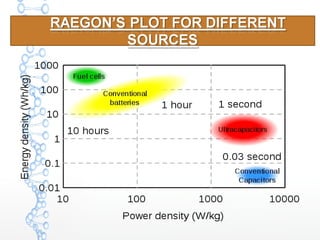
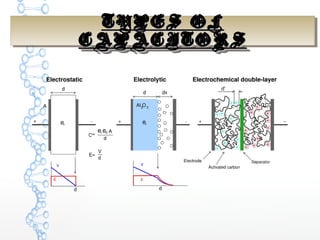
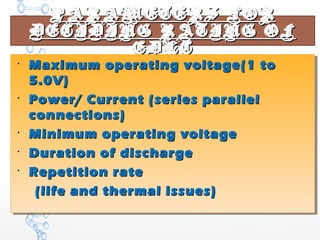
The document discusses the characteristics and applications of batteries and supercapacitors, highlighting their energy storage capabilities and limitations. It details how supercapacitors can fulfill peak power requirements in various devices, while batteries generally store more energy but have narrower operational ranges and maintenance issues. Additionally, it outlines the construction, performance parameters, and manufacturing challenges of electric double layer capacitors (EDLC).