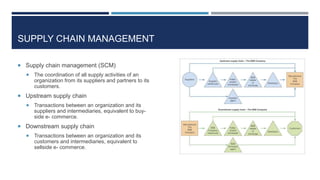
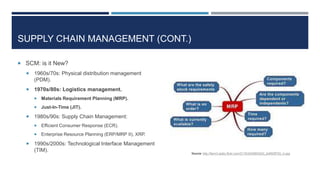
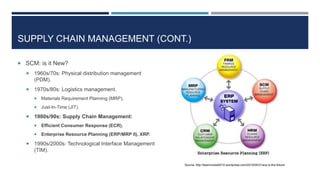
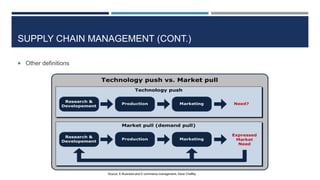
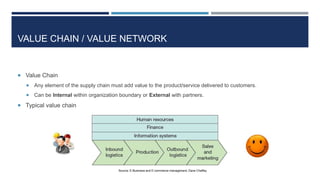
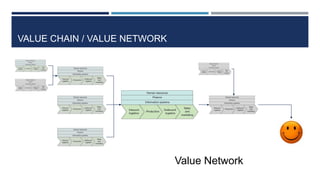
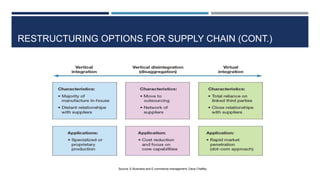
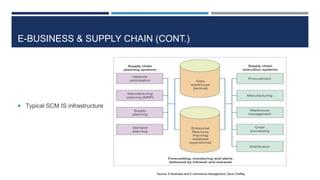
This document discusses supply chain management and related topics. It begins with an overview of supply chain management, defining it as the coordination of supply chain activities from suppliers to customers. It then covers value chains and networks, options for restructuring supply chains, the role of e-business in supply chains, and trends in supply chain management. Key points include how information systems help integrate supply chain activities and data, and how trends involve simplification, adaptability, sustainability, and collaboration across supply chains.