Synthesis of water based mud (wbm)
- 1. 1 Drilling Engineering TITLE: Synthesis of Water Based Mud (WBM) Author name: Mahmood Abdul-Jabbar hebah
- 2. 2 Acknowledgement “I would like to express my deepest appreciation to all those who provided me the possibility to complete this experiment. I would also like to show my deepest gratitude to my lecturer, Dr. Mahmood for giving me a good guideline for this experiment throughout numerous consultations. Moreover, I would like to appreciate the crucial role of the staff of APU University who gave the permission to use all equipment and necessary materials to complete the laboratory, and also a special thanks goes to my group who did well in the lab to success in this experiment. Last but not least, many thanks go to the head of the APU University whose have invested his full effort in guiding the students to achieving their goals.”
- 3. 3 Table of Contents Abstract ........................................................................................................................................... 5 Objective:........................................................................................................................................ 5 Introduction..................................................................................................................................... 6 Theory and Literature Review ........................................................................................................ 7 Apparatus & Materials.................................................................................................................... 8 Methodology................................................................................................................................. 17 Results and Discussions................................................................................................................ 19 Discussions.................................................................................................................................... 24 Conclusion .................................................................................................................................... 25 Suggestion..................................................................................................................................... 26 Refremces...................................................................................................................................... 27
- 4. 4 List of Figure Figure(3):Mud mixer....................................................................................................................... 8 Figure(4):Mud balance................................................................................................................... 9 Figure(5):Rheometer...................................................................................................................... 9 Figure(6):Thermometer................................................................................................................ 10 Figure(7):Filter press with cylinder of gas................................................................................... 10 Figure(8):Graduated cylinder....................................................................................................... 11 Figure(9):PH meter ...................................................................................................................... 11 Figure(10):PH paper .................................................................................................................... 12 Figure(11):Resistivity meter ........................................................................................................ 12 Figure(12):Filter paper................................................................................................................. 13 Figure(13):Beaker ........................................................................................................................ 13 Figure(14):Lid of the filter press.................................................................................................. 14 Figure(15):Ring............................................................................................................................ 14 Figure(16):Electronic balance...................................................................................................... 14 Figure(17):Vernier Caliper .......................................................................................................... 15 Figure(18):Bentonite.................................................................................................................... 15 Figure (19): Barite ....................................................................................................................... 16 Figure (20): Depth Vs mud density19 ........................................................................................ 19 List of Table & Graph Table 1- case study data ............................................................................................................... 19 Table 2- parameters used for barite............................................................................................... 20 Table 3- Mud-1 properties .......................................................................................................... 20 Table 4- barite parameters needed ............................................................................................... 22 Table 5- Mud-2 properties .......................................................................................................... 22
- 5. 5 Abstract: This assignment was used to design a mud and preparing mud for a well having a depth of 10000ft and each depth consist of different pore pressure gradient and fracture gradient. It was important to take in consider the safety margins and the kick margins by adding to the pore pressure gradient 0.5ppg and subtracting from fracture pressure 0.5ppg as shown in table (1). Then it has been drew the mud window to create a proper mud to solve the issue in this assignment and become safer. Since there are two muds needed to be prepared for a well having a depth of 10000ft and each with different density, it is important to measure the amount of barite required in order to increase the density to the target wanted. has been created the mud with 10.9 ppg, after creating the mud for this density will be testing all the classification for this test and if it is goof or no. The temperature for this mud was 28.7C and the density has been measured as well which was 10.95 and the ph was 8. In addition, has been measured the viscosity at different speed by using viscometers the speed was at 5,6,100,200,300, and 600 rpm the results shows in table 3. Then it has been measured the gel strength at 10s and 10 mins which was 30, and 31ib.100ft2 respectively, then it has been calculated the plastic viscosity, apparent viscosity, and yield point by the equation given above, and the results mentioned in table 3. Lastly has been measure the filtrate volume for 5,10, 15,20,15 and 30mins the total volume which was at 30 mins with result about 16.5cc. then it has been measured the mud cake thickness for this type of mud which was 3.23mm. it was given some of the errors that faced while drilling a well, those problems were loss circulation, high and innovation and the stuck pipe. in the first step it has been designed the sample mud that required to use at the surface, while the pressure of the well increase it should increase the density of the mud to balance between the hydrostatic pressure with the formation pressure, so it has been increased the density of the mud by using the barite, the mud was 10, and 14ppg. Objective 1. To synthesis water-based mud (WBM) to improve drilling efficiency.
