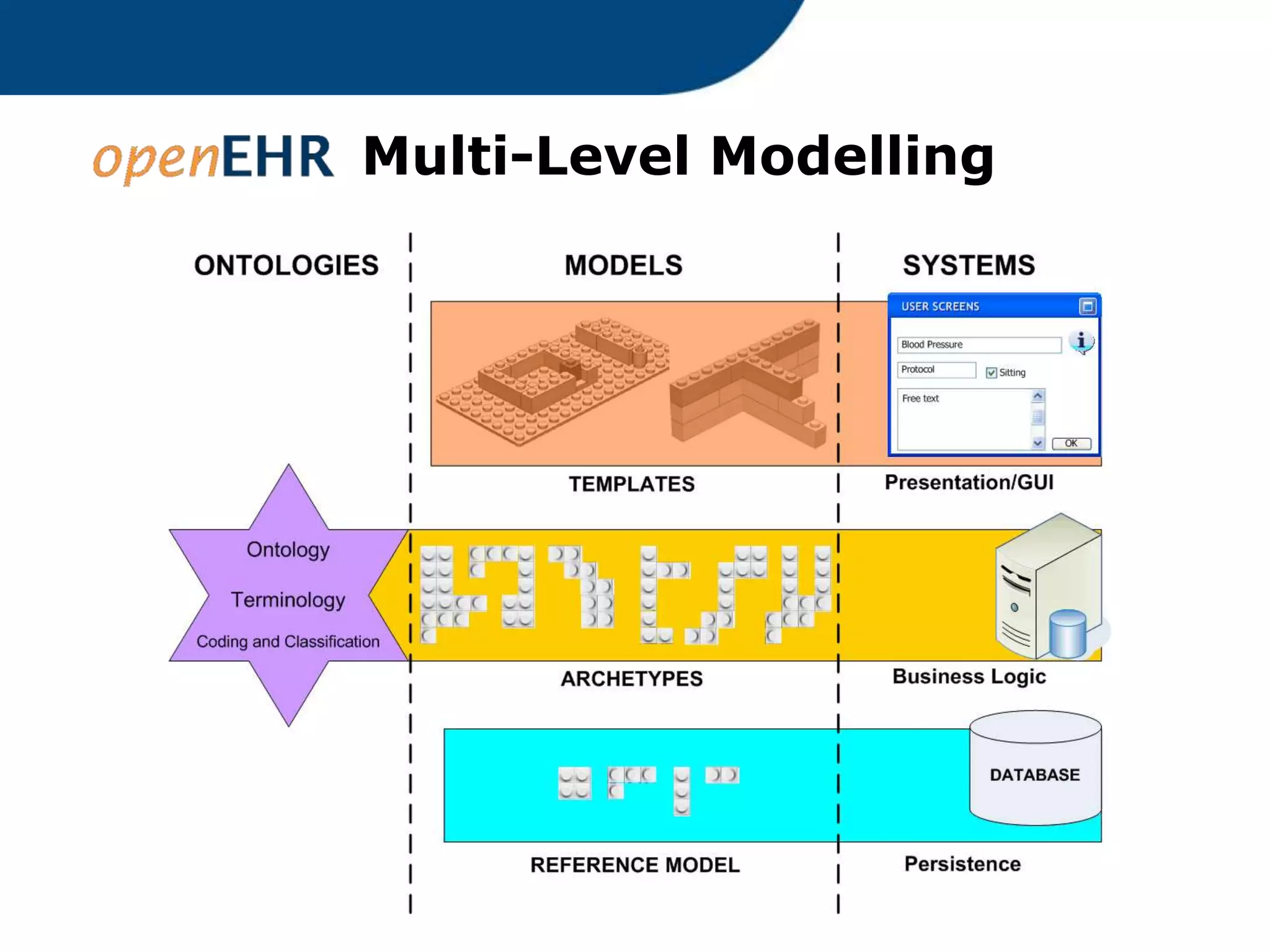
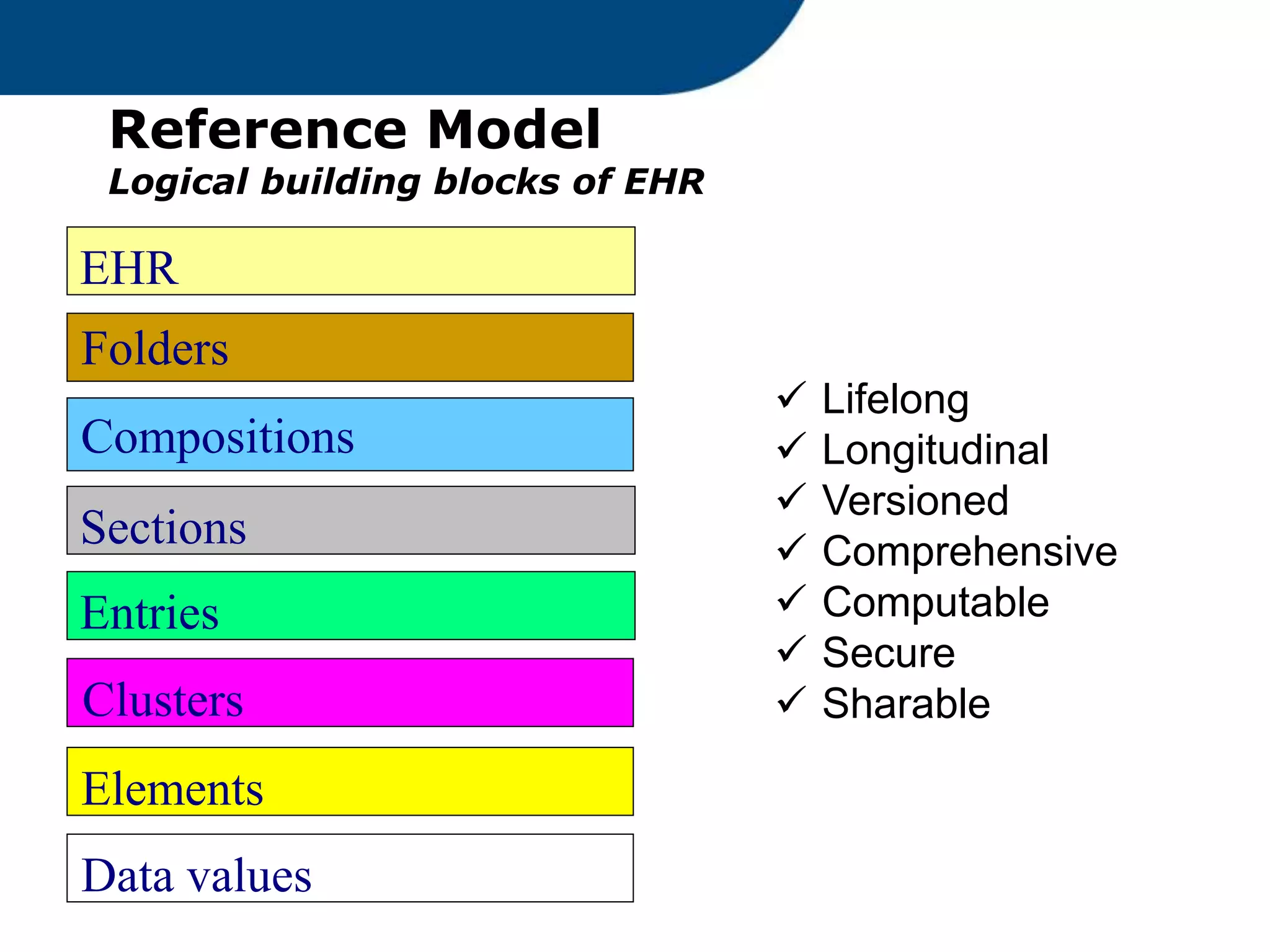
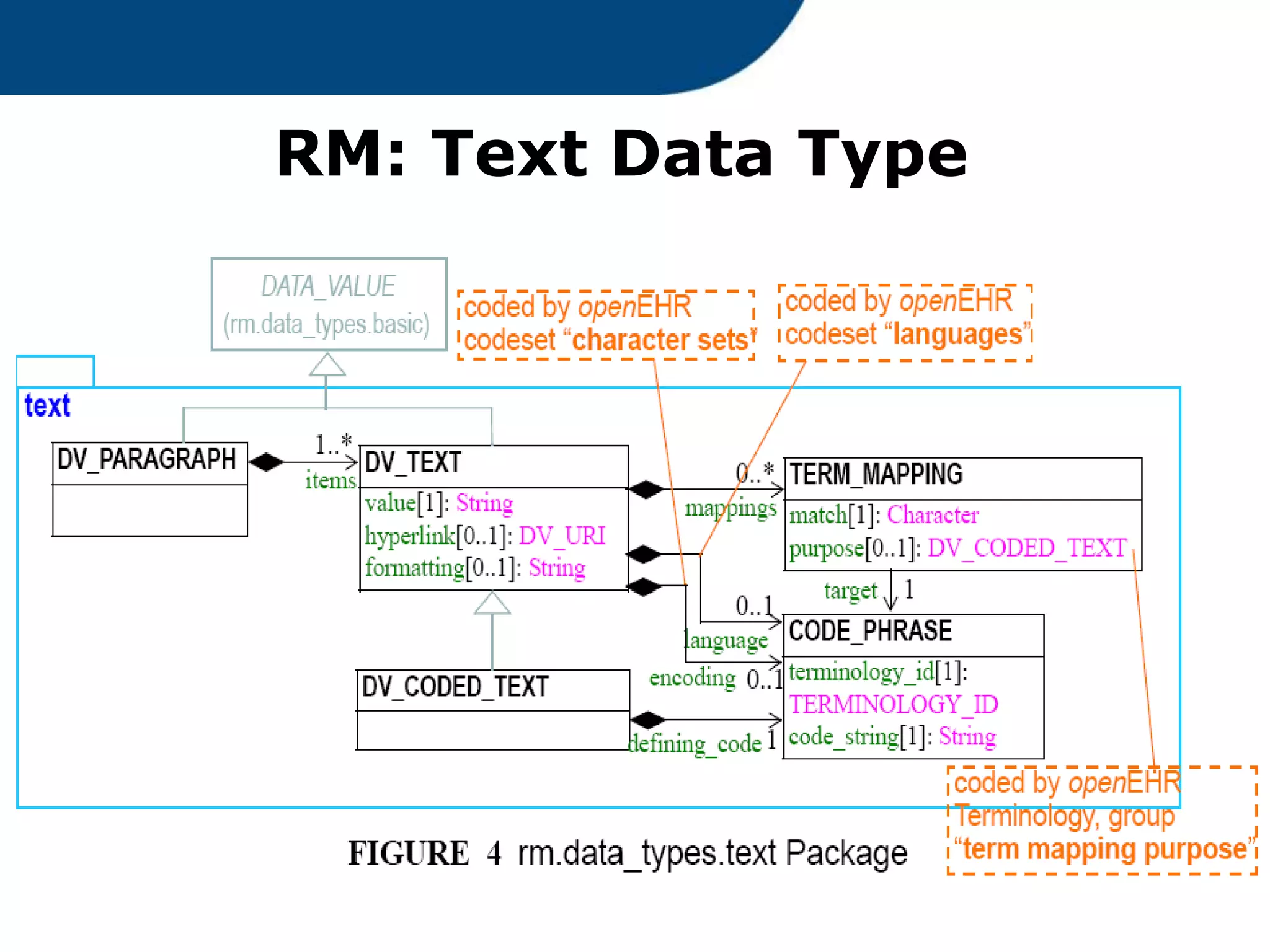
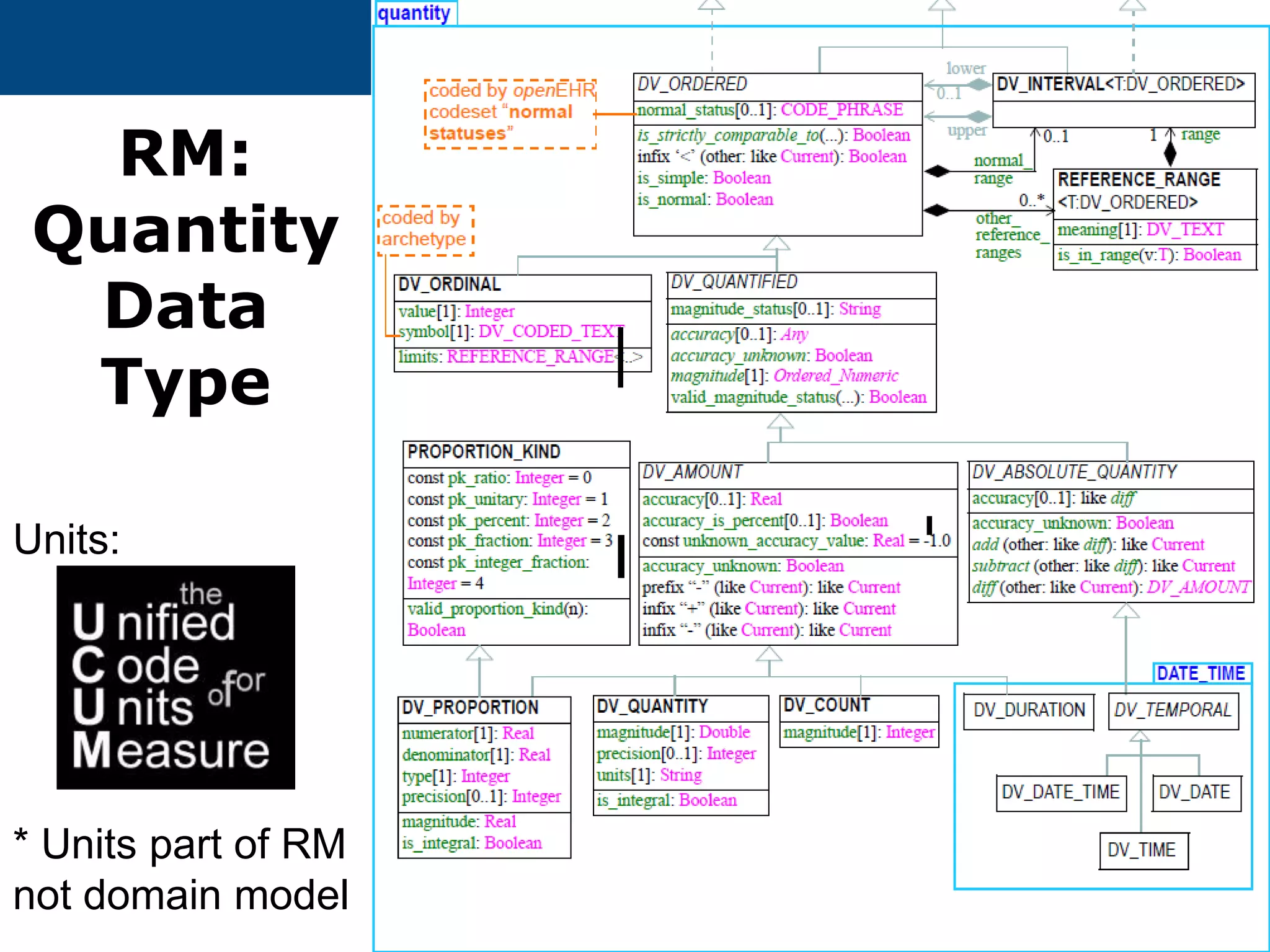
