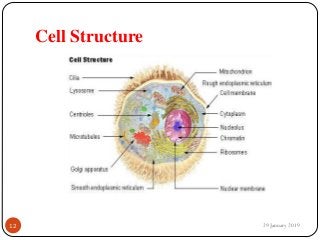
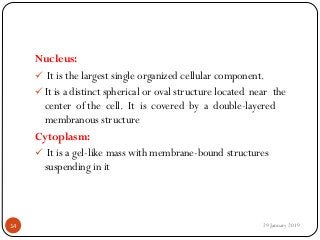
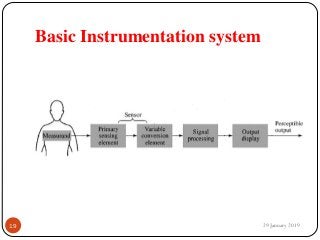
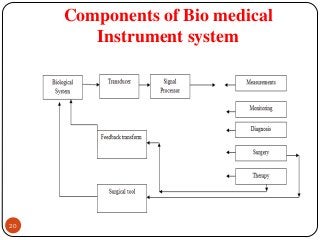
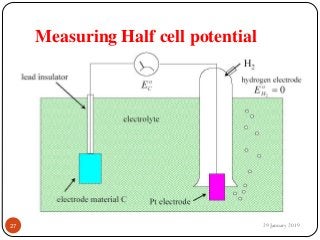
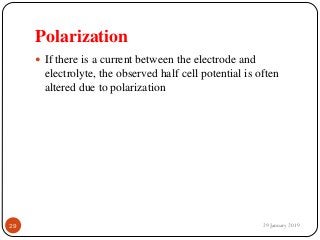
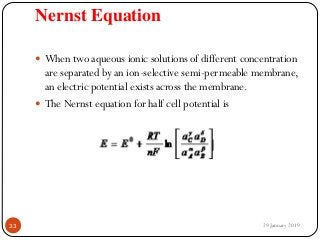
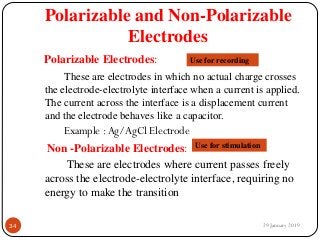
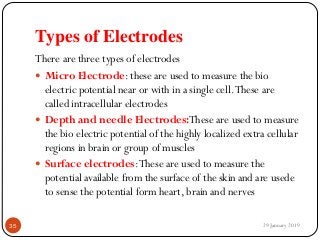
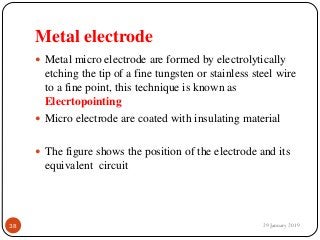
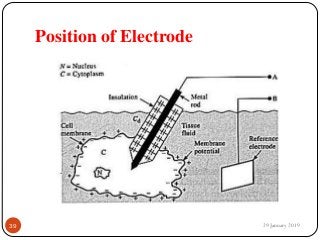
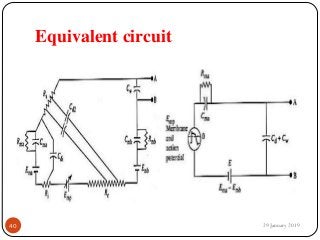
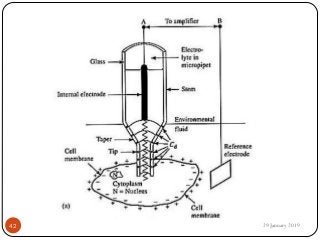
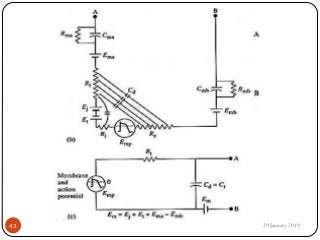
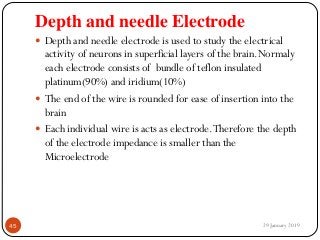
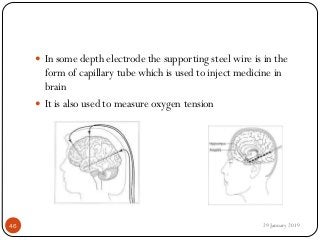
The document outlines the syllabus and introductory concepts of medical electronics, focusing on bio-potential recording, bioelectrical phenomena, and the design of biomedical instruments. It highlights the significance of electrodes, transducers, and various types of electrodes used for measuring bioelectric signals in clinical practice. Additionally, it discusses factors influencing the design and functionality of medical devices, emphasizing accuracy, sensitivity, and safety.