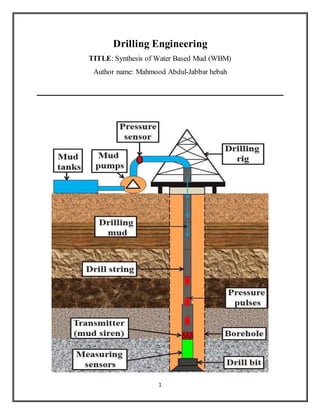
- 6. 6 Introduction “Drilling mud is utilized to help the drilling of boreholes into the earth. Generally used while drilling a reservoir or creating a hole on the earth to extract the hydrocarbon and natural gas water wells and exploration drilling rigs, drilling fluids are also used for easier boreholes, such as water wells. Liquid drilling fluid is often called drilling mud. The three main categories of drilling fluids are water-based muds (which can be dispersed and non-dispersed), non-aqueous muds, usually called oil-based mud, and gaseous drilling fluid, in which a variety of gases can be used. The functions of drilling liquids include hydrostatic pressure to prevent formation pressure while decreasing, it used to balance the pressure of the hydrostatic pressure and the formation pressure, and many more of the utilizes, it used from entering into the wellbore, to get exercise the bit cool and clean during drilling, holding away drill cuttings, and hanging the drilling waste while drilling is paused and when the going assemblage is introduced and away of the well.” “The drilling fluid used for your task is selected to avoid formation damage and limit corrosion. It is almost sure that problems will occur while heading a well, even in very carefully planned boreholes. For example, in areas through which similar drilling methods are being used, pit problems may have recently been reported where no such problems existed previously because formations are nonhomogeneous. As a result, two wells near the other person may have totally different geological conditions. In well planning, the important thing to obtaining objectives successfully is to design drilling programs on the basis of the expectation of potential whole problems rather than on extreme caution and containment.” “Drilling problems can be very costly. The most prevalent going problems include pipe stoke, lost circulation, hole change, pipe failures, borehole insecurity, mud contamination, formation destruction, hole cleaning, H2S-bearing development and shallow gas, equipment, and personnel- related problems Understanding and anticipating going problems, understanding their triggers, and planning solutions are necessary for overall-well-cost control and for successfully attaining the target zone (NOAH, 11/12/2012).”
- 7. 7 Theory and Literature Review “Many different types of water-based mud are used in drilling operations. Basic drilling fluid systems are usually converted to more complex systems as a well is deepened and the wellbore temperature and/or pressure increases. Several key factors affect the selection of drilling fluid systems for a specific condition. The most favorable drilling fluid for a well or interval should be based on the criteria as such;” 1- “Performance-inhibition, rheology, fluid loss and temperature.” 2- “Environment-damage to the environment should be avoided.” 3- “Safety-to all personnel.” 4- “Average cost.” “In this experiment has some problems that will solve by making a mud, these problems are:” “Pipe Sticking” “During drilling operations, a pipe is considered stuck if it cannot be freed and pulled out of the hole without damaging the pipe and without exceeding the drilling rig ’ s maximum allowed hook load. Differential pressure pipe sticking and mechanical pipe sticking are addressed in this section. Differential-pressure pipe sticking occurs when a portion of the drill string becomes embedded in a mud cake (an impermeable film of fine solids) that forms on the wall of a permeable formation during drilling.” “Loss of Circulation” “Lost circulation is defined as the uncontrolled flow of whole mud into a formation, sometimes referred to as thief zone. In partially lost circulation, mud continues to flow to the surface with some loss to the formation. Total lost circulation, however, occurs when all the mud flows into a formation with no return to the surface. If drilling continues in total lost circulation, it is referred to as blind drilling. This is not a common practice in the field unless the formation above the thief zone is mechanically stable, there is no production, and the fluid is clear water. Blind drilling also may continue if it is economically feasible and safe.”
