1. The document discusses various research study designs including qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches.
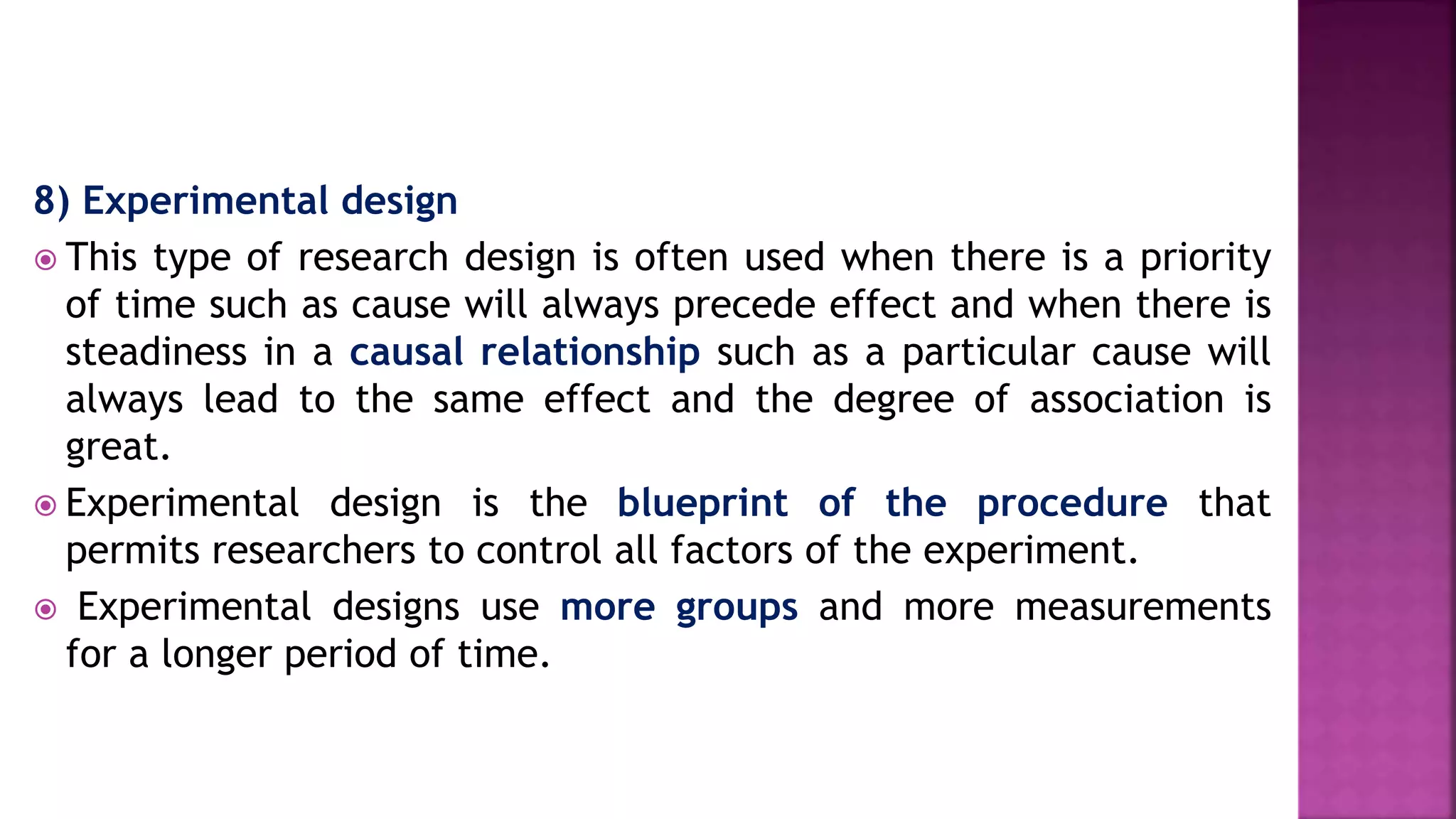
2. It provides details on specific designs like case studies, case control studies, action research, cohort studies, descriptive studies, cross-sectional studies, exploratory studies, experimental studies, and longitudinal studies.