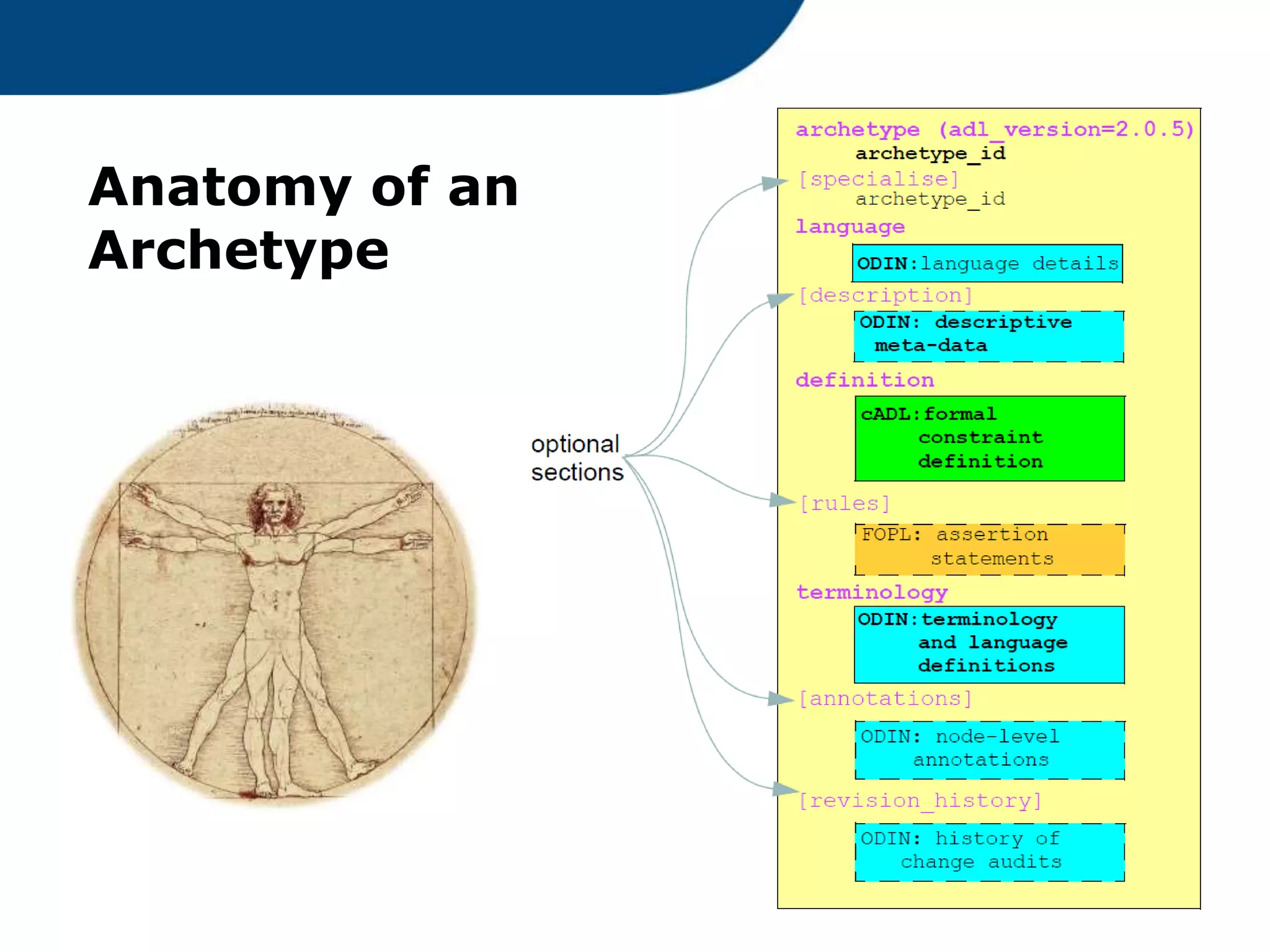
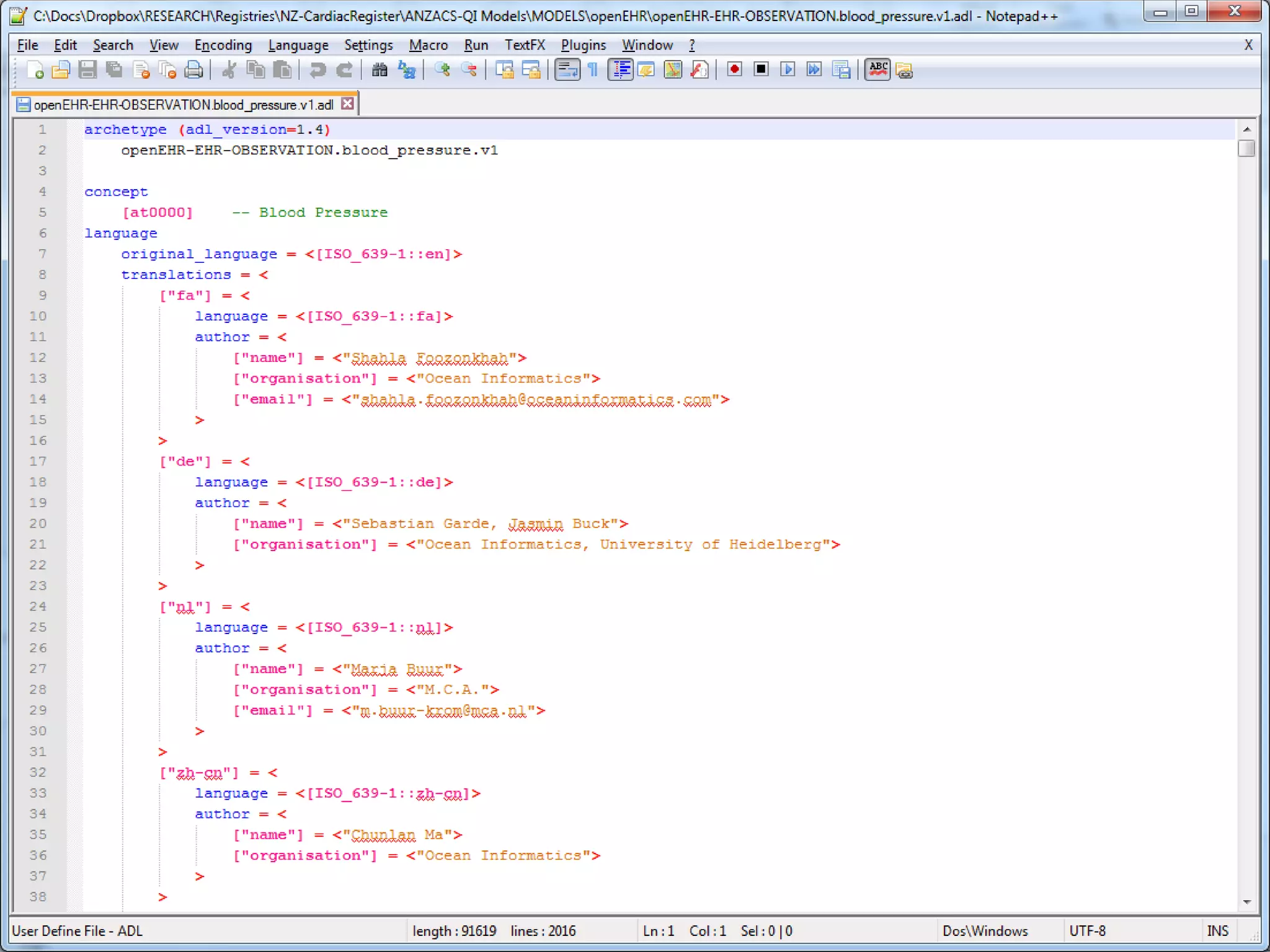
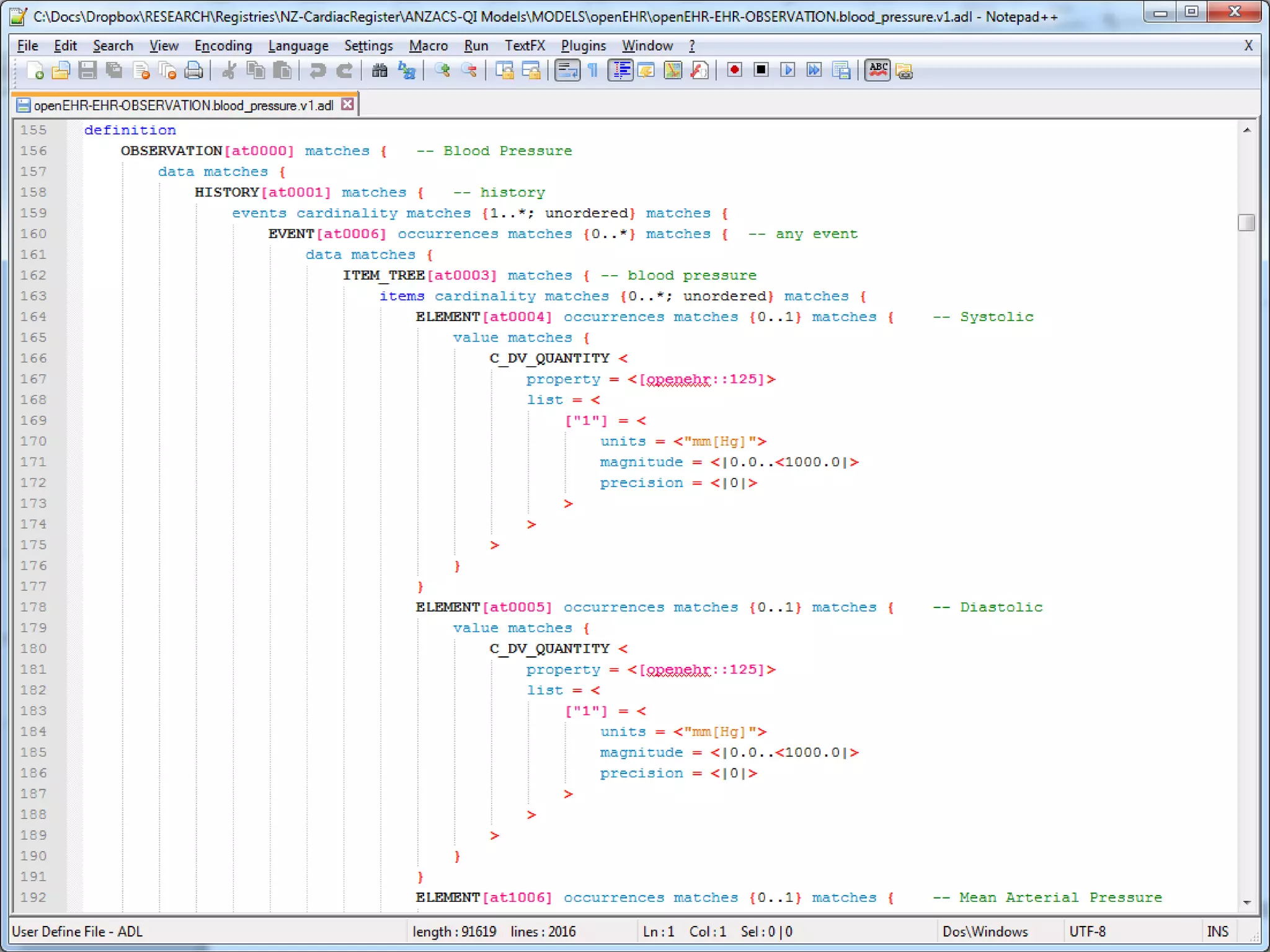