- 8. 8 “Hole Deviation” “Hole deviation is the unintentional departure of the drill bit from a preselected borehole trajectory. Whether drilling a straight or curved-hole section, the tendency of the bit to walk away from the desired path can lead to higher drilling costs and lease-boundary legal problems. Fig. 10.6 provides examples of hole deviations.” Apparatus & Materials “Mud mixer” “The mixer is used to prepare the mud sample with given some of bentonite or other chemicals that has been use in this experiment. Most drilling fluid formulations contain a base liquid and additives which must be dissolved or mechanically dispersed into the liquid to form a homogenous fluid.” Figure (1): Mud mixer
- 9. 9 “Mud balance” “A device to measure density (weight) of mud, cement or other liquid or slurry. A mud balance consists of a fixed-volume mud cup with a lid on one end of a graduated beam and a counterweight on the other end. A slider-weight can be moved along the beam, and a bubble indicates when the beam is level.” Figure (2): Mud balance “Rheometer” “The main objective is to find the apparent viscosity, plastic viscosity, yield point and true yield point for the given mud sample and gel strength.” Figure (3): Rheometer
- 10. 10 “Thermometer” “Using a thermometer to check your temperature in mud fluid after has been mad it by the mixer. A rise in your temperature is usually caused by an infection. When using any kind of thermometer, make sure you read and follow the instructions that come with the thermometer.” Figure (4): Thermometer Filter press A filtration press with the cylinder of the nitrogen use to measure the water on the mud by measuring the time it takes around 30 mins to measure how much liquid in this mud, also it measure the permeability and the water loss of the mud, therefore, the test is done to determine the thickness of the mud cake. Figure (5): Filter press and cylinder of nitrogen
- 11. 11 Graduated cylinder The graduated cylinder use to measure the water loses on the mud, by using the filter press, it has been measured the water losses at 30 mins each 5 mins it has been recorded. it will mention the data in brief below on the calculation. Figure (6): Graduated cylinder “PH meter / ph paper” “PH meter is between a pH electrode and a reference electrode, and so the pH meter is sometimes referred to as a "potentiometric pH meter". The difference in electrical potential relates to the acidity or pH of the solution. A scientific instrument that measures the hydrogen-ion activity in water-based solutions, indicating its acidity or alkalinity expressed as ph. The pH meter measures the difference in electrical potential.” Figure (7): ph meter
- 12. 12 PH paper The ph paper use to determine the pH of the given sample. Figure (8): ph paper Resistivity meter This tester is used to measure the resistivity of mud. Figure (9): Resistivity meter
- 13. 13 Filter paper The filter paper use while measuring the water volume by using the filter press. Figure (10): Filter paper Beaker Use to measure the amount of water. Figure (11): Beaker
- 14. 14 Lid with valve This lid connect the filter press with a cylinder of nitrogen, and us to close the cup of the filter press while measuring the volume of water. Figure (12): Lid of the filter press Ring Use to prevent the seeps of gas, it is very important for safety. Figure (13): Ring “Electronic balance” “Use to measure the amount of bentonite and barite, which is very sensitive measurement tool” Figure (14): Electronic balance
- 15. 15 “Vernier caliper” “The Vernier use to measure the mud cake thickness of the mud. Parts of a Vernier caliper:” 1- “outside jaws: used to measure external diameter or width of an object.” 2- “Inside jaws used to measure internal diameter of an object.” 3- “Depth probe: used to measure depths of an object or a hole” 4- “Main scale: marked every mm.” 5- “Main scale: scale marked in inches and fractions.” 6- “Vernier scale gives interpolated measurements to 0.1 mm or better.” 7- “Vernier scale gives interpolated measurements in fractions of an inch.” 8- “Retainer: used to block movable part to allow the easy transferring of a measurement.” Figure (15): Vernier caliper “Bentonite” “Bentonite is a clay that has a particularly useful characteristic. It can absorb many times its weight in water. It is useful in drilling wells because water mixed with bentonite tends to coat the walls of the hole and keep it from collapsing. Drillers call this coating a filter cake.” Figure (16): Bentonite
- 16. 16 “Barite” “To increase the mud density, barite is also used in a wide variety of other applications including plastics, clutch pads, rubber mud flaps mold release compounds, radiation shielding, television and computer monitors, the sound-deadening material in automobiles, traffic cones, brake linings, paint and golf balls. Figure (17): Barite “Xanthan Gum” “Xanthan Gum is a high molecular weight Bio-Polymer that provides excellent Rheology Control for water based drilling, completion, and work-over fluids with a wide variety of brines. As a natural Bio-Degradable, Cream-Colored Powder, the Xanthan is carefully produced and controlled in a temperature-sensitive manufacturing facility similar to a Pure Culture Fermentation.” “Advantages of the xanthan gum” 1- “Can be used in a wide range of Drilling Fluid.” 2- “Additives with a variety of fluid formulations.” 3- “Effective in fresh water or sea water with common Brines, such as Sodium, Potassium, Calcium 4-hlorides, Calcium.” 4- “Bromides, and Zine Bromides.”
