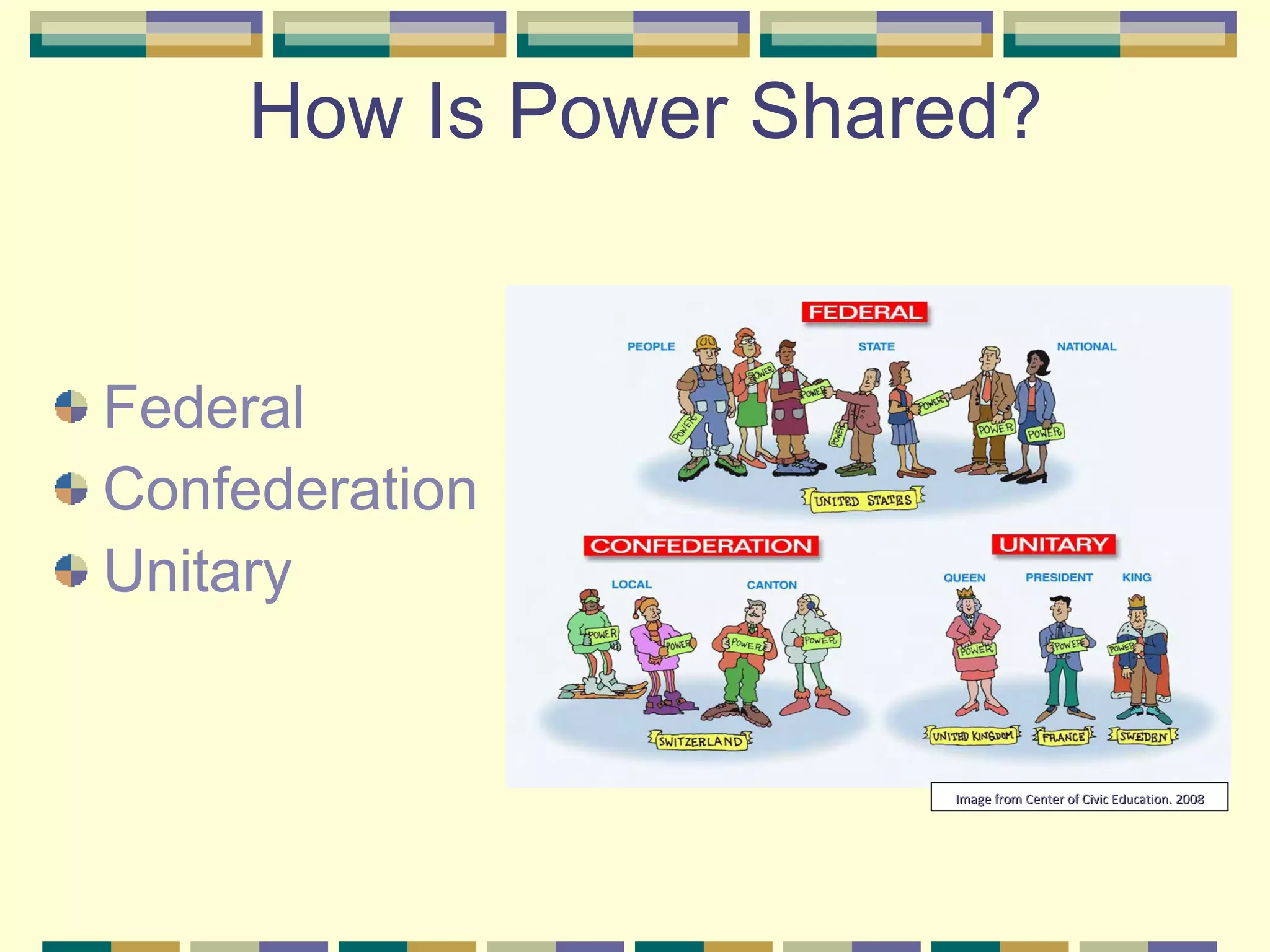
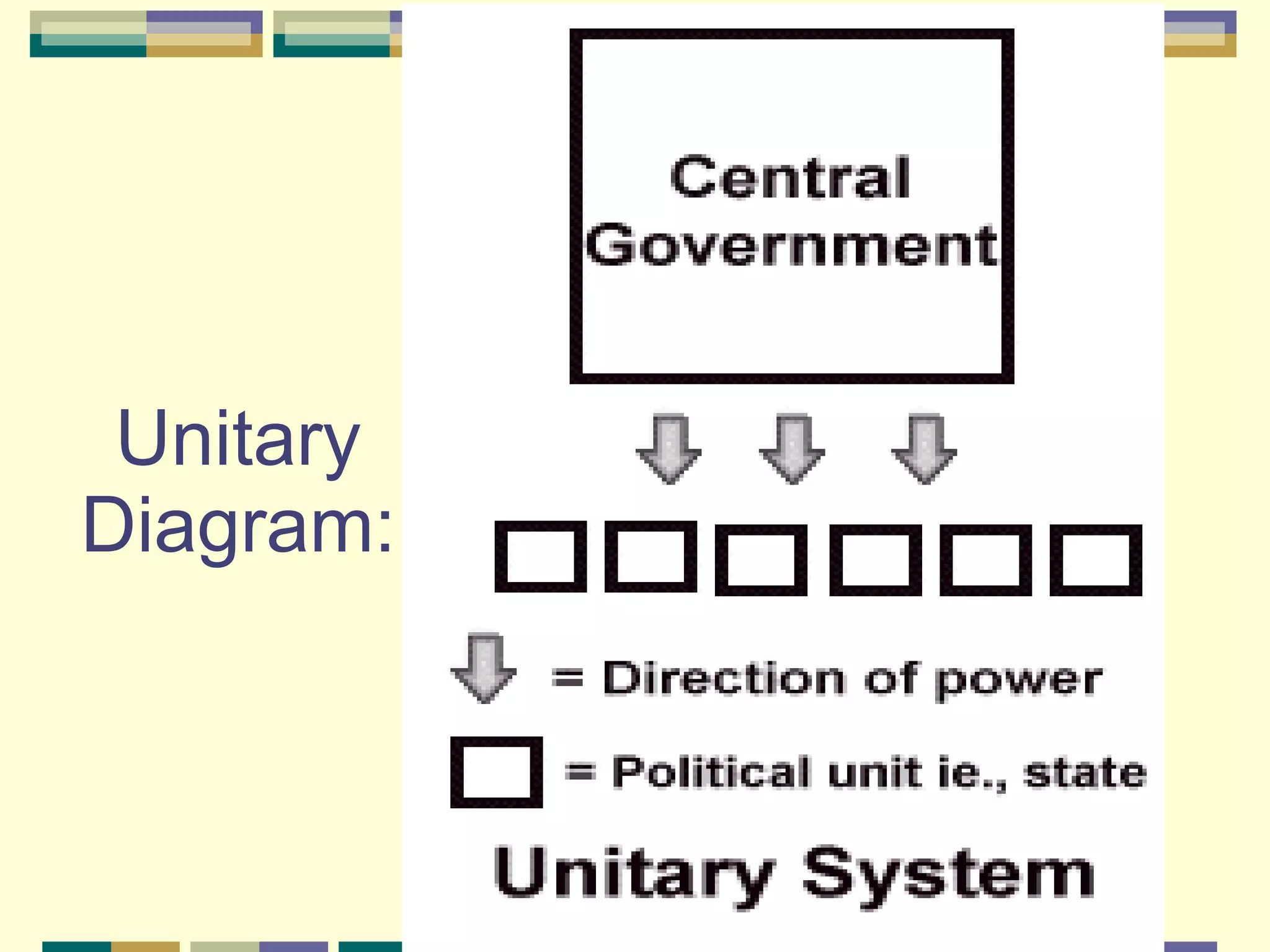
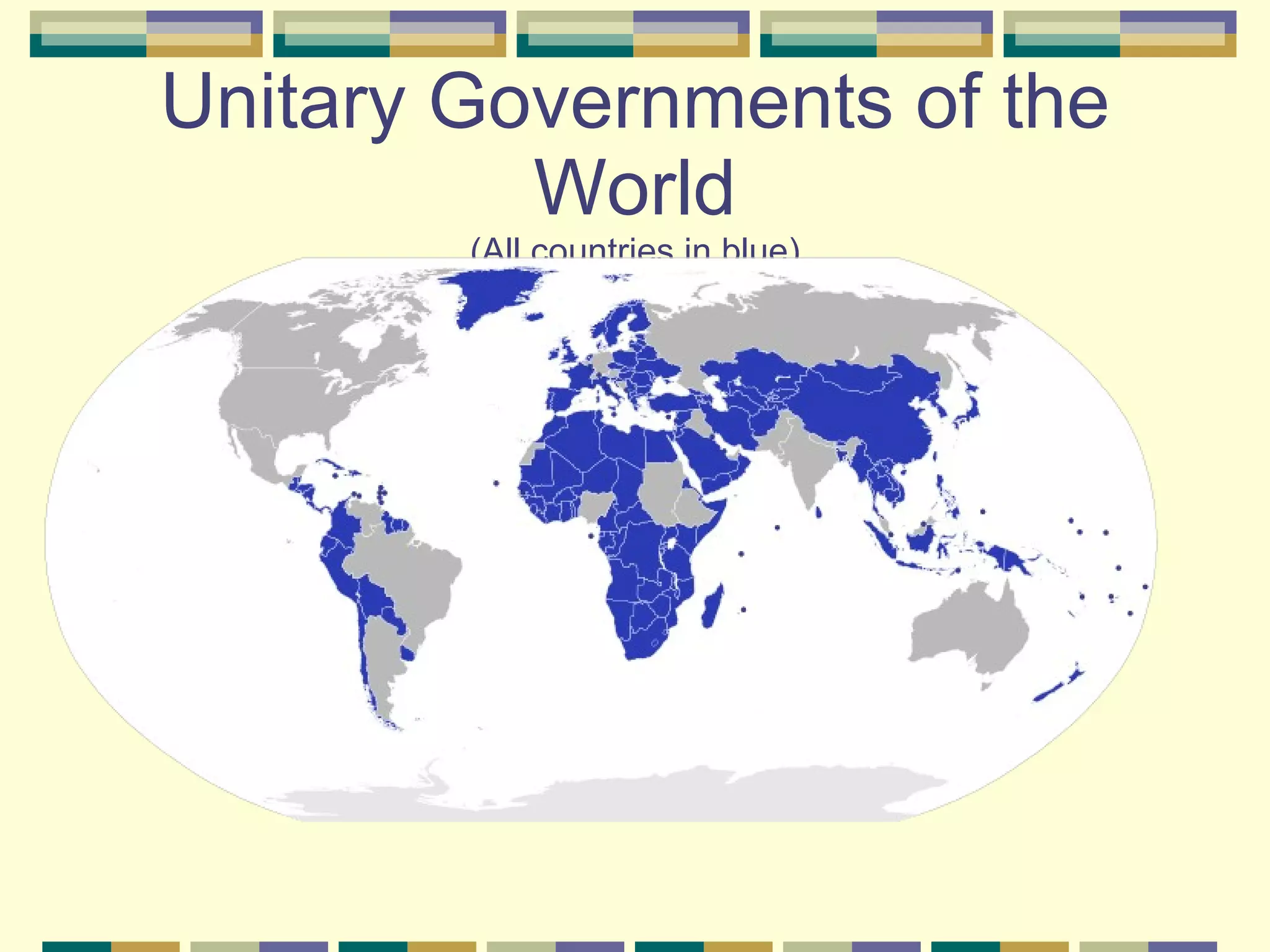
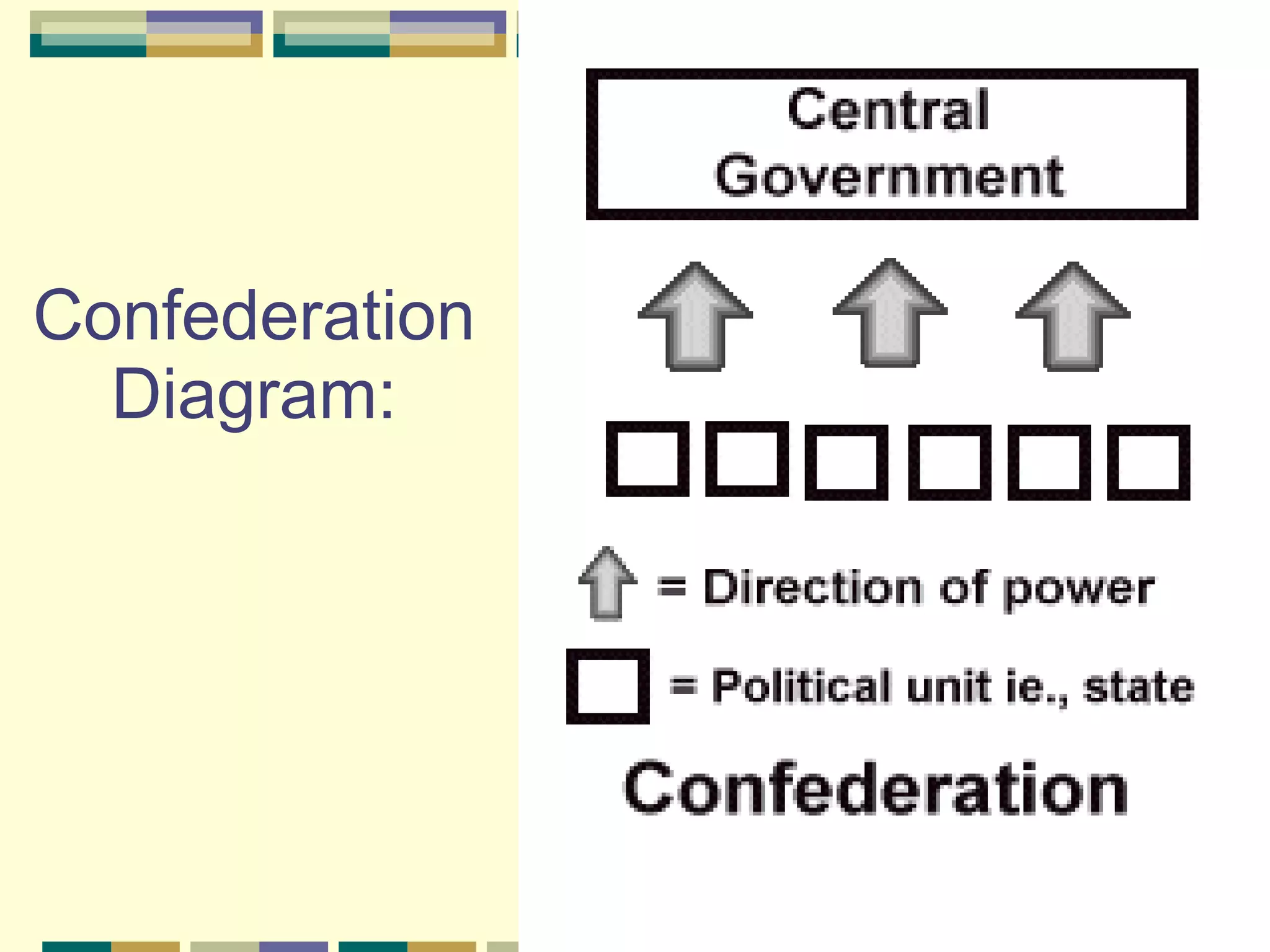
