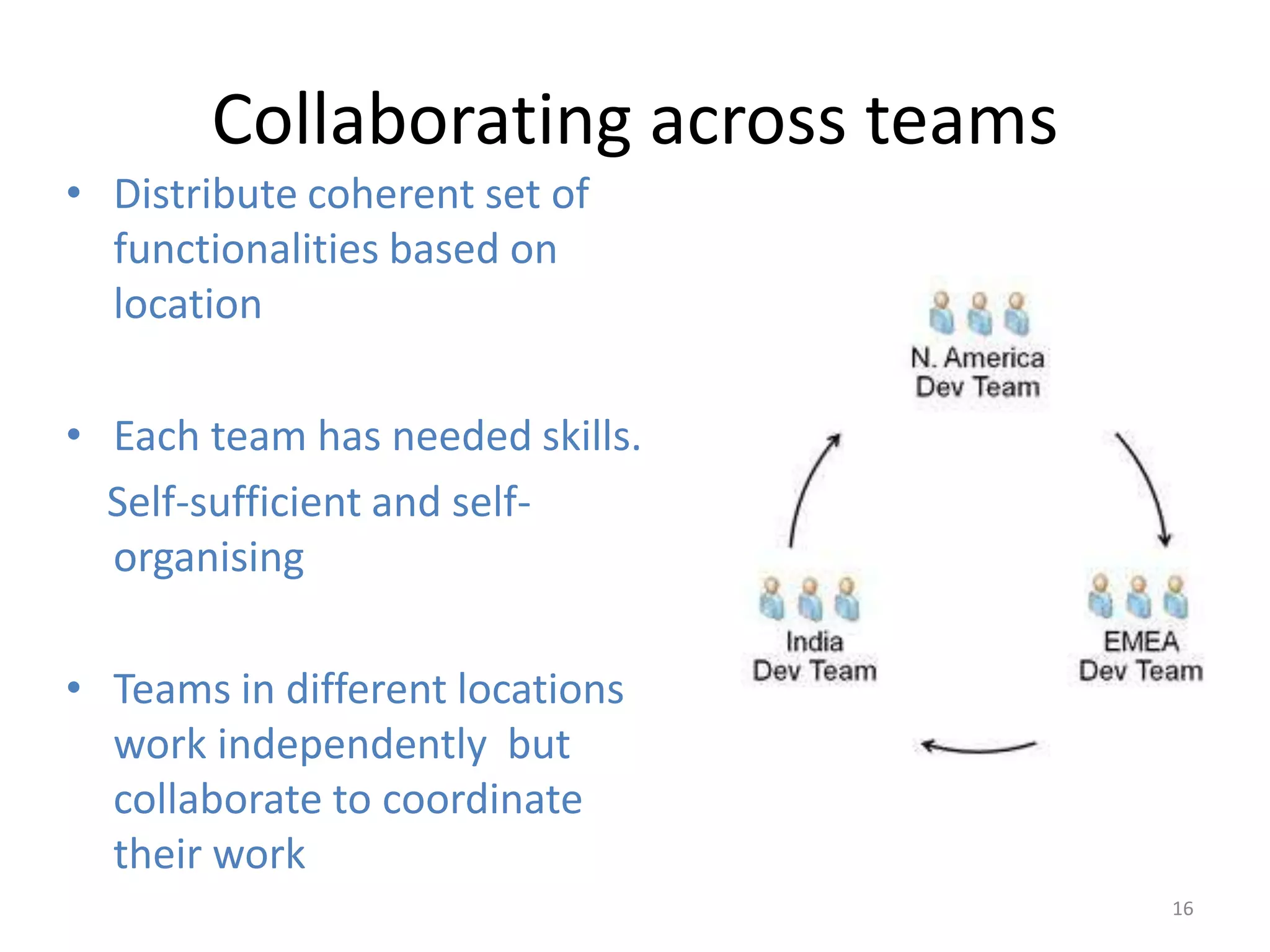
Effective agile teams are self-organizing, cross-functional, and stable. The ideal agile team has 3-10 co-located members with different skills who report to a single product owner. However, real-world teams are often larger, distributed, and made up of multiple sub-teams. Scaling agile requires integrating work across distributed sub-teams through practices like Scrum of Scrums, shared code repositories, and release planning. Agile people management focuses on resource mobilization, career guidance, and servant leadership to create autonomous, adaptive, accountable teams that have fun and get the job done.