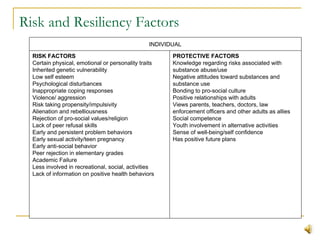
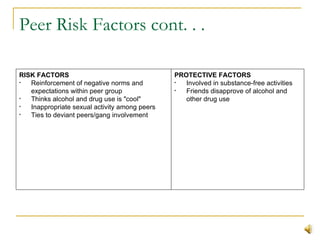
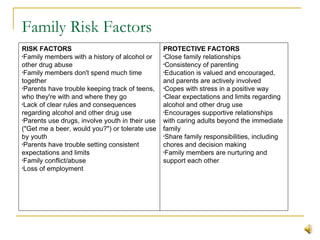
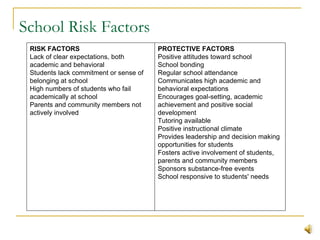
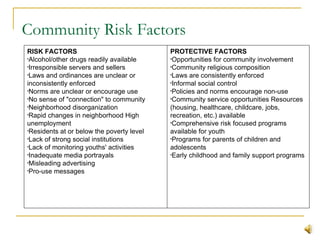
This document summarizes substance abuse prevention. It discusses substance use on a continuum from social to dependent use. Prevention aims to foster healthy behaviors and prevent issues. Risk factors for substance abuse include genetics, mental health issues, and social influences; protective factors enhance resilience. The document provides an overview of prevention goals and strategies at various levels, from individual to community. Resources for prevention programs are also listed.