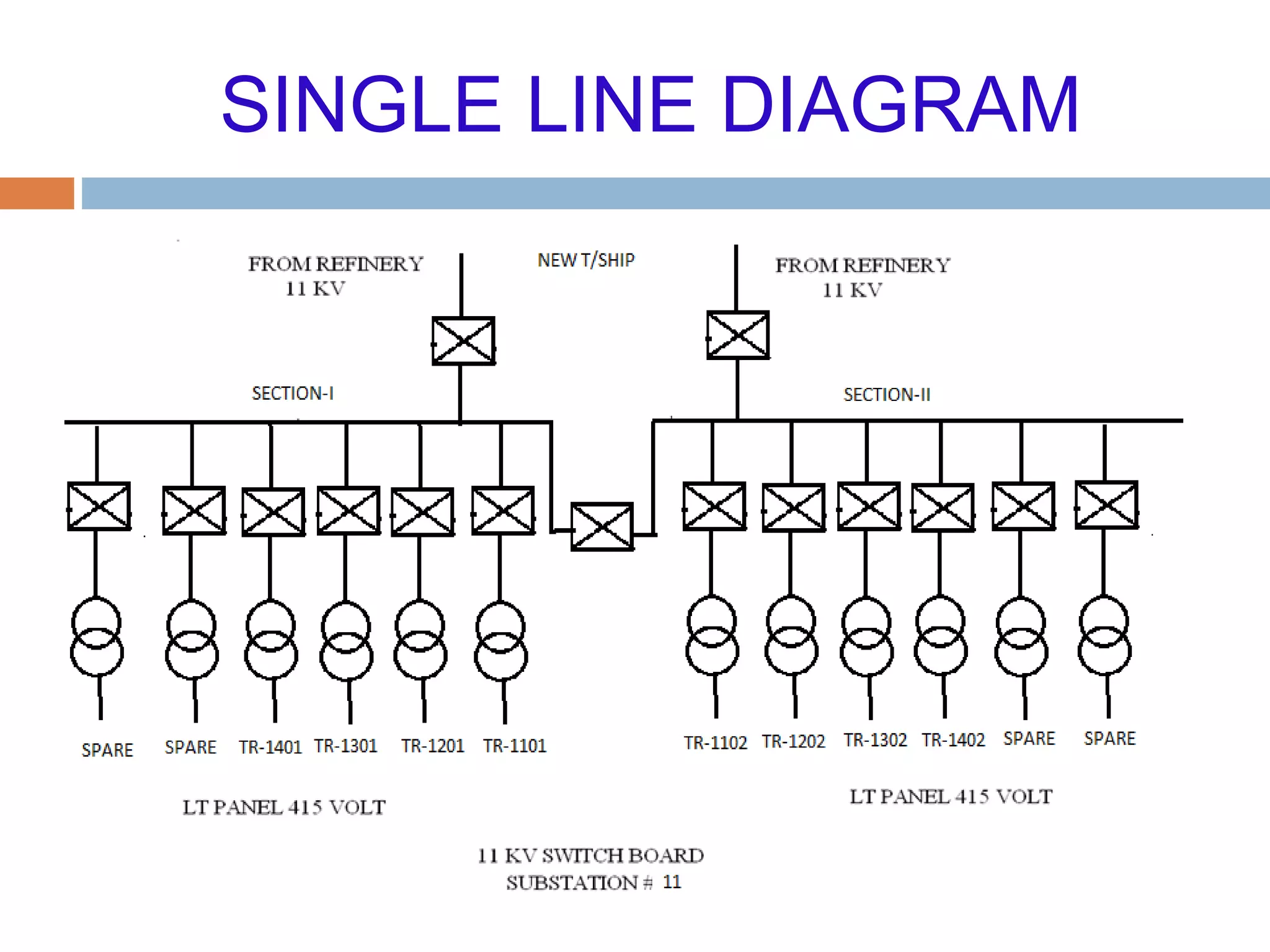
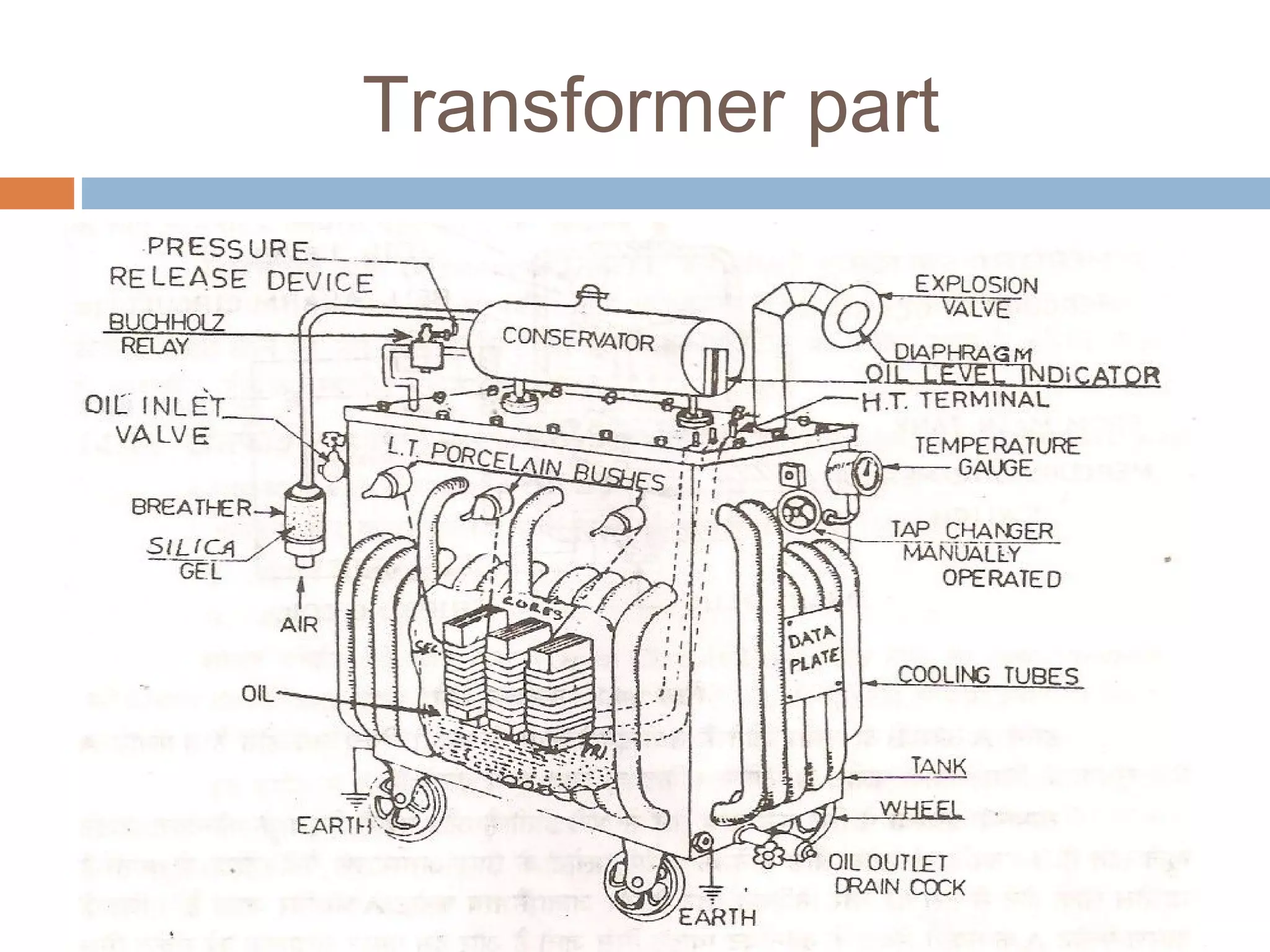
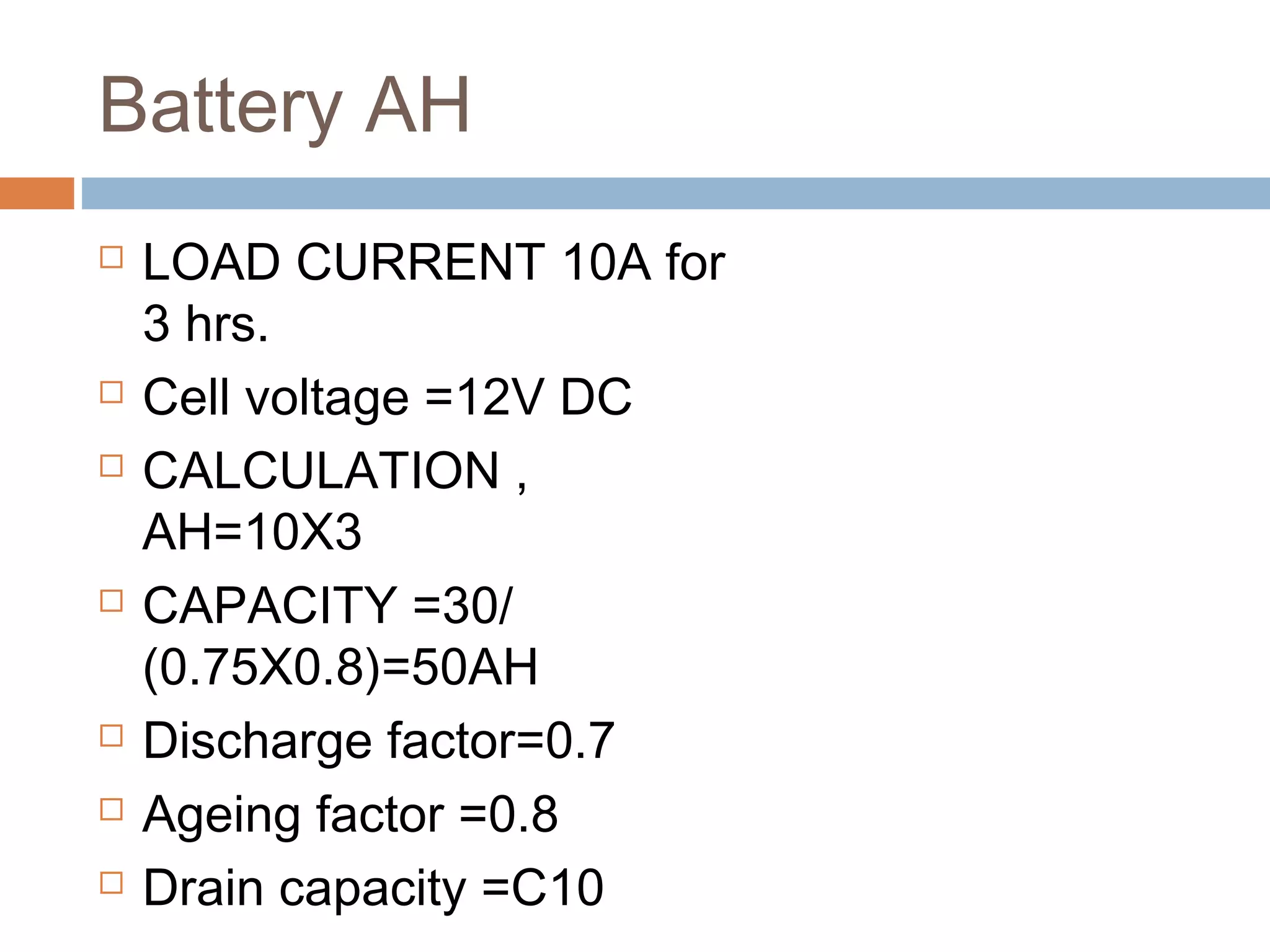
