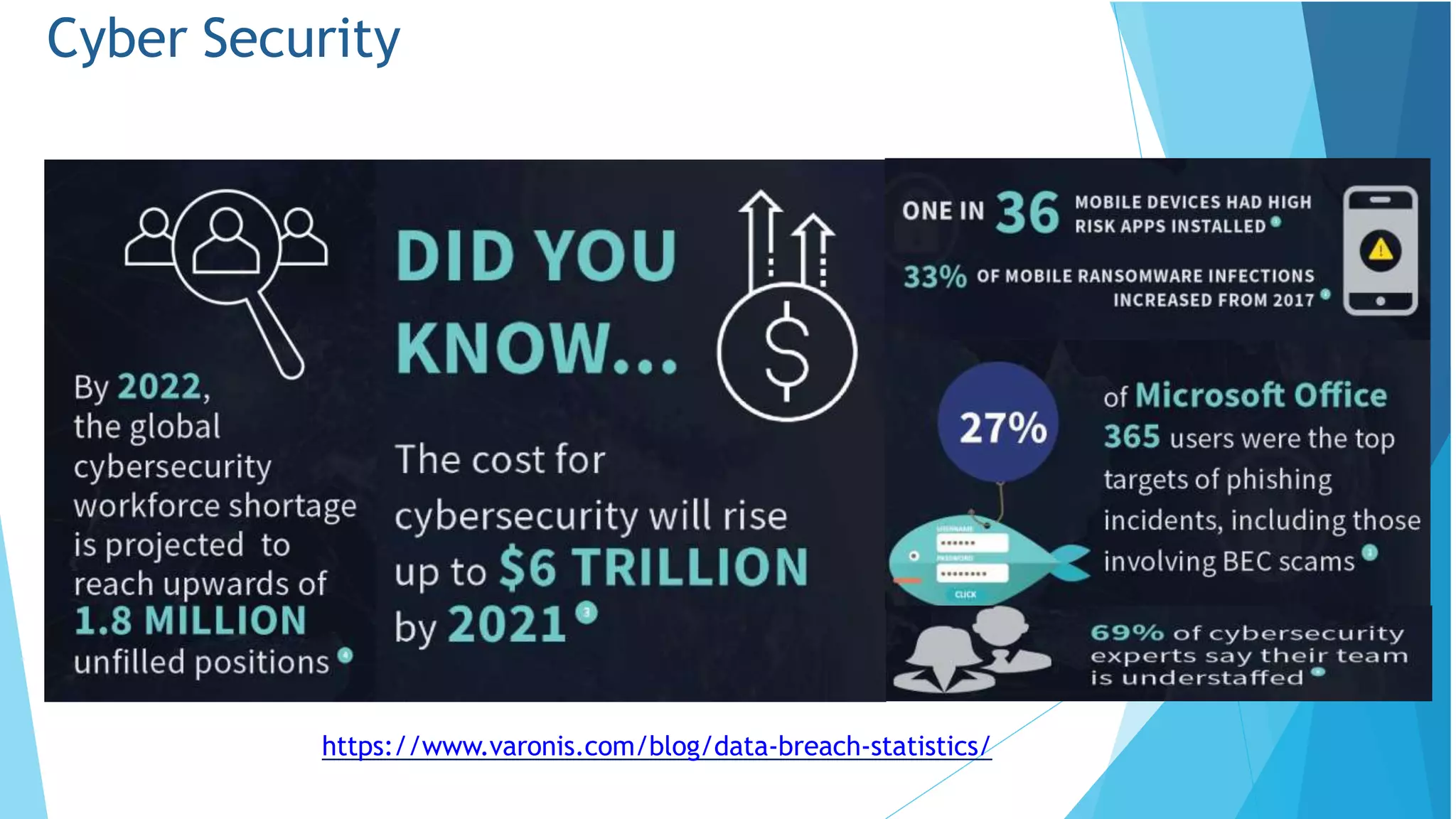
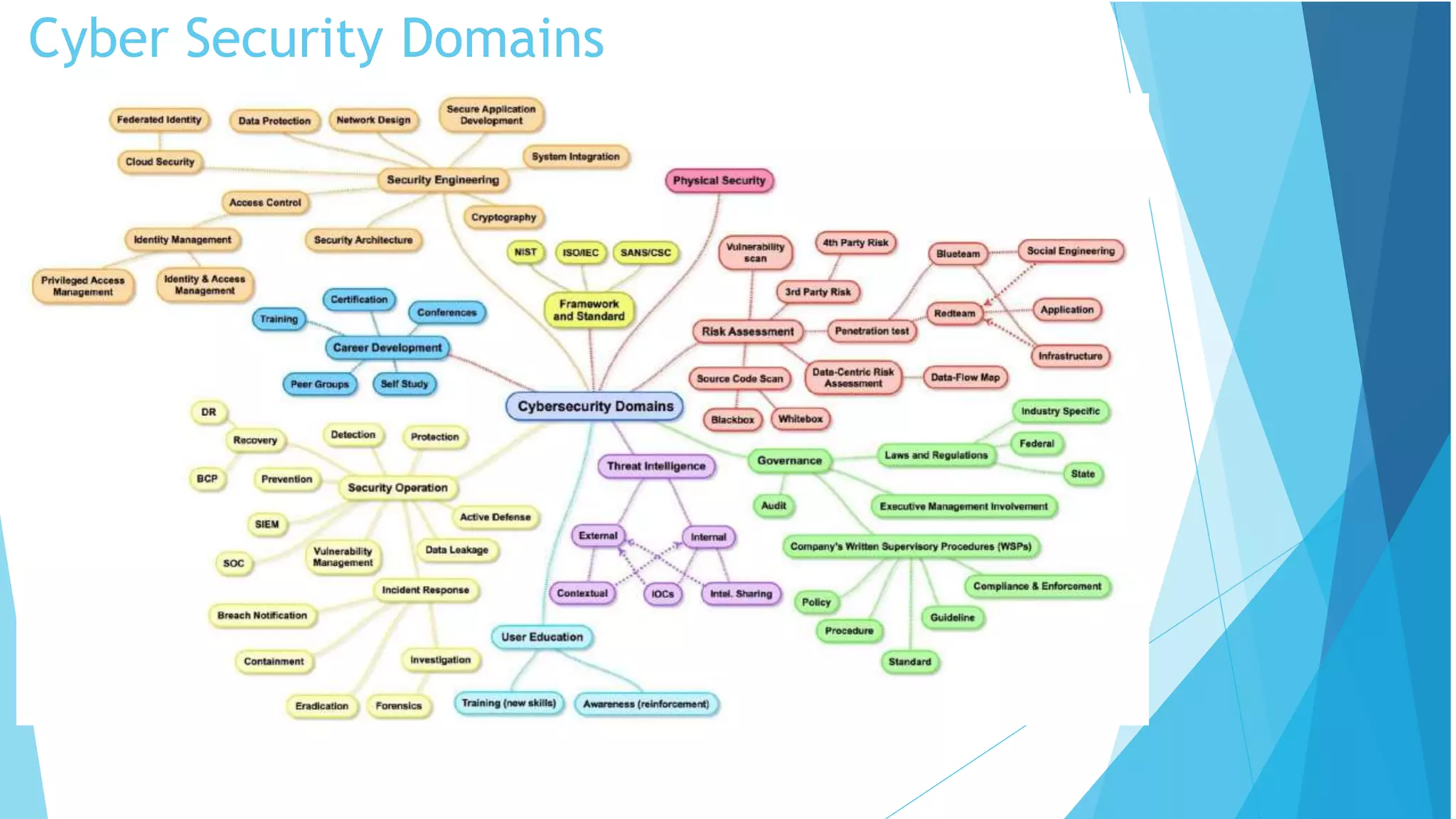
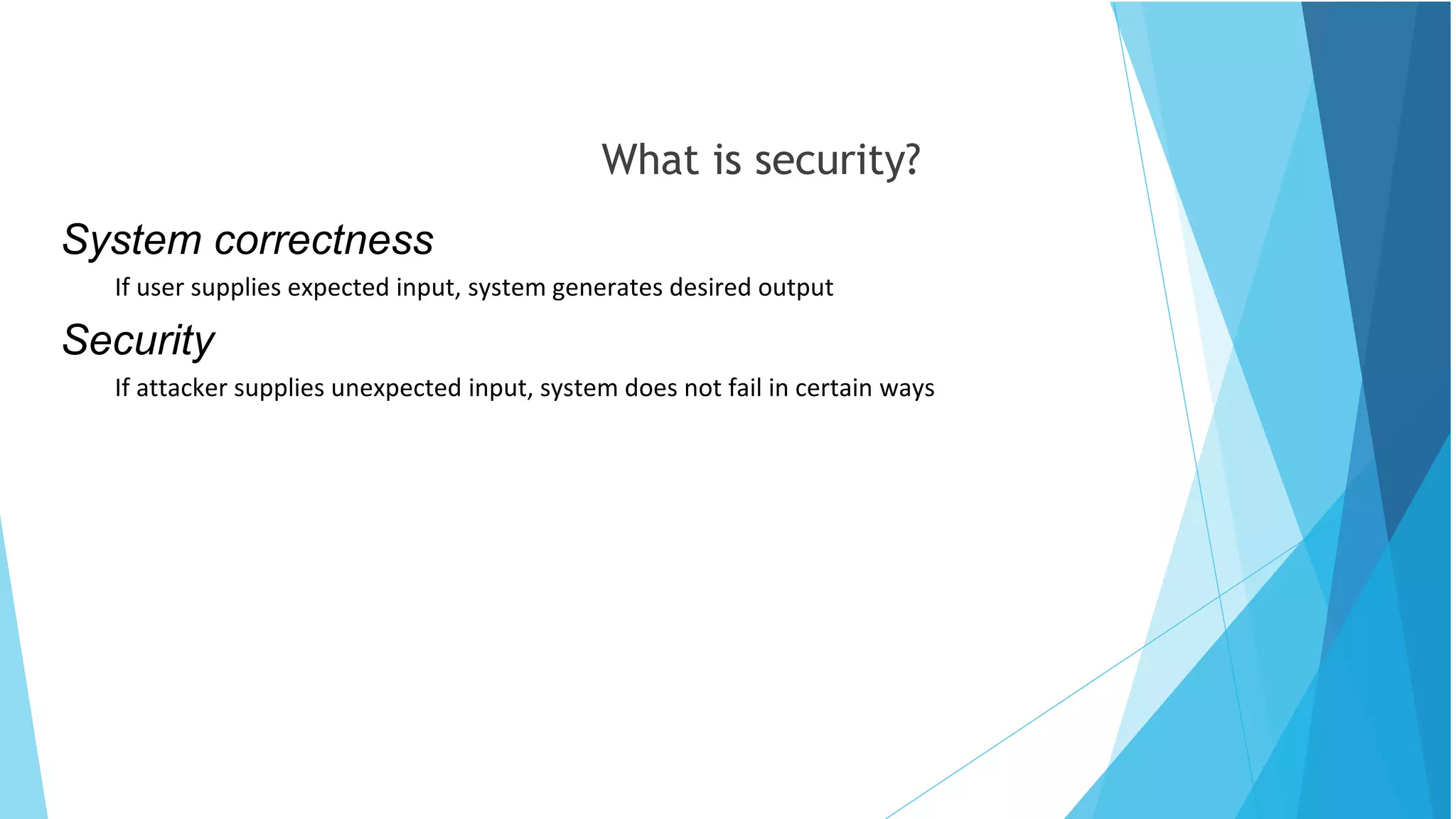
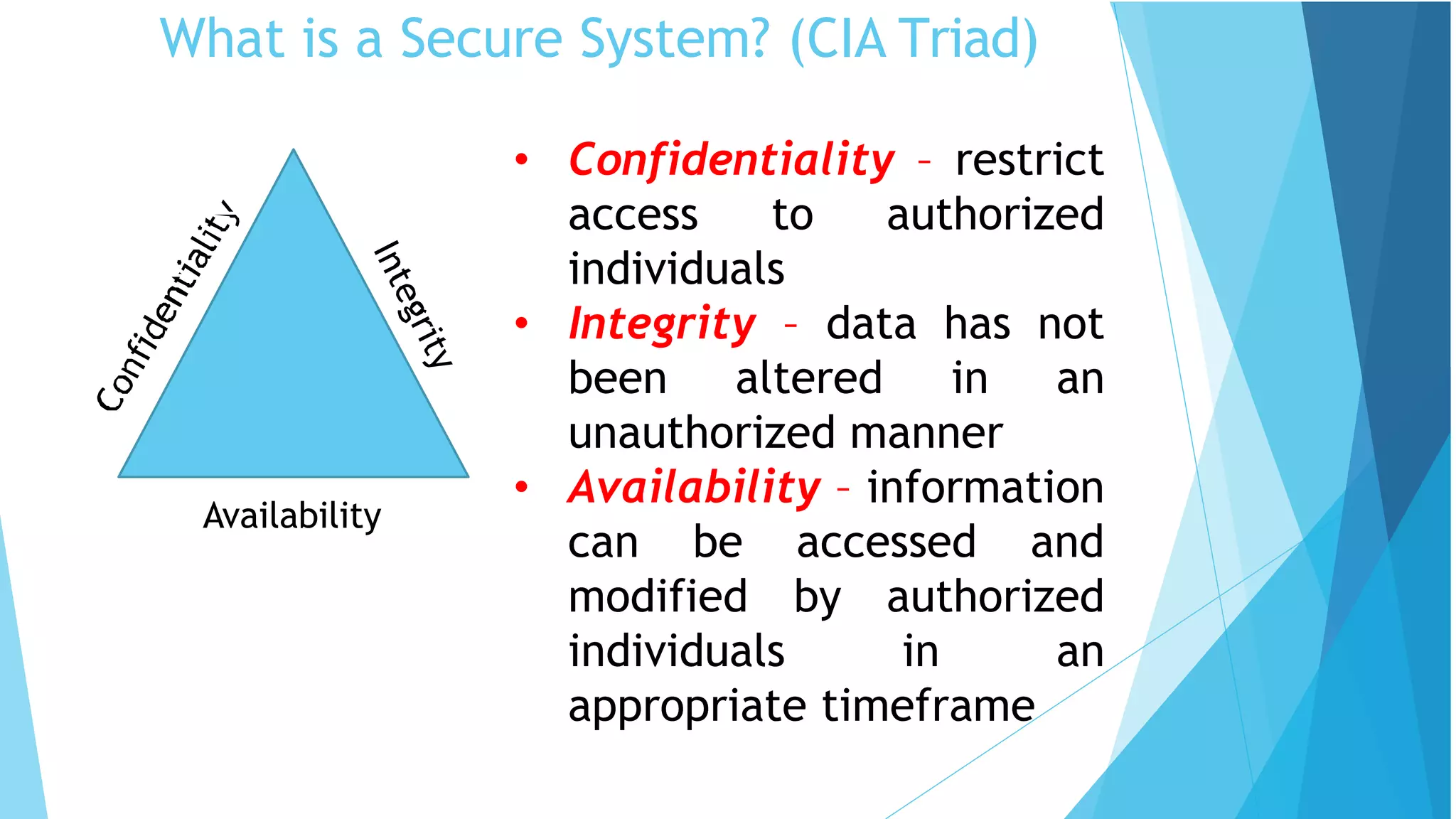
