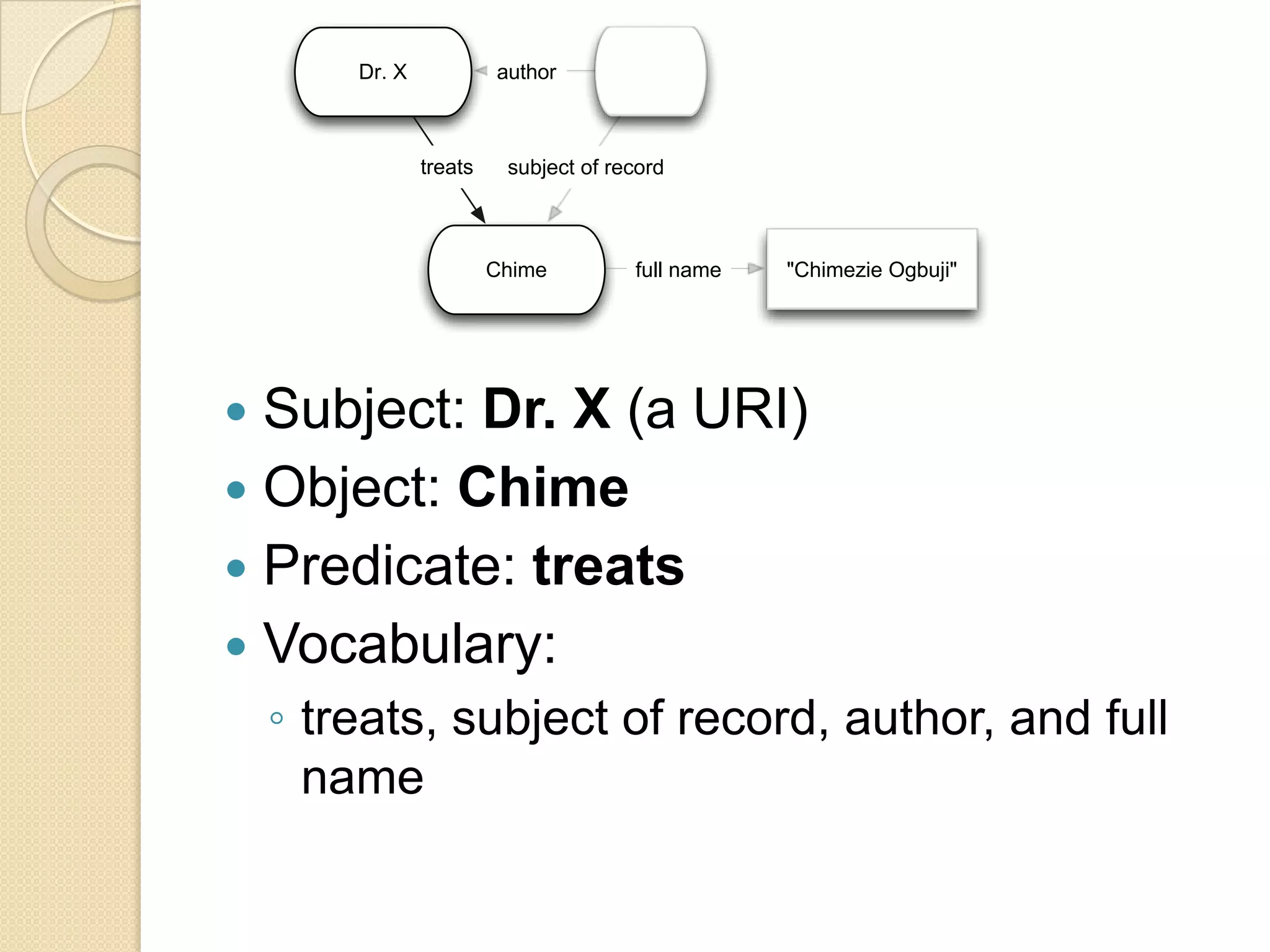
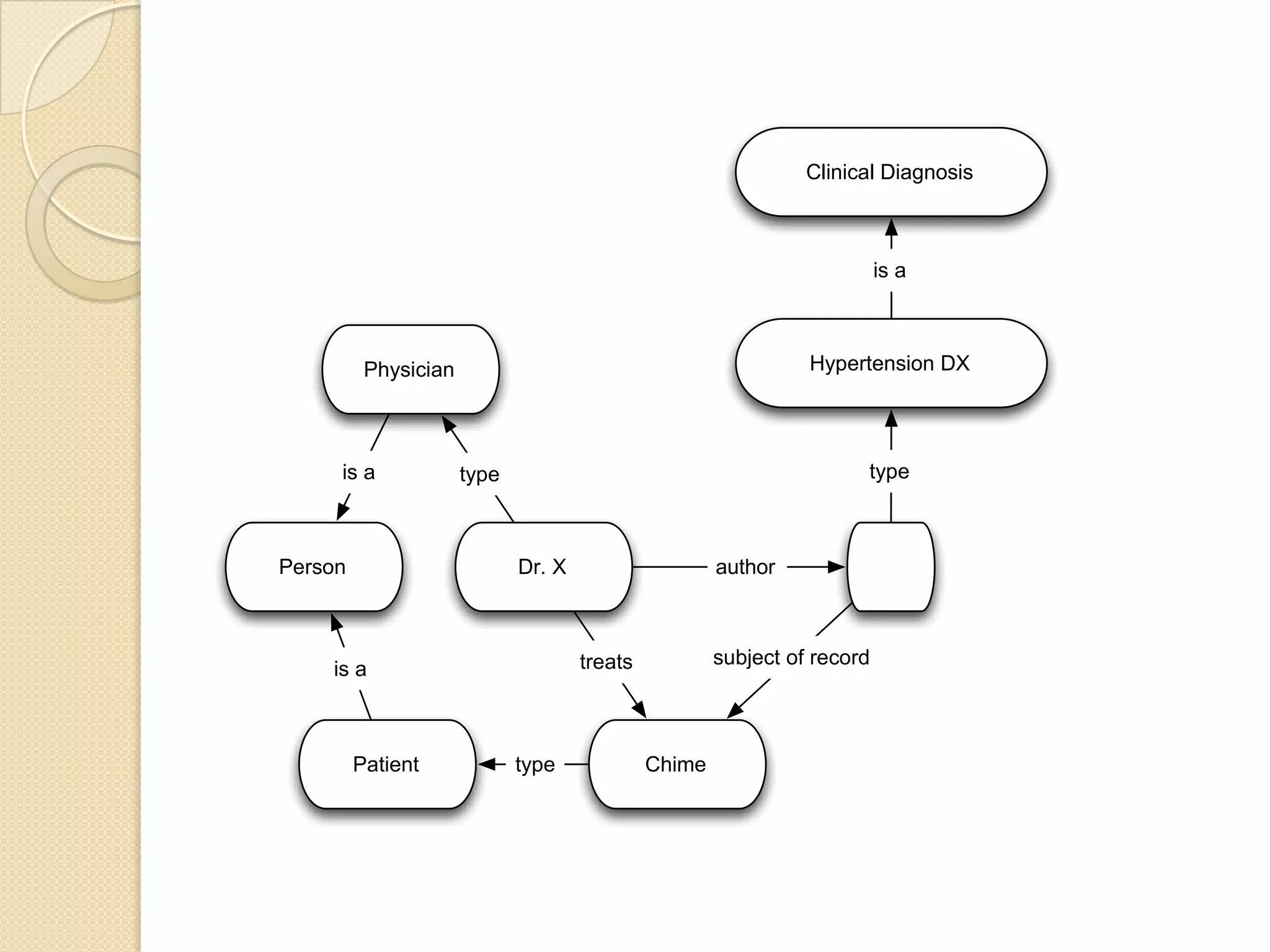
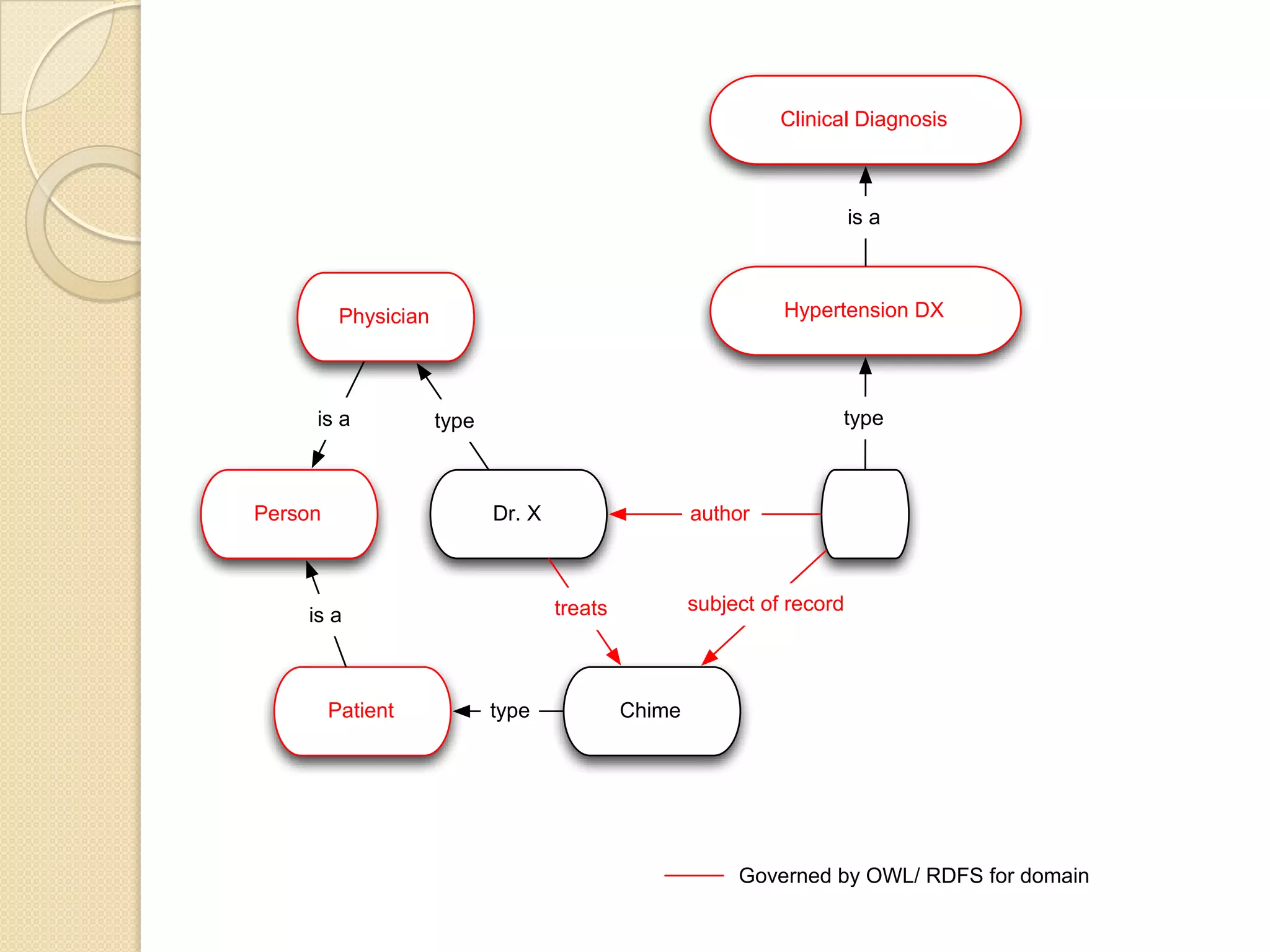
