1. The document presents a term paper on the electronic properties of graphene.
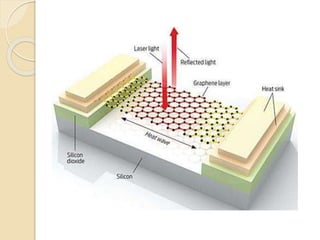
2. Graphene is a single-atom thick sheet of carbon that has extraordinary mechanical, optical, and electronic properties due to its atomic structure and pi orbitals.
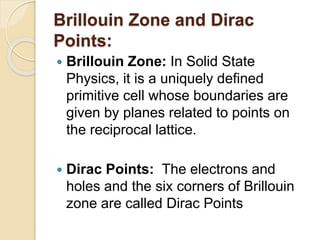
3. The paper discusses graphene's properties, electronic band structure, quantum Hall effect, and applications in areas like biosensing, optoelectronics, energy storage, and photovoltaics.