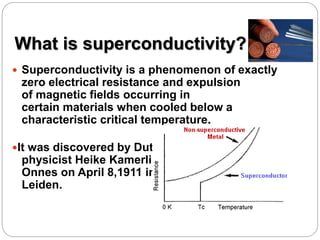
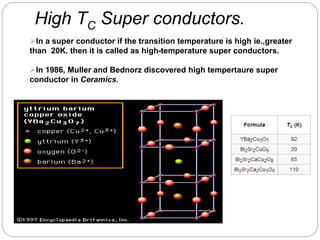
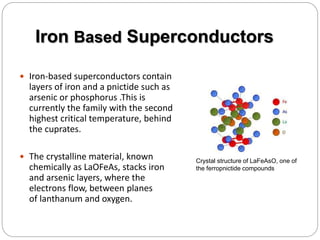
Superconductivity is a phenomenon where electrical resistance drops to exactly zero and magnetic fields are expelled when certain materials are cooled below a critical temperature. The document discusses several key aspects of superconductivity including the Meissner effect, the BCS theory of superconductivity, and different types of superconducting materials such as metal alloys, cuprates, iron-based, and organic superconductors. While superconductors have applications in areas like maglev trains, power transmission, and medical devices, limitations include the need for cryogenic cooling below 77K and brittleness of some materials.