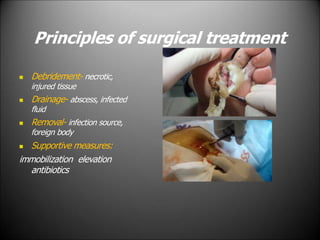
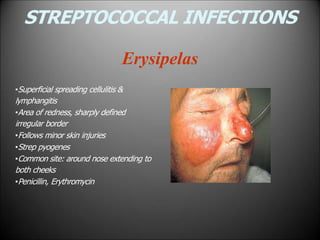
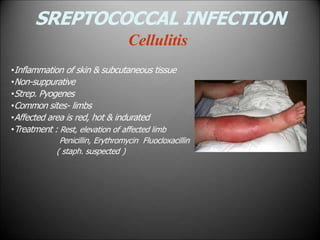
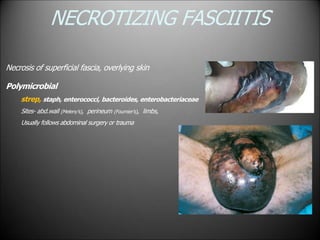
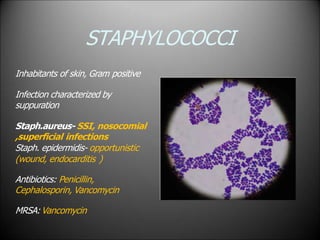
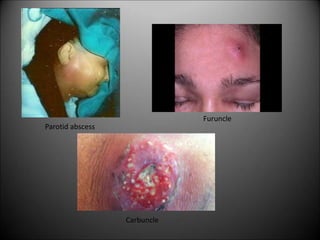
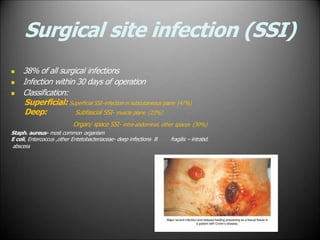
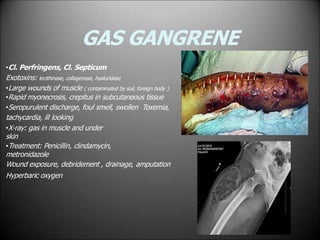
Surgical infections are a major challenge, accounting for 1 in 3 surgical patients. Factors like adequate microorganisms, virulence, suitable environment, and susceptible host contribute to infections. Common pathogens include Streptococci, Staphylococci, and Gram-negative organisms. Treatment involves debridement, drainage, antibiotic therapy tailored to the specific pathogen, and supportive measures. Antibiotic prophylaxis based on wound classification can help reduce postoperative infection risk.