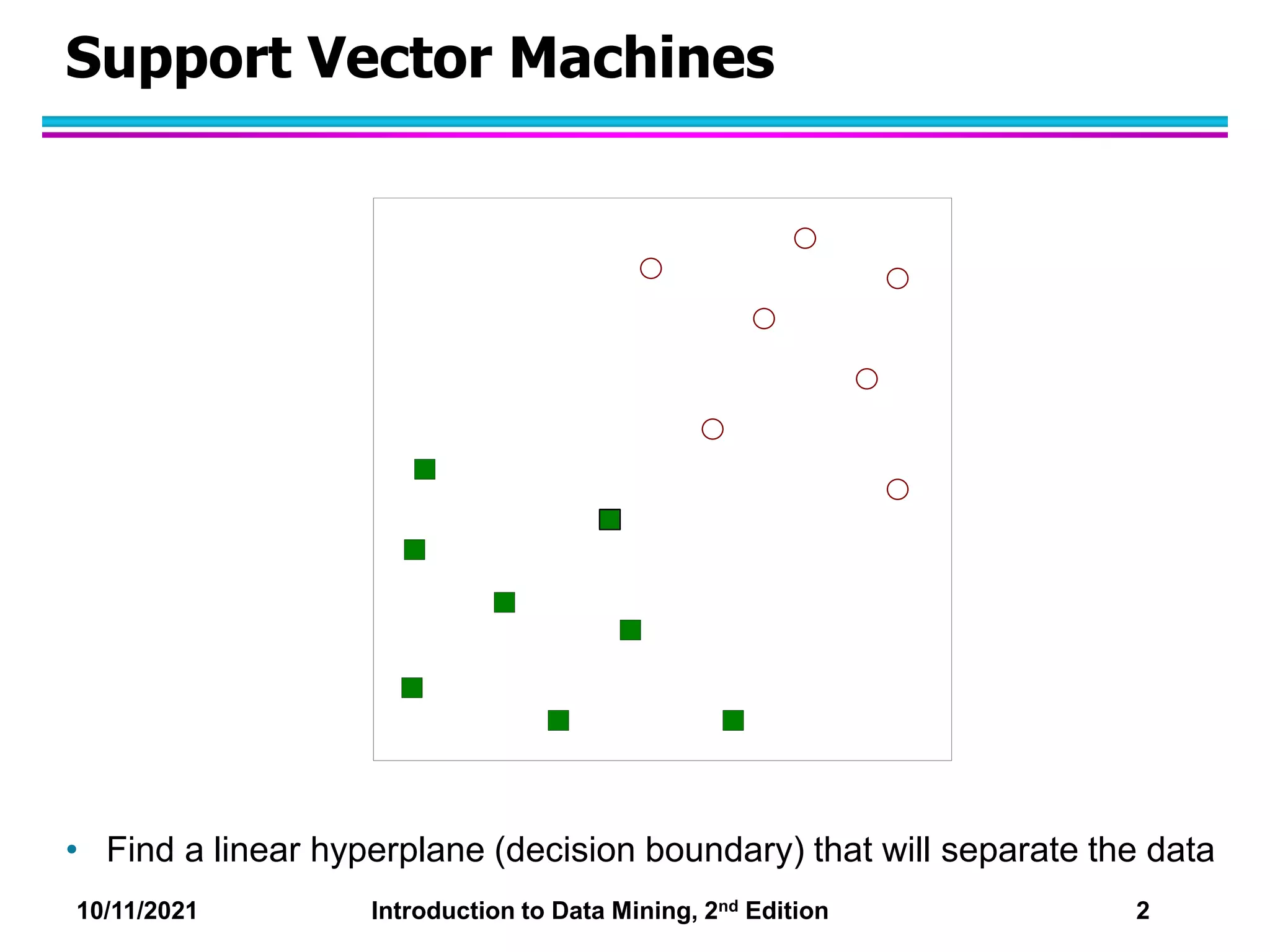
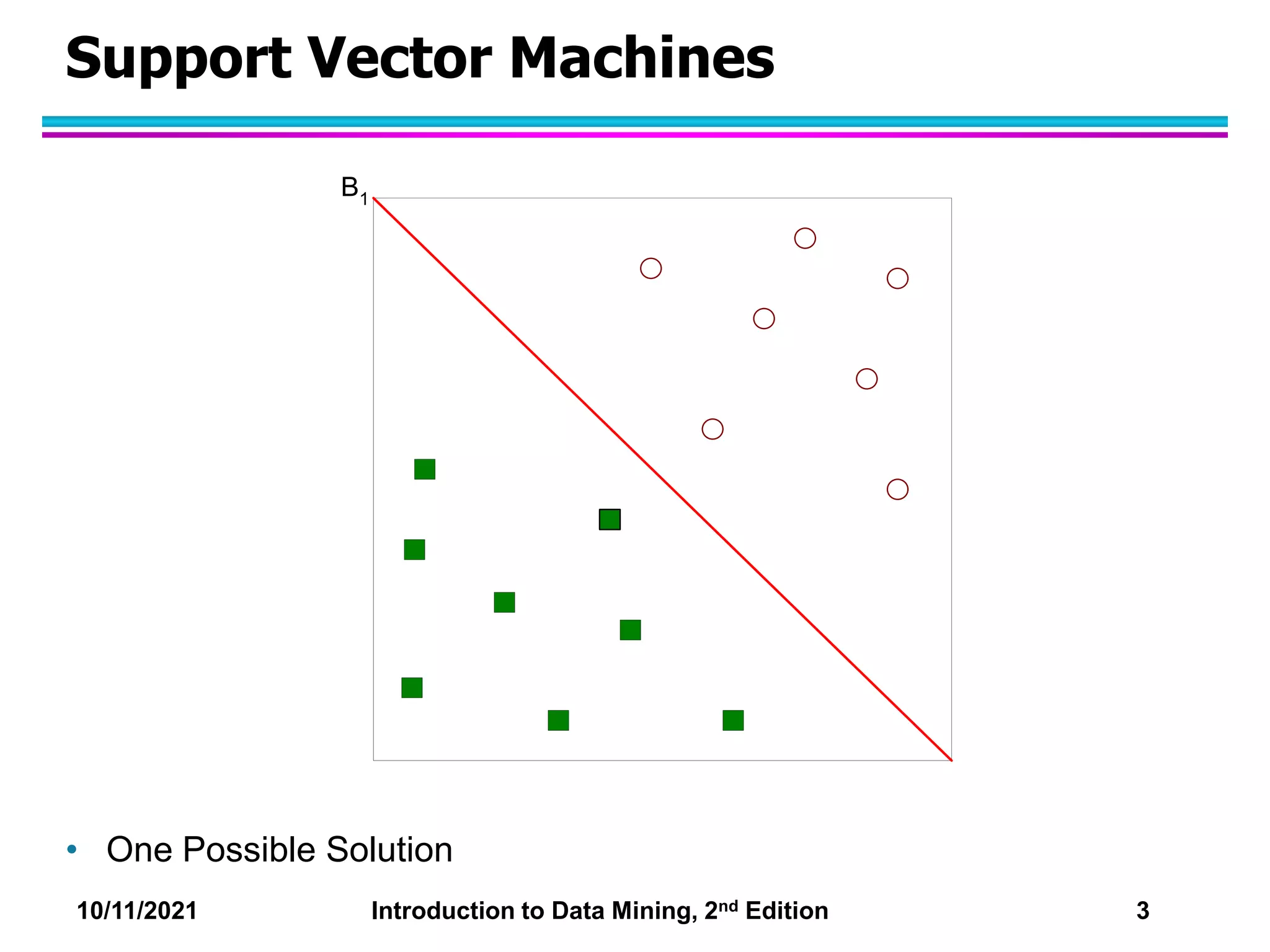
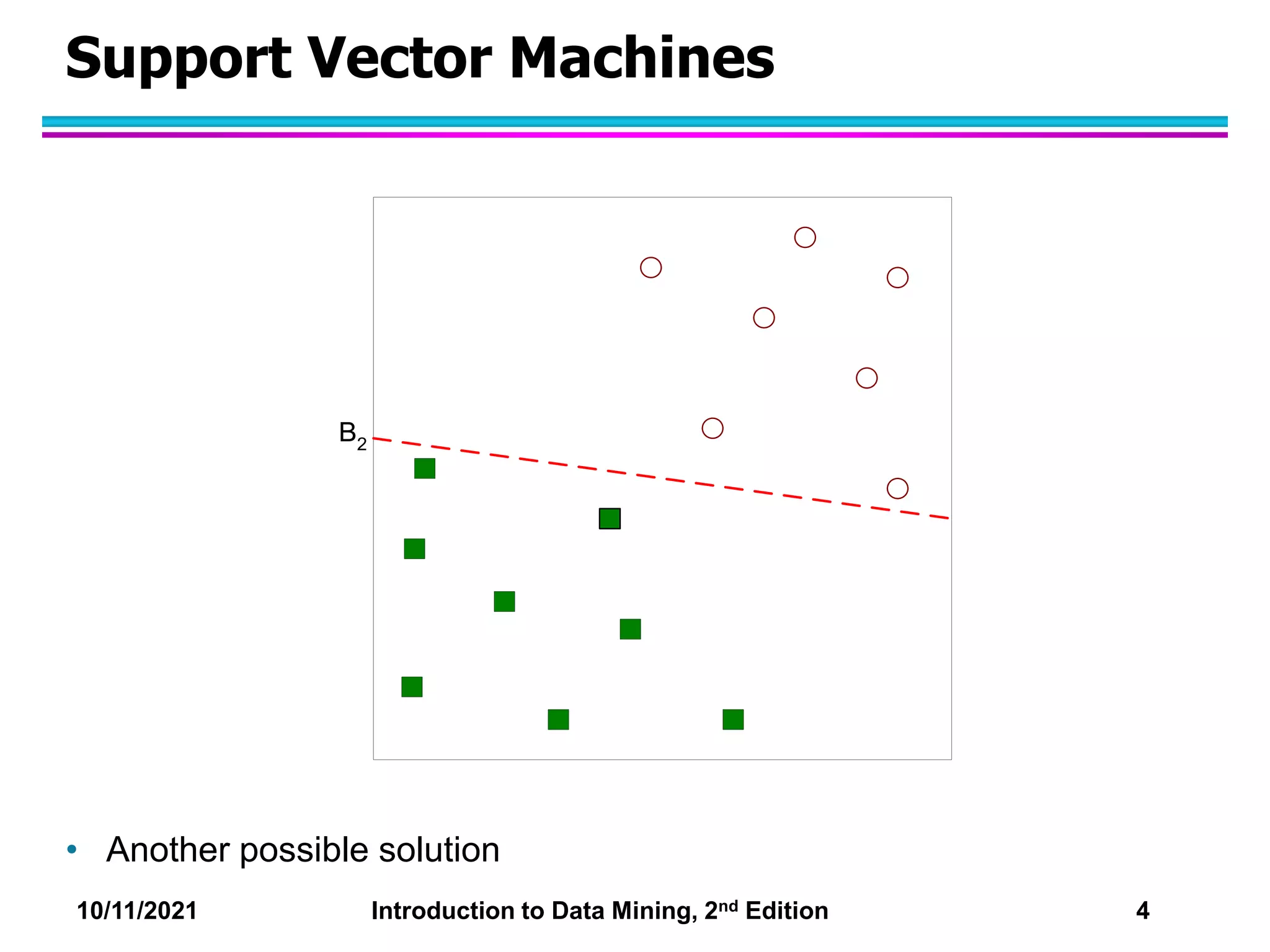
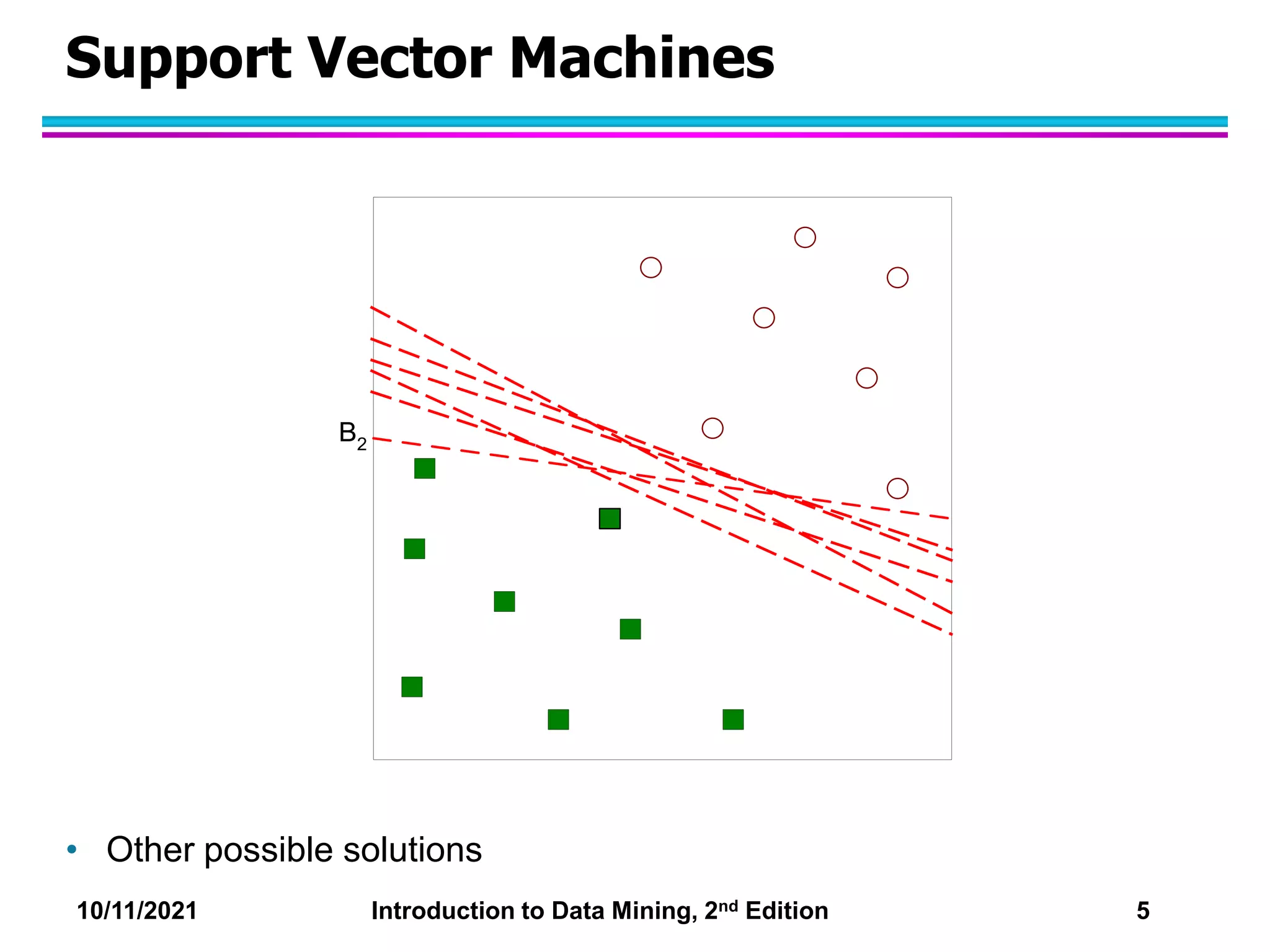
