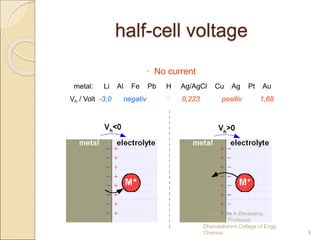
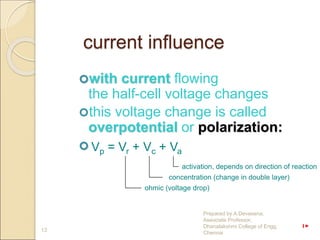
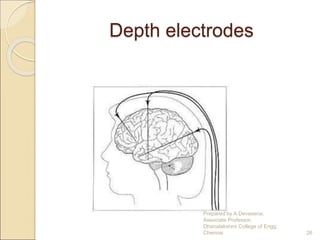
The document discusses biopotential electrodes and how they are used to detect electrical signals in the body. It explains that electrodes must form an interface with body tissues or fluids to detect signals, but this interface can cause issues if ions or electrons cannot freely cross. It also discusses different types of electrodes like surface electrodes, depth electrodes, and needle electrodes and how they interface with the body. The half-cell potential, polarization, equivalent circuit models, and sources of noise are also summarized.