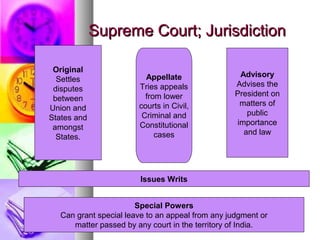
The judiciary in India consists of the Supreme Court and various high courts. The Supreme Court sits at the top and its rulings are binding on all other courts. It has original, appellate and advisory jurisdiction. Below the Supreme Court are the high courts in each state, which hear appeals from lower courts and have original jurisdiction over writ petitions. The independence of the judiciary is ensured through measures like the appointment and removal of judges being difficult political processes, financial independence, and immunity from criticism for judges' actions.