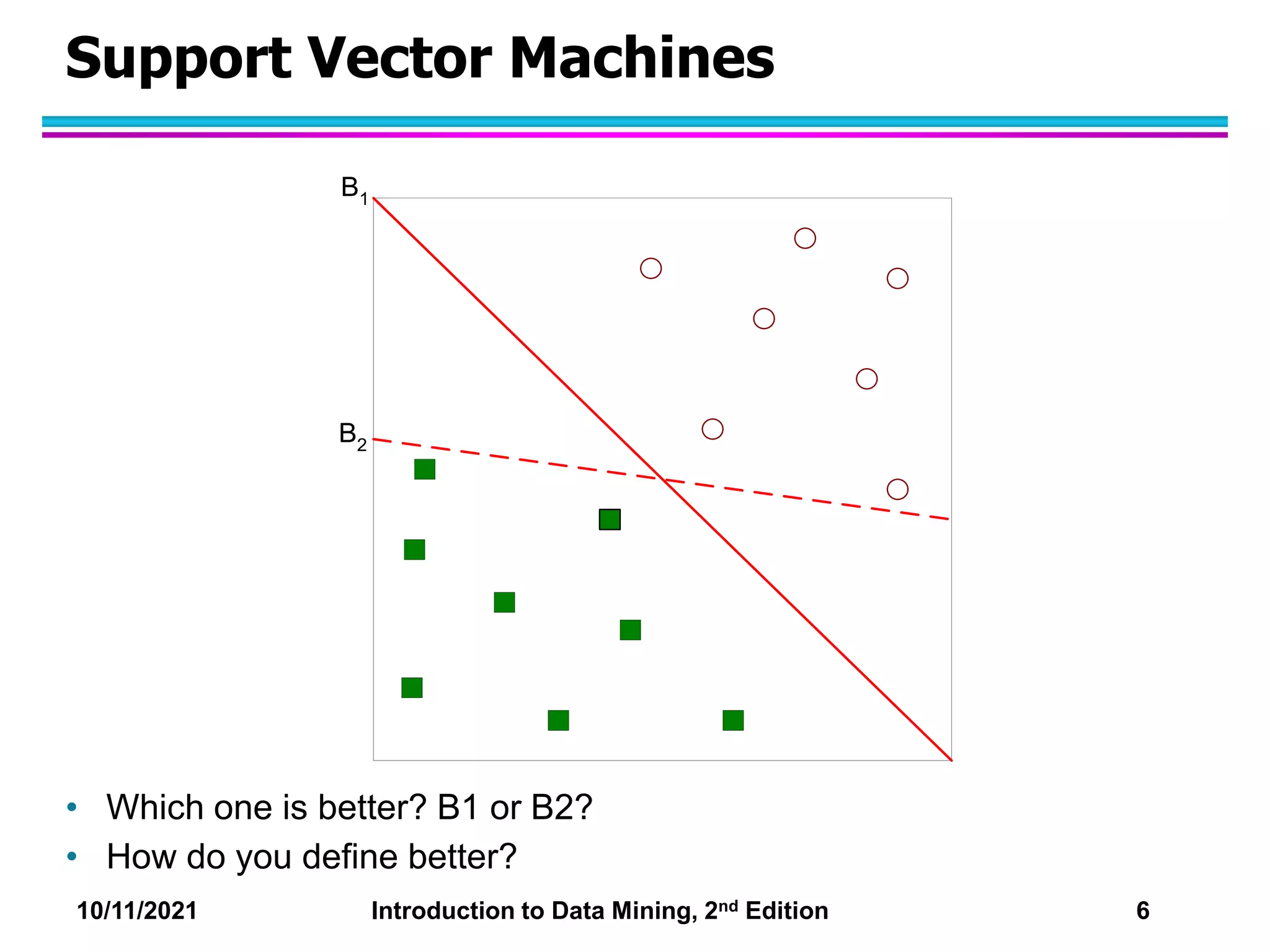
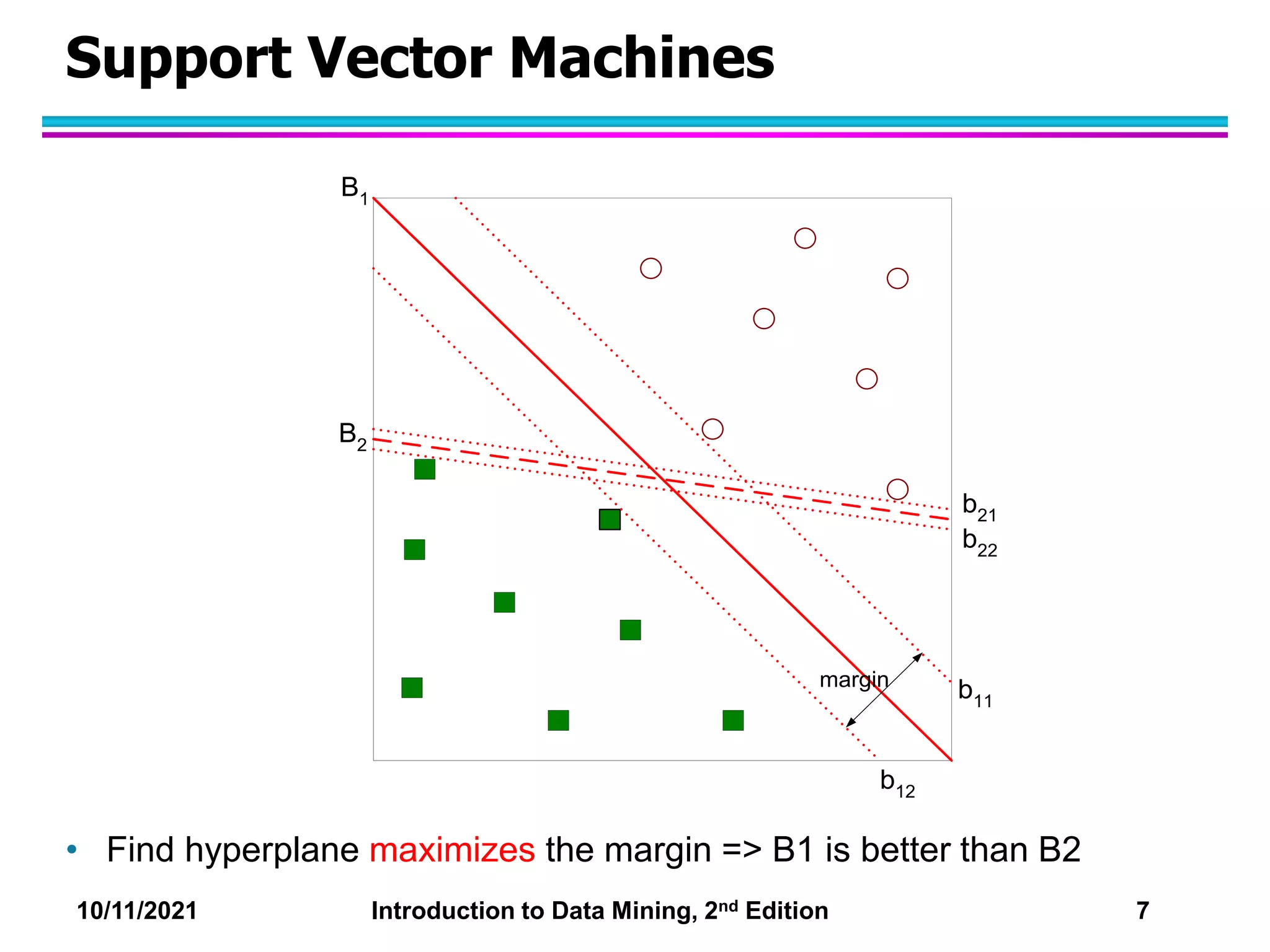
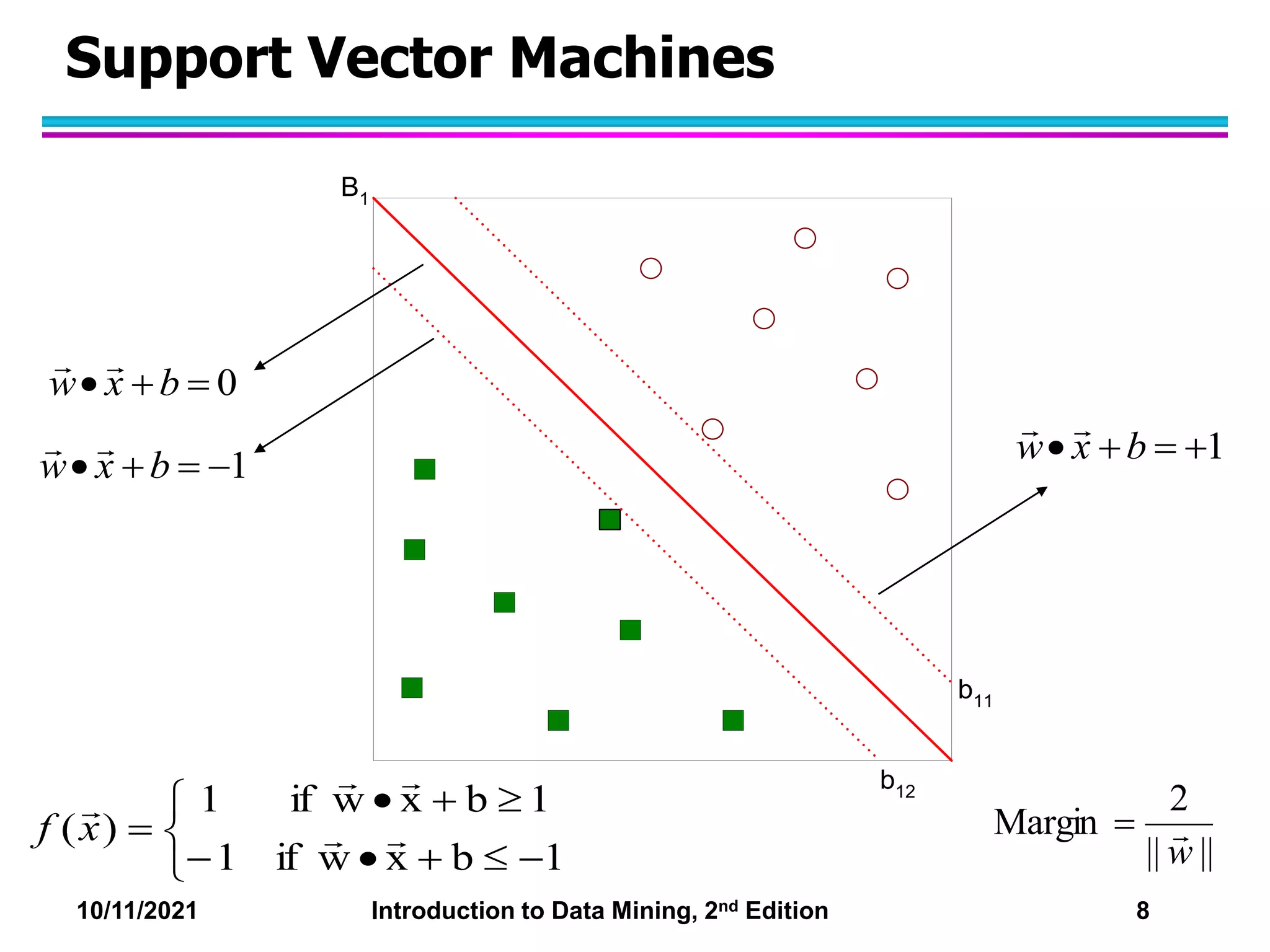
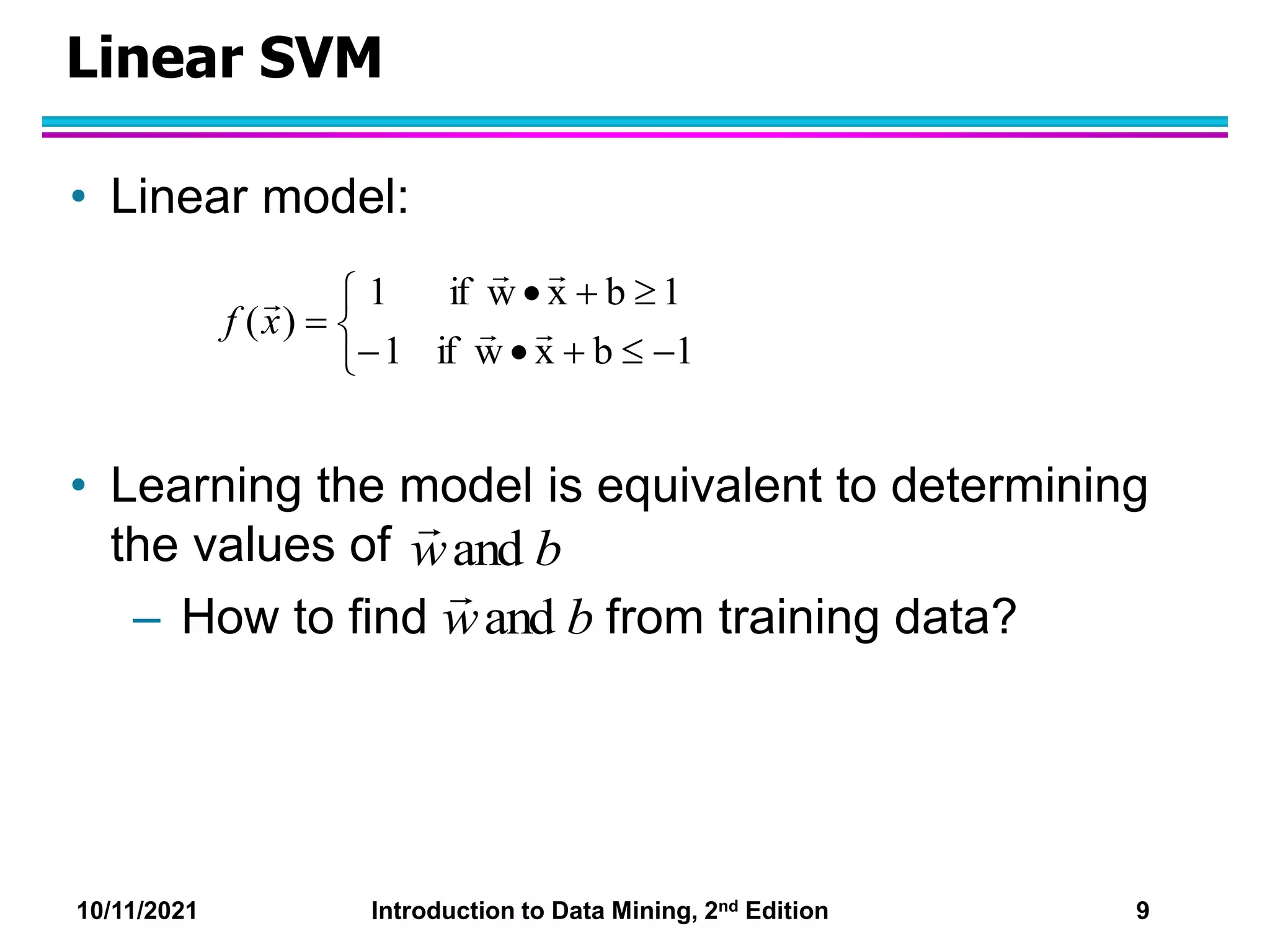
