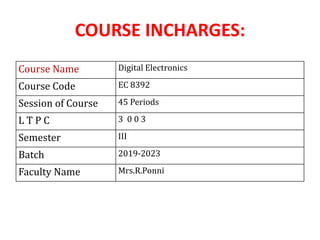
This document provides information on mapping course outcomes (COs), program outcomes (POs) and program specific outcomes (PSOs) for the subject Digital Electronics.
It begins with listing the 12 POs that engineering graduates are expected to achieve. It then provides the 3 PEOs and 3 PSOs for the Electronics and Communication Engineering program.
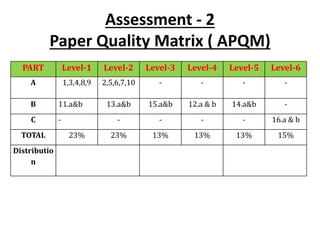
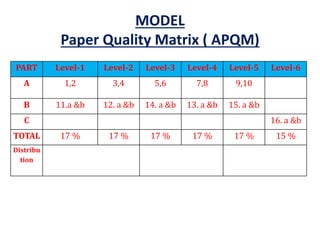
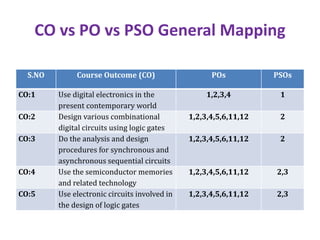
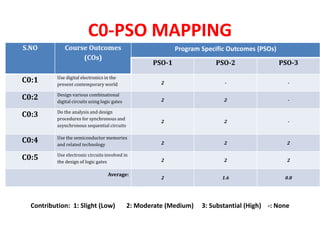
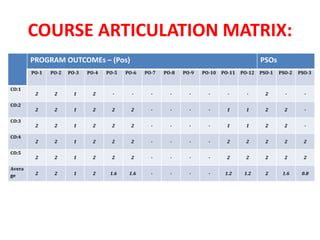
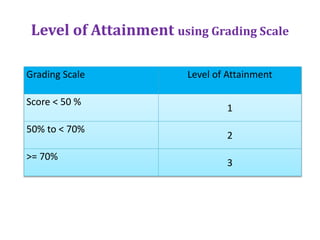
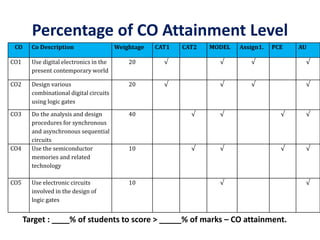
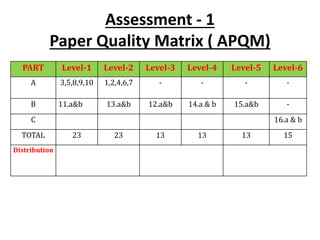
The document maps the 5 COs of the Digital Electronics course to the 12 POs and 3 PSOs, showing the level of contribution of each CO to achieving the outcomes. It also provides a course-PO matrix and course-PSO matrix to summarize this mapping.
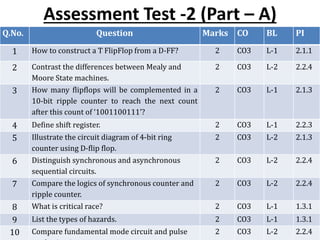
The document further provides details of the assessment plan, including the assessment tools to be






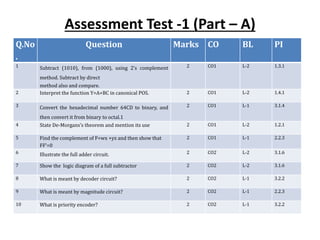
![Assessment Test -1 (Part –B & C)
Q.No. Question Marks CO BL PI
11.a. (i) Find the MSOP representation for F(A,B,C,D,E)= Σm(1,4,6,10, 20,22, 24,26)
+Σd(0,11,16,27) using K-Map. Draw the circuit of the minimal expression
using only NAND gates.
7 CO1 L-1 2.1.3
11.a. (ii) Implement Y= (AB)’+A+(B+C)’using NOR gates only. 6 CO1 L-1 2.1.3
11.b. (i) Simplify the Boolean expression using laws and rules of Boolean algebra Z =
[ AB’(C+BD) + (AB)’]C.
7 CO1 L-1 1.2.1
11.b. (ii) Define SOP and POS term. Convert the Boolean expression AB’C + B’CD +
AC’D to SOP form.
6 CO1 L-1 1.2.1
12.a. (i) Express the Boolean function F = XY + XZ in product of Maxterm 6 CO1 L-3 1.2.1
12.a. (ii) Solve and Reduce the following function using K-map technique. f (A, B, C,
D) = π (0, 3, 4, 7, 8, 10, 12, 14) + d (2, 6)
7 CO1 L-3 2.1.3
12.b. (i) State and prove De morgan’s theorem 3 CO1 L-3 1.2.1
12.b. (ii) Solve MinSOP and Max POS for F=b’c’d + bcd+acd’+ a’b’c+ a’bc’d. 10 CO1 L-3 2.1.3
13.a.(i) Summarize about don’t care conditions 6 CO1 L-2 2.1.3
13.a(ii) Relate the Boolean function D = (A’ + B) (B’ + C) as
(a) POS form (b) SOP form
7 CO1 L-2 2.1.3
13.b.(i) Implement the following Boolean function using 8 x 1 Multiplexer.
F(A,B,C,D)= Σm (1, 3, 4, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15)
7 CO2 L-2 2.4.1
13.b.(ii) Explain the concept of carry look ahead adder with neat logic diagram. 6 CO2 L-2 2.2.3
14.a. Examine the operation of BCD to Excess -3 code converter 13 CO2 L-4 2.2.3
14.b Examine and explain the operation of 3-bit magnitude comparator. 13 CO2 L-4 2.2.3
15.a. With neat circuit diagram, explain the working principle of 4-bit parallel
Adder/Subtractor.
13 CO2 L-5 2.4.2
15.b Design a BCD adder and explain its function with an example 13 CO2 L-5 2.4.2
16.a What are the advantages of using Quine McCluskey method? Estimate the
Minimal sum of products for the Boolean expression f(A, B,C, D) =Σm(1, 2, 3,
9, 12,13,14) + Σd(0,7,10, 15) using Quine McCluskey Tabular method.
15 CO1 L-6 2.4.1
16.b Design an even parity generator, that generates an even parity bit for every 15 CO2 L-6 2.2.3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalelectronics-221130131327-223963ad/85/DIGITAL-ELECTRONICS-pptx-15-320.jpg)