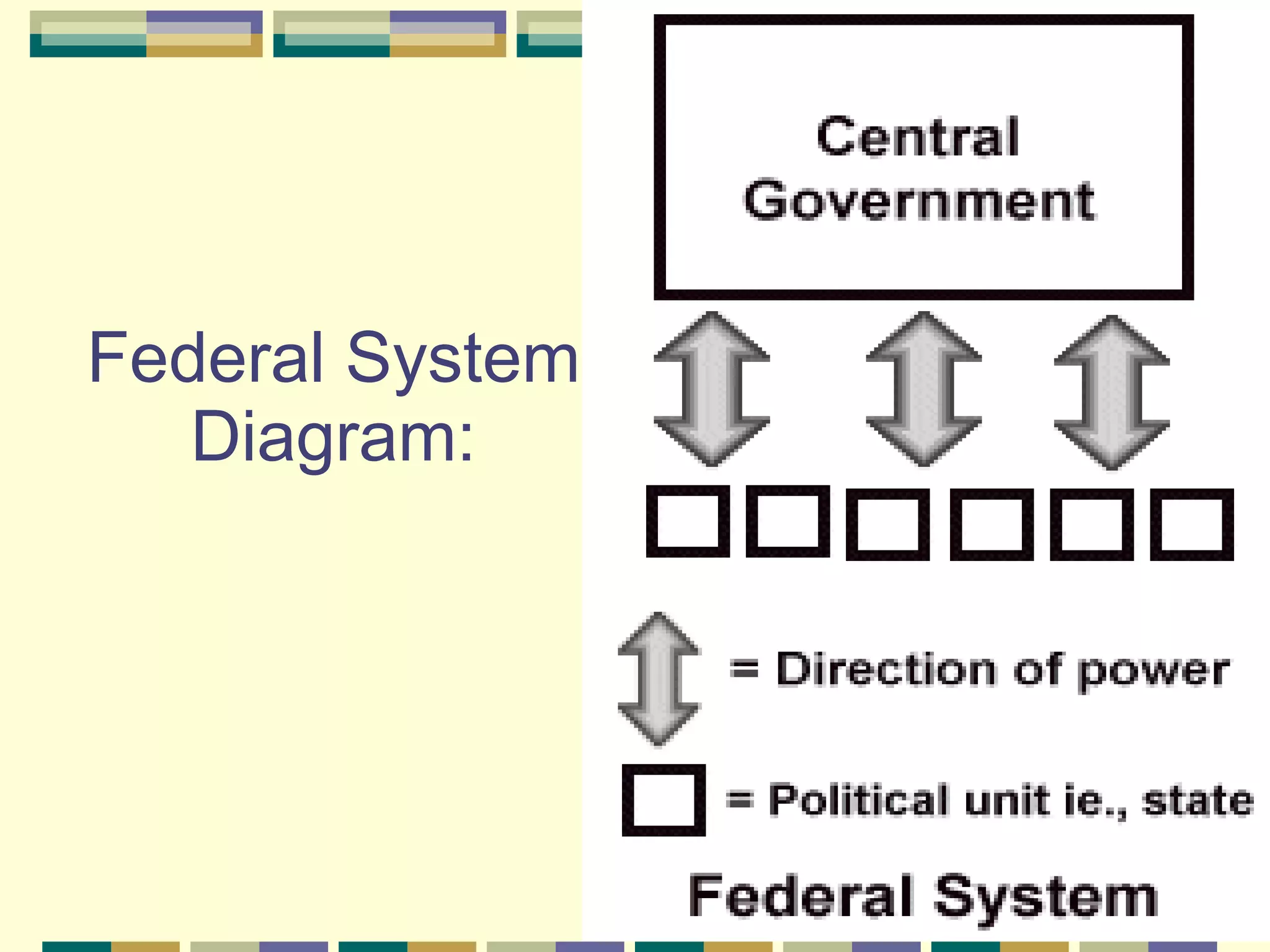
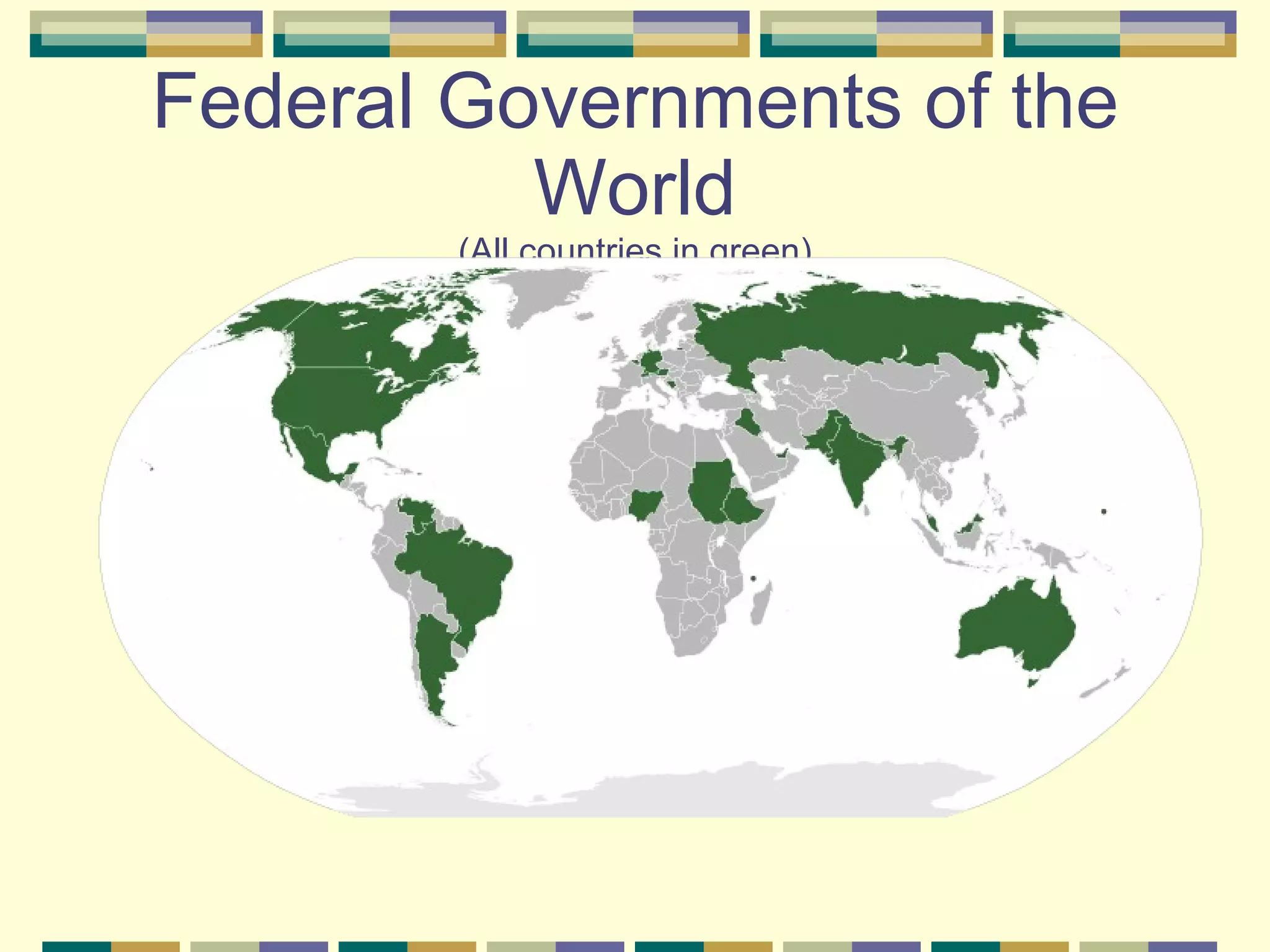
This document discusses different systems of government and how power is distributed in each. It explains that there are three main ways power can be shared: unitary governments have one central authority that controls everything; confederations involve a voluntary association of independent states under a weak central power; and federal governments share power between a central national government and states or provinces that have considerable self-rule. The document provides examples of countries that use each system and diagrams to illustrate how power is divided in unitary, confederation, and federal systems.