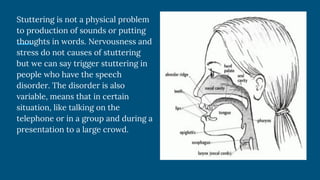
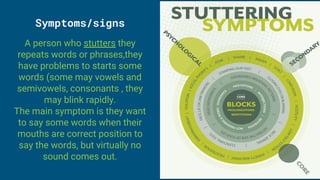
Stuttering and stammering refer to the same speech disorder characterized by involuntary repetitions or prolongations of sounds, syllables, words or phrases as well as blocks of speech. It affects less than 1% of adults but is most common in children during language development. Symptoms include repetitions, hesitations, difficulties starting words, rapid blinking and tension in the face and body. While stress and anxiety do not cause stuttering, they can trigger episodes in those with the disorder. Treatment involves learning strategies from speech therapists to control speech rate and use techniques like modification therapy or fluency shaping therapy to manage stuttering.