- 17. 17 Methodology: Methodology: The data of the reservoir was given which were surface depth (4500ft) and the total length of the well (20000ft) It was required to design a mud for flowing problems: Loss circulation High sand innovation Stuck pipe It has been made the mud for 4 times: First mud that has been made from the surface to 2500ft 1-The mud mixture was contained of (350 pure water + 20grams of Bentonite) 2- It was mixed for 15 mins to make a good mud 3- After the mud was made, it has been measured the characteristics of this mud which were ph, temperature, density, and the viscosity 4- The temperature of this mud was 31.5c 5- The ph was measured as well which was (8) 6- The viscosity has been tested at each speed Second mud was made to balance the hydrostatic pressure, by increasing the mud density, the depth was from 2500ft to 5000ft 1-The mud mixture was contained of (350 pure water 20 grams of Bentonite) 2- The mud was mixed for 5 mins, then switched the machine of to calculate the amount of the barite. 3- It has been calculated the amount of the barite that has been added.
- 18. 18 4- The amount of the barite which was calculated, it has been added to the mud to increase the density, and mixed for 15 mins 5-It has been measured the temperature 6- The ph was tested which was (8) 7- The density of the mud was measured to know if the mud density increased or not 8- Viscosity was tested by using the viscometer Third mud was made to solve the loss circulation at the depth 5000ft to 7000ft 1-The mud mixture was contained of (350 pure water + 20grams of bentonite + 70.4grams of Barite) 2- It has been added 2 grams of xanthan gum to solve this kind of problem 3- It has been mixed by a mixer for 15 mins 4- The temperature of this mud was measured by the thermometer 5- After the temperature has been measured, the ph was tested 6- The density of this mud was tested by using the mud balance 7-the mud cake and the filter volume were measured Fourth mud that was designed to avoid the errors of stuck pipe 1-The mud mixture was contained of (350 pure water + 20grams of bentonite + 70.4grams of Barite), then it was mixed for 5 mins 2- It was calculated the amount of water that was added to solve the problems of the stuck pipe 3- The water that was calculated, has been added to the mud, then it mixed for 15 mins 4- It have measured the temperature and the ph 5- The density of this mud was tested after the ph and Temperature 6- It has been measured the viscosity.