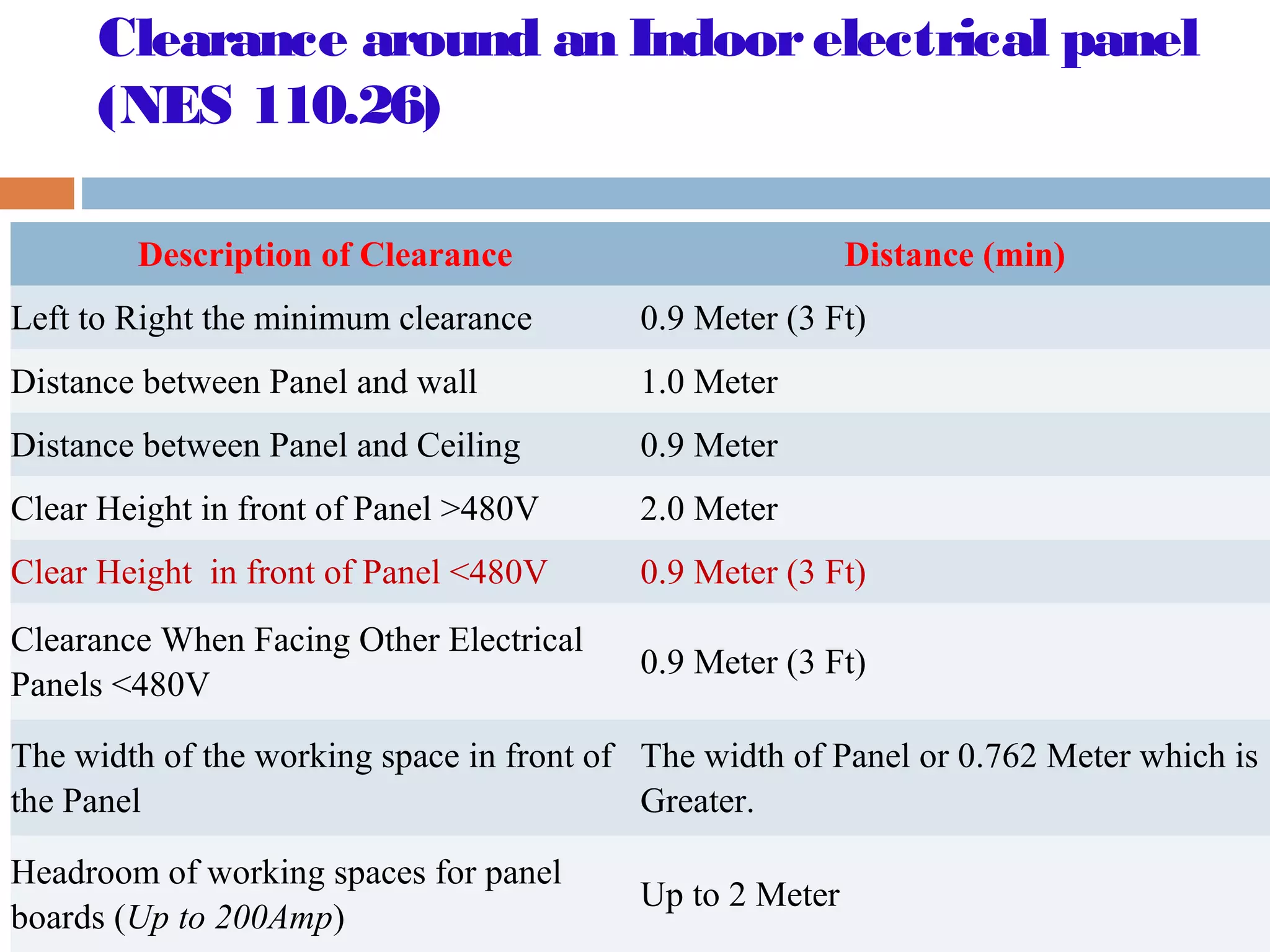
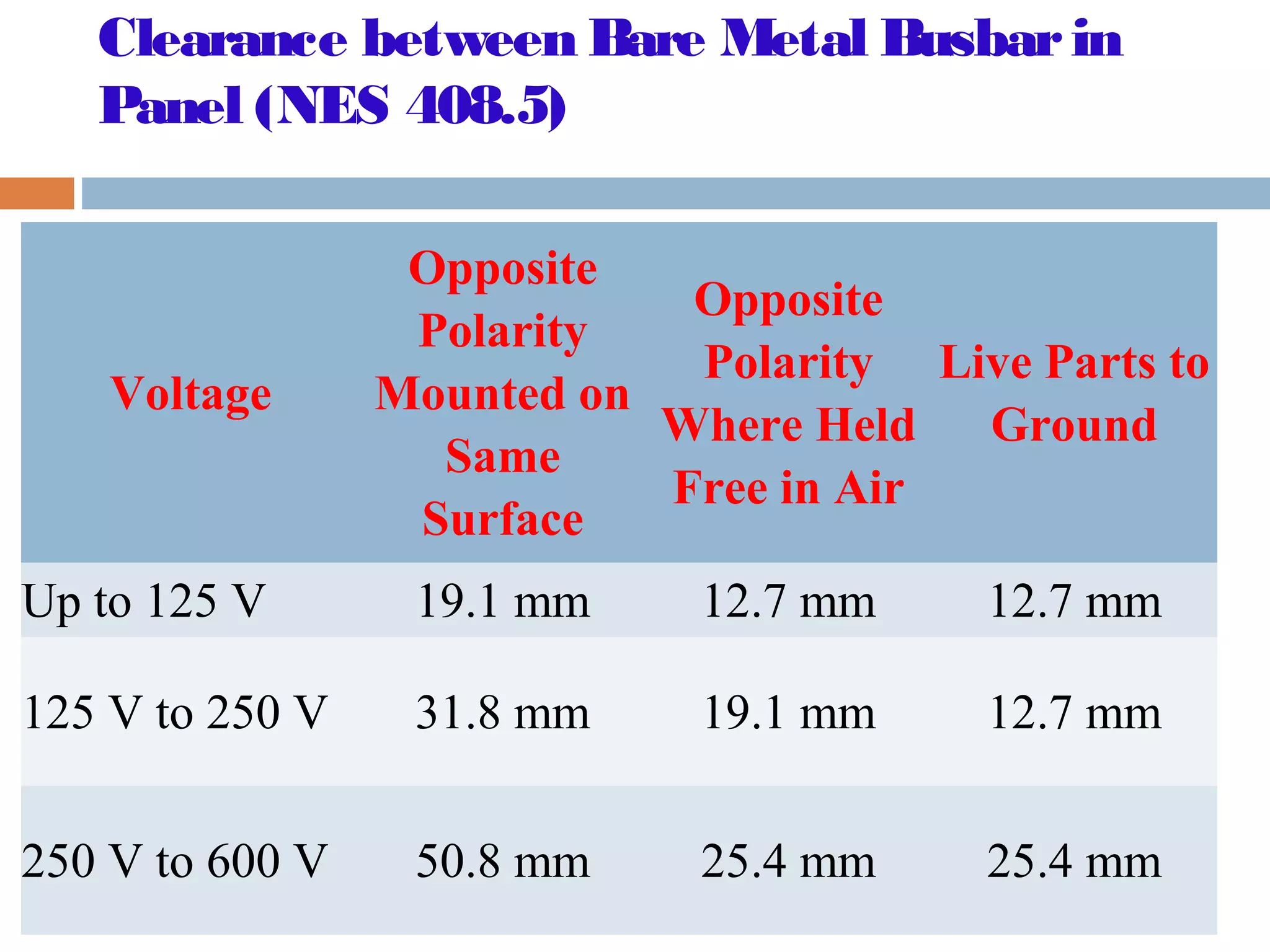
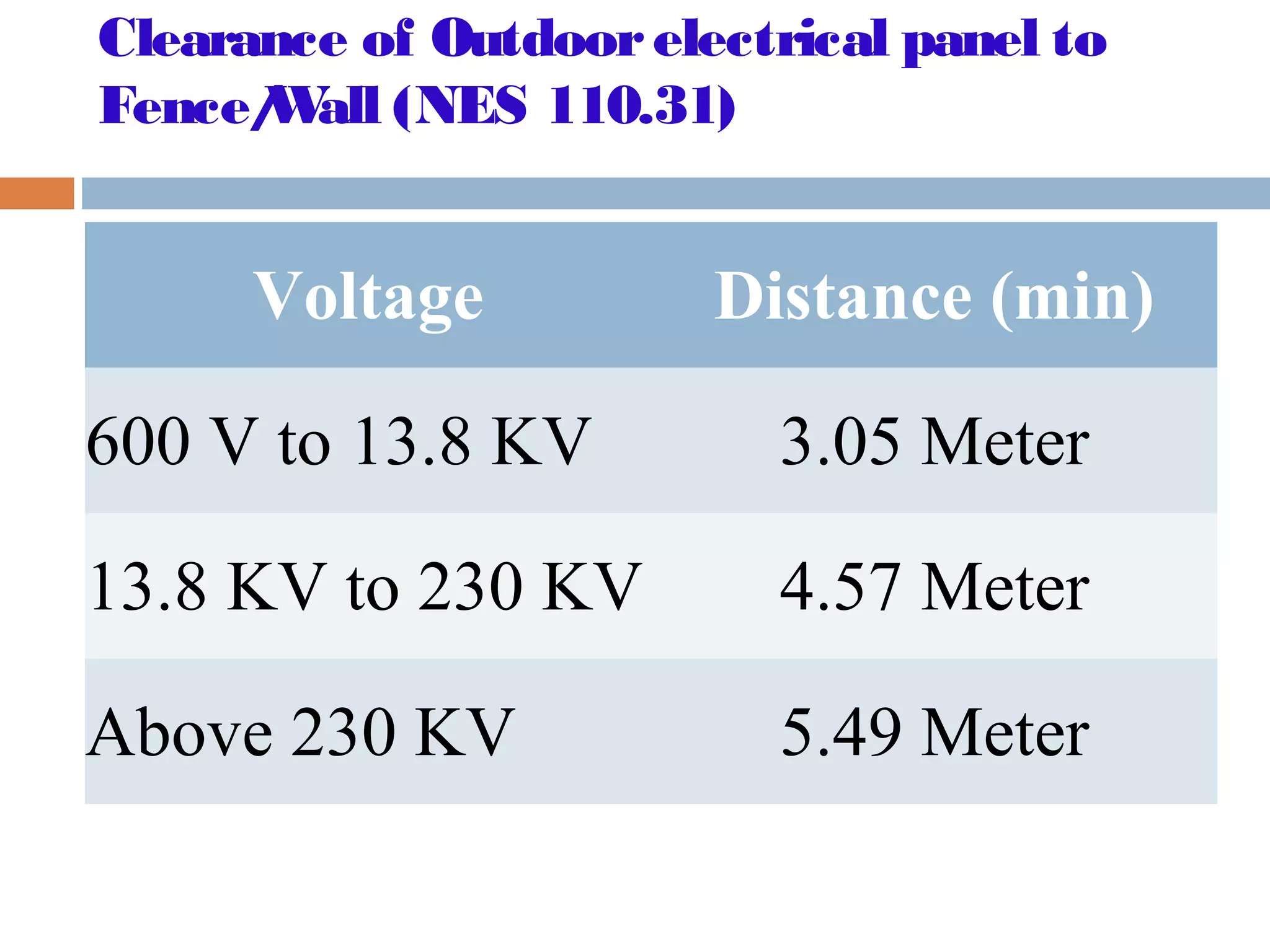
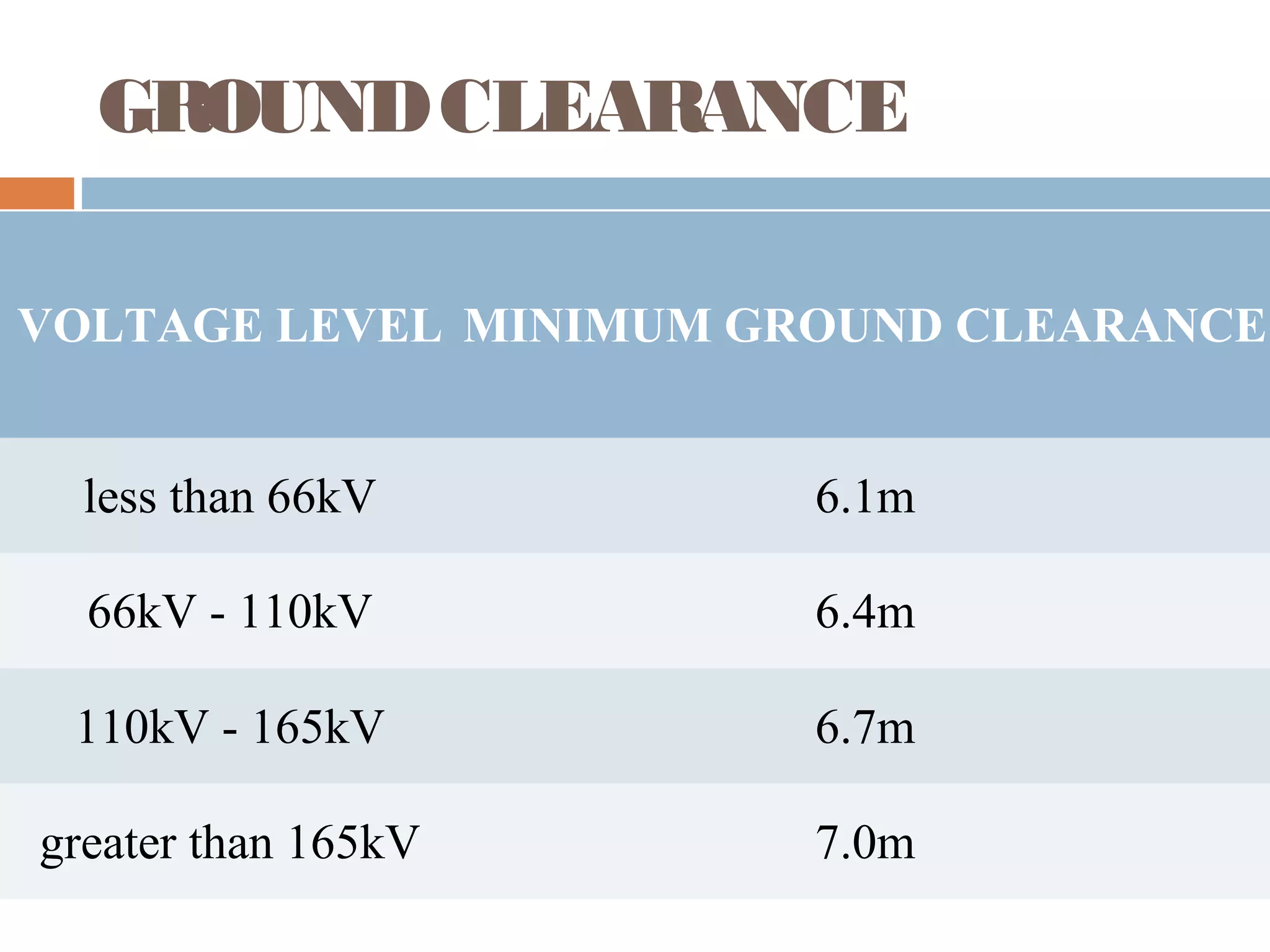