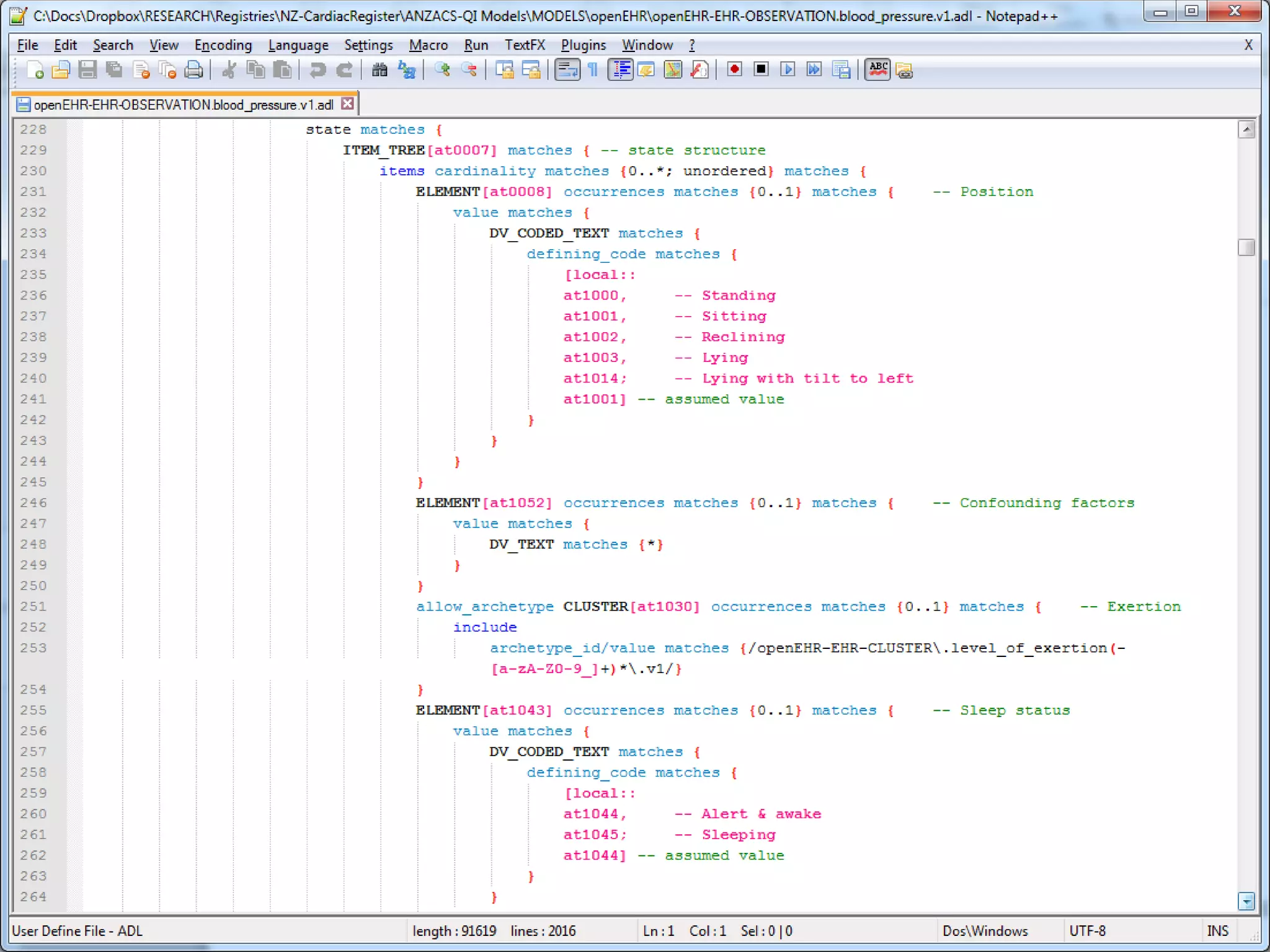
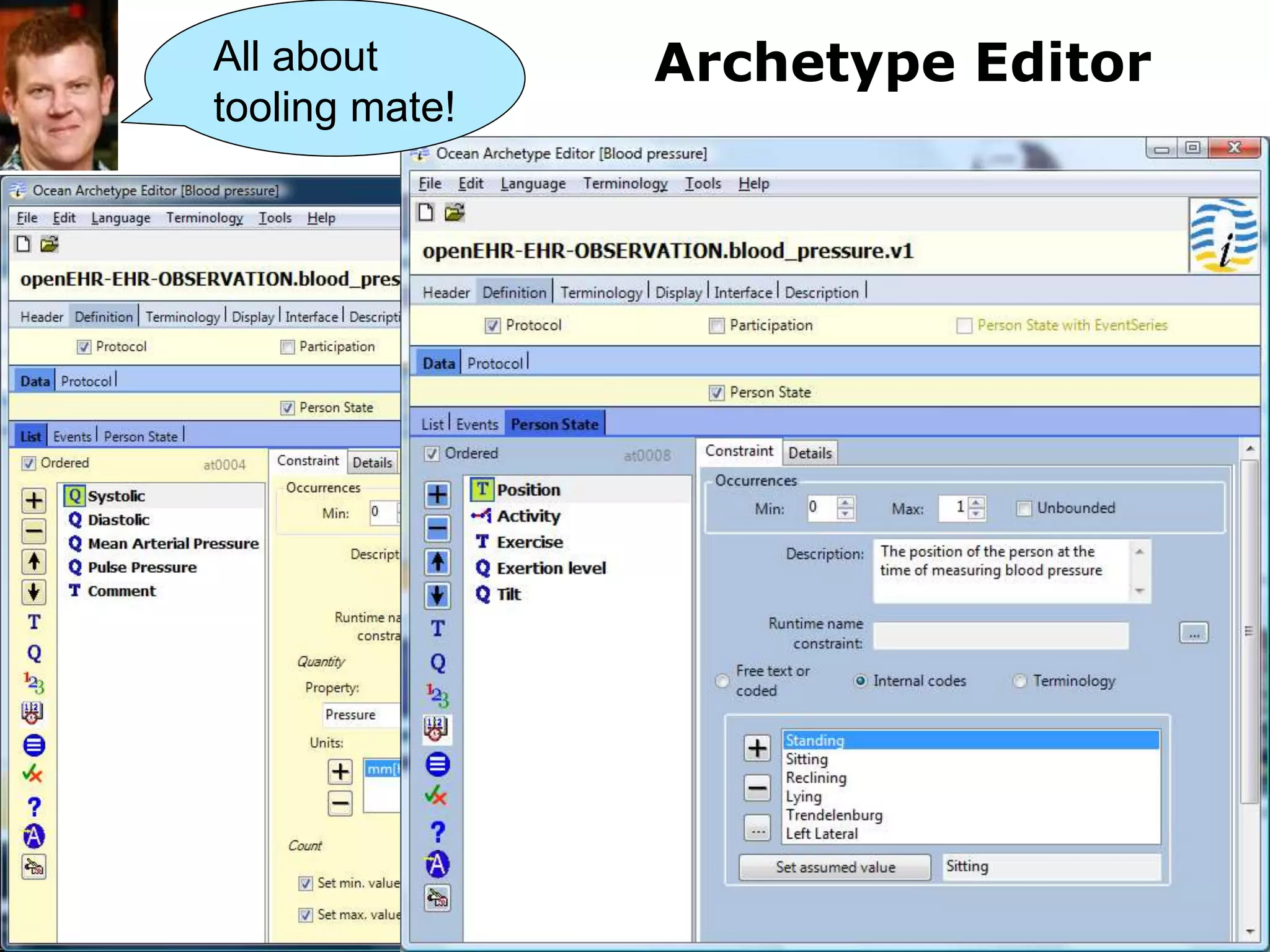
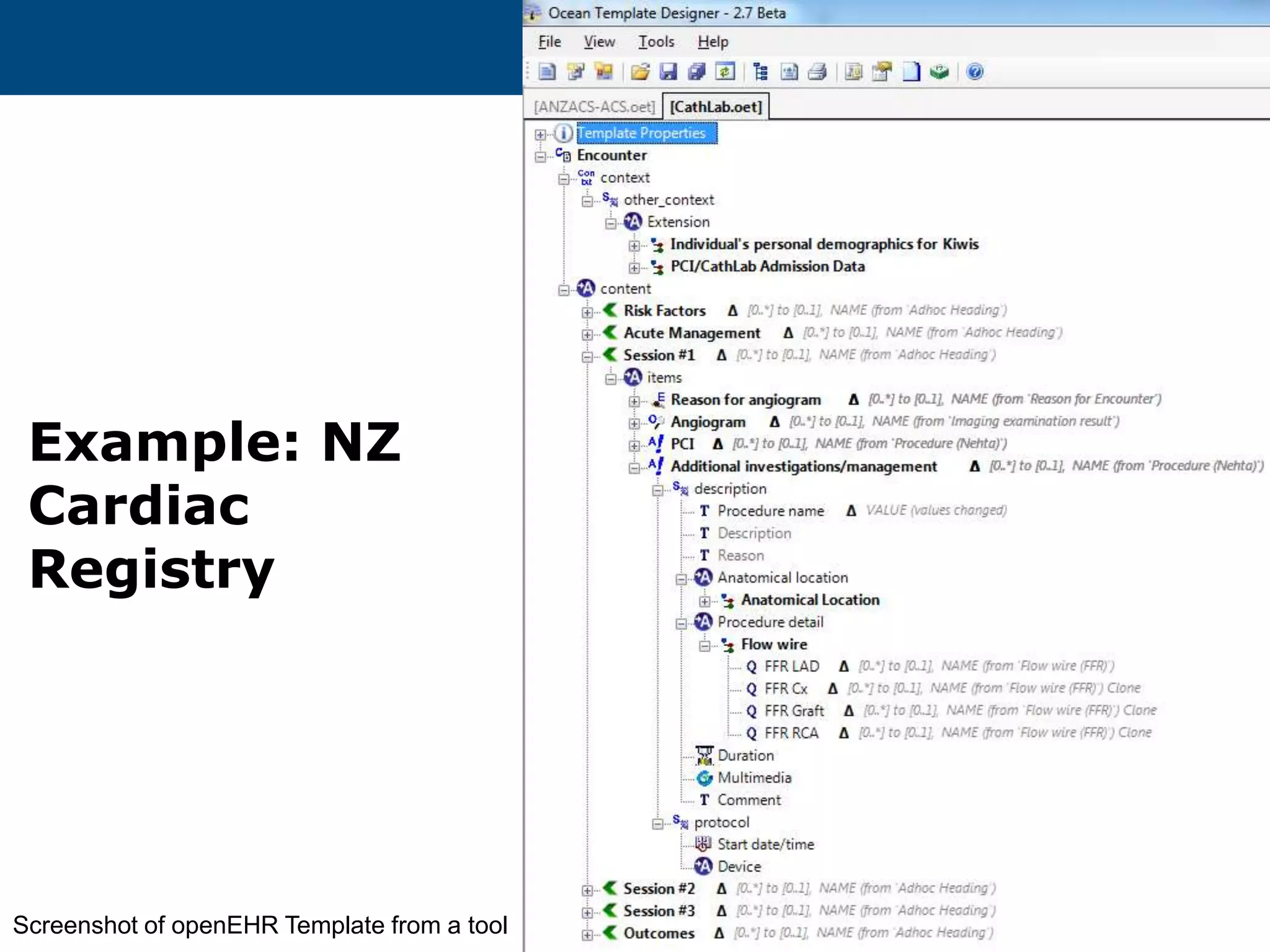
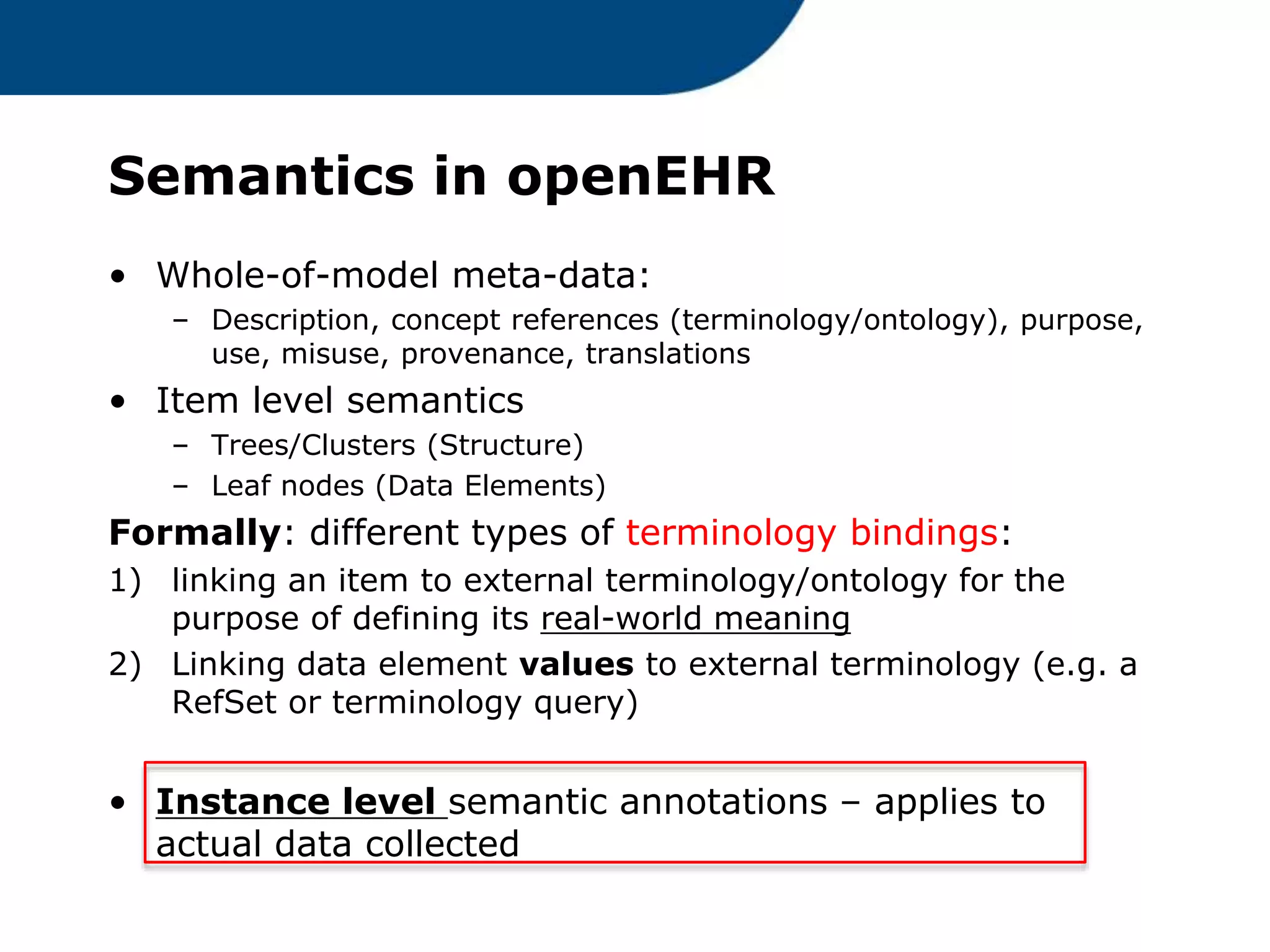