- 19. 19 Results and Discussions This task required to prepare a mud for a well having a depth of 10000ft and each depth consist of different pore pressure gradient and fracture gradient. It was important to take in consider the safety margins and the kick margins by adding to the pore pressure gradient 0.5ppg and subtracting from fracture pressure 0.5ppg as shown in table 1. Table 1- case study data , Figure 1- Depth Vs mud density
- 20. 20 Since there are two muds needed to be prepared for a well having a depth of 10000ft and each with different density, it is important to measure the amount of barite required in order to increase the density to the target wanted. In order to calculate the proper amount of barite needed to increase the density to 10.9ppg and 14ppg a certain equation was given, Drilling fluid-1 (10.9ppg) Table 2- parameters used for barite The amount of barite needed to increase the density of mud-1 = 137.24g Table 3- Mud-1 properties No. Apparatus Property Result 1 Thermometer Temperature (°C) 28.7 °C 2 Mud Balance Density (ppg) 10.9 ppg 3 pH Meter / pH Paper pH Value 8 Rheology (cP) 3 rpm 21 cP 6 rpm 21 cP 100 rpm 24 cP 200 rpm 26 cP 300 rpm 30 cP
- 21. 21 4 Rotational Viscometer 600 rpm 42 cP Plastic Viscosity (cP) Plastic viscosity (cp)= [600 rpm reading] – [300 rpm reading] 42 – 30 = 12 cP Apparent Viscosity (cP) Apparent viscosity (cp) = [600 rpm reading] / 2 42 ÷ 2 = 21 cP Yield Point (lb/100 ft2) Yield Point (Ib/1002) = [300rpm reading] – Plastic viscosity 30 – 12 = 28 lb/100 ft2 Gel Strength (lb/100 ft2) 3(10 sec) 30 lb/100 ft2 3 (10 min) 31 lb/100 ft2 5 LPLT Filter Press Filtrate Volume (cc) 5 min 7 (cc) 10 min 9 (cc) 15 min 11 (cc) 20 min 13 (cc) 25 min 14 (cc) 30 min 16.5 (cc) 6 Vernier Caliper Mud cake Thickness (mm) 3.23 mm The equation needed to calculate the plastic viscosity, Plastic viscosity (cp)= [600 rpm reading] – [300 rpm reading] The equation needed to calculate the Apparent viscosity, Apparent viscosity (cp) = [600 rpm reading] / 2 The equation needed to calculate the Yield Point, Yield Point (Ib/1002) = [300rpm reading] – Plastic viscosity
- 22. 22 Drilling fluid-2 (14ppg) Table 4- barite parameters needed The amount of barite needed to increase the density of mud-1 = 374.5g Table 5- Mud-2 properties No. Apparatus Property Result 1 Thermometer Temperature (°C) 31.3 °C 2 Mud Balance Density (ppg) 14.95 ppg 3 pH Meter / pH Paper pH Value 7 4 Rotational Viscometer Rheology (cP) 3 rpm 29 cP 6 rpm 31 cP 100 rpm 35 cP 200 rpm 40 cP 300 rpm 45 cP 600 rpm 58 cP Plastic Viscosity (cP) Plastic viscosity (cp)= [600 rpm reading] – [300 rpm reading] 48 – 45 = 13 cP
- 23. 23 Apparent Viscosity (cP) Apparent viscosity (cp) = [600 rpm reading] / 2 58 ÷ 2 = 29 cP Yield Point (lb/100 ft2) Yield Point (Ib/1002) = [300rpm reading] – Plastic viscosity 45 – 13 = 32 lb/100 ft2 Gel Strength (lb/100 ft2) 3(10 sec) 59 lb/100 ft2 3 (10 min) 59.5 lb/100 ft2 5 LPLT Filter Press Filtrate Volume (cc) 5 min 9.5 (cc) 10 min 13.5 (cc) 15 min 16.5 (cc) 20 min 19 (cc) 25 min 21.5 (cc) 30 min 24 (cc) 6 Vernier Caliper Mud cake Thickness (mm) 4.9 mm
- 24. 24 Discussion This assignment was used to design a mud and preparing mud for a well having a depth of 10000ft and each depth consist of different pore pressure gradient and fracture gradient. It was important to take in consider the safety margins and the kick margins by adding to the pore pressure gradient 0.5ppg and subtracting from fracture pressure 0.5ppg as shown in table (1). Then it has been drew the mud window to create a proper mud to solve the issue in this assignment and become safer. Since there are two muds needed to be prepared for a well having a depth of 10000ft and each with different density, it is important to measure the amount of barite required in order to increase the density to the target wanted. In order to calculate the proper amount of barite needed to increase the density to 10.9ppg and 14ppg a certain equation has been used this equation is below. First of all, has been created the mud with 10.9 ppg, after creating the mud for this density will be testing all the classification for this test and if it is goof or no. The temperature for this mud was 28.7C and the density has been measured as well which was 10.95 and the ph was 8. In addition, has been measured the viscosity at different speed by using viscometers the speed was at 5,6,100,200,300, and 600 rpm the results shows in table 3. Then it has been measured the gel strength at 10s