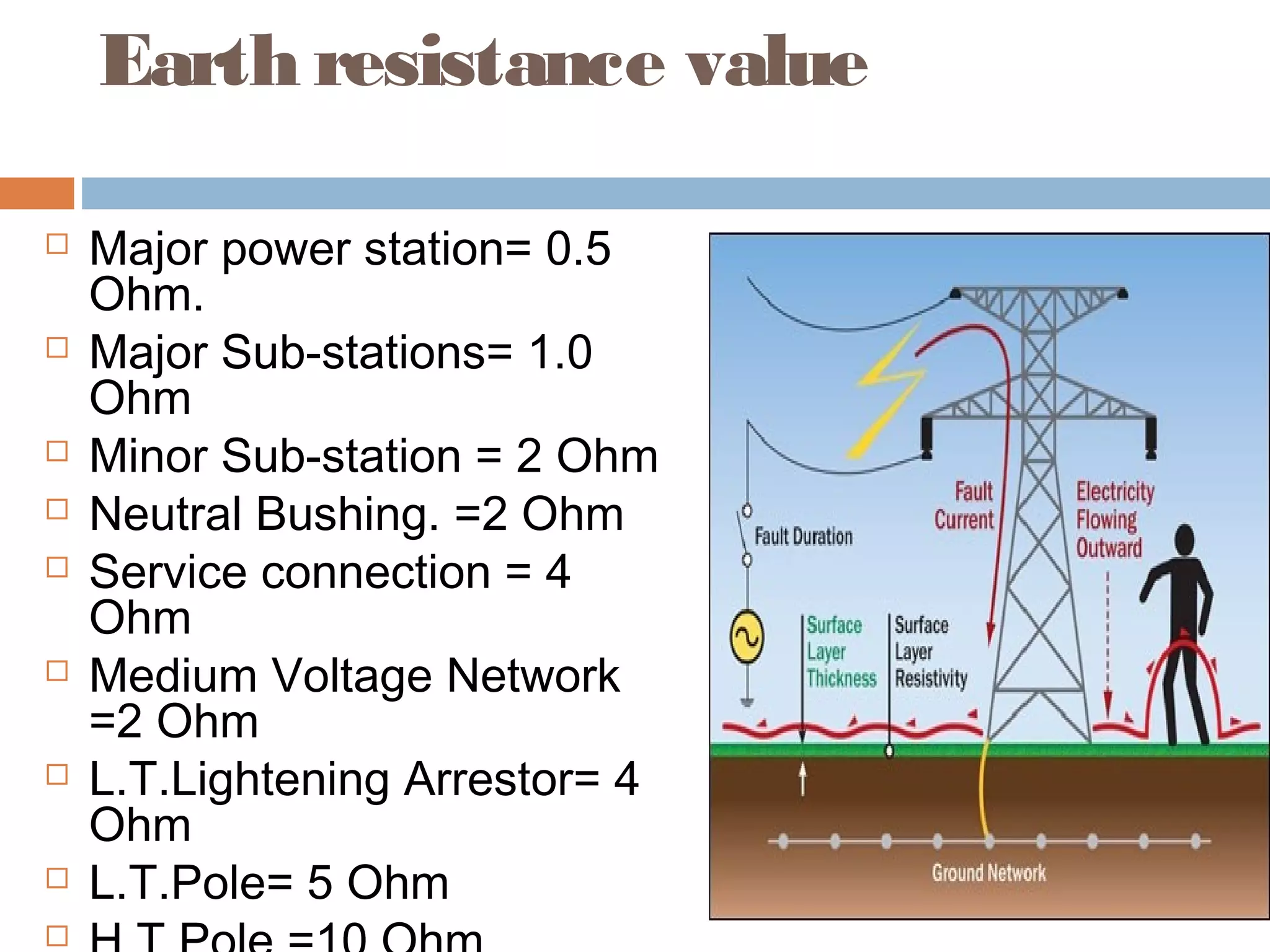
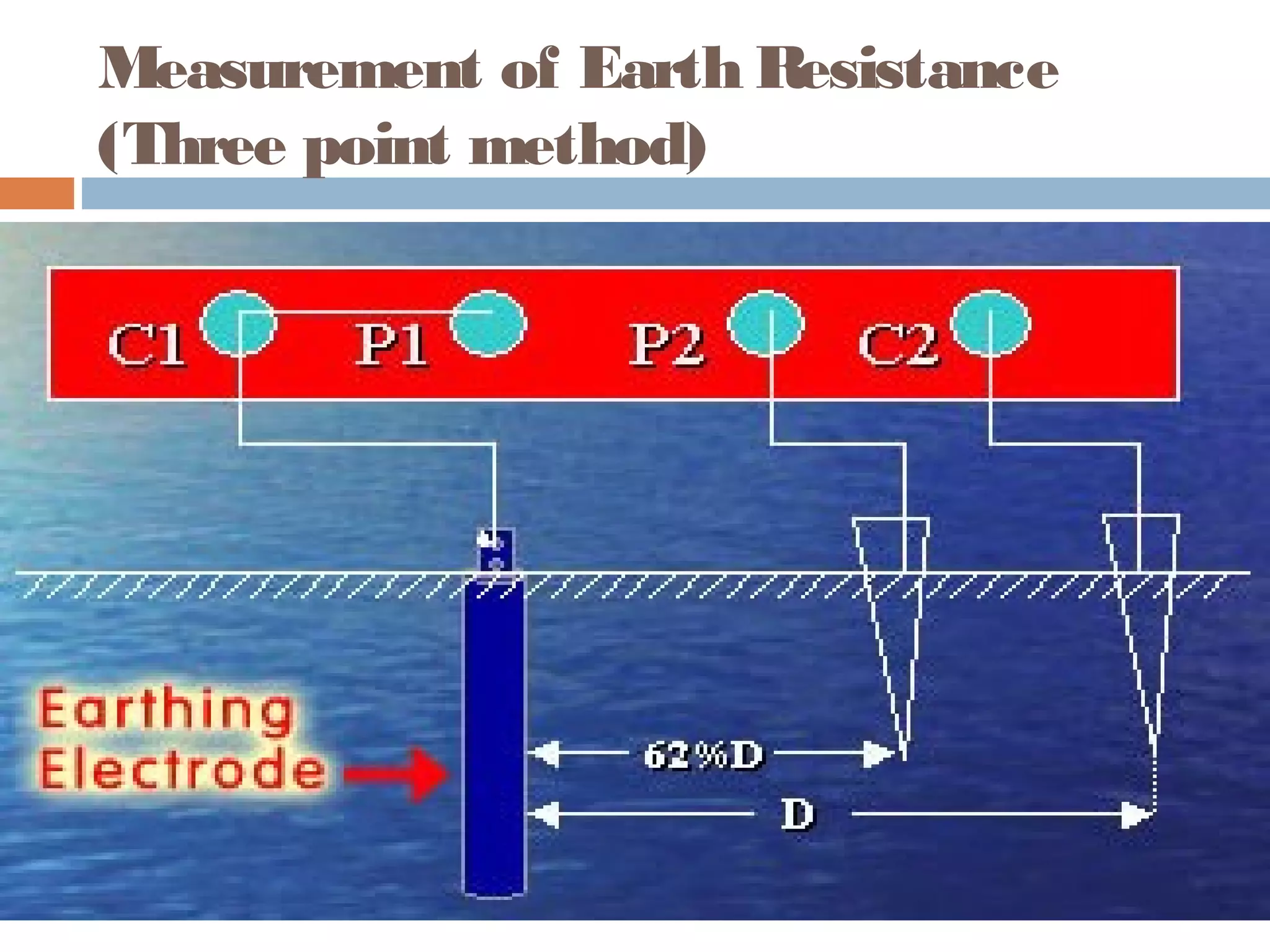
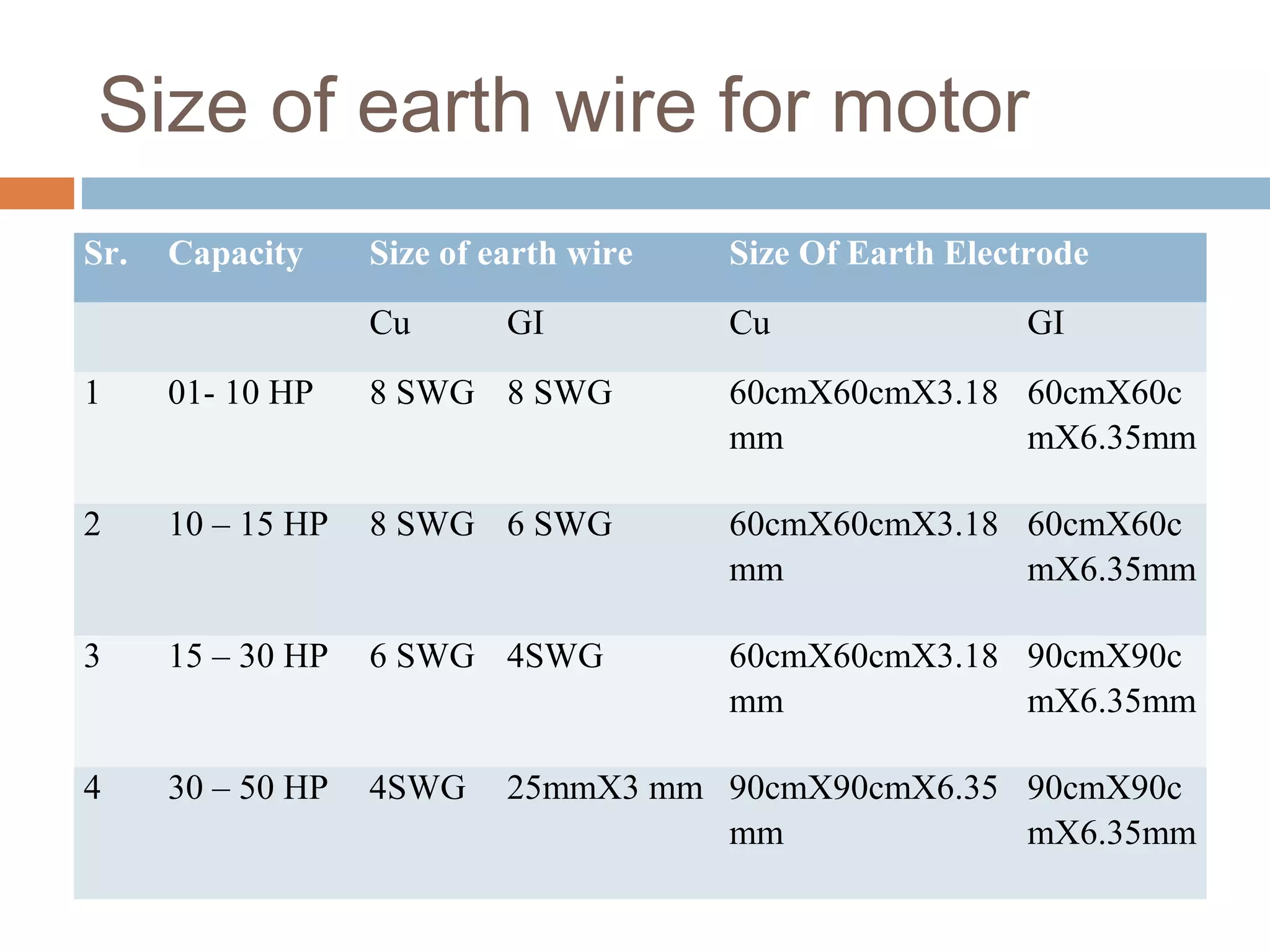