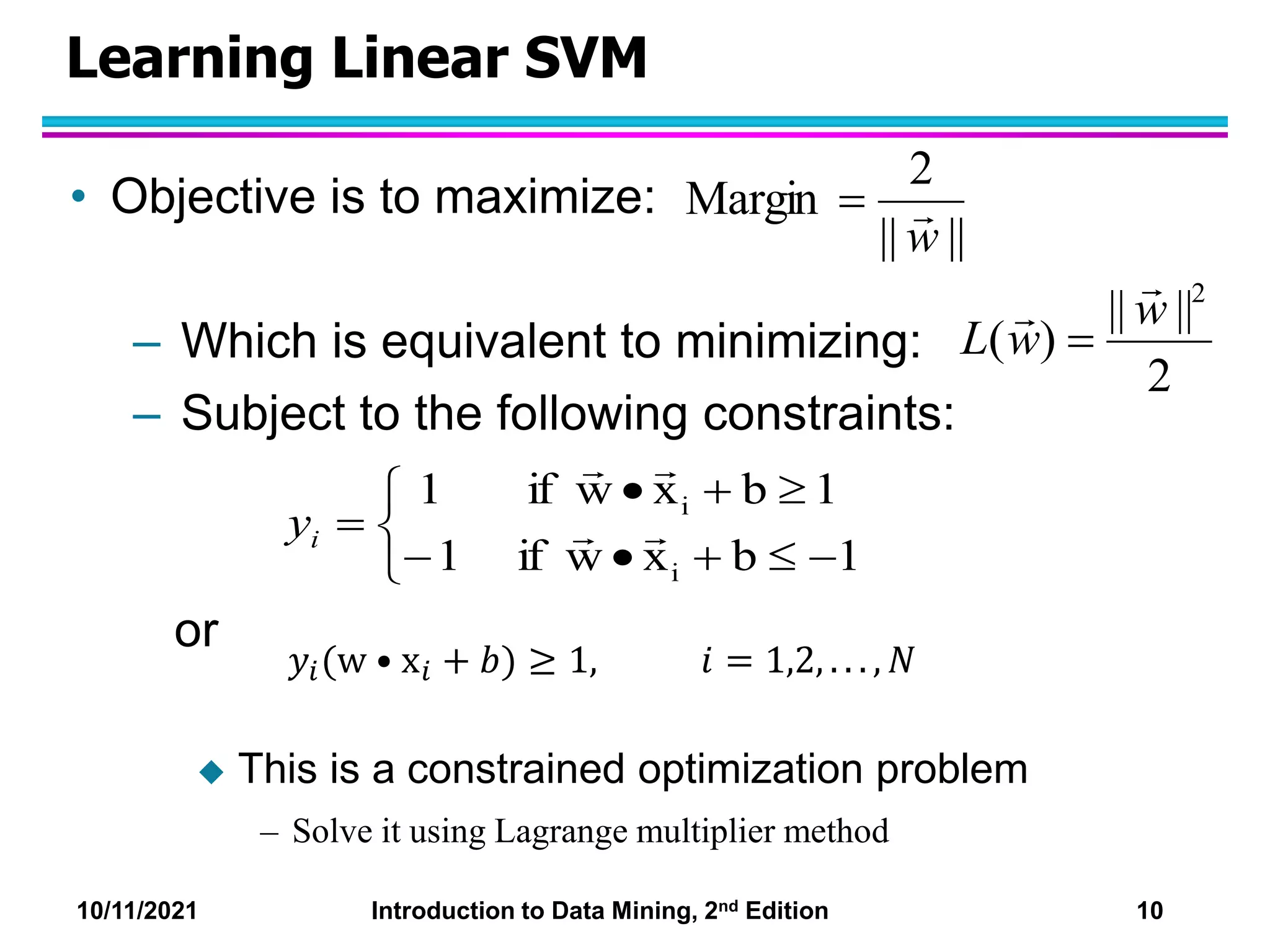
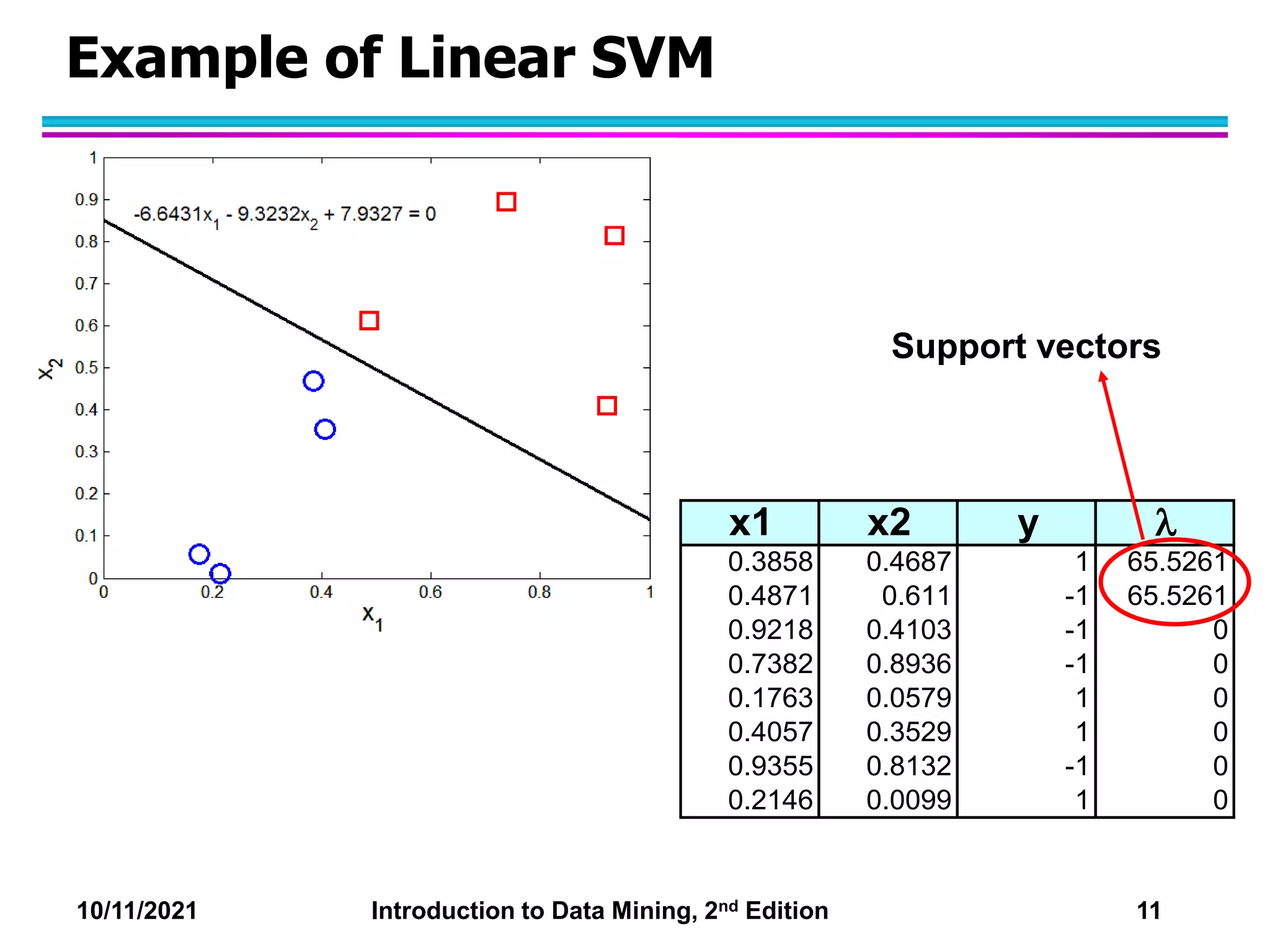
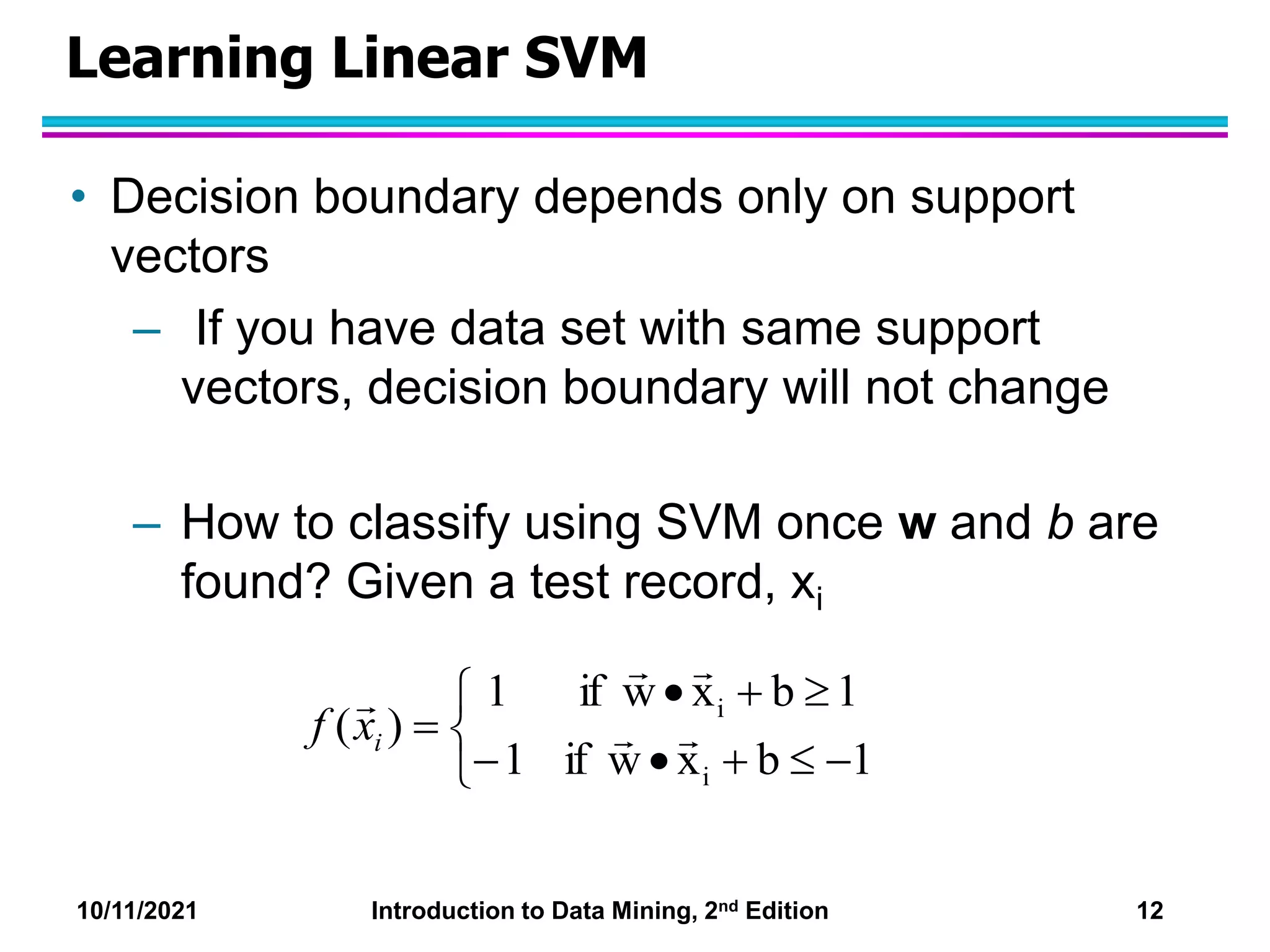
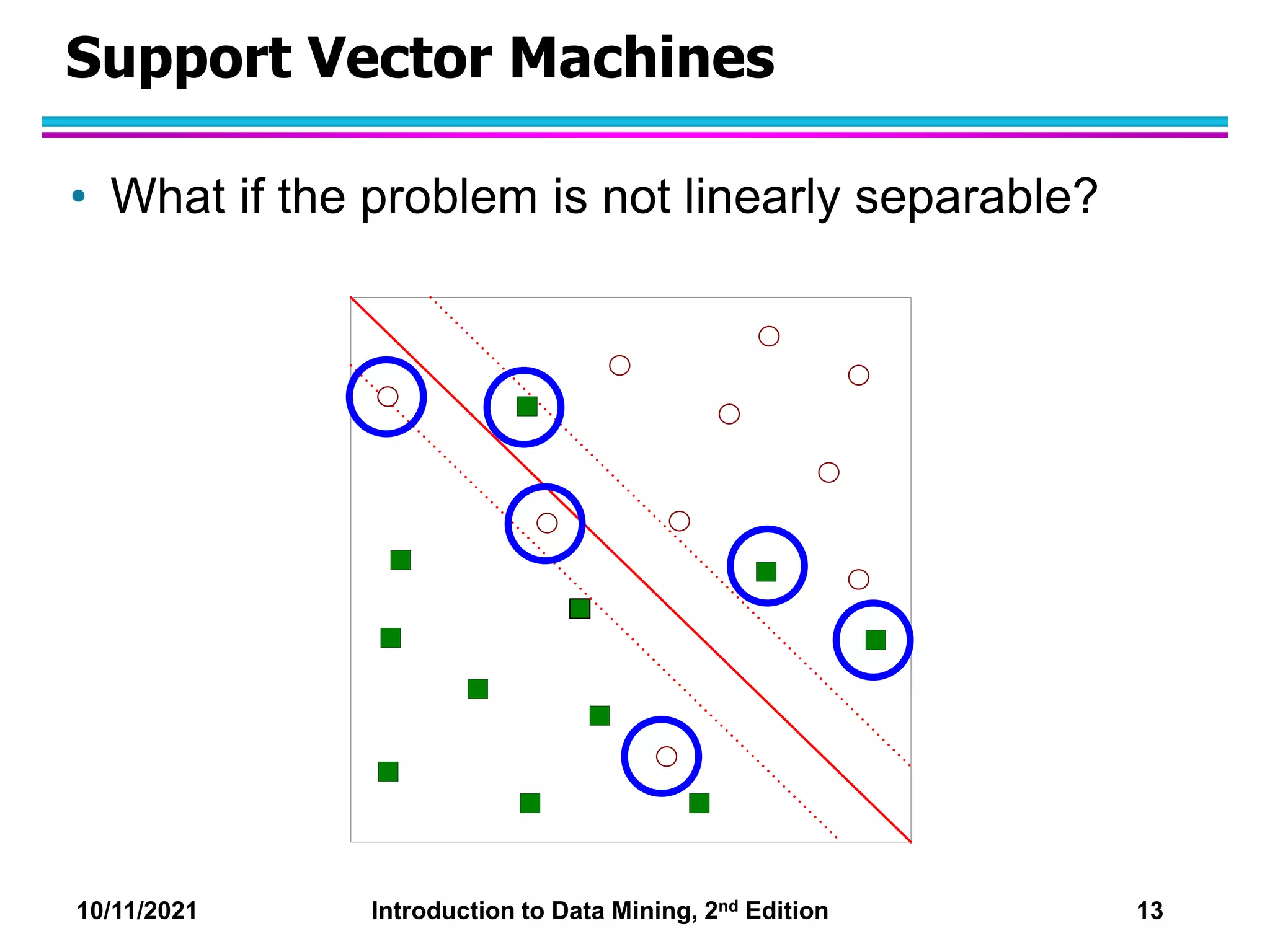