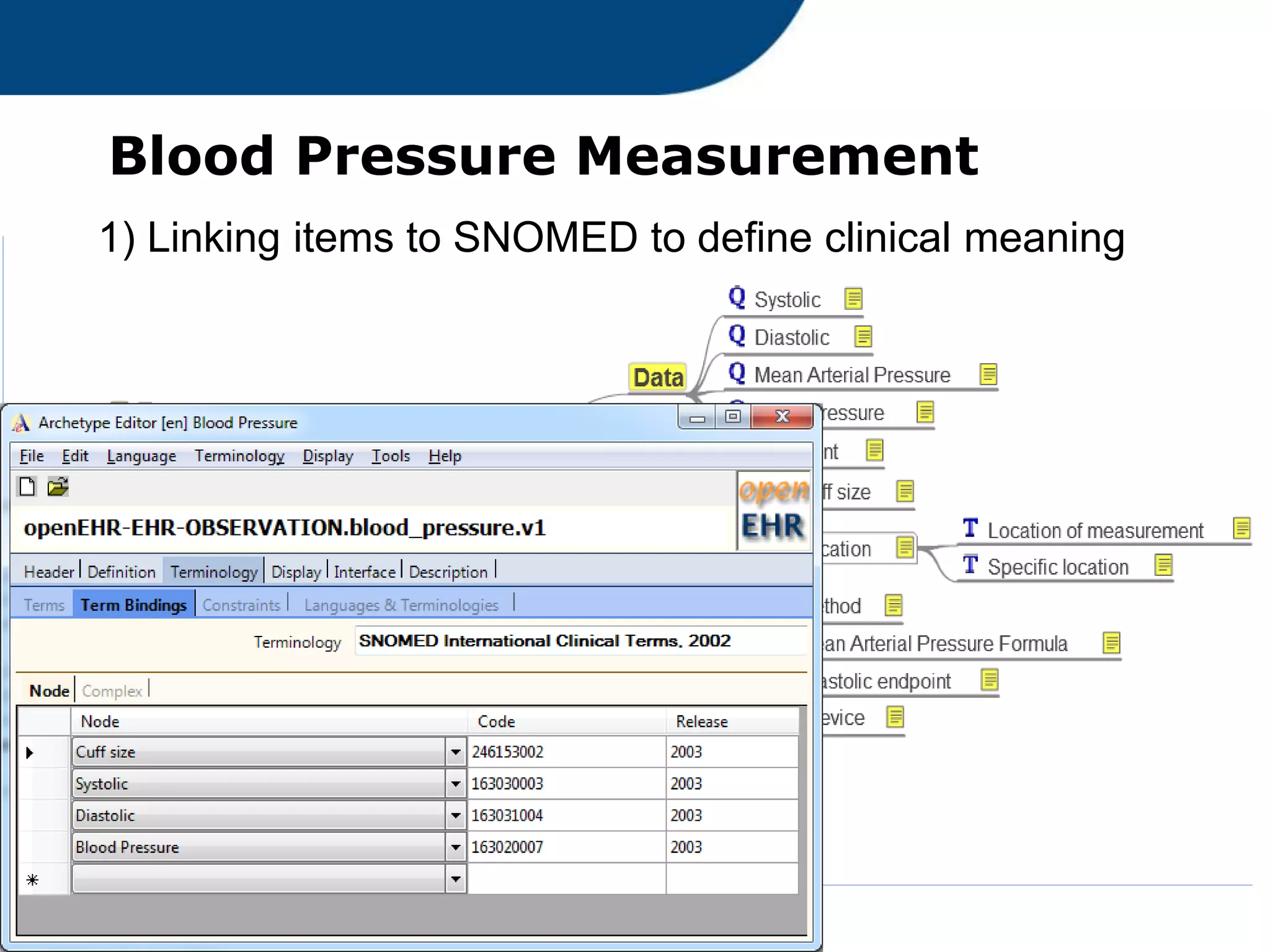
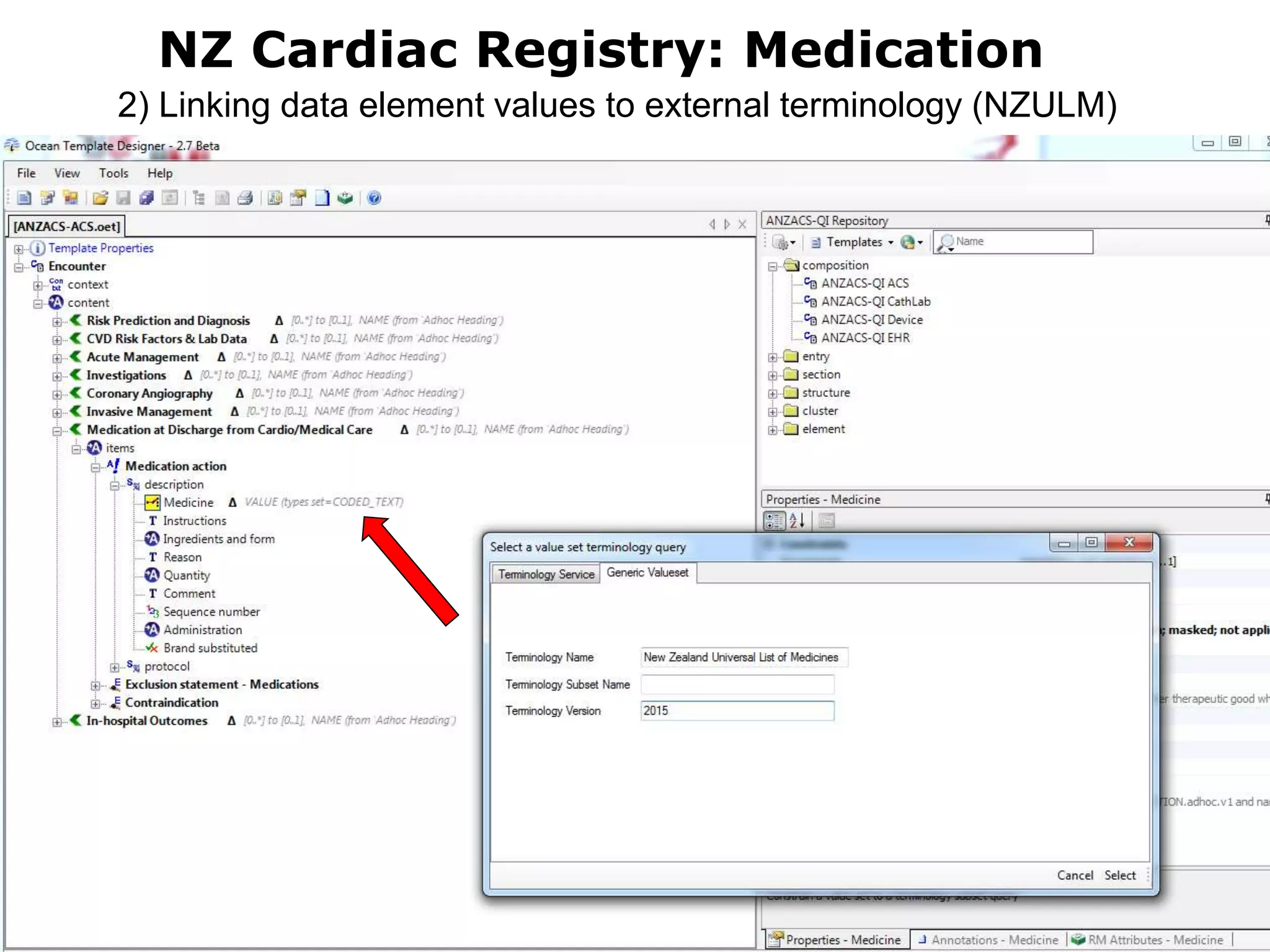
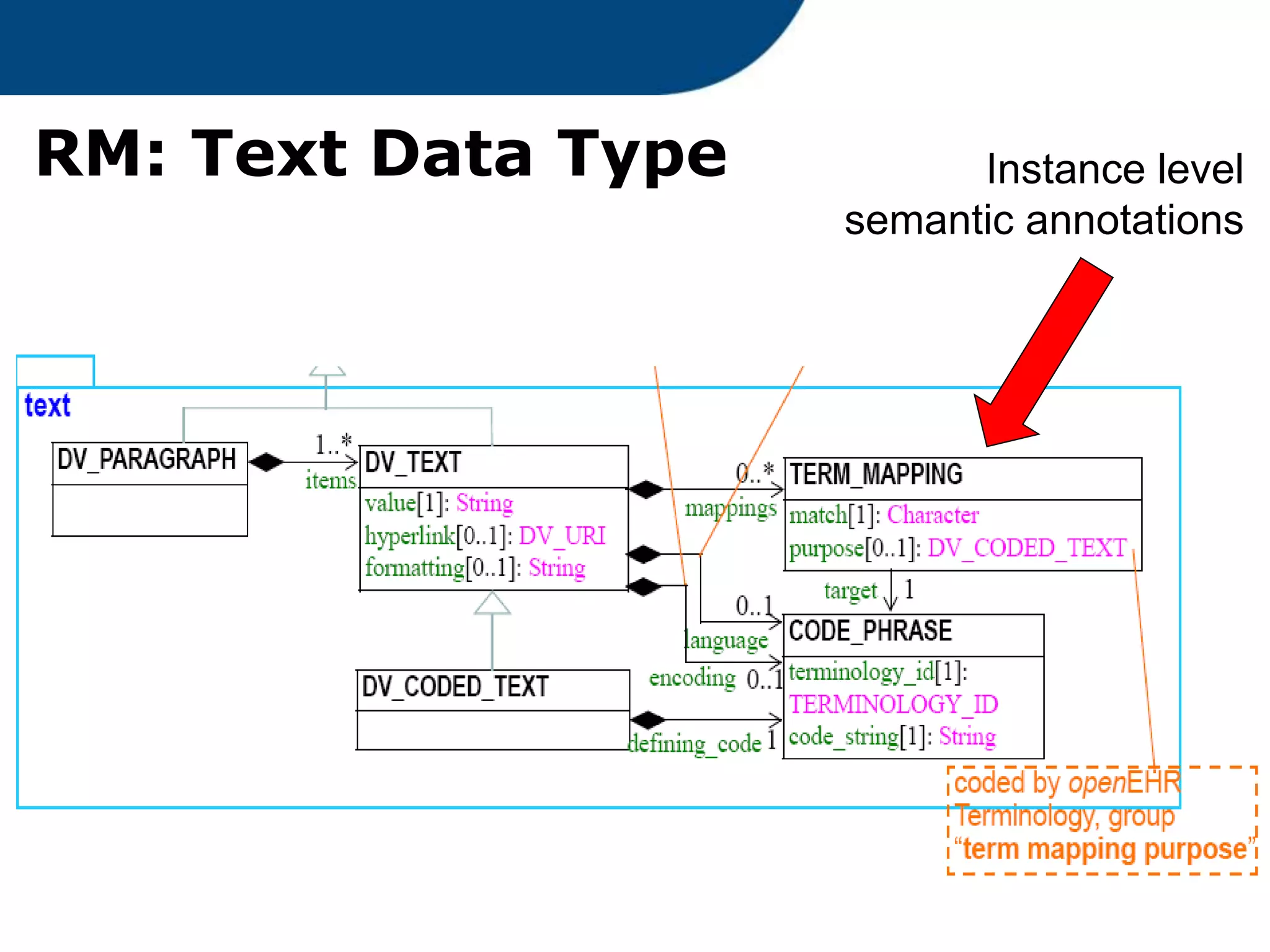
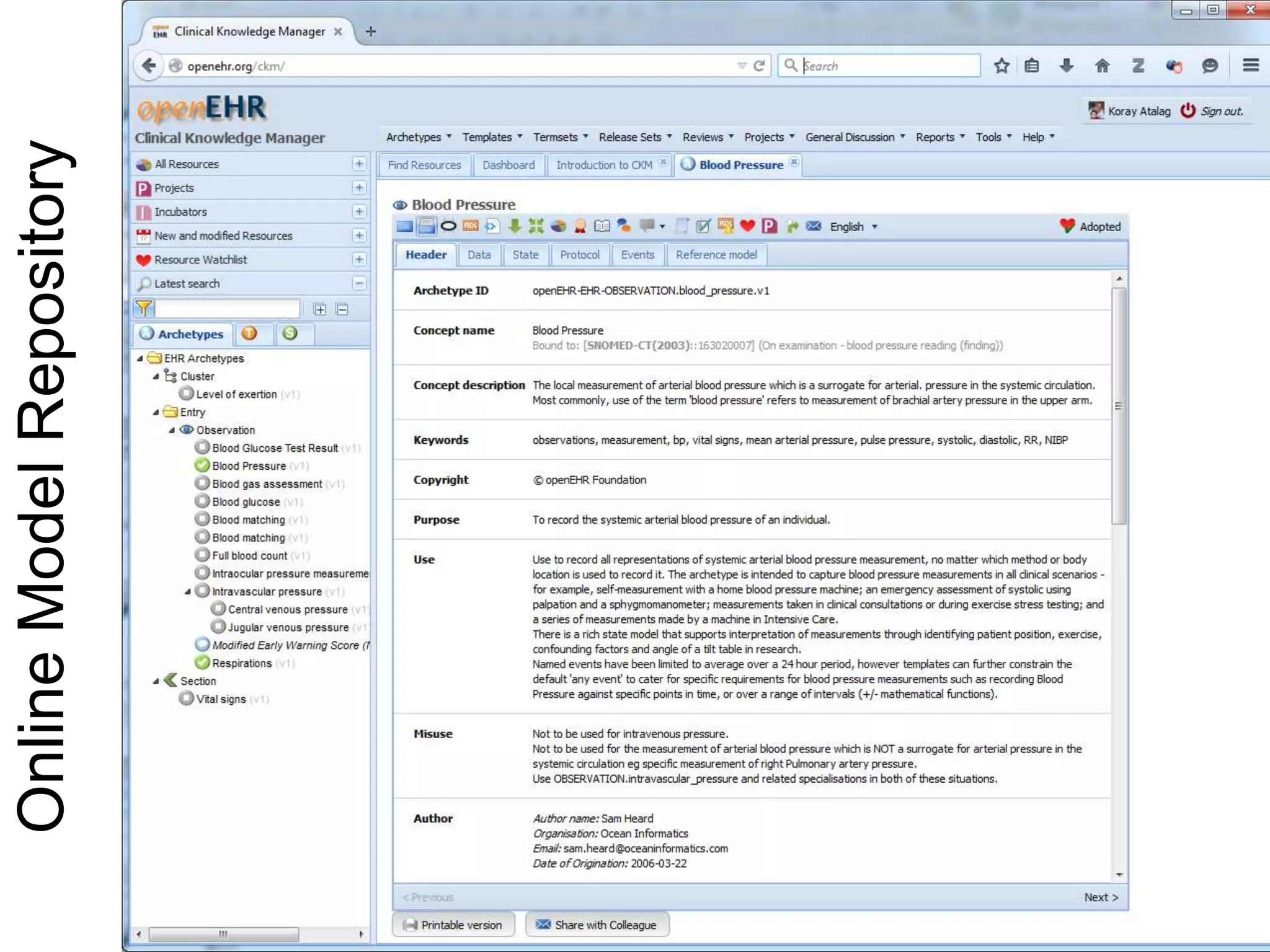
