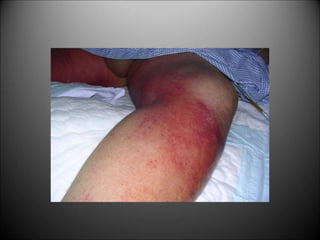
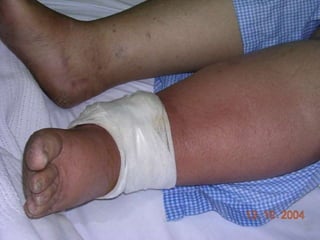
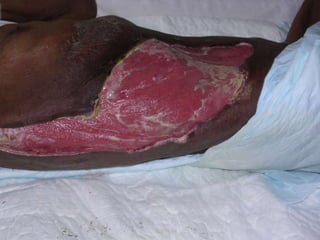
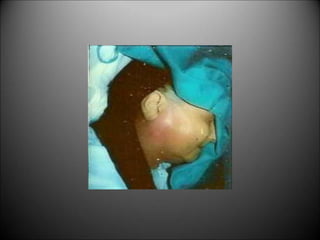
This document discusses surgical infections and the use of antibiotics. It defines surgical infections and notes they account for 1/3 of surgical patients and increased healthcare costs. Factors that contribute to infections include adequate microorganisms, virulence, suitable environment, and susceptible host. Common pathogens include Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Enterobacteriaceae, Clostridia, Pseudomonas, and Bacteroides fragilis. Antibiotics are used both therapeutically to treat existing infections and prophylactically to reduce wound infection risk. Guidelines recommend different antibiotic regimens based on the surgical wound classification and infection type.