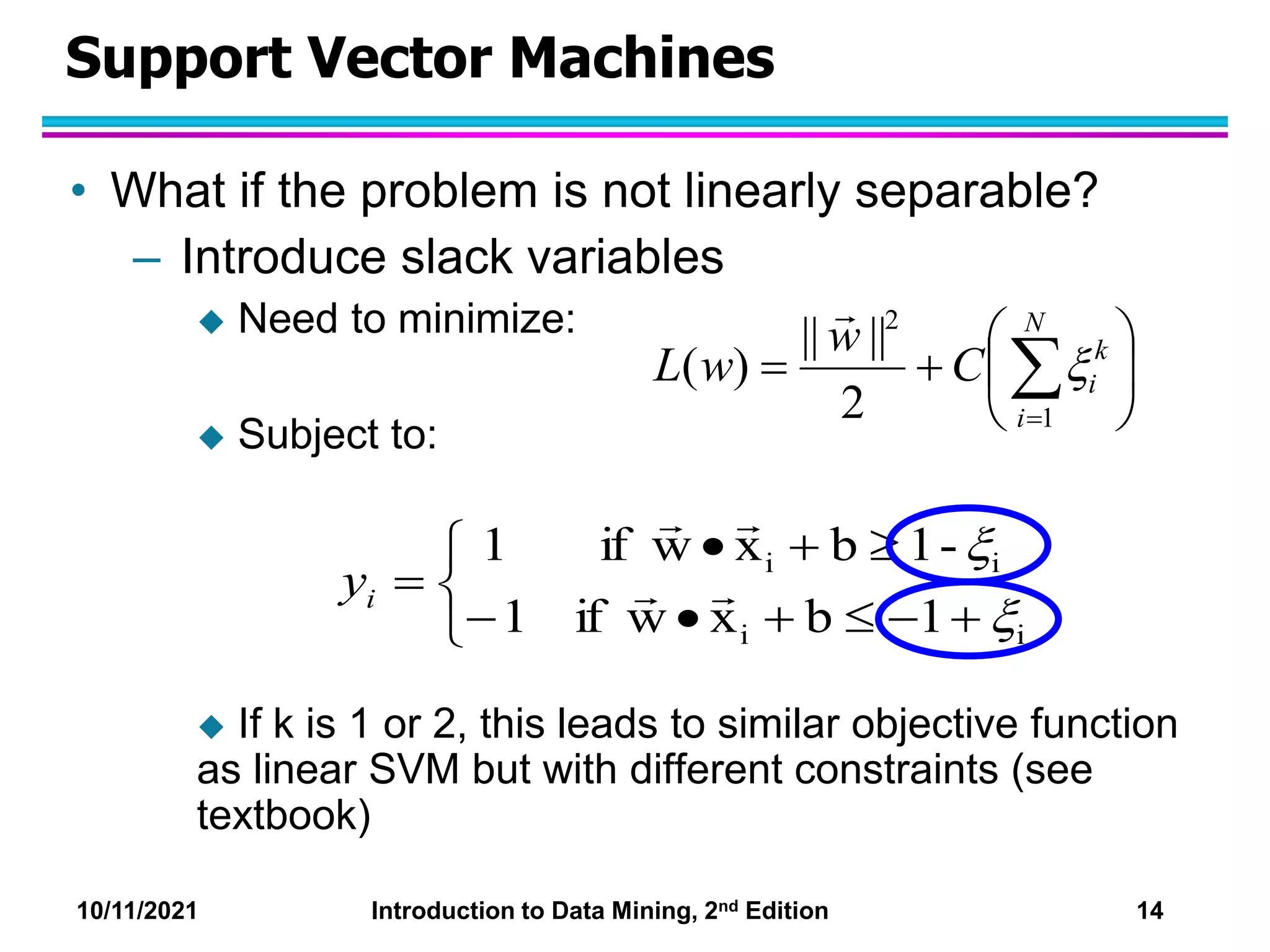
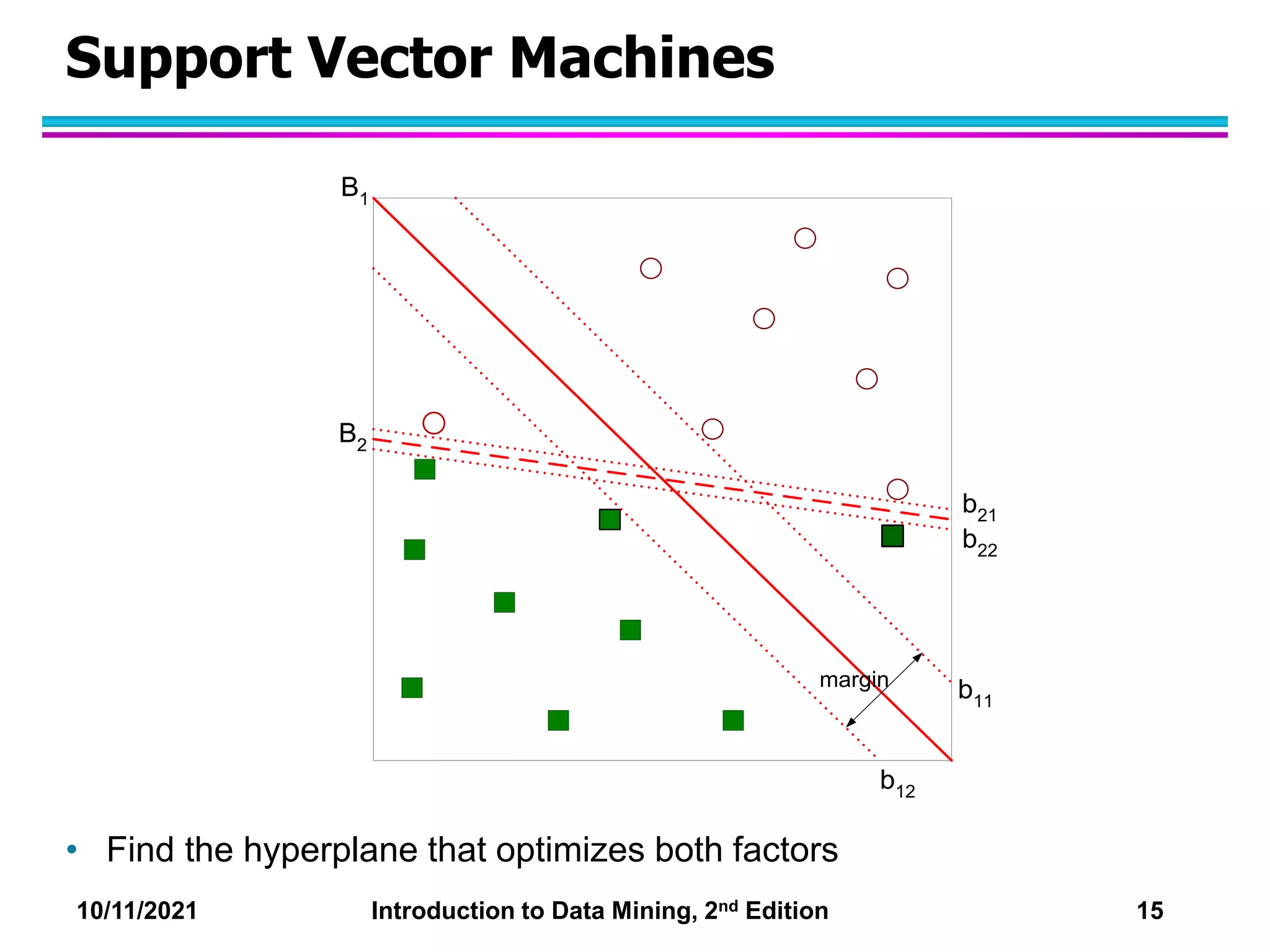
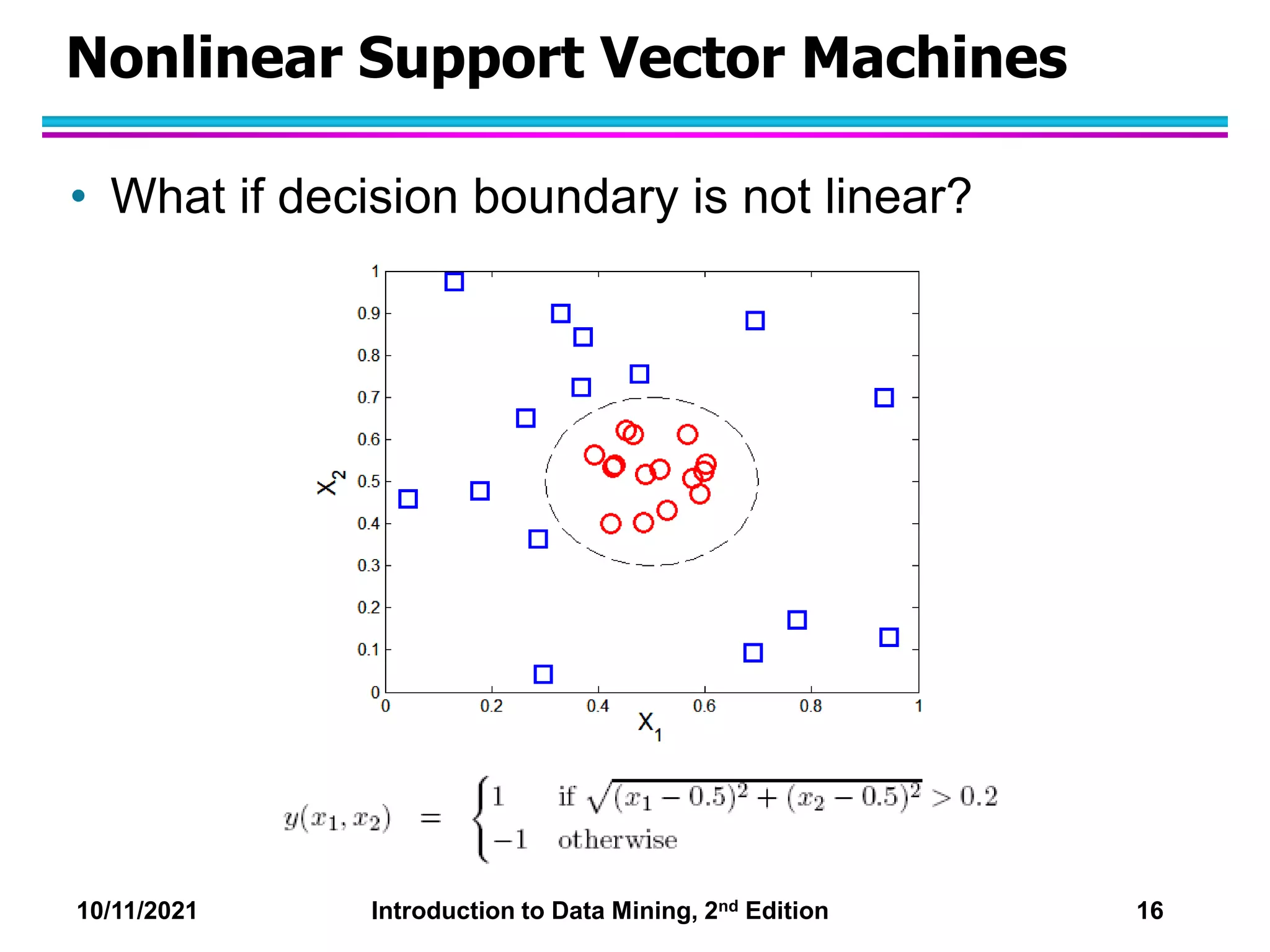
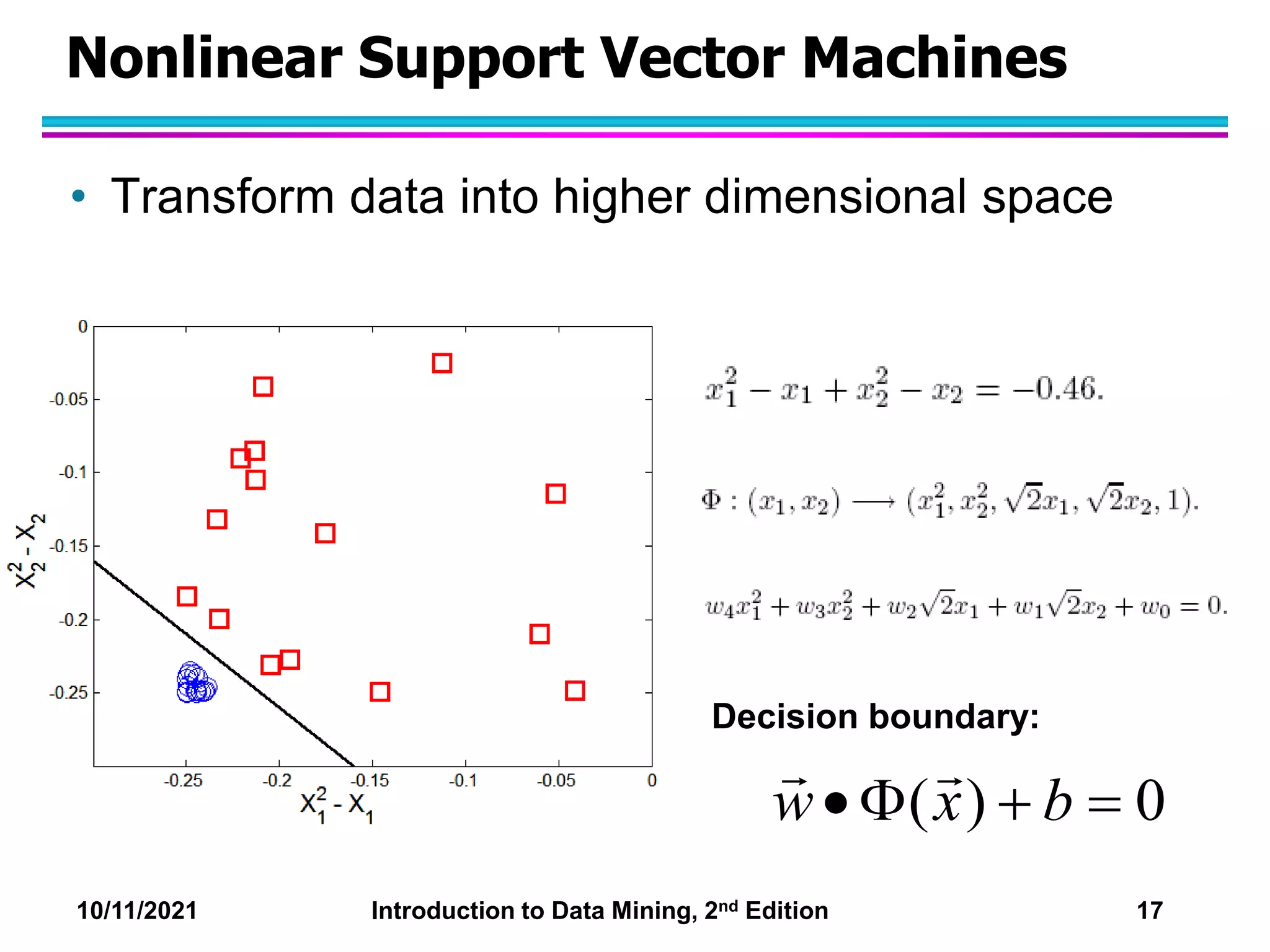