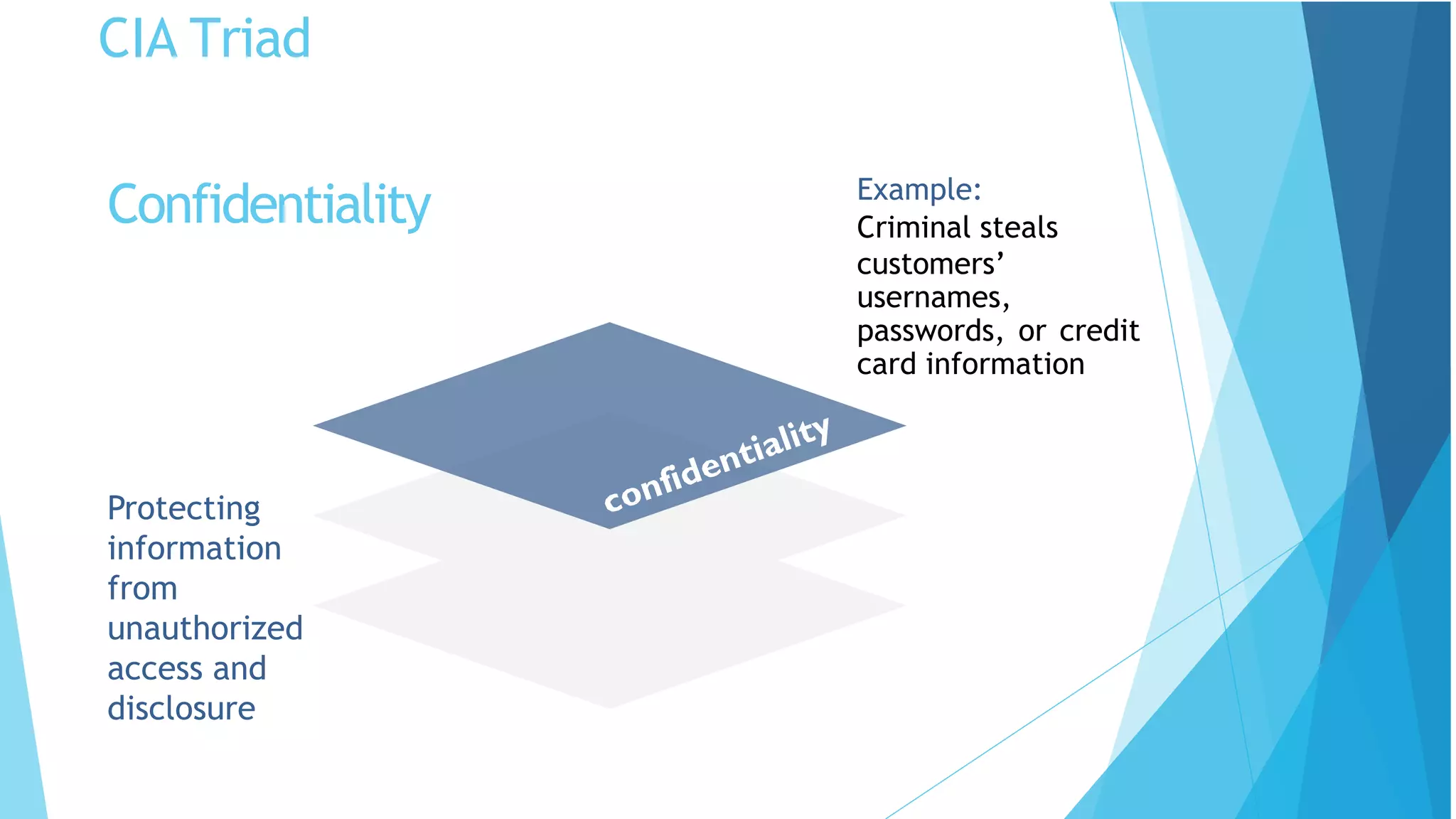
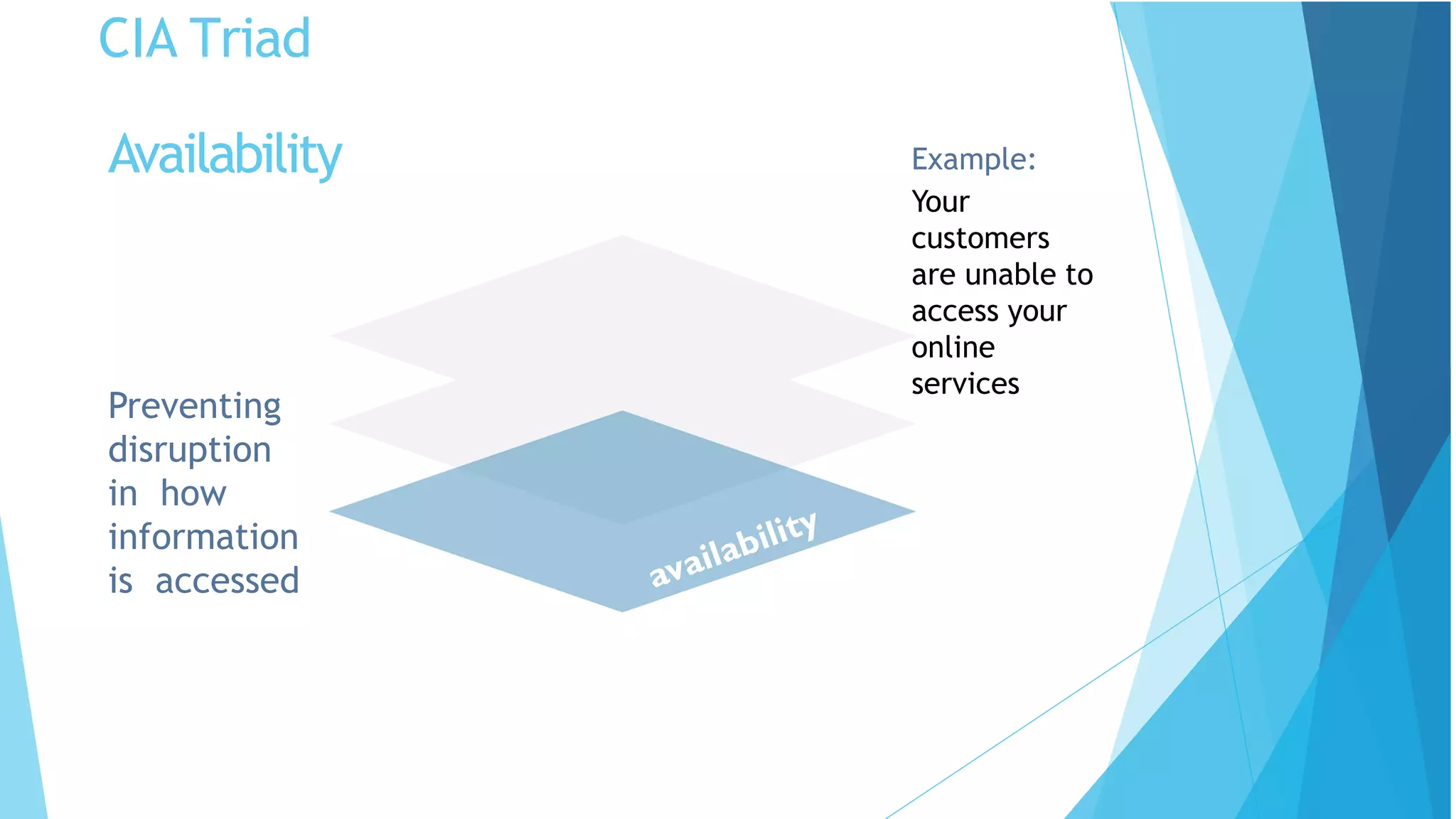
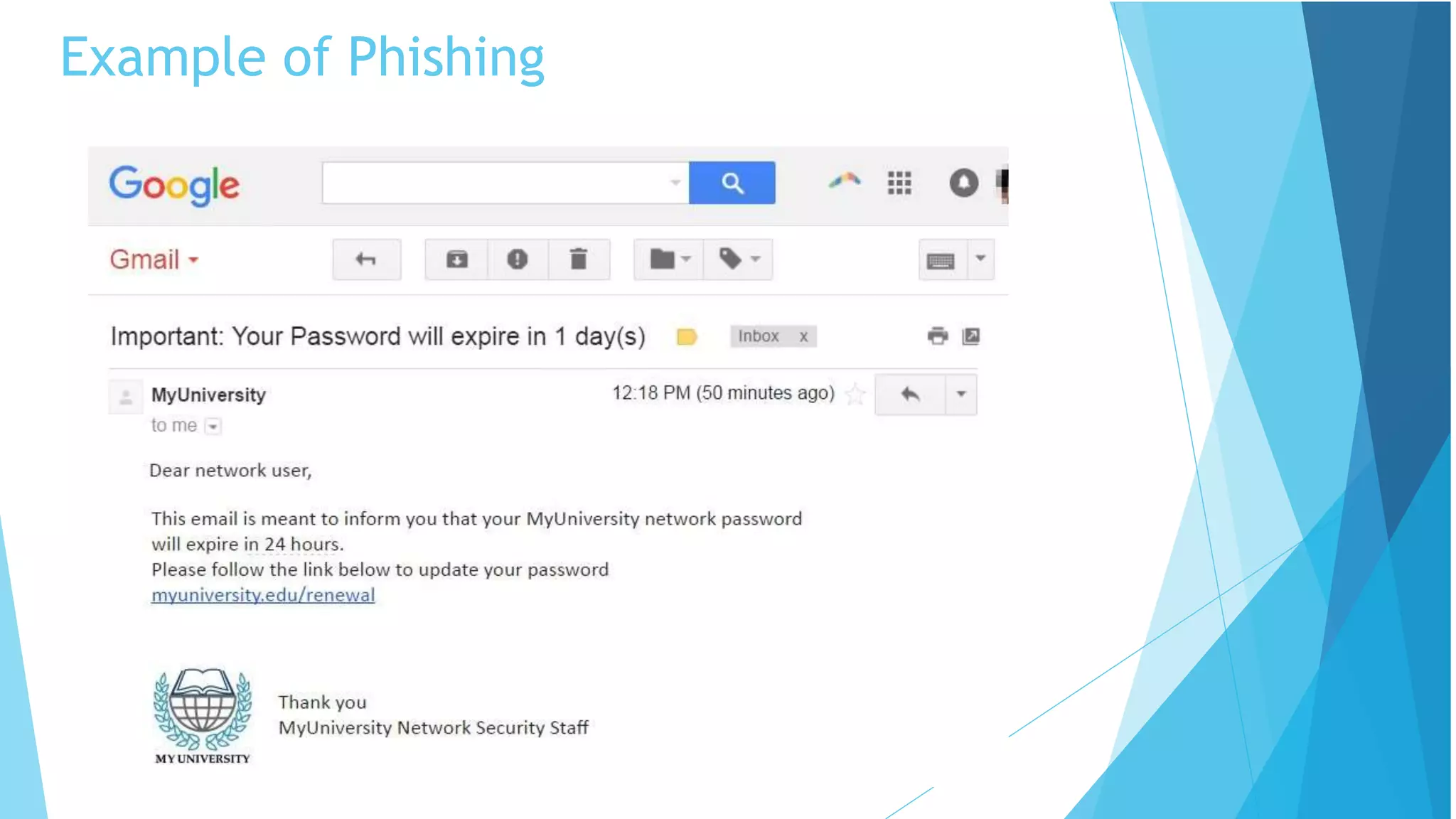
