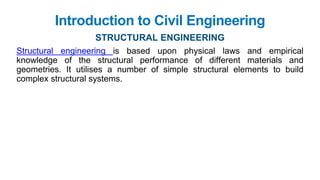
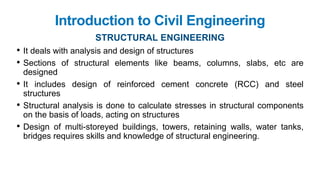
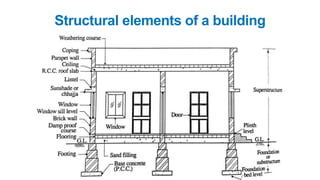
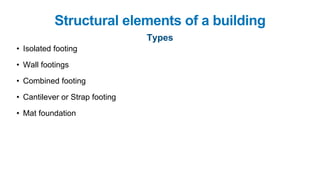
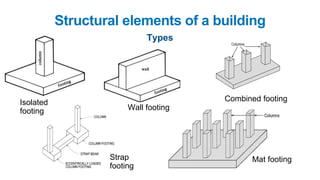
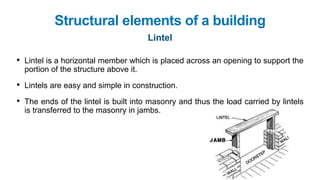
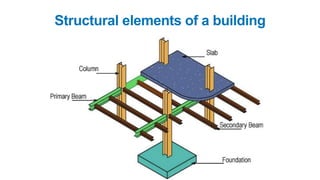
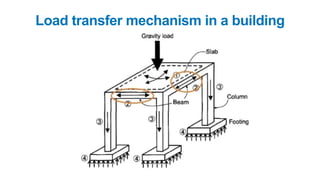
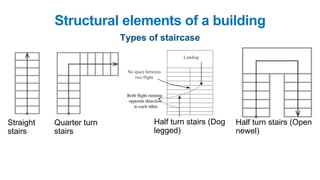
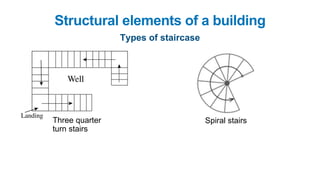
The document provides a comprehensive overview of civil engineering, covering its definition, various subfields, and fundamental concepts including surveying, structural, geotechnical, hydraulics, transportation, environmental engineering, and construction management. It details essential construction materials such as bricks, cement, concrete, and steel, outlining their properties, uses, and the characteristics of good materials. Additionally, it explains structural elements like foundations, plinths, lintels, and columns, emphasizing their significance in supporting and stabilizing structures.