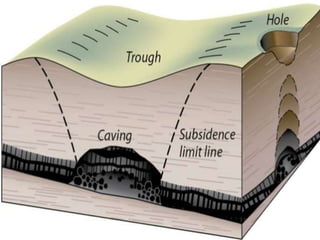
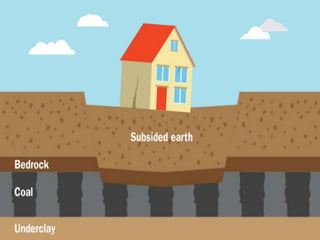
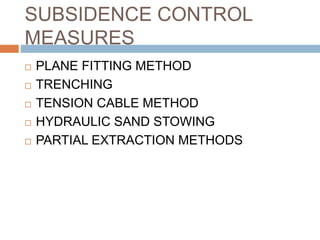
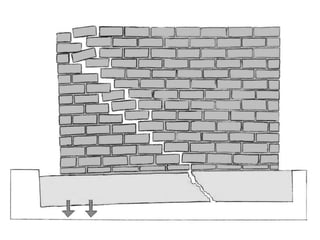
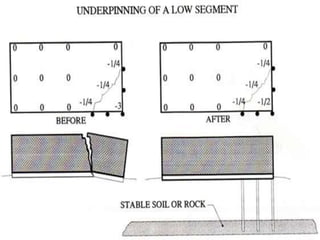
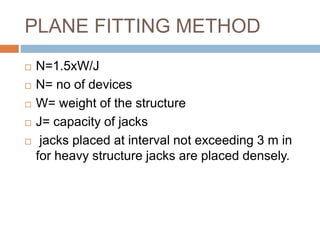
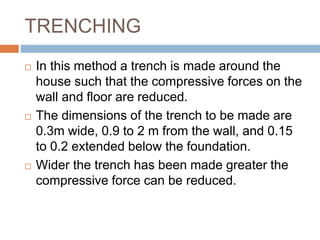
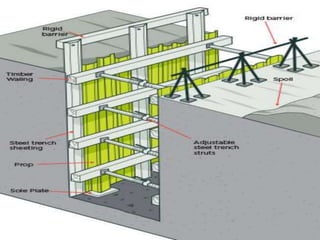
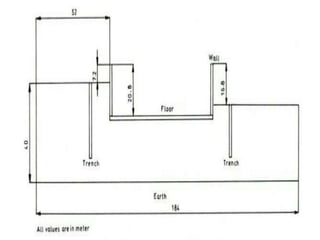
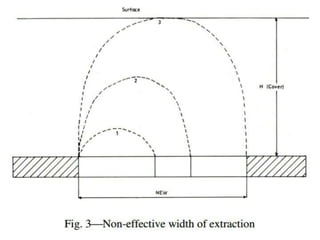
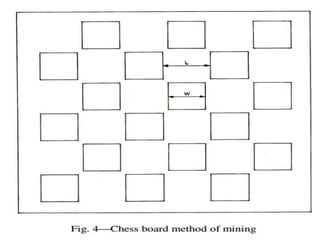
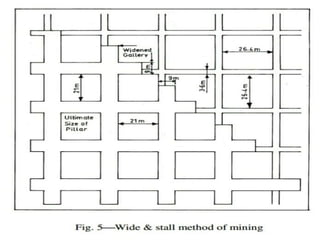
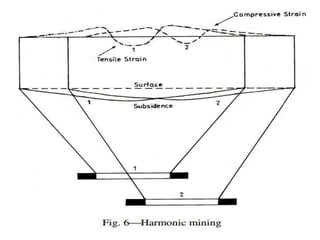
The document discusses subsidence control in coal mines, highlighting two main types of subsidence: pothole and trough subsidence, and their impacts on surface structures. Various control measures are detailed, including plane fitting, trenching, tension cables, hydraulic sand stowing, and partial extraction methods, each aimed at minimizing subsidence and protecting surface infrastructures. The effectiveness of these methods, particularly hydraulic sand stowing, is emphasized, with specific strategies for extraction that balance coal recovery and surface stability.