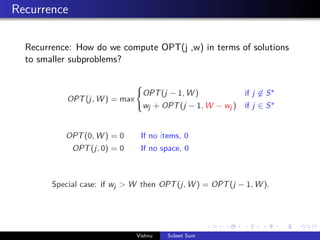
This document discusses the subset sum problem and how to solve it using dynamic programming. It introduces the problem of finding a subset of items that maximizes the total weight without exceeding a given bound. It describes using dynamic programming to build a solution by solving smaller subproblems and storing their results in a table. The dynamic programming algorithm runs in pseudo-polynomial time O(nW) where n is the number of items and W is the weight bound.