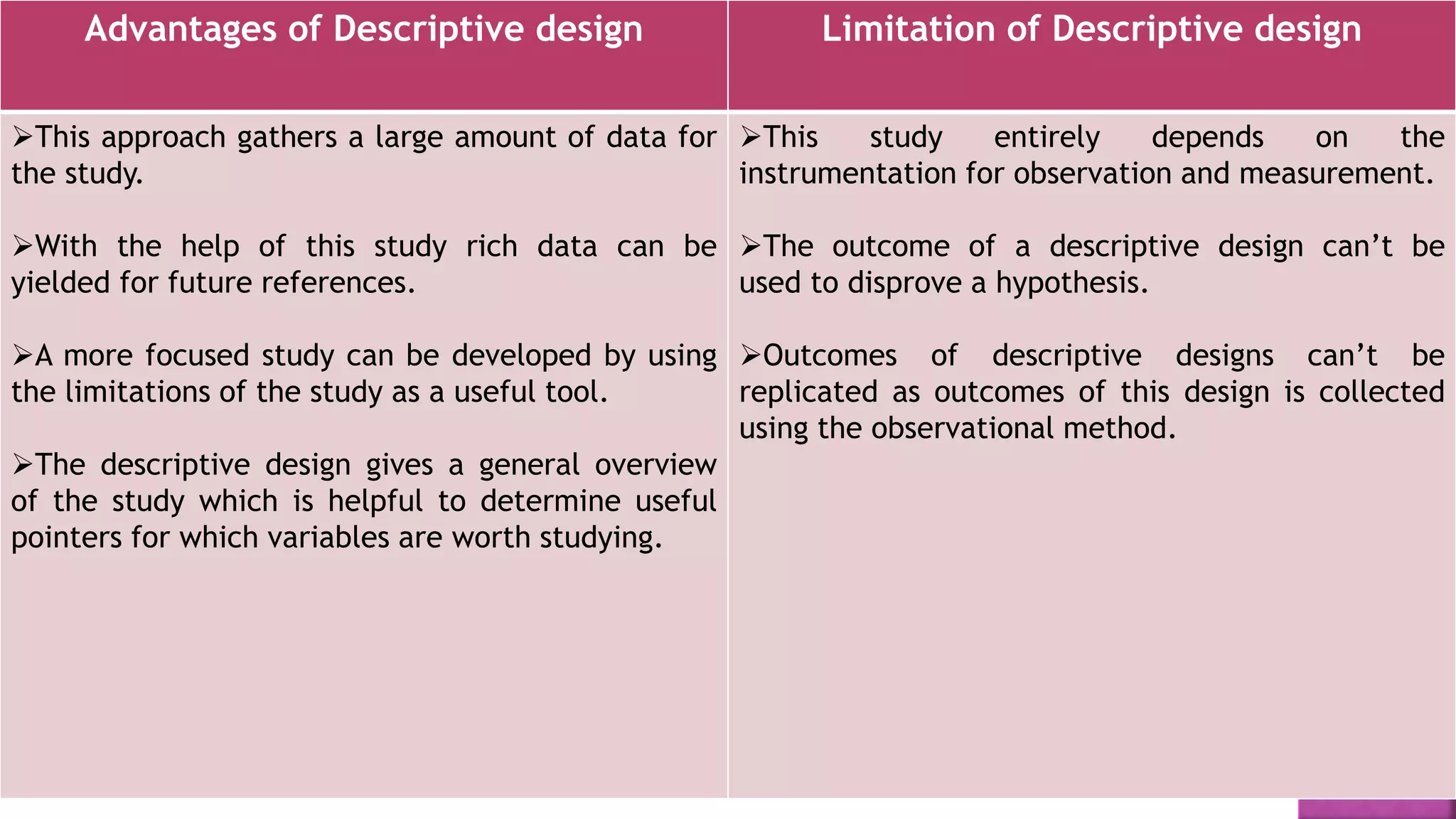
3. The advantages and limitations of each design are outlined to help researchers select the most appropriate design for their study.