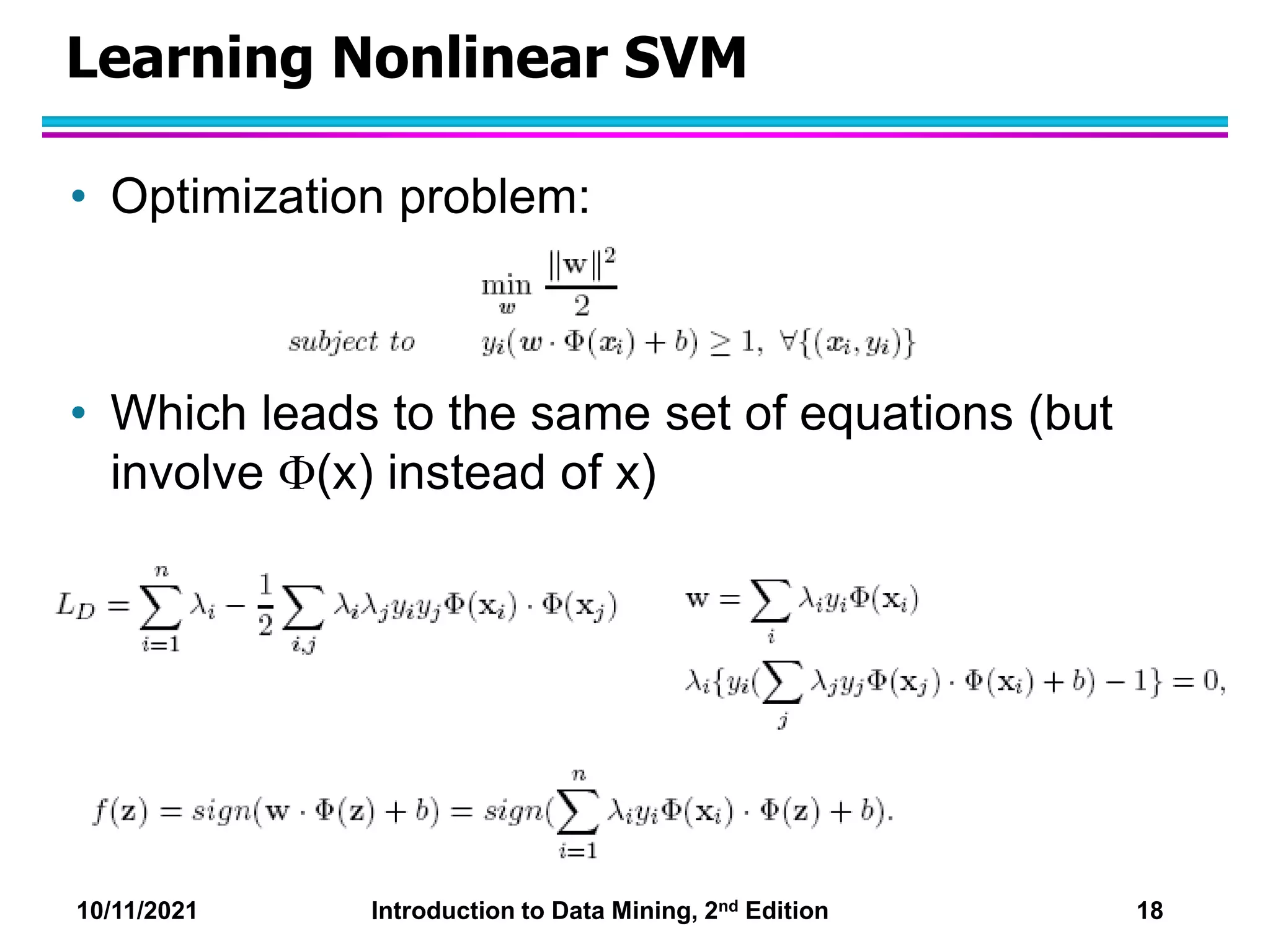
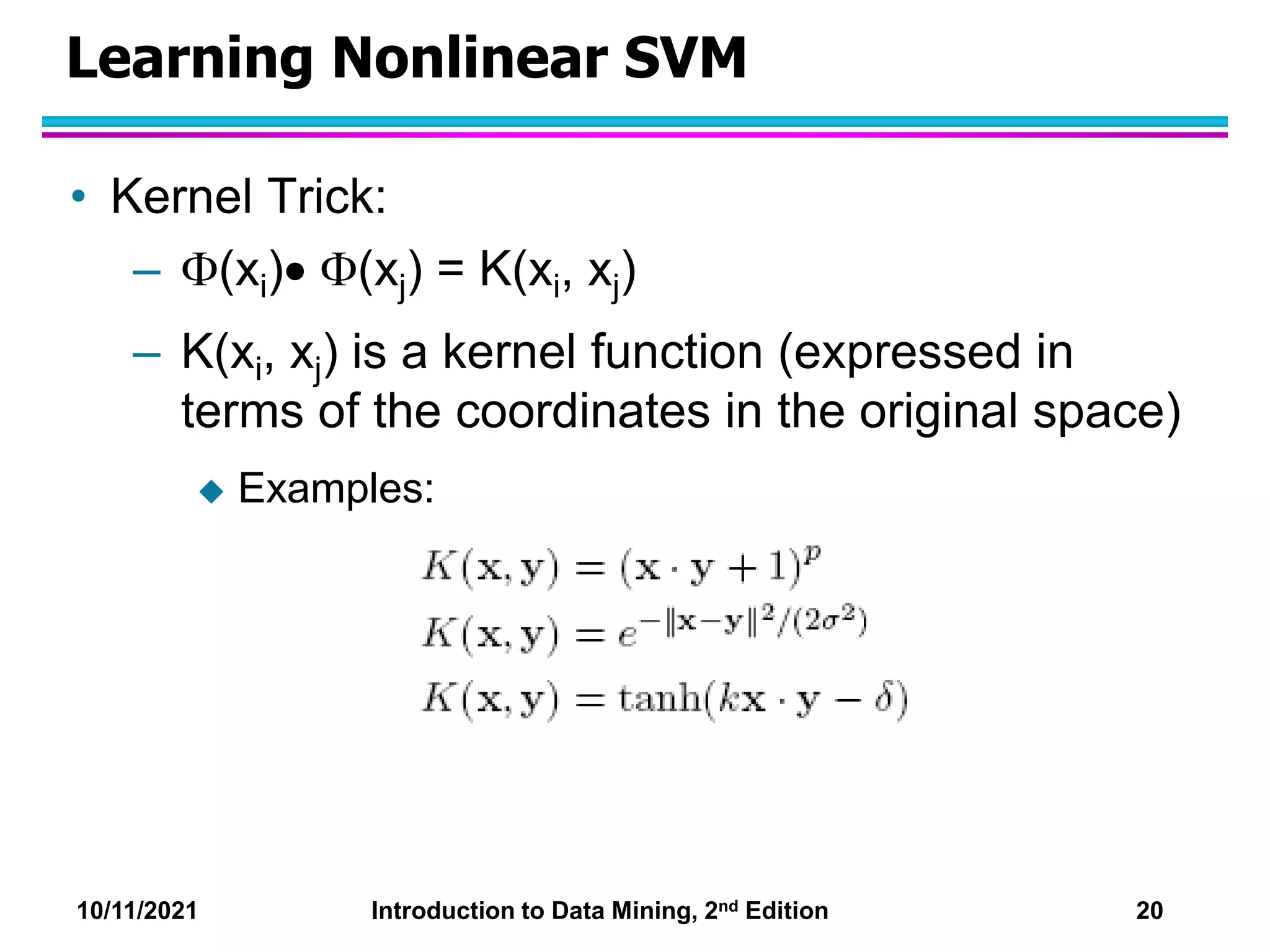
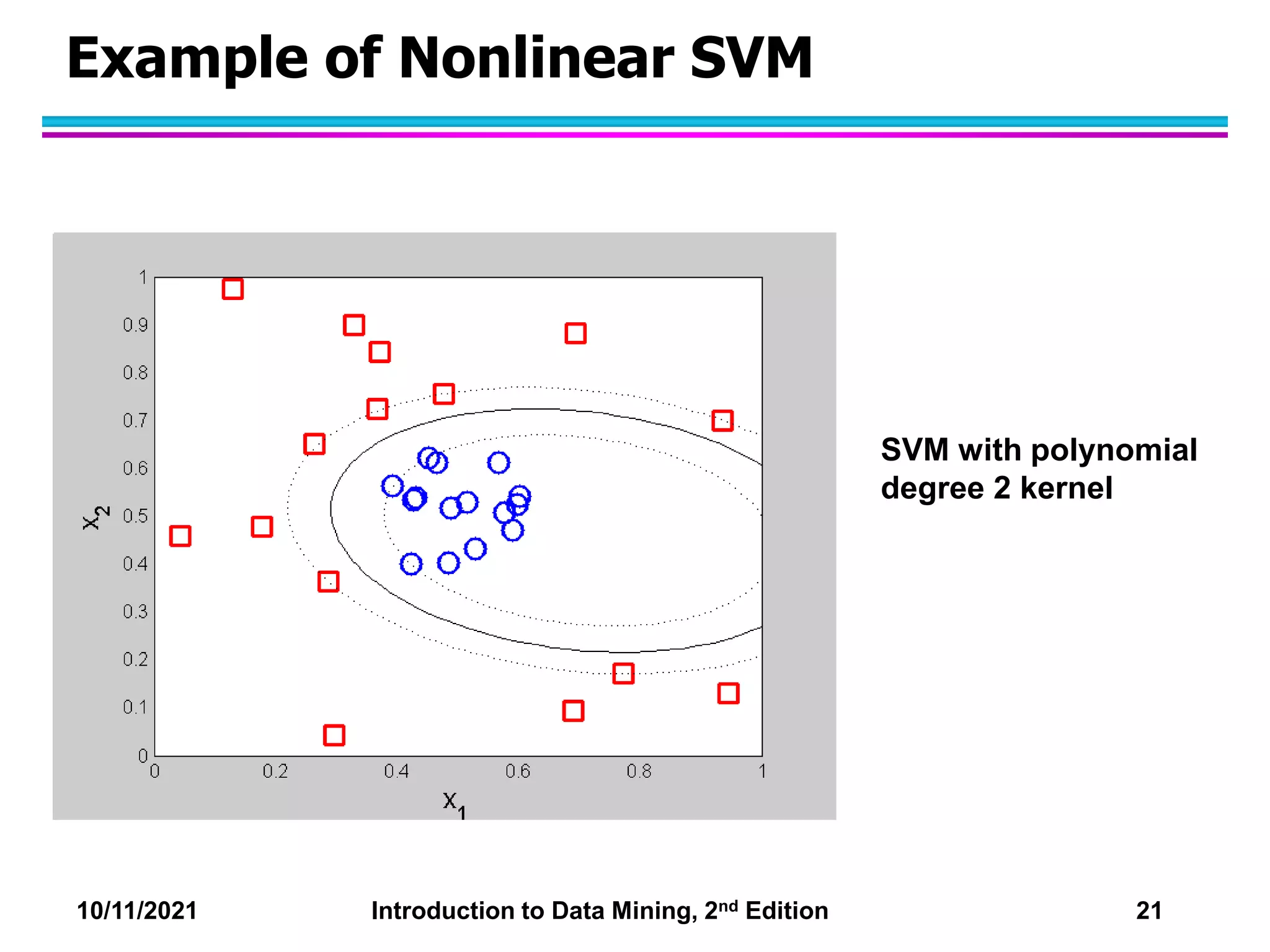
This document discusses support vector machines (SVMs) for classification. It explains that SVMs find the optimal separating hyperplane that maximizes the margin between classes. When data is not linearly separable, slack variables are introduced to handle misclassified points. Nonlinear SVMs transform data into a higher dimensional space using kernels to allow for nonlinear decision boundaries. Kernel functions like polynomial or RBF kernels are used to efficiently compute dot products in this transformed space without explicitly knowing the mapping.