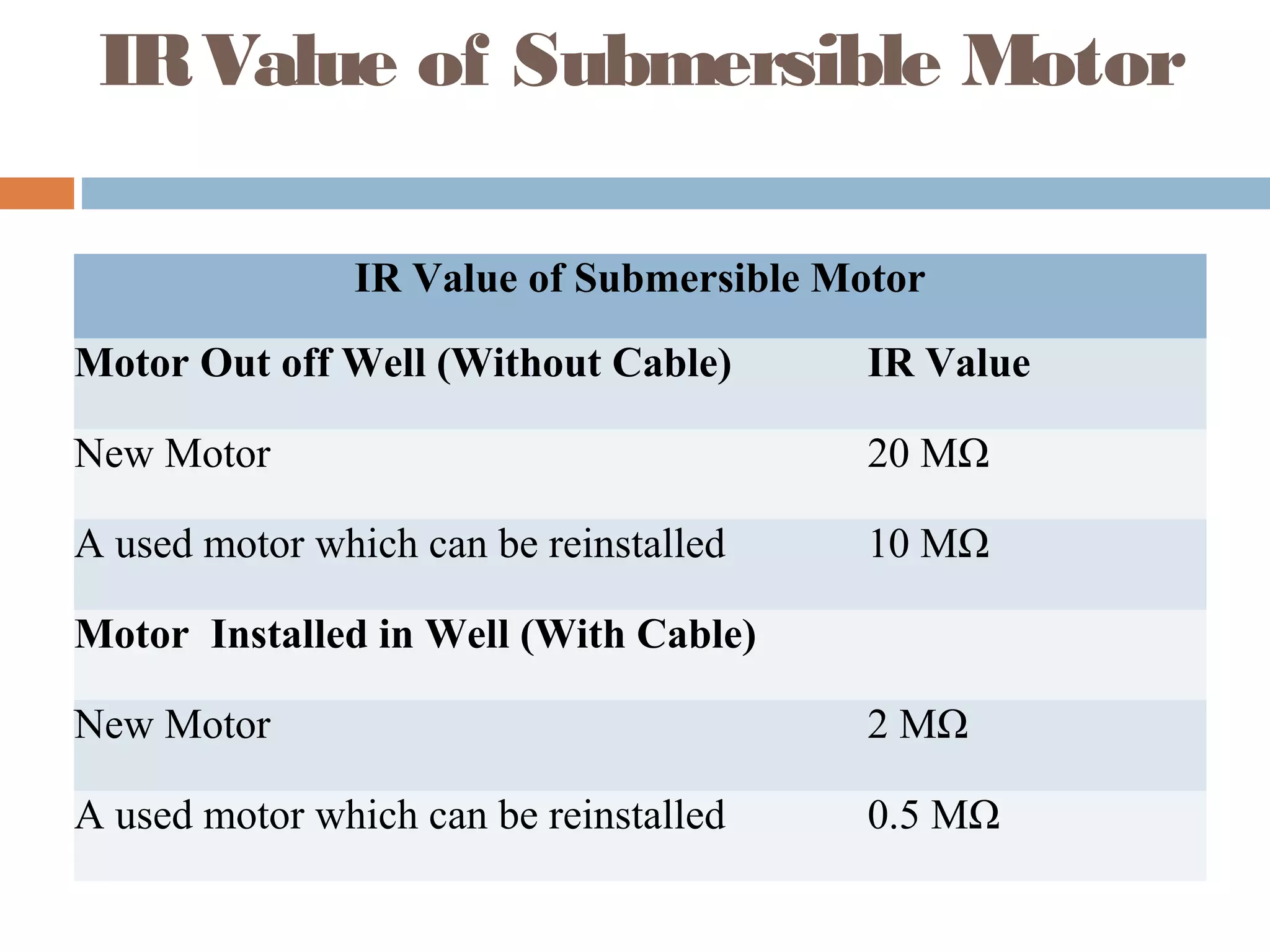
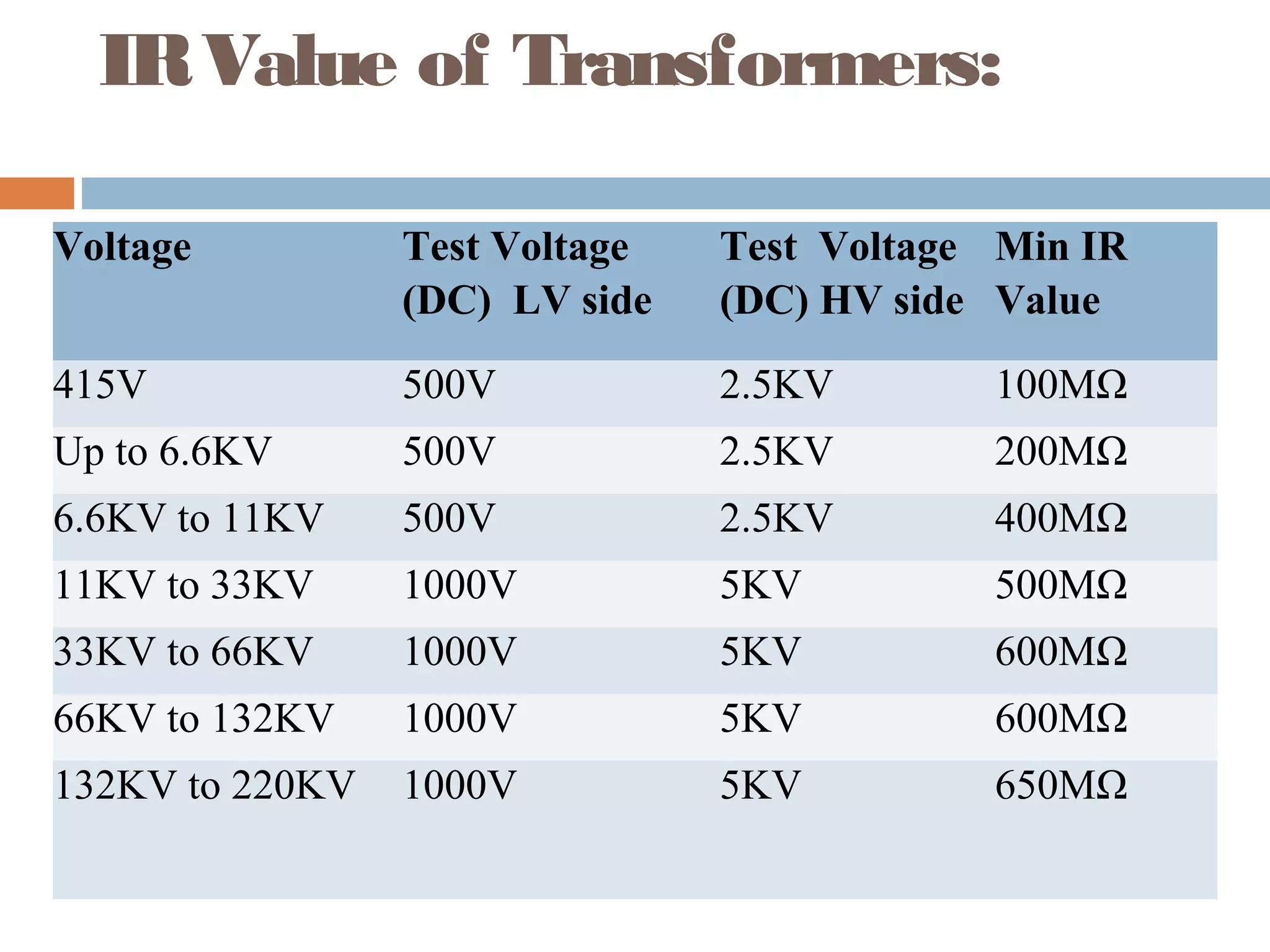
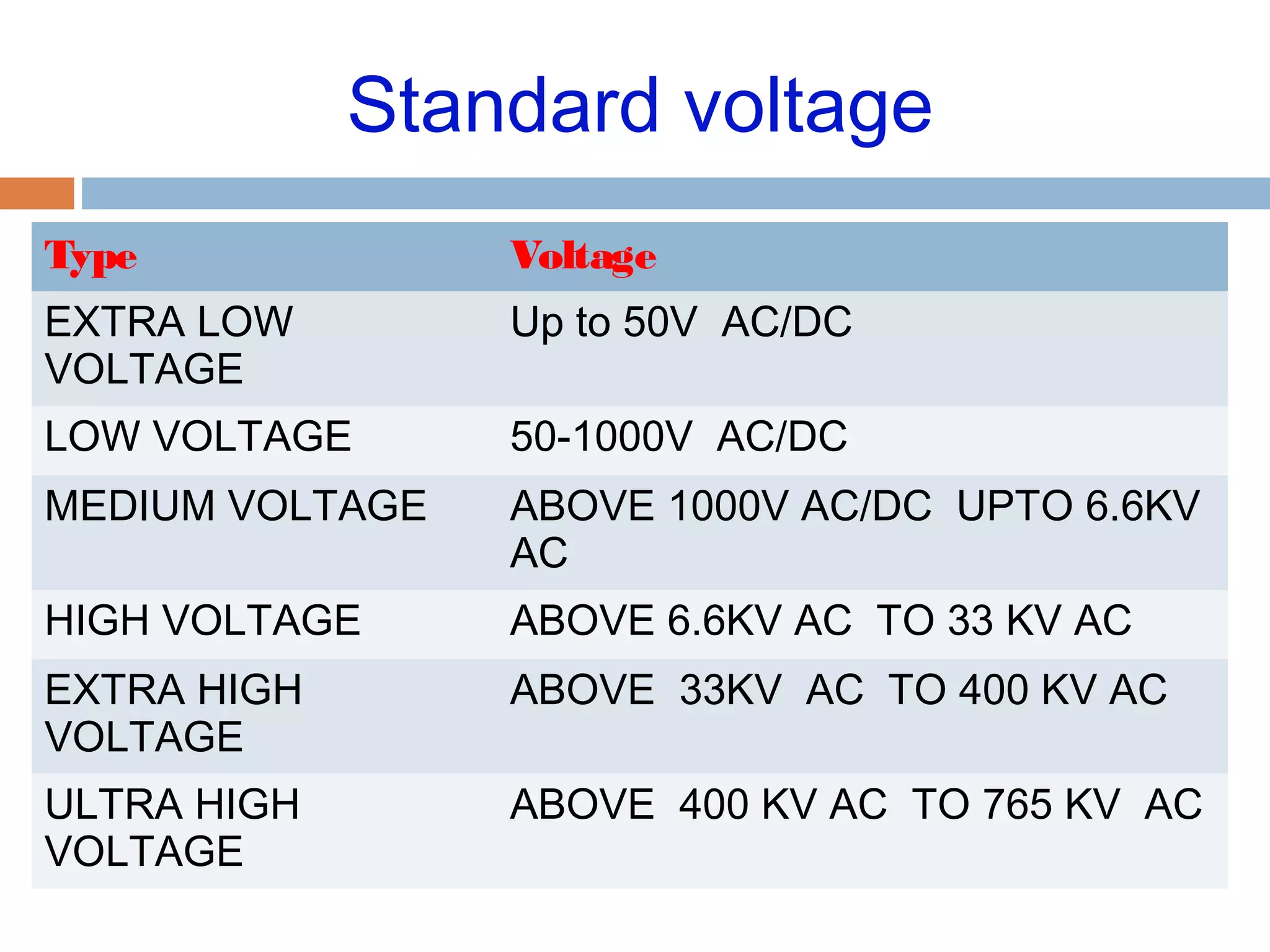
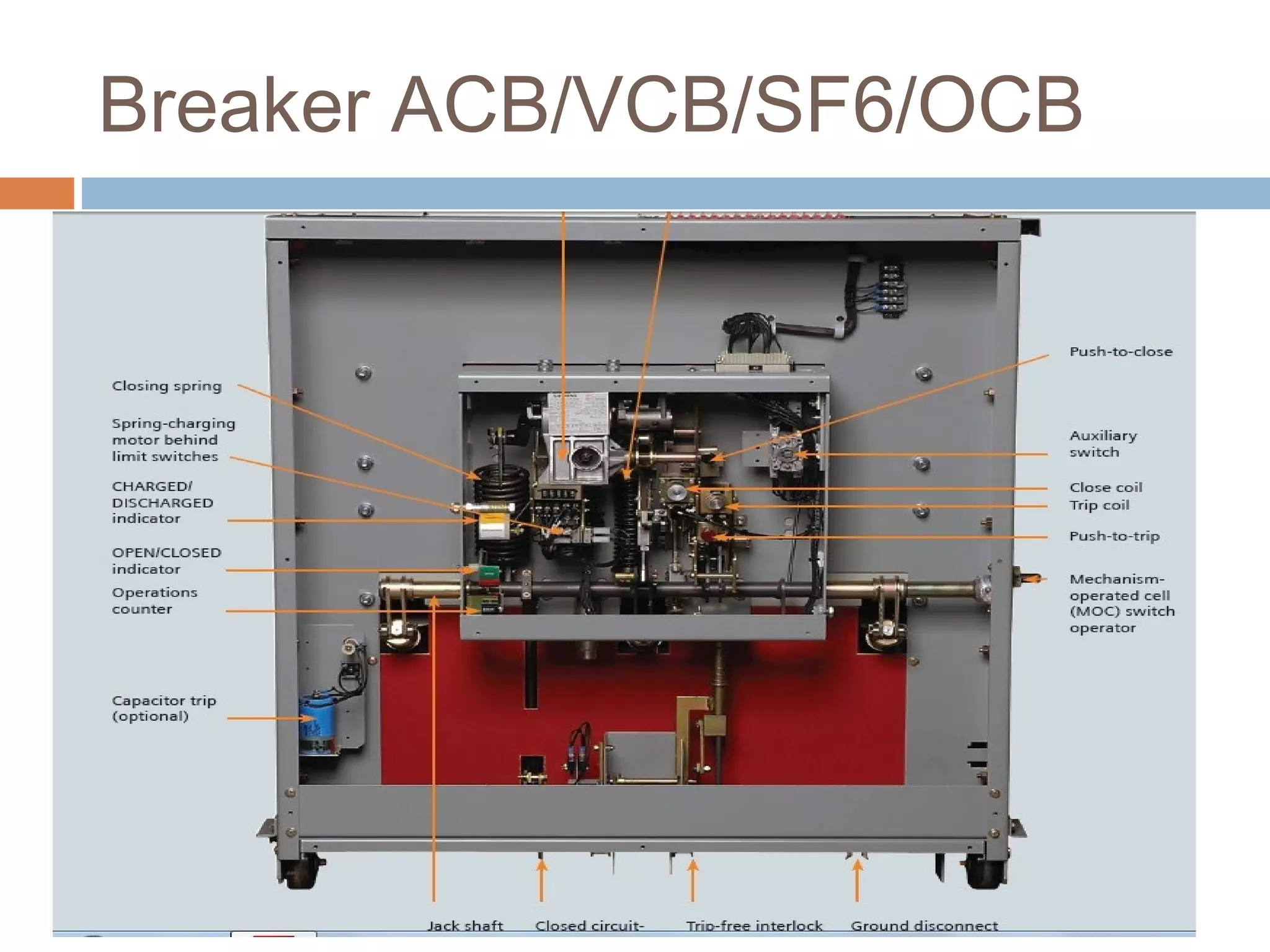