and 10 mins which was 30, and 31ib.100ft2 respectively, then it has been calculated the plastic viscosity, apparent viscosity, and yield point by the equation given above, and the results mentioned in table 3. Lastly has been measure the filtrate volume for 5,10, 15,20,15 and 30mins the total volume which was at 30 mins with result about 16.5cc. then it has been measured the mud cake thickness for this type of mud which was 3.23mm. Second of all, has been made the Drilling fluid-2 which required density about 14ppg, after the mud has been created will be measured its properties. Firstly, it has measured the temperature which was at 31.3C, and the density was 14.05 which is good as needed, the ph has been reduced if compared with first mud the ph for this md is 7.second, it has been measured the viscosity with 3,6,100, 200, 300, and 600rpm by using the viscometers Machin and the results mentioned on table 5, after that has been calculated the plastic viscosity, apparent viscosity and yield point for this mud which was higher than the first shamble and the results mentioned on table 5. After that has been found the gel strength at 10s and 10 mins which were 59, and 59.5 ib/100ft2 respectively,
- 25. 25 this gel strength is higher than the mud with 10ppg. Lastly, has been measured the water volume by using the filter press and the total volume for this mud was 24cc which is higher than the mud with 10ppg. Then it has measured the mud cake thickness which was4.9mm more than the last mud which was 3.23mm. Last but not less this assignment was interesting and helpful for the student to get knowledge of the drilling mud, also how to solve the problems that will affect on the drill bit and how to use create the proper mud for it, this assignment it will help the student a lot in the future. Conclusion In summary; this experiment was helpful for a student to get knowledge on the drilling mud, and designed the best mud for different problems, it was given some of the errors that faced while drilling a well, those problems were loss circulation, high and innovation and the stuck pipe. in the first step it has been designed the sample mud that required to use at the surface, while the pressure of the well increase it should increase the density of the mud to balance between the hydrostatic pressure with the formation pressure, so it has been increased the density of the mud by using the barite, the mud was 10, and 14ppg. Each mud types used for different depth the higher depth will be used the higher density need to prevent any collapse or burst, so we have to create a prober mud types while drilling a well.
- 26. 26 Suggestion It is very important to know the errors that will face in the experiment to avoid it. However, in this assignment, there is some suggestion that will reduce the problems while creating the mud as well as the test of the drilling mud. I suggest this experiment could be more accurate if the procedure was repeated at least 5 times and the average results were obtained but time was not in our favor. 1- Should be calculated the volume of barite to increase the mud and use the Electronic balance to measure the volume of the barite, it very sensitive. 2-The experiment would have also been more accurate if it was performed more carefully and less mud was lost due to spilling or splashing when in the blender. 3- Make sure that the Electronic balance clean there is not any sand on it, then restart to use, this is to avoid the errors that will come in the amount of the barite. 4- Clean the mud balance to avoid the result of the density, there are different fluid each fluid has different density, so it needs to clean it every time. 5-when it measures the gel strength, it should take rest for 5 mins to get the proper result because the Rheometer is very sensitive to the viscosity. 6-make sure there is no seeps of the gas while using the Filter press. 7-To improve the quality of the experiment it is suggested that more advanced tools were used in the experiment such as a more advanced weigh or viscometer.
- 27. 27 References Mitchell,R.F.,26 April 2017. PEH:Drilling Problemsand Solutions. [Online] Available at:http://petrowiki.org/PEH:Drilling_Problems_and_Solutions [Accessed 25 2 2021]. NOAH,A.Z., 11/12/2012. Controlslossesin Depleted Reservoirsand high-permeability formationsusing Nanomaterialasa new mud. [Online] Available at:http://www.lifesciencesite.com/lsj/life0902s/030_11165life0902s_161_170.pdf [Accessed 25 2 2021].
