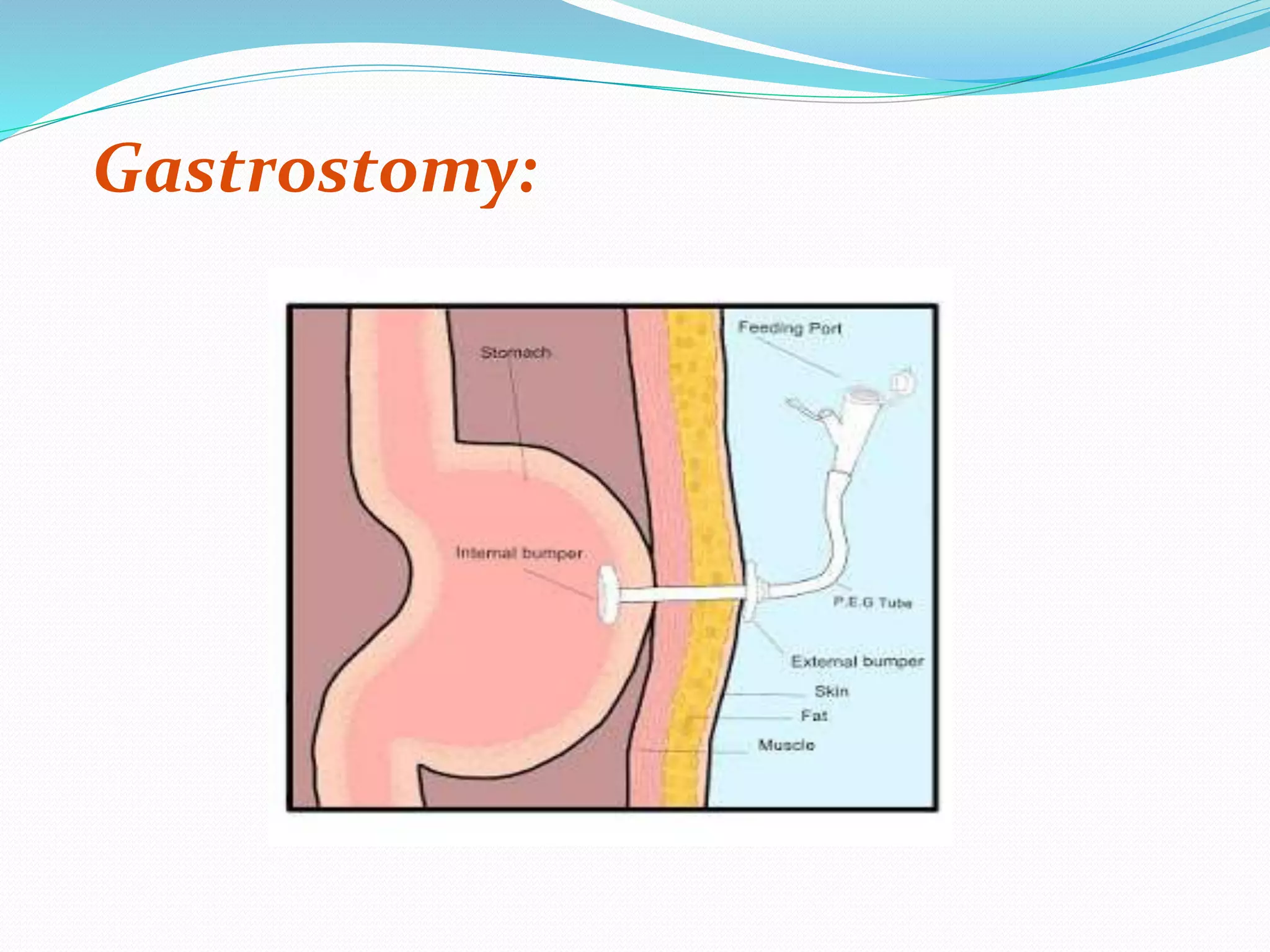
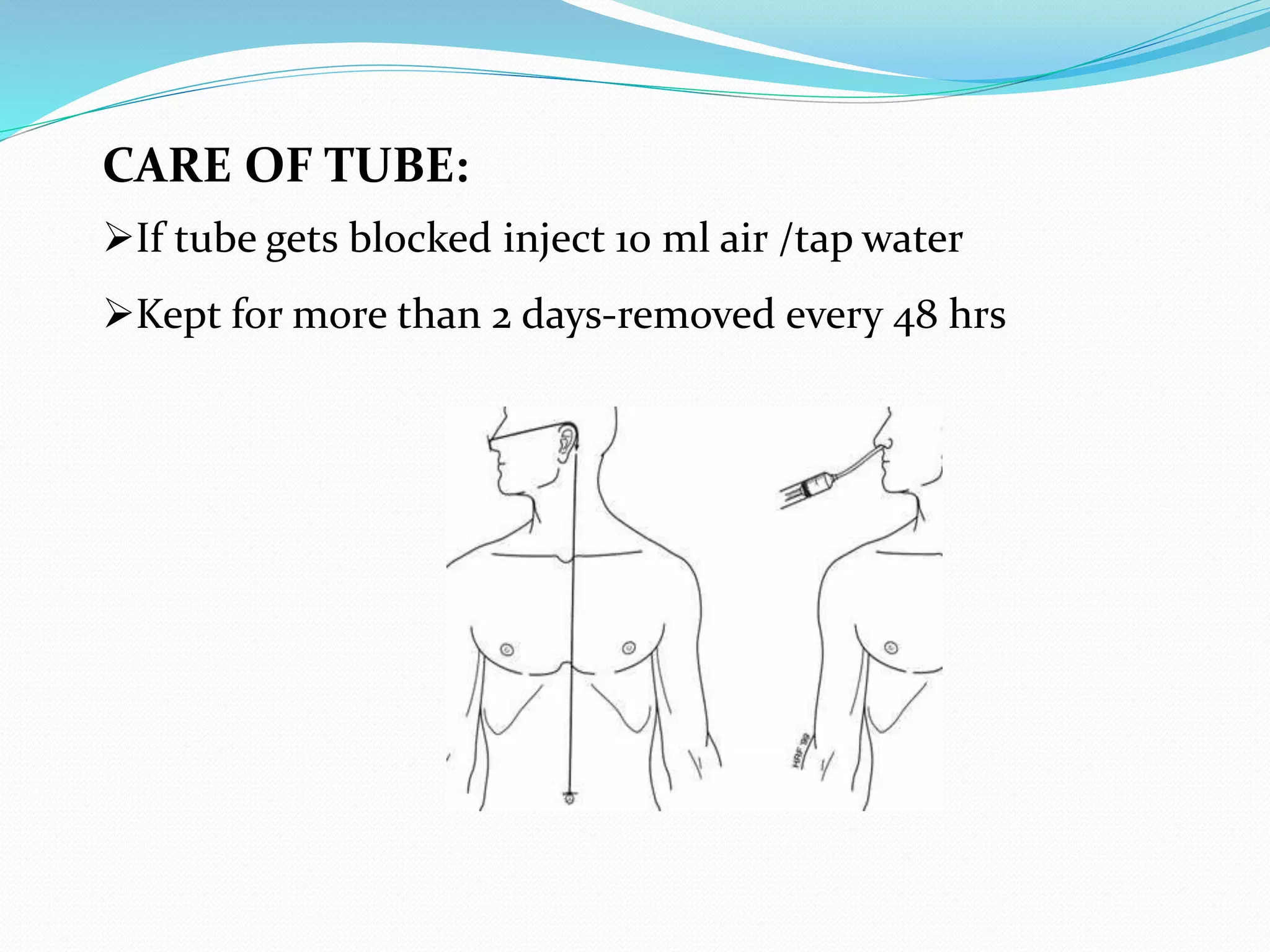
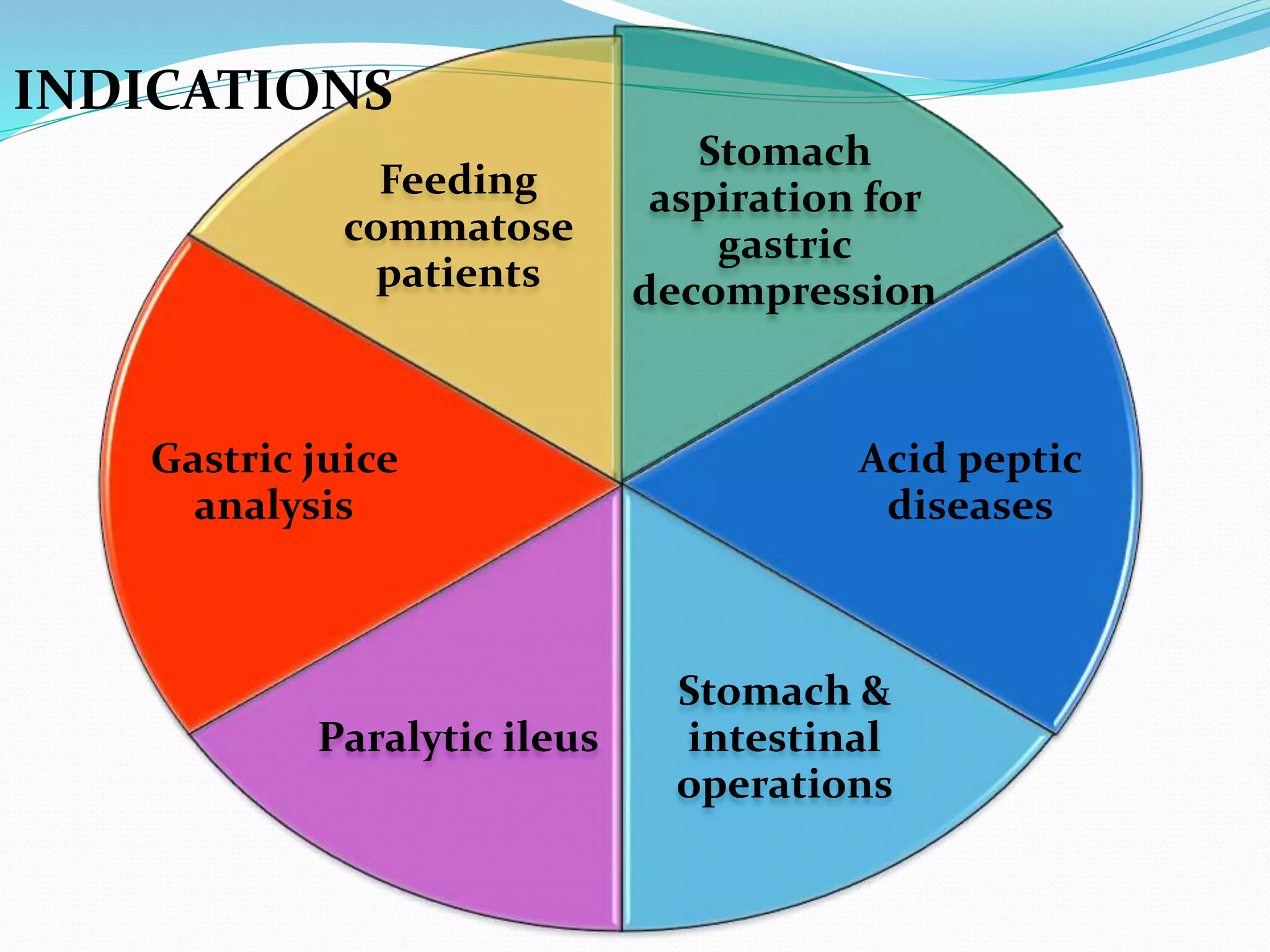
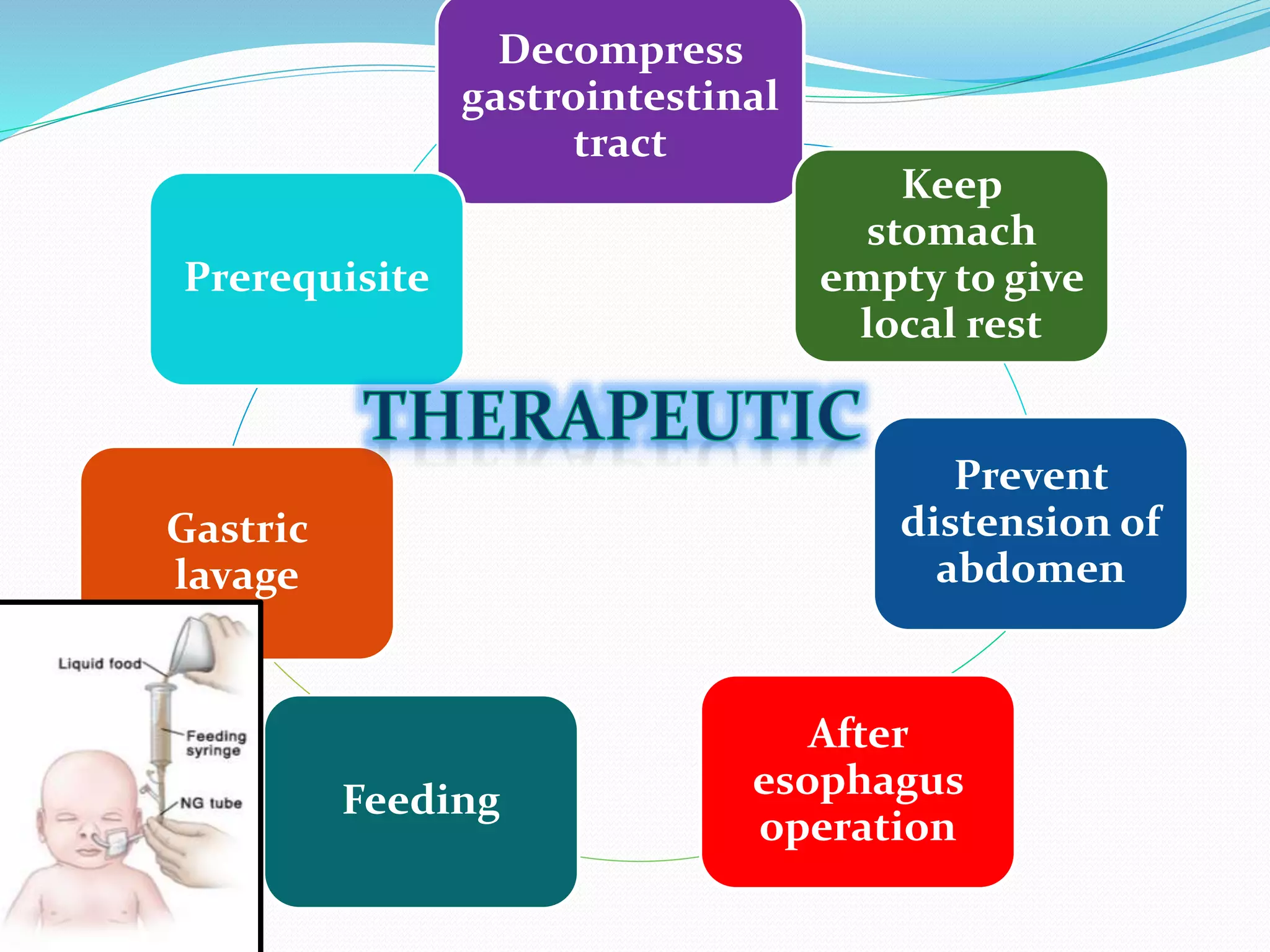