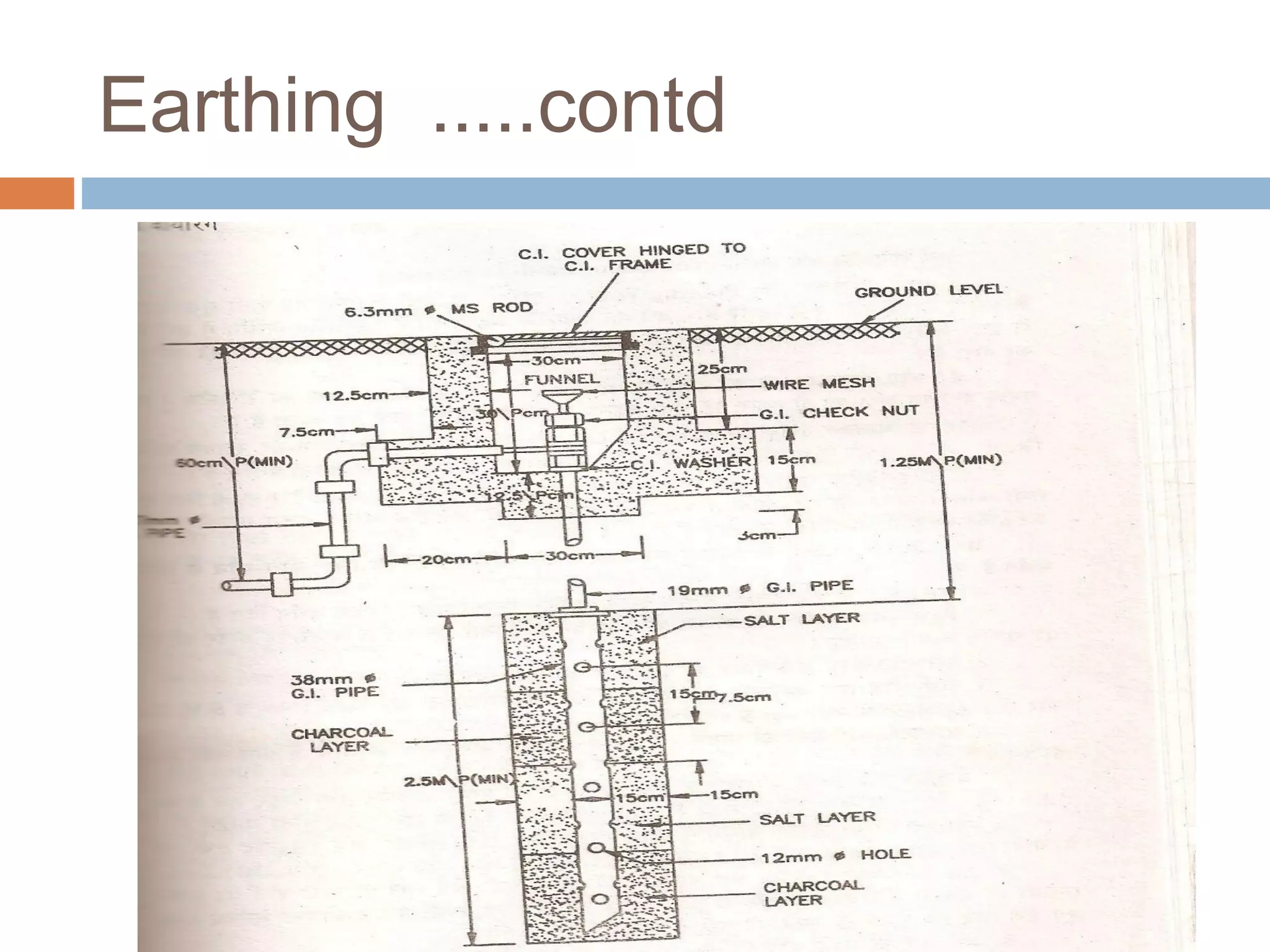
This document provides an overview of electrical substations, including their classification, components, and specifications. It discusses the different types of substations based on voltage levels, configuration, and application. It also describes the primary functions and components of outdoor switchyards, including incoming and outgoing lines, transformers, circuit breakers, and earthing systems. Clearance requirements and specifications for indoor electrical panels, busbars, grounding, and cabling are also outlined.