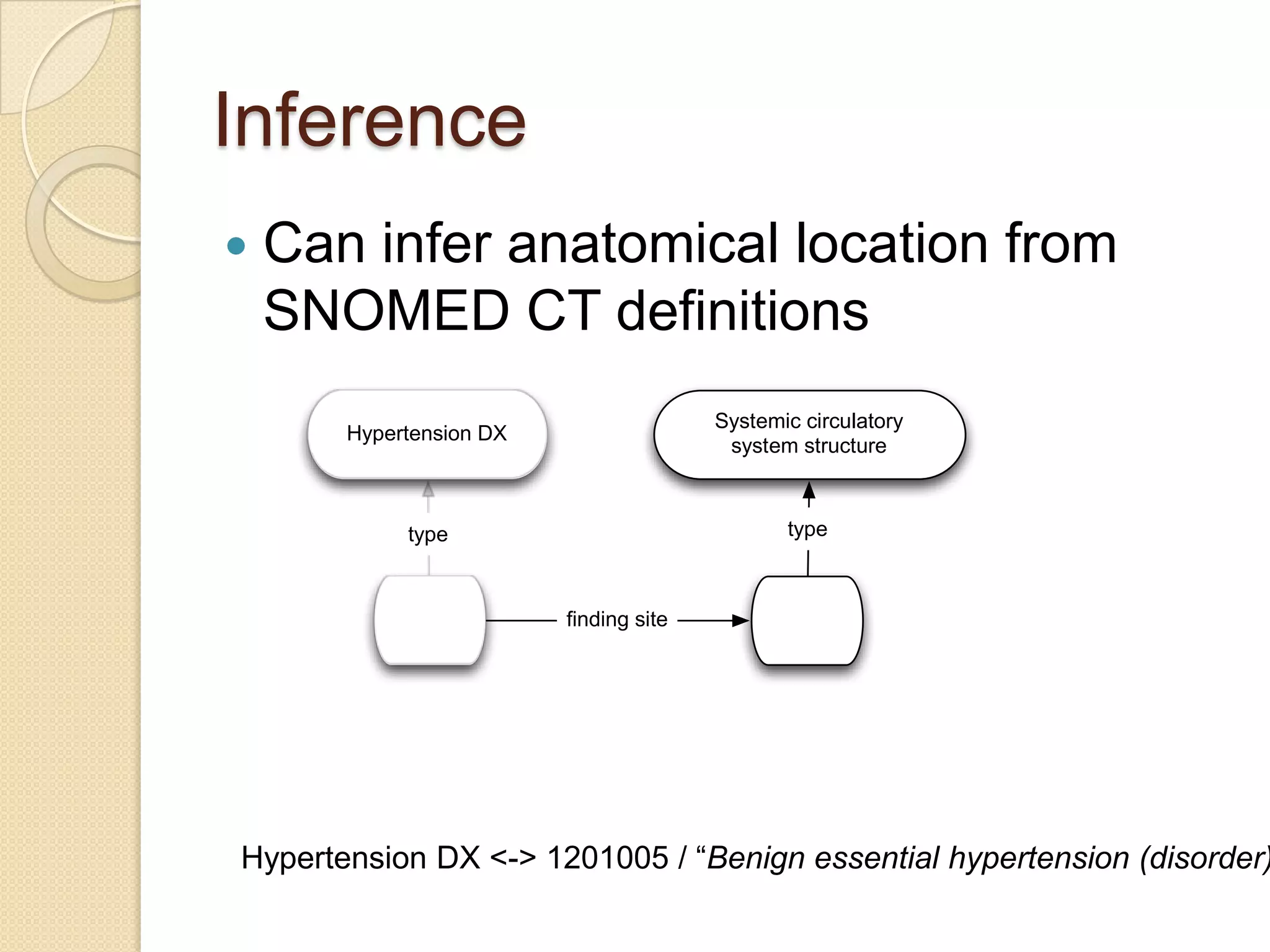
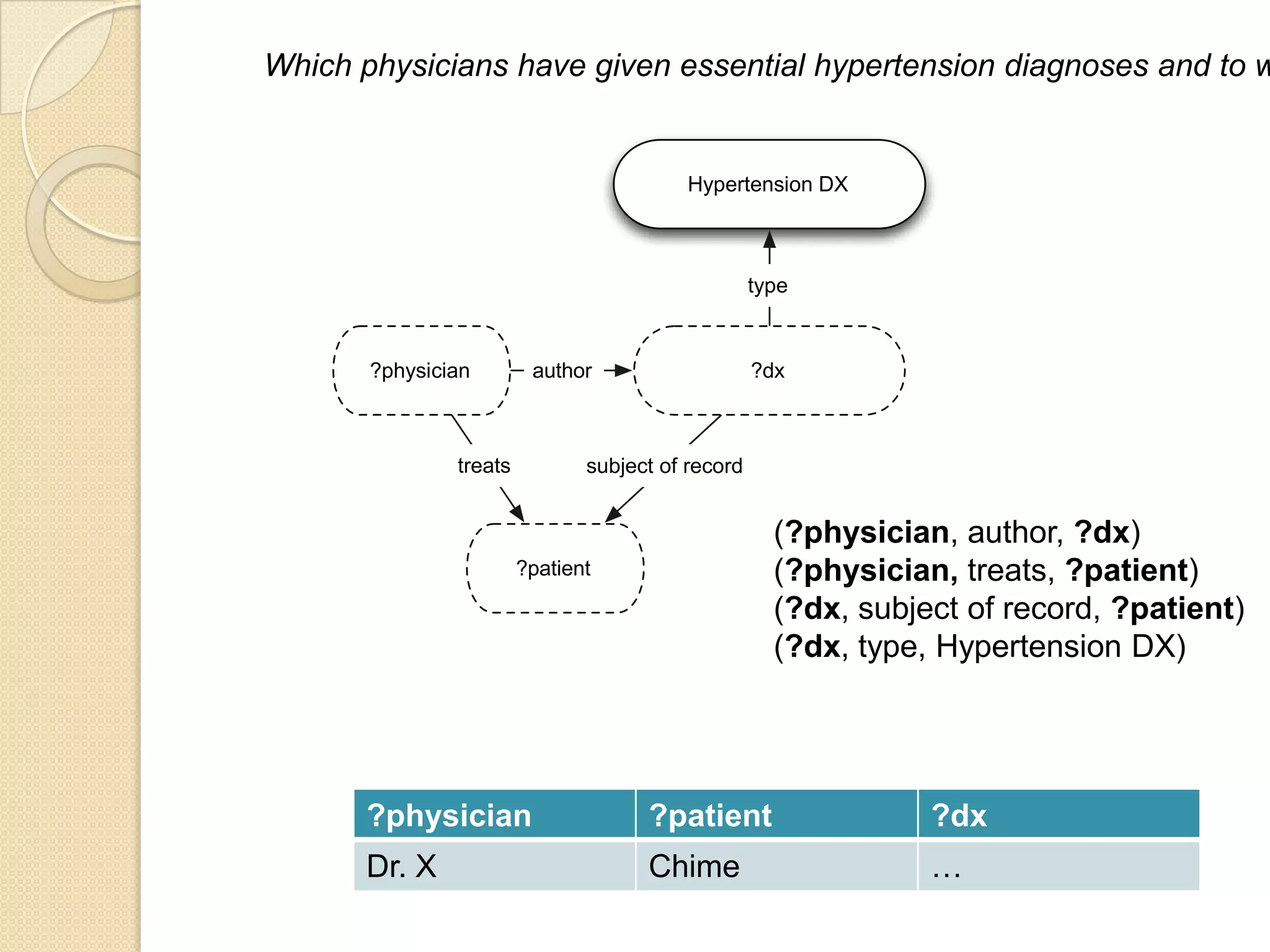
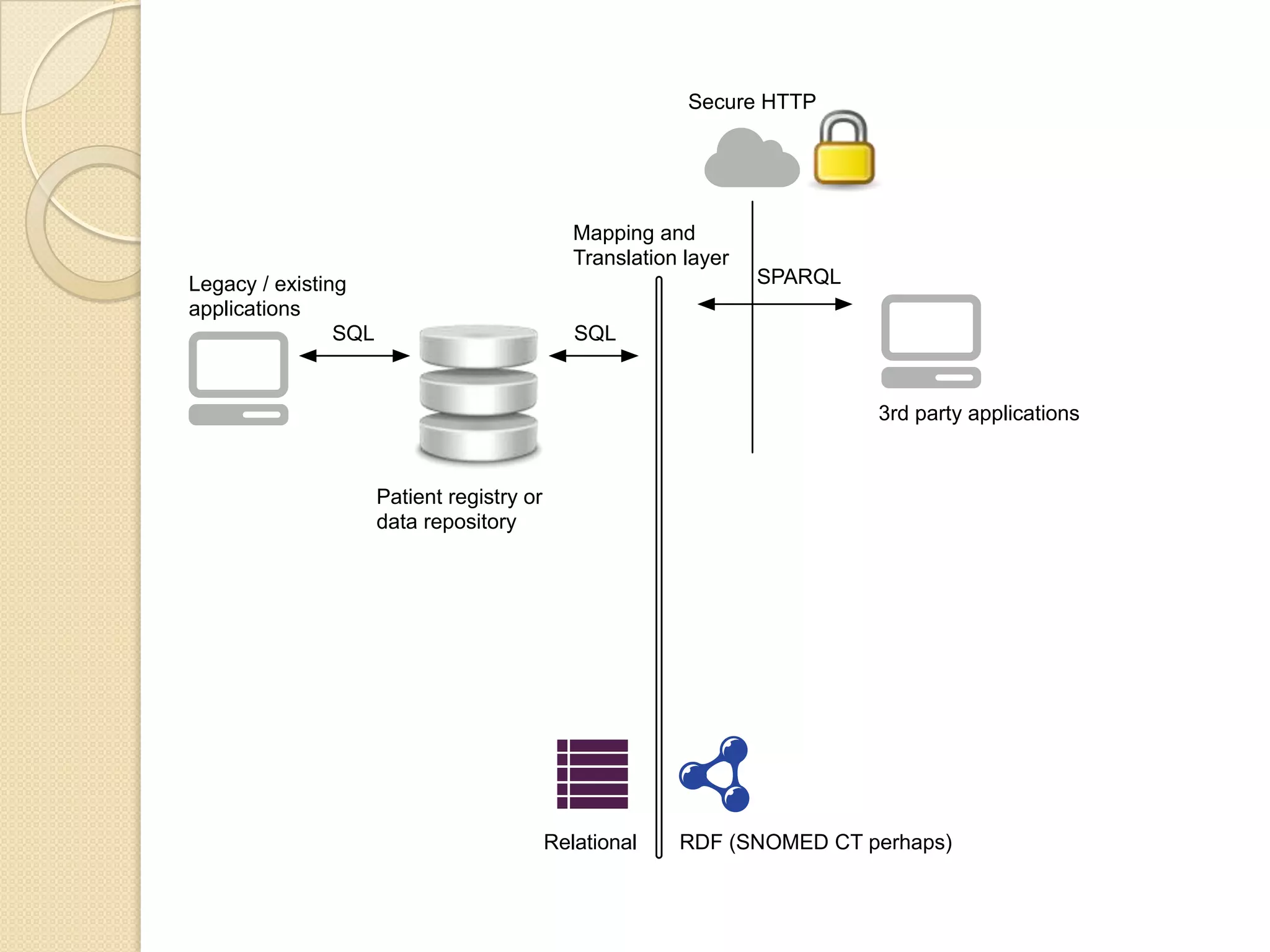
The document discusses the application of semantic web technologies in medical informatics, highlighting challenges such as semantic interoperability and the integration of electronic health records. It emphasizes the importance of structured data, controlled vocabularies, and standard querying interfaces for achieving effective data exchange across clinical systems. Key technologies mentioned include RDF, OWL, and SPARQL, with examples from institutions like Cleveland Clinic and Mayo Clinic illustrating practical implementation.