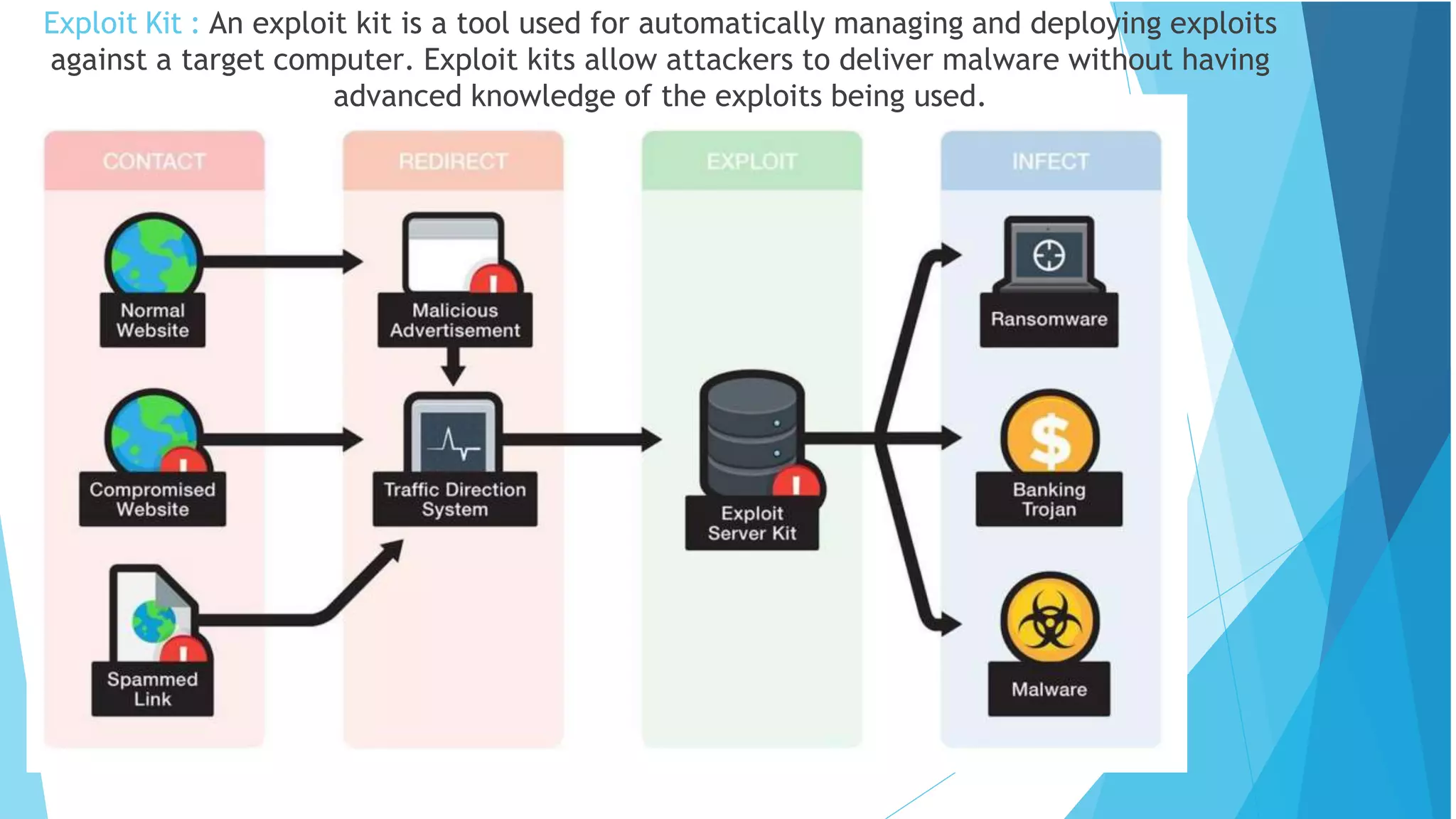
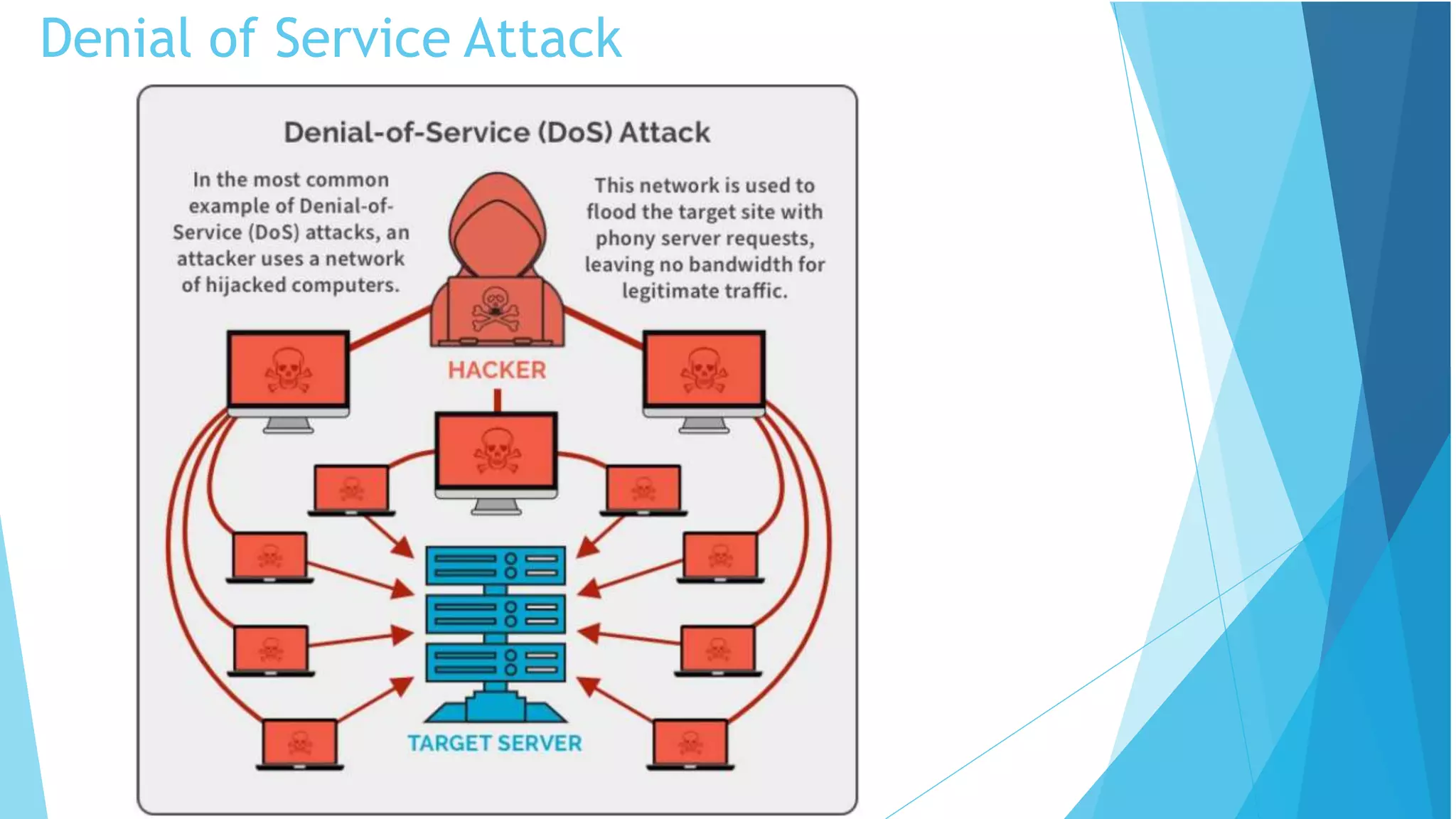
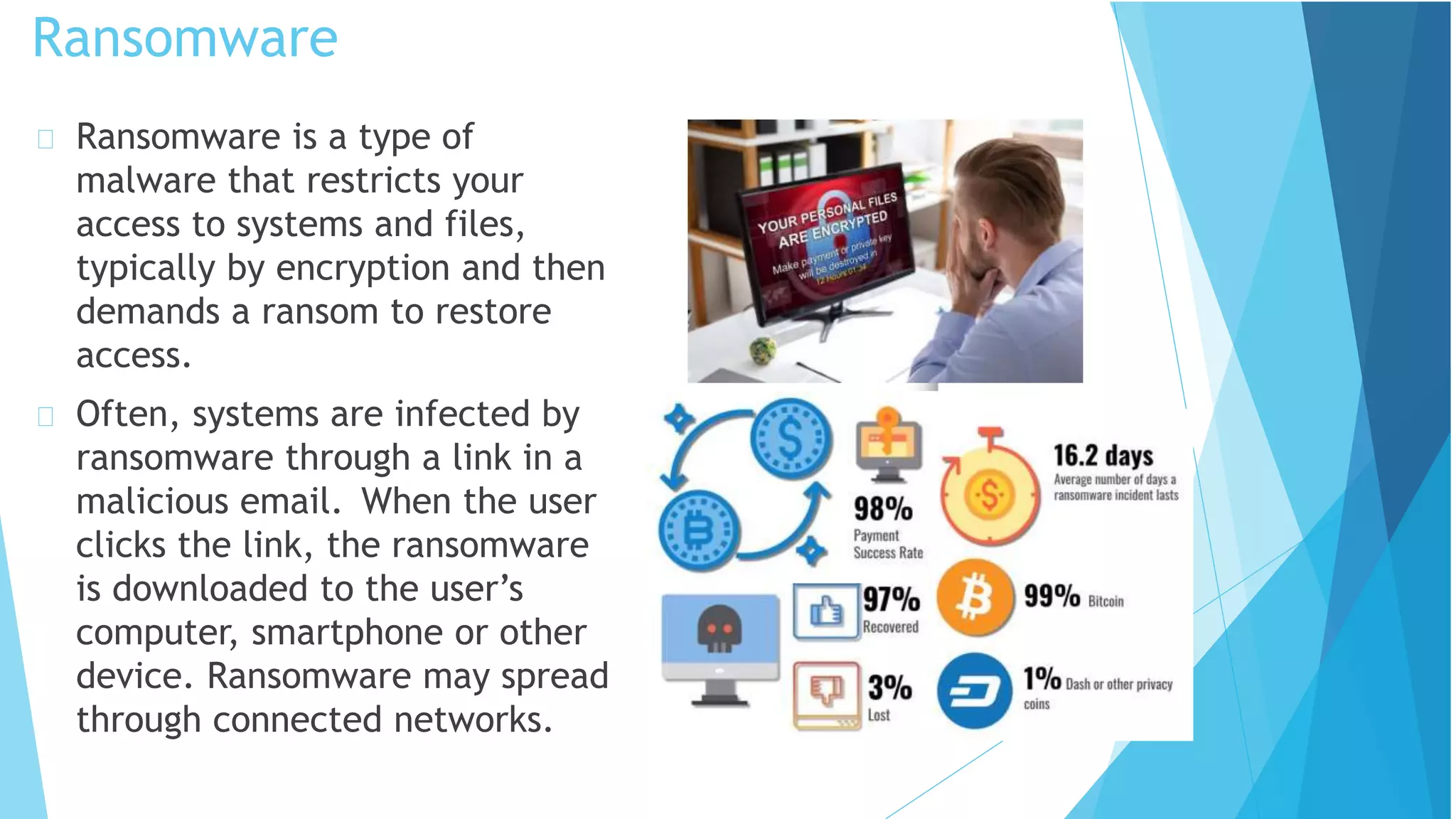
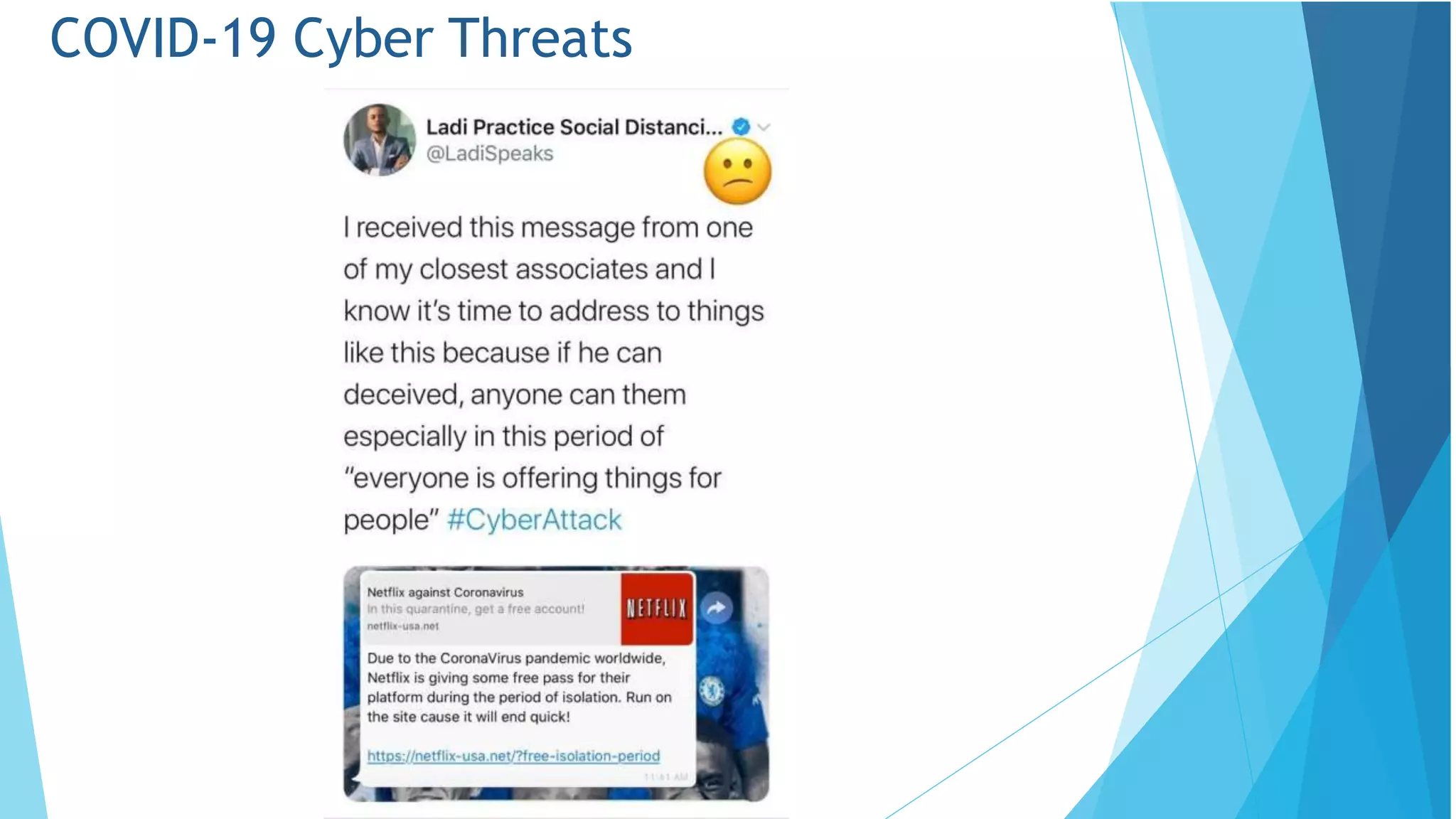