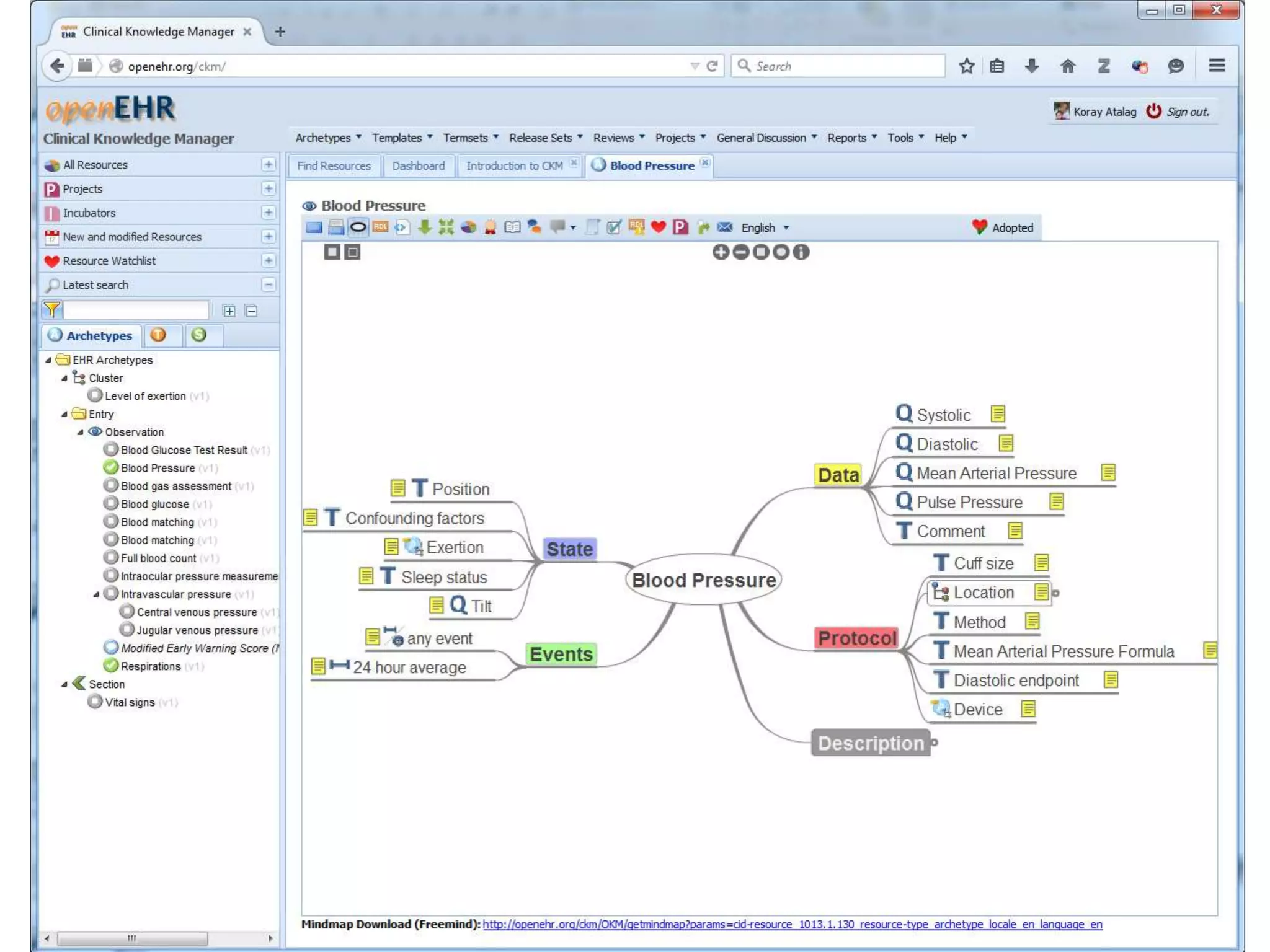
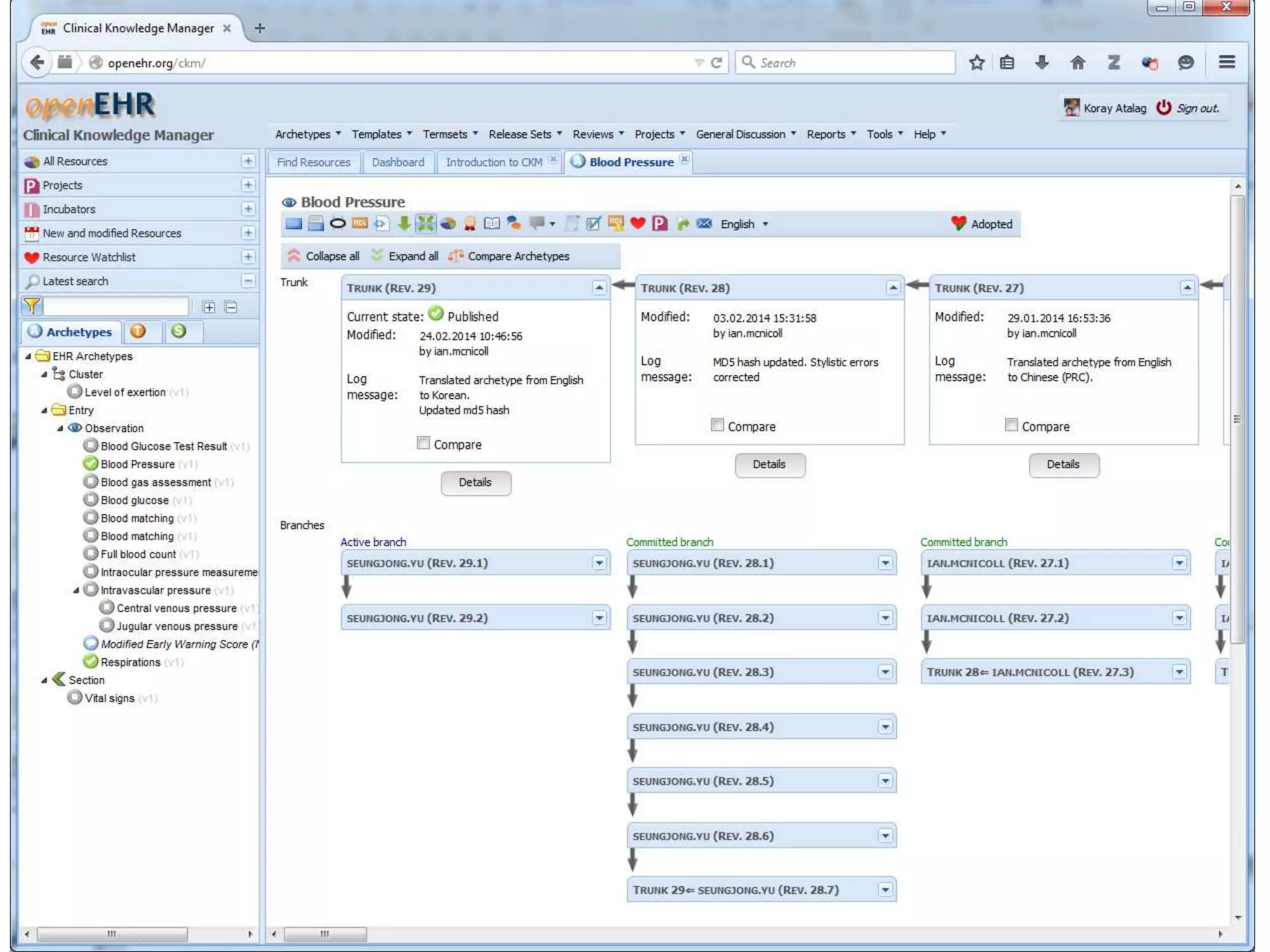
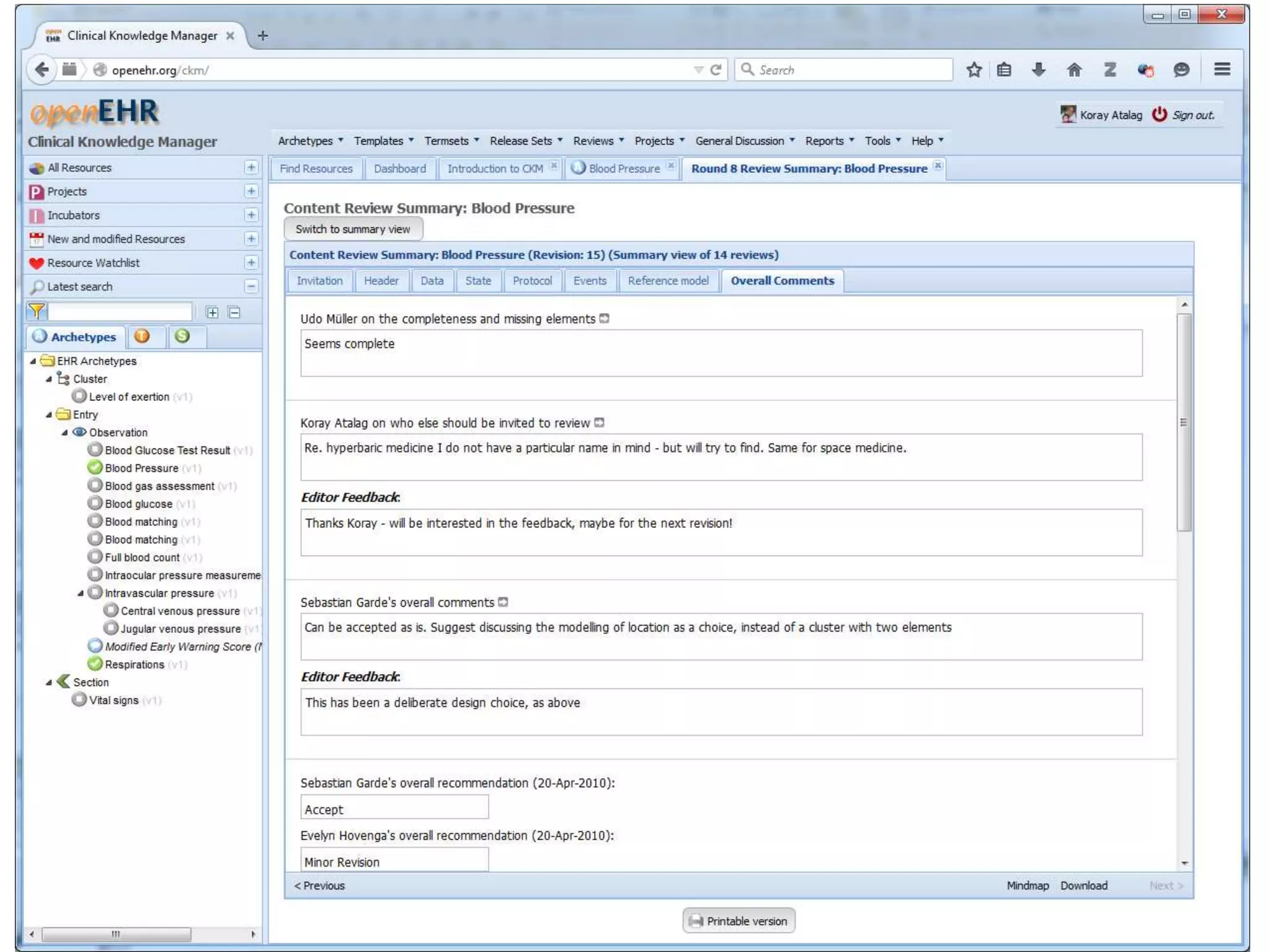
The document provides an overview of the OpenEHR framework, which is designed for representing health information through a multi-level modeling approach and archetypes. OpenEHR, established in 2001, emphasizes the separation of clinical and technical domains and offers tools for modeling, governance, and repository management. The framework is supported by an international community and is extensively used in research to create person-centered and computable health records.