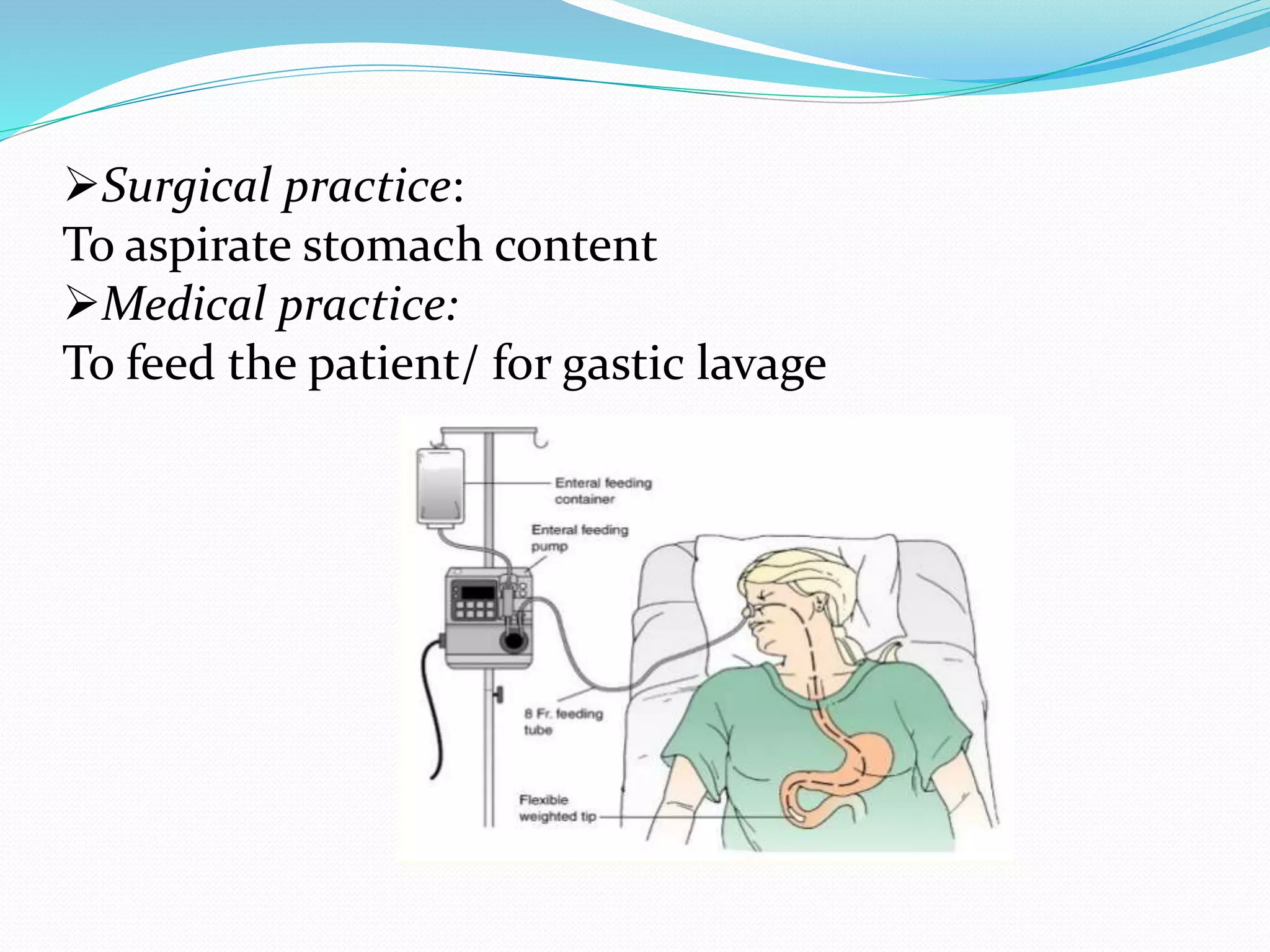
Short, medium, and long tubes are used to pass through the nose into the stomach or small intestine. They range from 10F to 20F in size and 105-120 cm in length. Tubes are sterilized using gamma ray irradiation, ethylene oxide gas, or boiling. Tubes are inserted by measuring the distance from the nose to earlobe and sternum to determine the proper length, lubricating the tube, cleaning the nostril, and slowly advancing the tube while the patient is in a sitting or Fowler's position. Tubes are used for therapeutic purposes like decompressing the gastrointestinal tract or diagnostic purposes like gastric juice analysis. Complications can include sinusitis, epistaxis, otitis media