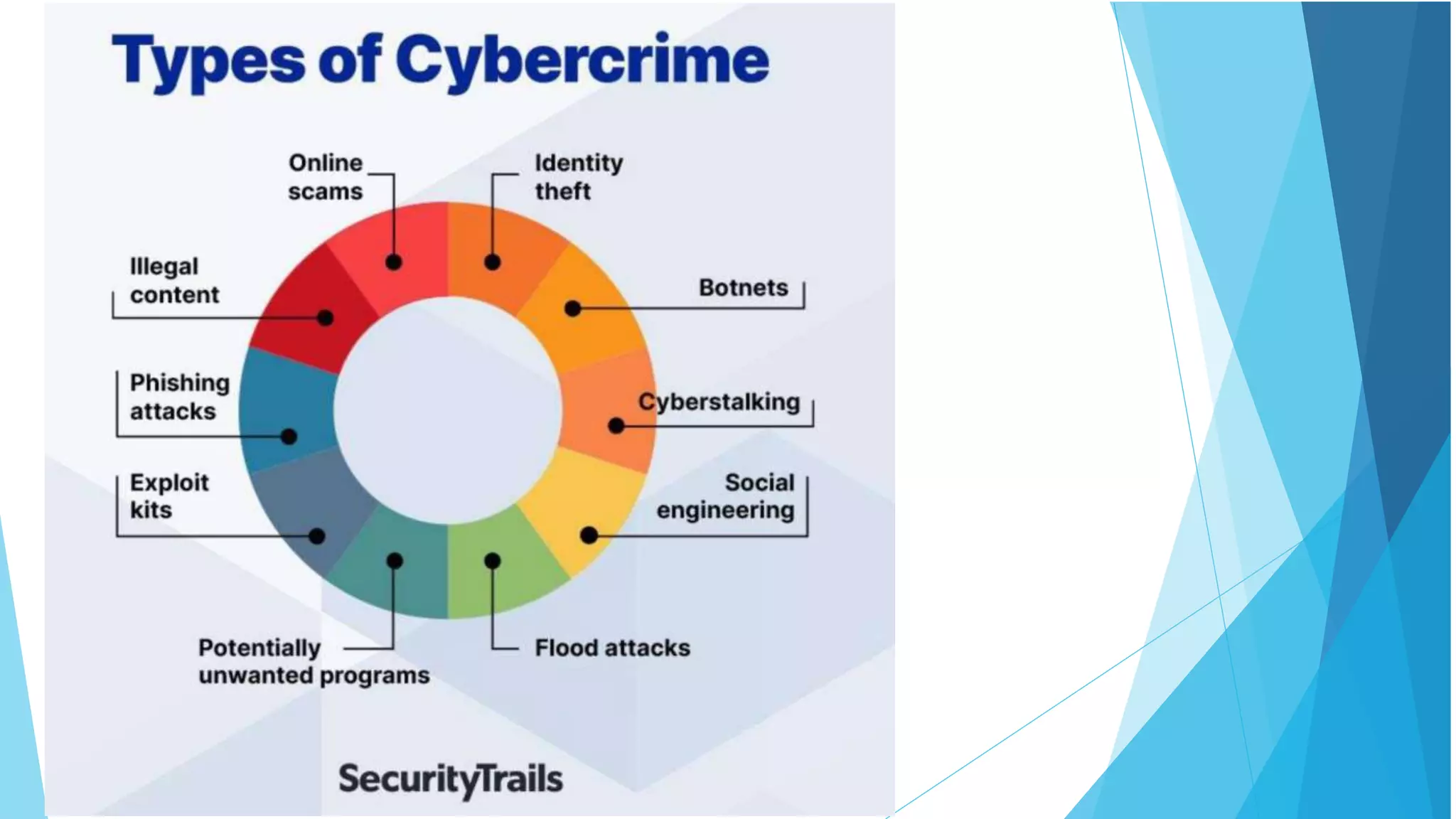
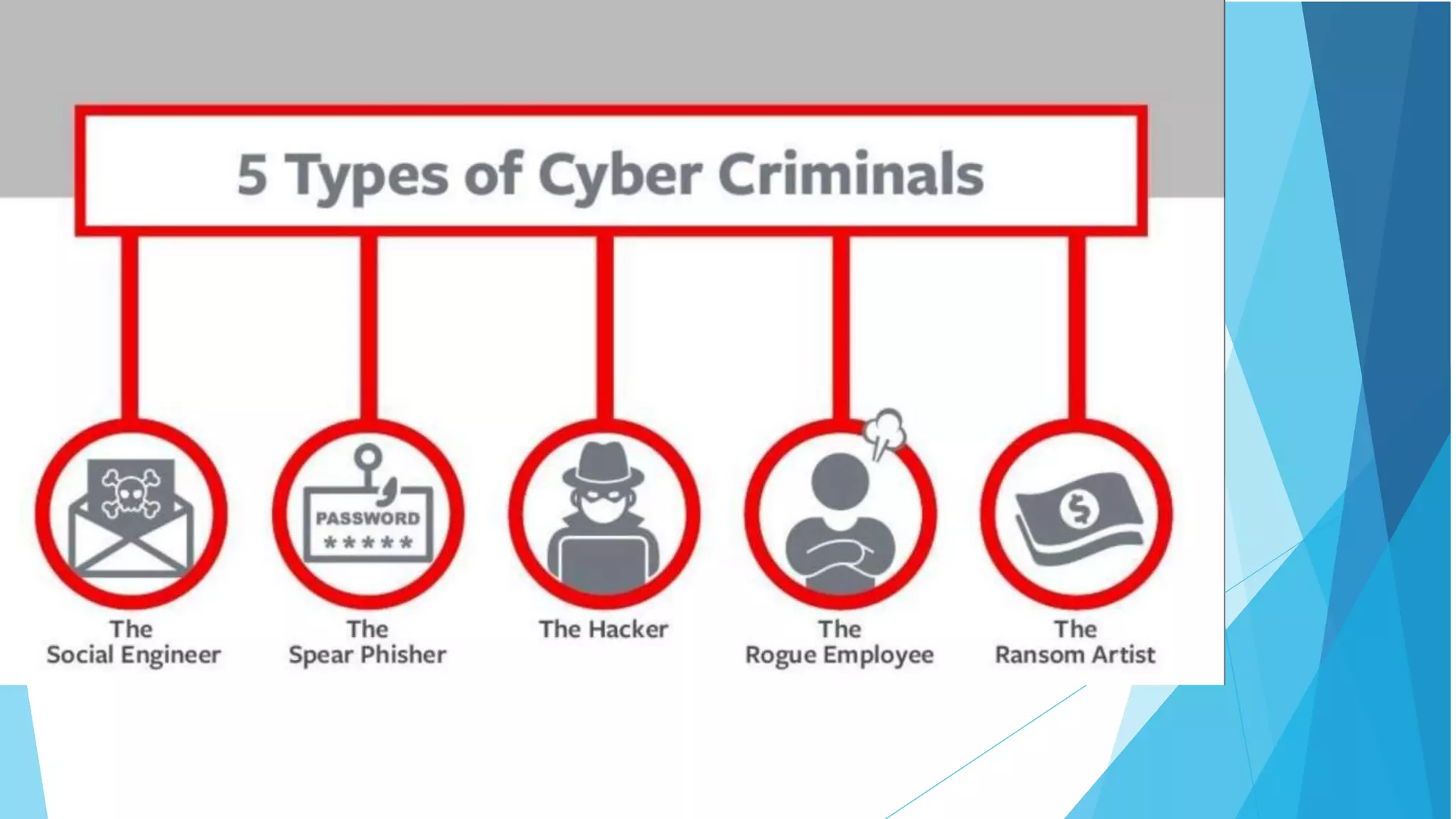
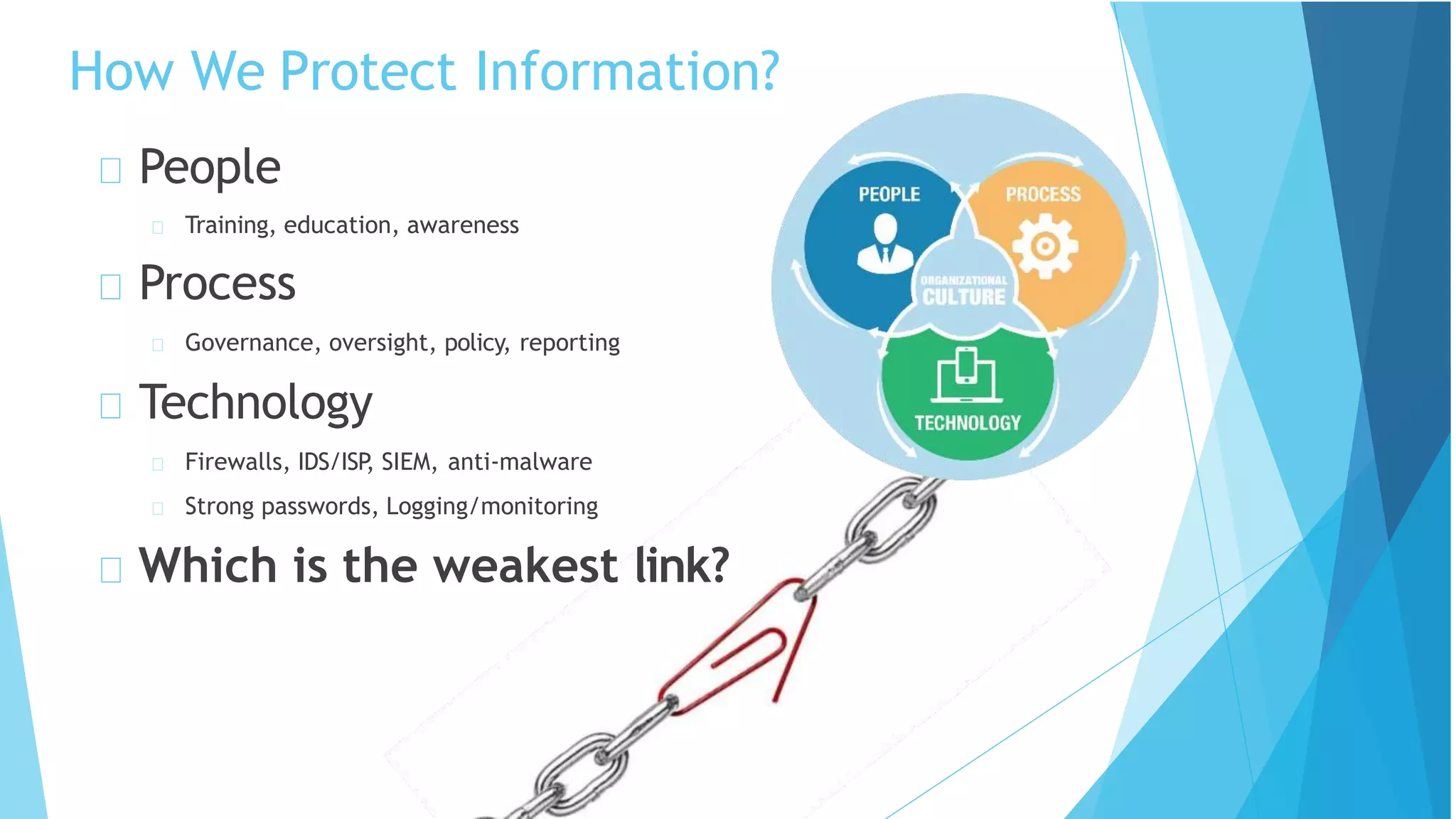
This document discusses computer and cyber security. It begins by noting that the only truly secure system is one that is powered off, locked away, and guarded. It then discusses how the internet allows attackers to work remotely from anywhere. Common cyber attack vectors include web browsers, IM clients, web applications, and excessive user rights. Cyber security aims to protect computers and data in the same way we secure our homes from threats. The domains of cyber security include confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. Threats include phishing, social engineering, malware like ransomware, and more.